Abstract
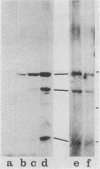
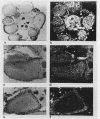
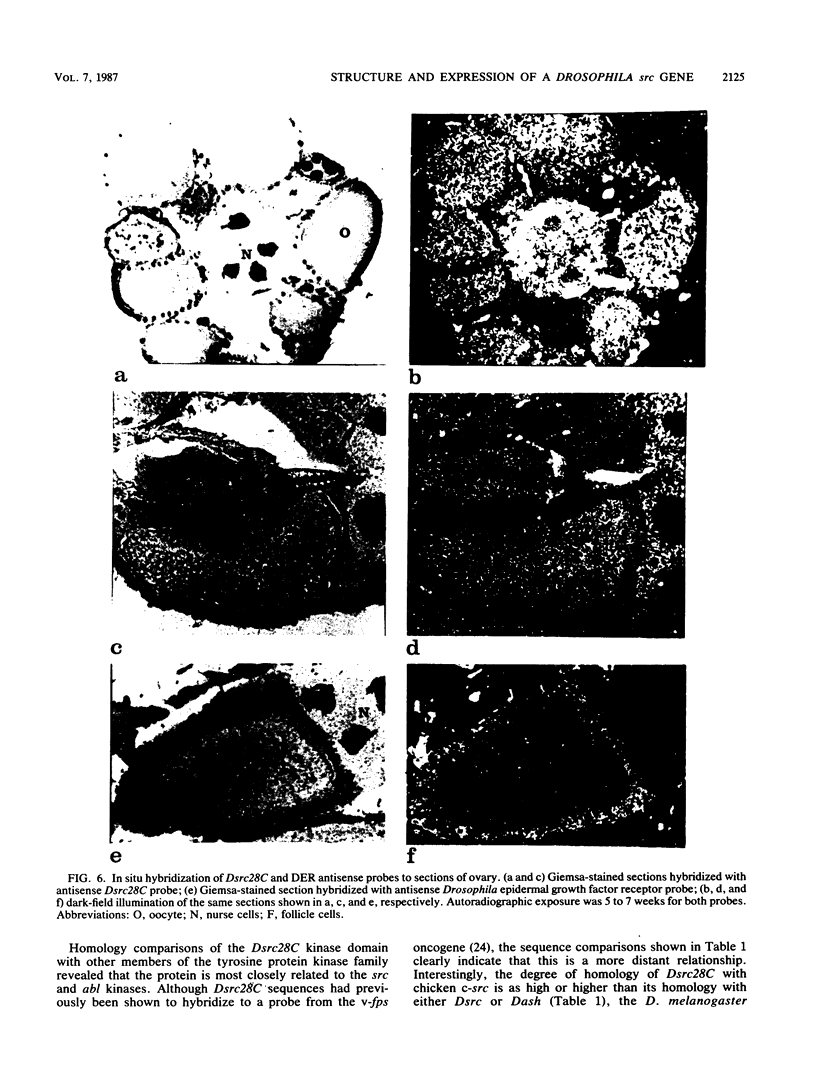
We have sequenced a cDNA clone for the Drosophila melanogaster gene Dsrc28C, a homolog of the vertebrate gene c-src. The cDNA contains a single open reading frame encoding a protein of 66 kilodaltons which contains features highly conserved within the src family of tyrosine protein kinases. Novel structural features of the Dsrc28C protein include a basic pI and a polyglycine domain near the amino terminus. Cell-free translation of in vitro-transcribed RNA yielded a protein of the predicted size which could be immunoprecipitated by anti-v-src antisera. RNA blot hybridization revealed that the gene is expressed predominantly during embryogenesis, in imaginal disks of third-instar larvae, and in adult females. In situ hybridization showed that expression in adult females is largely confined to nurse cells and developing oocytes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Neriah Y., Bernards A., Paskind M., Daley G. Q., Baltimore D. Alternative 5' exons in c-abl mRNA. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Mahaffey J. W., Bond B. J., Davidson N. Transcripts of the six Drosophila actin genes accumulate in a stage- and tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Levine M., Garber R. L., Gehring W. J. An improved in situ hybridization method for the detection of cellular RNAs in Drosophila tissue sections and its application for localizing transcripts of the homeotic Antennapedia gene complex. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):617–623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Falk H., Einat P., Shilo B. Z., Hoffmann F. M. Drosophila melanogaster DNA clones homologous to vertebrate oncogenes: evidence for a common ancestor to the src and abl cellular genes. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):589–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90478-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev Z., Leibovitz N., Segev O., Shilo B. Z. Expression of the src and abl cellular oncogenes during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):982–984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Glazer L., Segal D., Schlessinger J., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila EGF receptor gene homolog: conservation of both hormone binding and kinase domains. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;10:1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60727-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter E. D., Segal D., Glazer L., Shilo B. Z. Alternative 5' exons and tissue-specific expression of the Drosophila EGF receptor homolog transcripts. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1091–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Drees B., Kornberg T., Bishop J. M. The nucleotide sequence and the tissue-specific expression of Drosophila c-src. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Kornberg T. B., Bishop J. M. Three loci related to the src oncogene and tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity in Drosophila. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):837–839. doi: 10.1038/302837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford J., Burckhardt J., Butler B., Pirrotta V. Alternative processing and developmental control of the transcripts of the Drosophila abl oncogene homologue. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2609–2615. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Homology among oncogenes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;123:73–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70810-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S. C., Madhavan K., Bilodeau-Wentworth D. Maternal inheritance of transcripts from three Drosophila src-related genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2153–2170. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S. C., Vincent W. S., 3rd, Bilodeau-Wentworth D. A Drosophila genomic sequence with homology to human epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):178–180. doi: 10.1038/314178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaciuk P., Shalloway D. Features of the pp60v-src carboxyl terminus that are required for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2807–2819. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]