Abstract
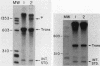
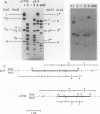
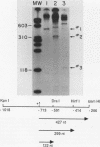
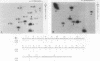
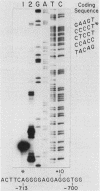
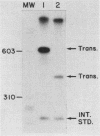
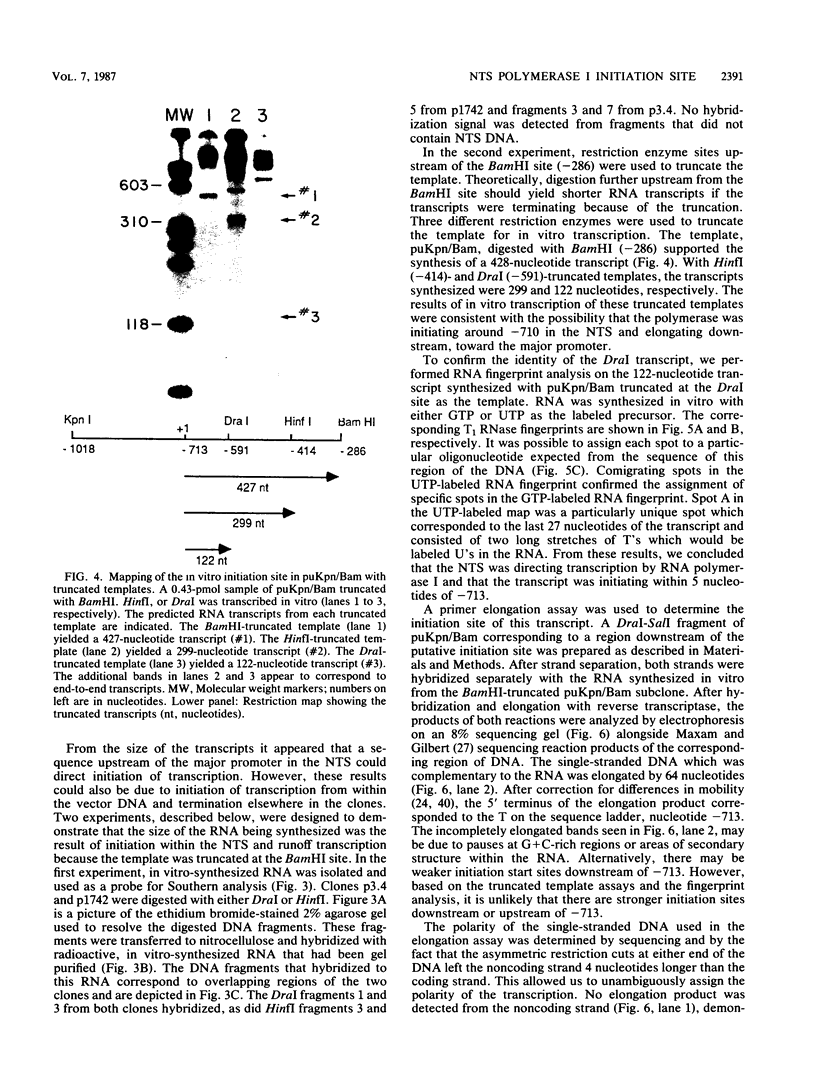
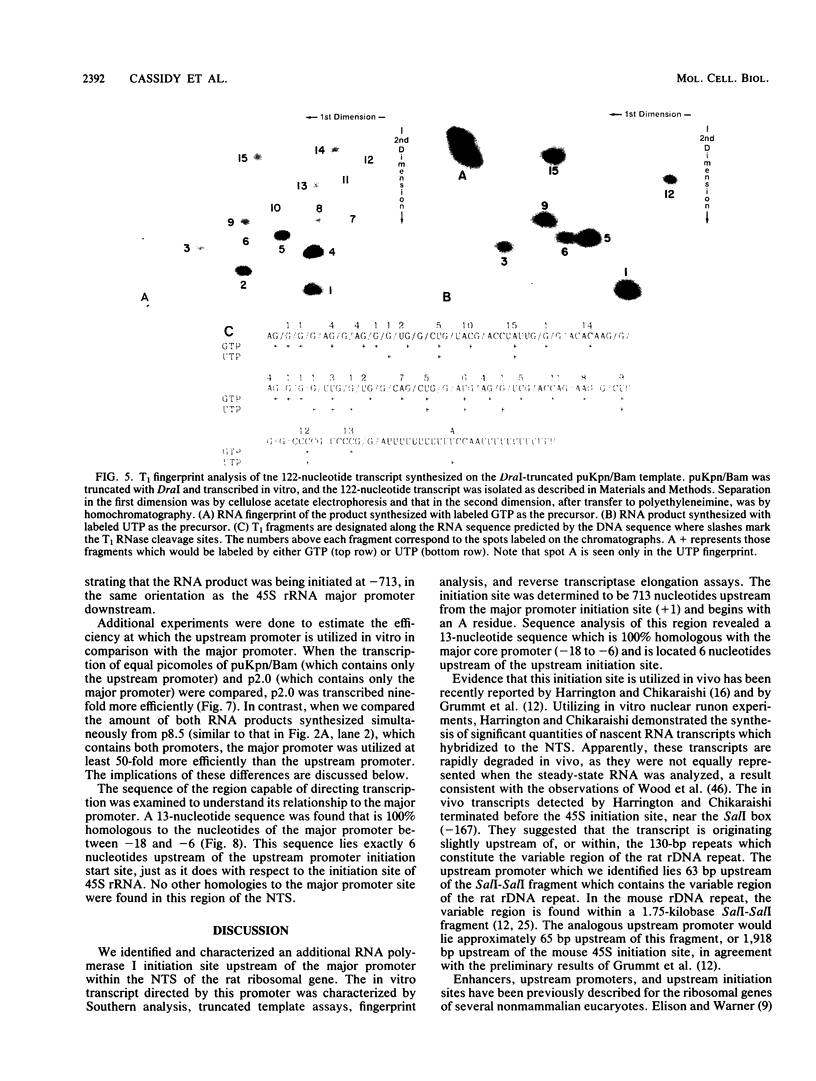
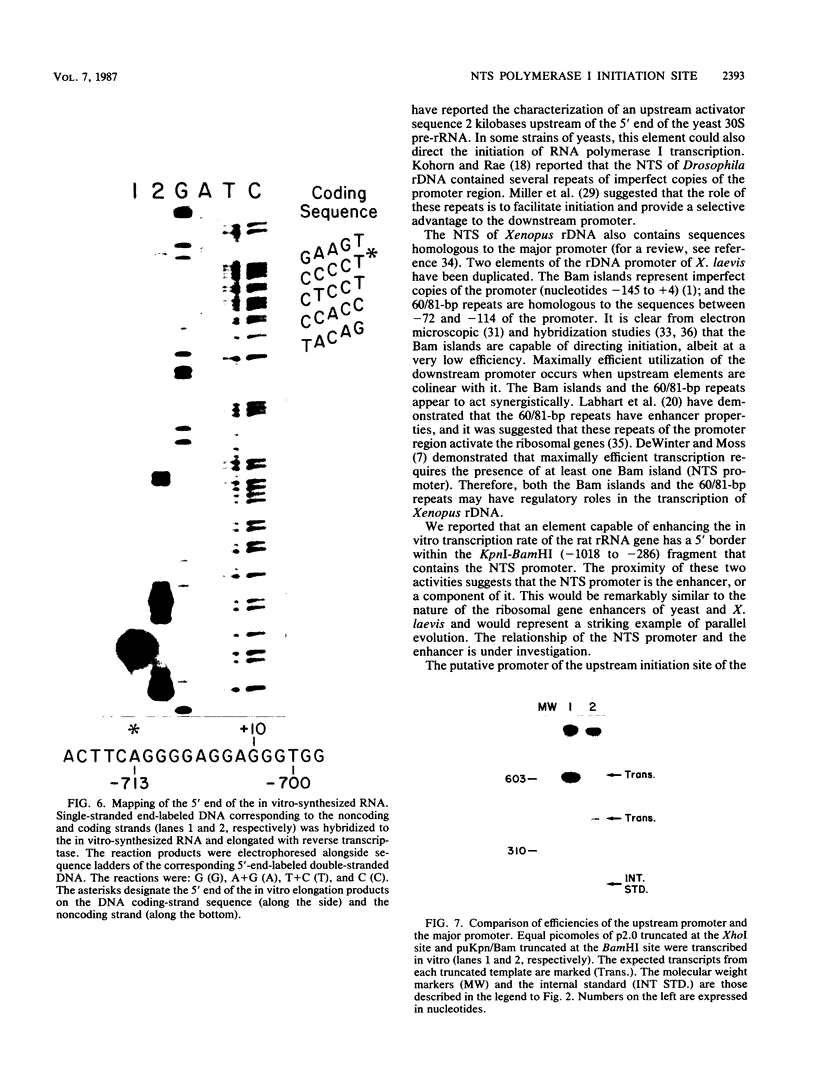
We identified and characterized an additional promoter within the nontranscribed spacer (NTS) of the rat ribosomal gene repeat that is capable of supporting initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I in vitro. Within this promoter there is a sequence of 13 nucleotides which is 100% homologous to nucleotides -18 to -6 (+1 being the first nucleotide of 45S rRNA) of the major promoter of 45S pre-rRNA and is located between nucleotides -731 and -719. To identify the exact location of the upstream initiation site, the RNA synthesized in vitro from this new promoter was gel isolated and subjected to fingerprint analysis, Southern hybridization, and reverse transcriptase elongation. Based on these analyses, the in vitro-synthesized RNA initiates with an A at nucleotide -713. When compared individually, the upstream promoter was transcribed ninefold less efficiently than the major promoter. When templates which contain both promoters on the same piece of DNA were transcribed, the major promoter was at least 50-fold more efficient.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F., Barrell B. G. The sequence of 5 s ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):379–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy B. G., Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Transcriptional role for the nontranscribed spacer of rat ribosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2766–2773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Buttgereit D., Grummt I. A purified transcription factor (TIF-IB) binds to essential sequences of the mouse rDNA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):604–608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Normann A., Ohrlein A., Grummt I. The core promoter of mouse rDNA consists of two functionally distinct domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7581–7595. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. Spacer promoters are essential for efficient enhancement of X. laevis ribosomal transcription. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90765-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar V. N., Miller D. A., Miller O. J. Transcription of mouse rDNA and associated formation of the nucleolus organizer region after gene transfer and amplification in Chinese hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2943–2950. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. The major promoter element of rRNA transcription in yeast lies 2 kb upstream. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Nucleotide sequence requirements for specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6908–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Rosenbauer H., Niedermeyer I., Maier U., Ohrlein A. A repeated 18 bp sequence motif in the mouse rDNA spacer mediates binding of a nuclear factor and transcription termination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):837–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiner M. M., Smale S. T., Tjian R. Two distinct promoter elements in the human rRNA gene identified by linker scanning mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):227–235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. A., Chikaraishi D. M. Transcription of spacer sequences flanking the rat 45S ribosomal DNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):314–325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Nagamine M., Sasaki T., Takakusa N., Miwa T., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Presence of a limited number of essential nucleotides in the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3515–3532. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Nagamine M., Sasaki T., Takakusa N., Miwa T., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Presence of a limited number of essential nucleotides in the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3515–3532. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Localization of DNA sequences promoting RNA polymerase I activity in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3265–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. Nontranscribed spacer sequences promote in vitro transcription of Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6879–6886. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Enhancer-like properties of the 60/81 bp elements in the ribosomal gene spacer of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Smale S. T., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. Regulation of human ribosomal RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3558–3562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Rebbert M. L., Dawid I. B. Nucleotide sequence of the initiation site for ribosomal RNA transcription in Drosophila melanogaster: comparison of genes with and without insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1513–1517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal R. K. The organization and transcription of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:115–160. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Hayward D. C., Glover D. M. Transcription of the 'non-transcribed' spacer of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):11–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. A complex control region of the mouse rRNA gene directs accurate initiation by RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):554–562. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan G. T., Reeder R. H., Bakken A. H. Transcription in cloned spacers of Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6490–6494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. The putative promoter of a Xenopus laevis ribosomal gene is reduplicated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3733–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H. Enhancers and ribosomal gene spacers. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Roan J. G., Dunaway M. Spacer regulation of Xenopus ribosomal gene transcription: competition in oocytes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Achermann H., Crippa M. Transcription of spacer sequences in genes coding for ribosomal RNA in Xenopus cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer L. D., Miller O. L., Jr Electron microscopic study of Saccharomyces cerevisiae rDNA chromatin replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1148–1157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. A., Ohrlein A., Grummt I. In vitro mutagenesis and transcriptional analysis of a mouse ribosomal promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. E., Yip M., Holland M. J. Characterization of an RNA polymerase I-dependent promoter within the spacer region of yeast ribosomal cistrons. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9905–9915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandelt C., Grummt I. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes is a prerequisite for ribosomal DNA transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3795–3809. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. M., Bowman L. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Transcription of the mouse ribosomal spacer region. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):822–828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto O., Takakusa N., Mishima Y., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Determination of the promoter region of mouse ribosomal RNA gene by an in vitro transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):299–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Partial nucleotide sequence of a 3.4 kb fragment from the rat ribosomal DNA nontranscribed spacer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5557–5557. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Subrahmanyam C. S., Cassidy B., Rothblum L. I. Characterization of rat ribosomal DNA II. identification of the highly repetitive DNA in the 3' non-transcribed spacer. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavachev L. P., Georgiev O. I., Braga E. A., Avdonina T. A., Bogomolova A. E., Zhurkin V. B., Nosikov V. V., Hadjiolov A. A. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the spacer regions flanking the rat rRNA transcription unit and identification of repetitive elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2799–2810. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]