Abstract
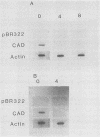
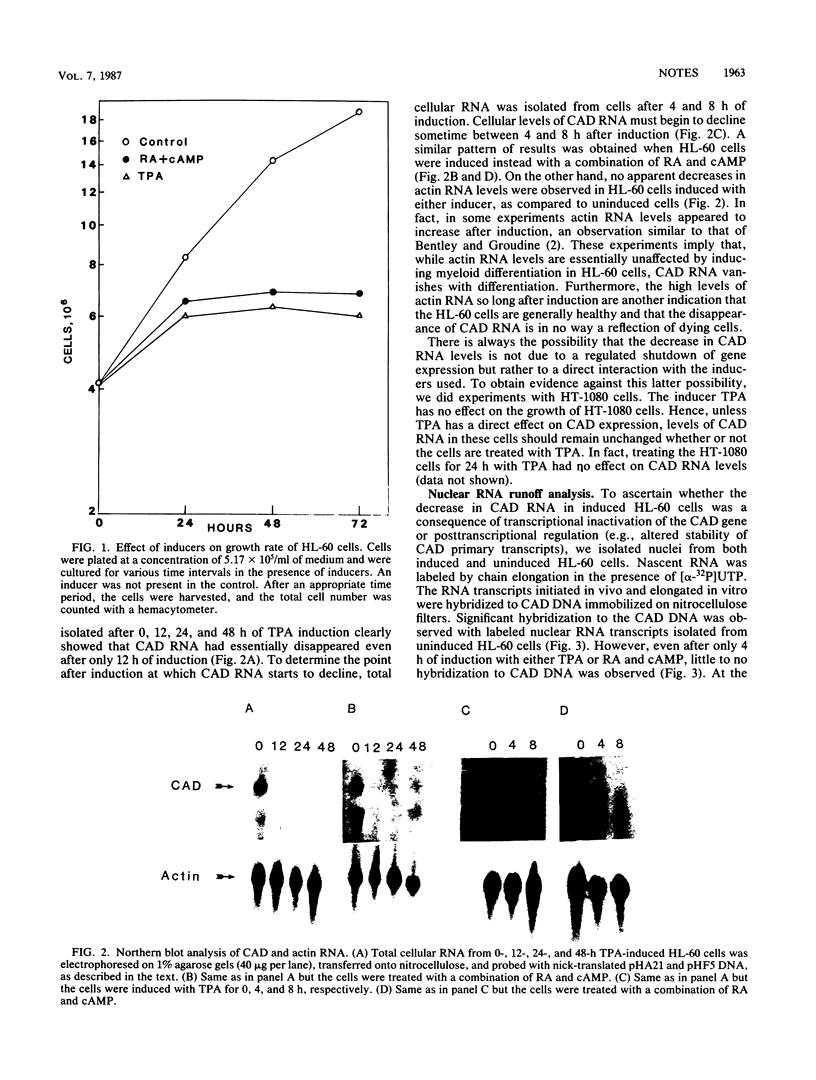
CAD codes for a trifunctional protein involved in the catalysis of the first three enzymatic activities in the de novo pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway, namely, carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase II (EC 6.3.5.5), aspartate transcarbamylase (EC 2.1.3.2), and dihydroorotase (EC 3.5.2.3). CAD regulation was studied in the human promyelocyte leukemic line HL-60 as it differentiated into monocytic or granulocytic lineages after induction by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate or trans-retinoic acid and dibutyryl cyclic AMP, respectively. Within 12 h of induction of HL-60 cells with either inducer, total cellular levels of CAD RNA essentially disappeared. On the other hand, no apparent decreases in beta-actin RNA levels were seen even 48 h after HL-60 cells were induced, as compared with untreated cells. With nuclear runoff assays, it was clearly shown that the inactivation of CAD gene expression during the induction of HL-60 cells with either inducer was at the transcriptional level. The nuclear runoff experiments also demonstrated that the CAD gene expression was shut down in less than 4 h after induction, well before morphological changes were observed in these cells. At the enzymatic level, the activity of aspartate transcarbamylase, one of the three enzymes encoded by the CAD gene, decreased by about half within 24 h of induction, suggesting a CAD protein half-life of 24 h in differentiating HL-60 cells. Nevertheless, this means that significant levels of aspartate transcarbamylase activity remained even after the cells have stopped proliferating. From the RNA data, it is clear that CAD gene expression is rapidly turned off as promyelocytes begin to terminally differentiate into macrophages and granulocytes. We suspect that the inactivation of the CAD gene in induced HL-60 cells is a consequence of the differentiating cells leaving the cell cycle and becoming nonproliferating.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Selective multiplication of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1357–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Selonick S. E., Collins S. J. Induction of differentiation of the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60) by retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALVA E., COHEN P. P. Carbamyl phosphate-aspartate transcarbamylase activity in regenerating rat liver. Cancer Res. 1959 Jul;19(6 Pt 1):679–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALVA E., LOWENSTEIN J. M., COHEN P. P. Carbamyl phosphate-aspartate transcarbamylase activity in tumors. Cancer Res. 1959 Jan;19(1):101–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. J., Jones M. E. Effect of 6-azauridine on de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis in cultured Ehrlich ascites cells. Orotate inhibition of dihydroorotase and dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4908–4914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman P. F., Suttle D. P., Stark G. R. Purification from hamster cells of the multifunctional protein that initiates de novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6379–6385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad A. H., Ruddle F. H. Regulation of thymidylate synthetase activity in cultured mammalian cells. J Cell Sci. 1972 Mar;10(2):471–486. doi: 10.1242/jcs.10.2.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. N., Carnright D. V., Patterson D. Biochemical genetic analysis of pyrimidine biosynthesis in mammalian cells: III. Association of carbamyl phosphate synthetase, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotase in mutants of cultured Chinese hamster cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Mar;5(2):175–191. doi: 10.1007/BF01539159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. J., Murtaugh M. P., Moore W. T., Jr, Johnson G. S., Lucas D. Retinoic acid-induced expression of tissue transglutaminase in human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5166–5174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galofré A., Kretchmer N. Biosynthesis of pyrimidines by various organs of the chick during embryogenesis. Pediatr Res. 1970 Jan;4(1):55–62. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197001000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson S. L., Wu J. S., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA metabolism in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogenraad N. J., Levine R. L., Kretchmer N. Copurification of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase and aspartate transcarbamoylase from mouse spleen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):981–988. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90808-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenh C. H., Geyer P. K., Johnson L. F. Control of thymidylate synthase mRNA content and gene transcription in an overproducing mouse cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2527–2532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIM S., COHEN P. P. TRANSCARBAMYLASE ACTIVITY IN FETAL LIVER AND IN LIVER OF PARTIALLY HEPATECTOMIZED PARABIOTIC RATS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Mar;109:421–428. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90385-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Growth-dependent expression of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA from modular cDNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1598–1608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leys E. J., Kellems R. E. Control of dihydrofolate reductase messenger ribonucleic acid production. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):961–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao W. S., Heller R., Green P., Stark G. R. Regulation of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase-aspartate transcarbamoylase-dihydroorotase gene expression in growing and arrested cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15577–15581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebermann D., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Sachs L. Regulation of gene expression by tumor promoters. II. Control of cell shape and developmental programs for macrophages and granulocytes in human myeloid leukemic cells. Int J Cancer. 1981 Sep 15;28(3):285–291. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Slate D. L., Schimke R. T. S phase-specific synthesis of dihydrofolate reductase in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4985–4989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murao S., Gemmell M. A., Callaham M. F., Anderson N. L., Huberman E. Control of macrophage cell differentiation in human promyelocytic HL-60 leukemia cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4989–4996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDMANN Y., HURWITZ R., KRETCHMER N. ACTIVITY OF ASPARTATE TRANSCARBAMYLASE IN HEART AND LIVER OF THE DEVELOPING RAT. Nature. 1964 Feb 8;201:616–617. doi: 10.1038/201616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Wahl G. M., Coleman P. F., Stark G. R. N-(Phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells overaccumulate a single mRNA coding for the multifunctional protein that catalyzes the first steps of UMP synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):974–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Carnright D. V. Biochemical genetic analysis of pyrimidine biosynthesis in mammalian cells: I. Isolation of a mutant defective in the early steps of de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Sep;3(5):483–495. doi: 10.1007/BF01539120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago C., Collins M., Johnson L. F. In vitro and in vivo analysis of the control of dihydrofolate reductase gene transcription in serum-stimulated mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Jan;118(1):79–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shambaugh G. E., 3rd, Mrozak S. C., Metzger B. E., Freinkel N. Glutamine-dependent carbamyl phosphate synthetase during fetal and neonatal life in the rat. Dev Biol. 1974 Mar;37(1):171–185. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoaf W. T., Jones M. E. Uridylic acid synthesis in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma. Properties, subcellular distribution, and nature of enzyme complexes of the six biosynthetic enzymes. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 9;12(21):4039–4051. doi: 10.1021/bi00745a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]