Abstract
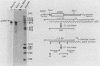
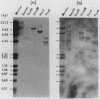
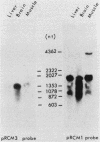
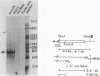
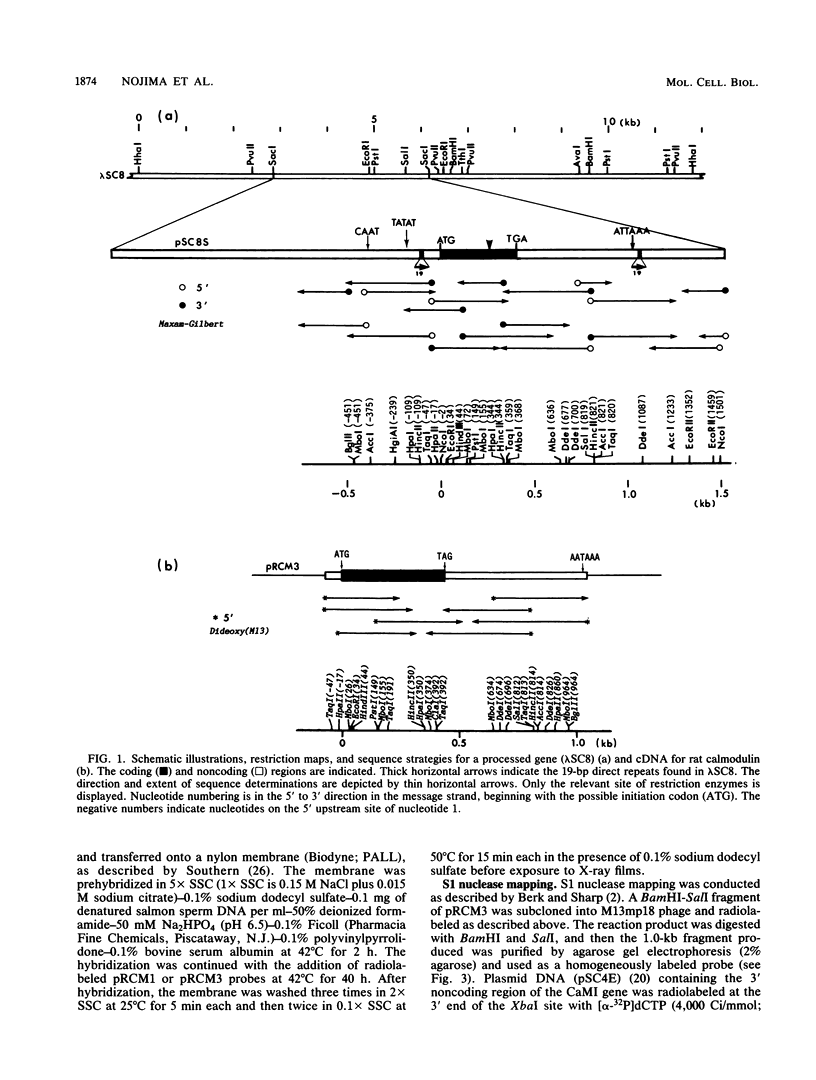
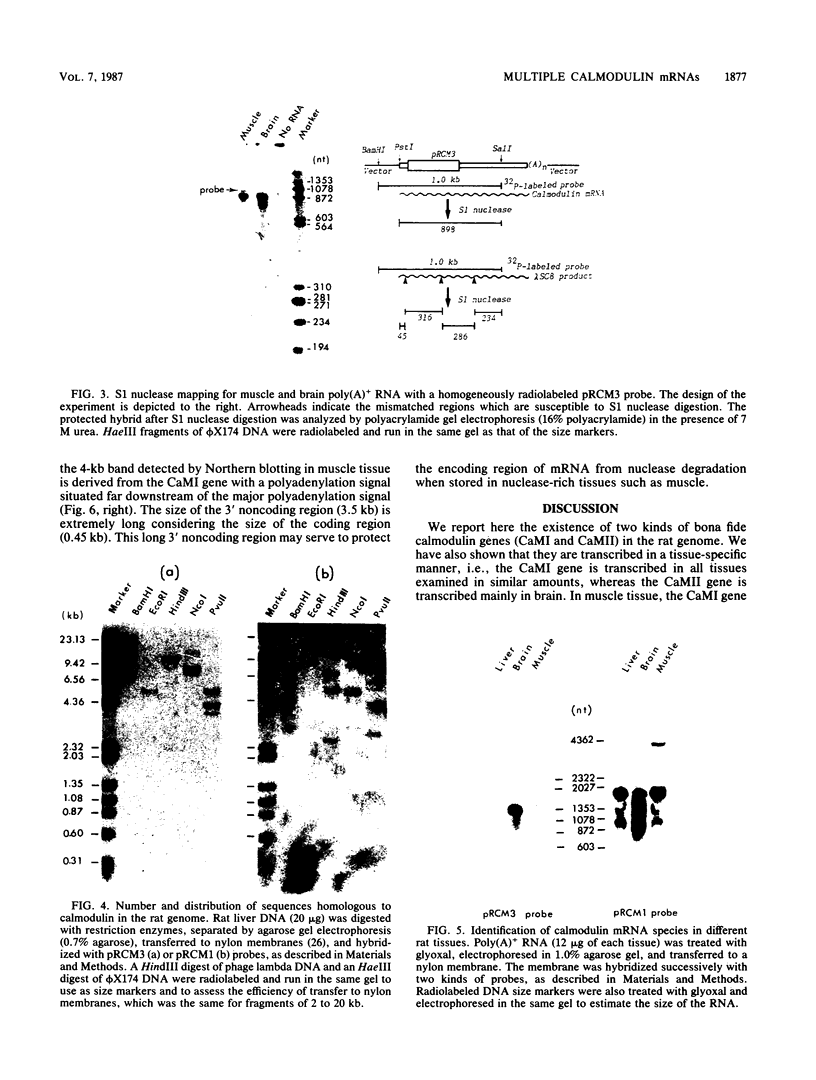
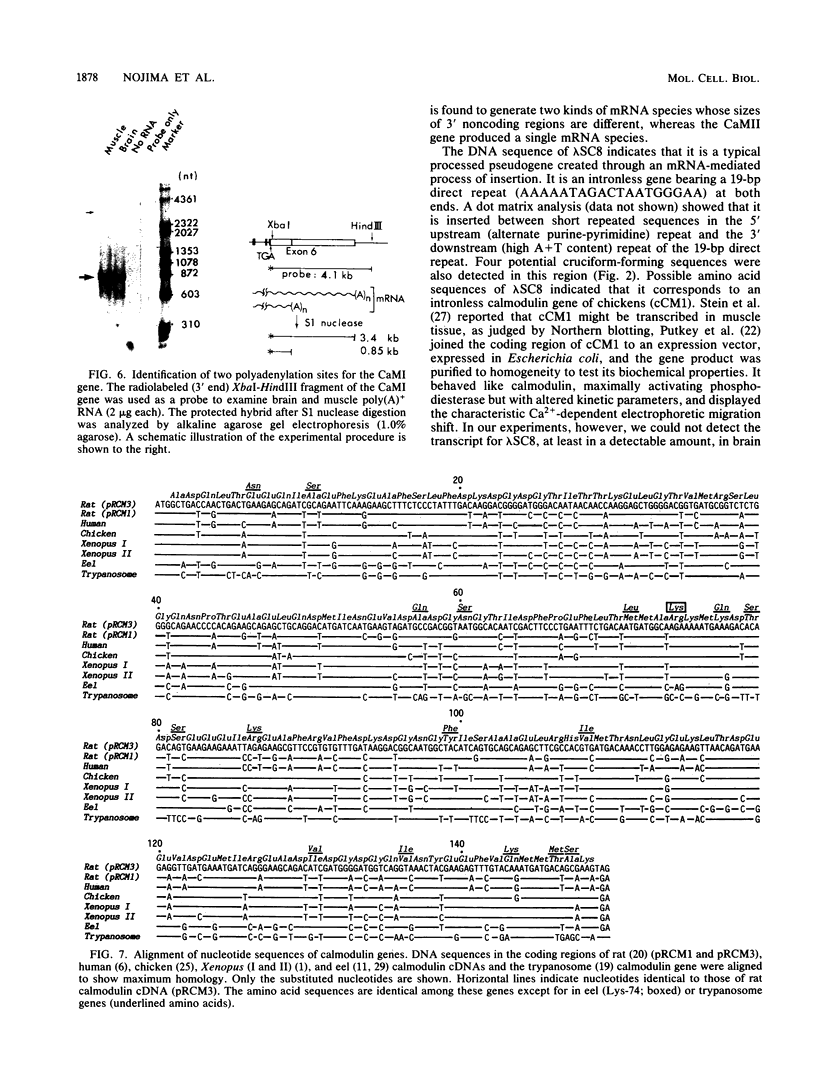
We have observed three calmodulin mRNA species in rat tissues. In order to know from how many expressed genes they are derived, we have investigated the genomic organization of calmodulin genes in the rat genome. From a rat brain cDNA library, we obtained two kinds of cDNAs (pRCM1 and pRCM3) encoding authentic calmodulin. DNA sequence analysis of these cDNA clones revealed substitutions of nucleotides at 73 positions of 450 nucleotides in the coding region, although the amino acid sequences of these calmodulins are exactly the same. DNA sequences in the 5' and 3' noncoding regions are quite different between these two cDNAs. From these results, we conclude that they are derived from two distinct bona fide calmodulin genes, CaMI (pRCM1) and CaMII (pRCM3). Total genomic Southern hybridization suggested four distinct calmodulin-related genes in the rat genome. By cloning and sequencing the calmodulin-related genes from rat genomic libraries, we demonstrated that the other two genes are processed pseudogenes generated from the CaMI (lambda SC9) and CaMII (lambda SC8) genes, respectively, through an mRNA-mediated process of insertions. Northern blotting showed that the CaMI gene is transcribed in liver, muscle, and brain in similar amounts, whereas the CaMII gene is transcribed mainly in brain. S1 nuclease mapping indicated that the CaMI gene produced two mRNA species (1.7 and 4 kilobases), whereas the CaMII gene expressed a single mRNA species (1.4 kilobases).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnou N. P., O'Brien S. J., Shimada T., Nash W. G., Chen M. J., Nienhuis A. W. Chromosomal organization of the human dihydrofolate reductase genes: dispersion, selective amplification, and a novel form of polymorphism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5170–5174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chafouleas J. G., Bolton W. E., Hidaka H., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Means A. R. Calmodulin and the cell cycle: involvement in regulation of cell-cycle progression. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chafouleas J. G., Bolton W. E., Means A. R. Potentiation of bleomycin lethality by anticalmodulin drugs: a role for calmodulin in DNA repair. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1346–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.6203171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chafouleas J. G., Lagacé L., Bolton W. E., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Means A. R. Changes in calmodulin and its mRNA accompany reentry of quiescent (G0) cells into the cell cycle. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. J., Shimada T., Moulton A. D., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. Intronless human dihydrofolate reductase genes are derived from processed RNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7435–7439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y. H., Dawid I. B. Isolation and characterization of calmodulin genes from Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):507–513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldhagen H., Clarke M. Identification of the single gene for calmodulin in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1851–1854. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:333–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Vanaman T. C. Calmodulin. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:213–321. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagacé L., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Means A. R. Identification of multiple species of calmodulin messenger RNA using a full length complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1684–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Tash J. S., Chafouleas J. G. Physiological implications of the presence, distribution, and regulation of calmodulin in eukaryotic cells. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):1–39. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munjaal R. P., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Dedman J. R., Means A. R. A cloned calmodulin structural gene probe is complementary to DNA sequences from diverse species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima H., Sokabe H. Structure of a gene for rat calmodulin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima H., Sokabe H. Structure of rat calmodulin processed genes with implications for a mRNA-mediated process of insertion. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Slaughter G. R., Means A. R. Bacterial expression and characterization of proteins derived from the chicken calmodulin cDNA and a calmodulin processed gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4704–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Ts'ui K. F., Tanaka T., Lagacé L., Stein J. P., Lai E. C., Means A. R. Chicken calmodulin genes. A species comparison of cDNA sequences and isolation of a genomic clone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11864–11870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C. Processed pseudogenes for rat cytochrome c are preferentially derived from one of three alternate mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2279–2288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Munjaal R. P., Lagace L., Lai E. C., O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Tissue-specific expression of a chicken calmodulin pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6485–6489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Young A. S., Ruben L., Patton C. L., Richards F. F. Calmodulin genes in trypanosomes are tandemly repeated and produce multiple mRNAs with a common 5' leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshney U., Gedamu L. Human metallothionein MT-I and MT-II processed genes. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzynczak E. J., Perham R. N. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding human calmodulin. Biochem Int. 1984 Aug;9(2):177–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]