Abstract
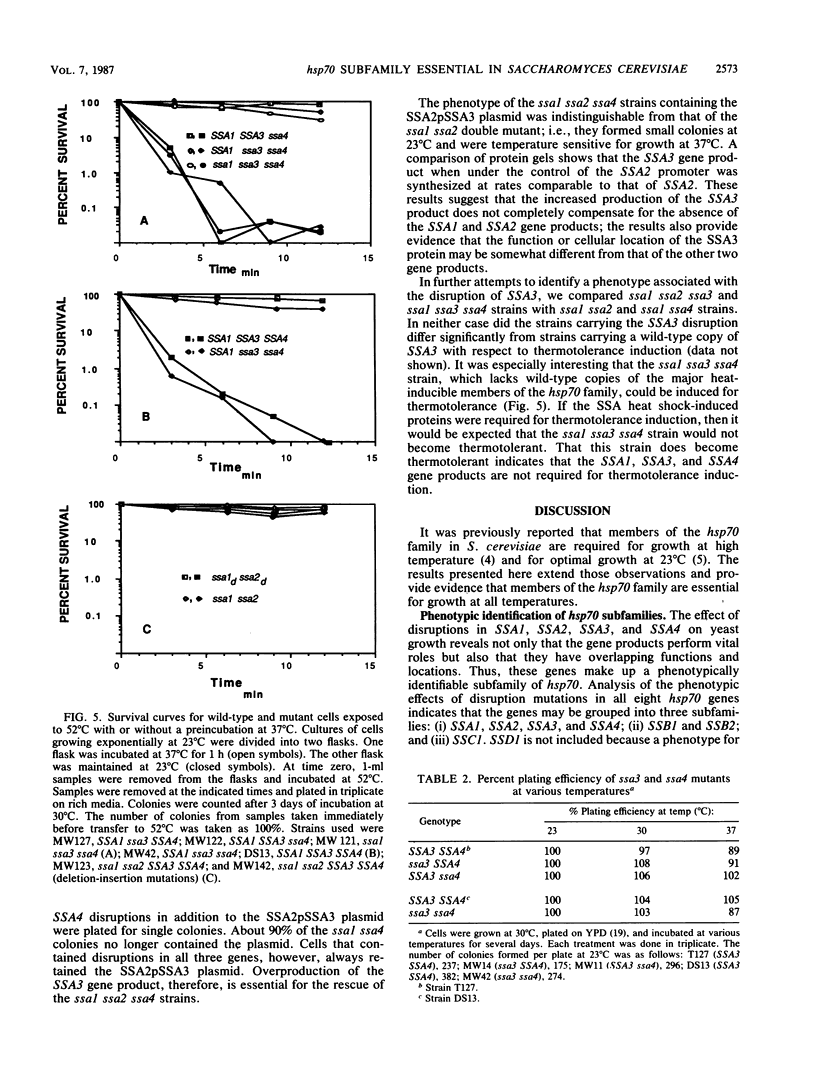
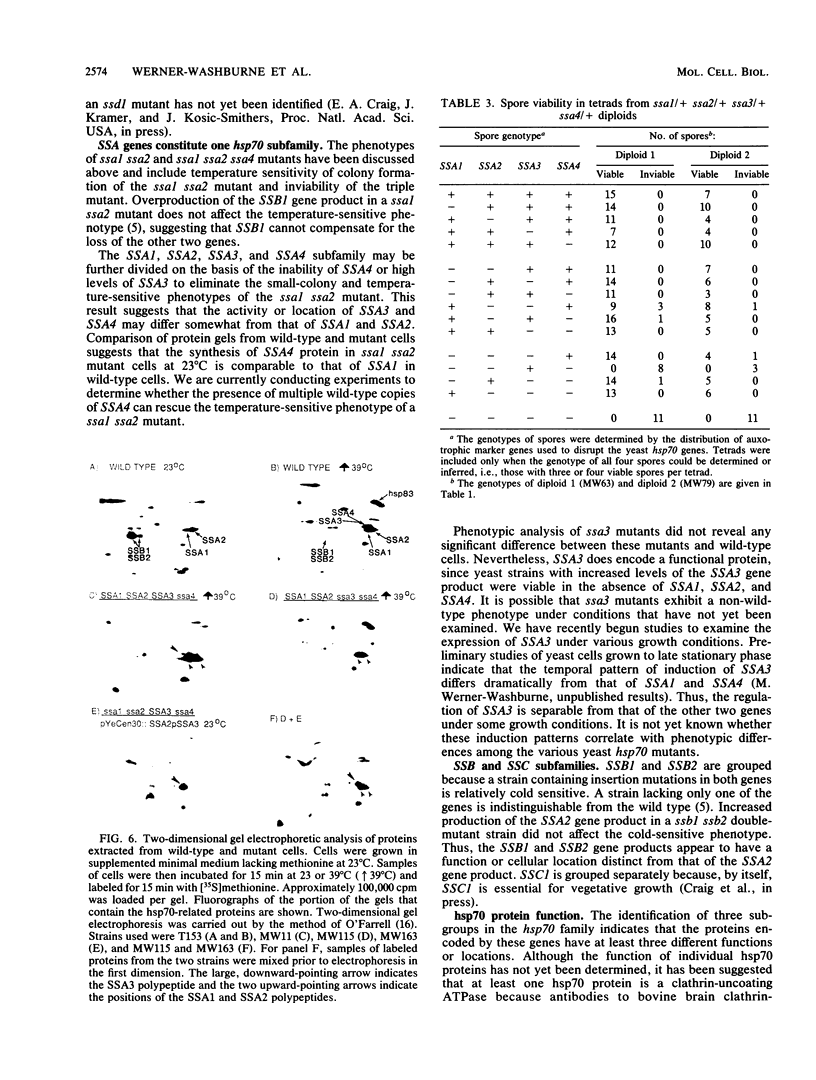
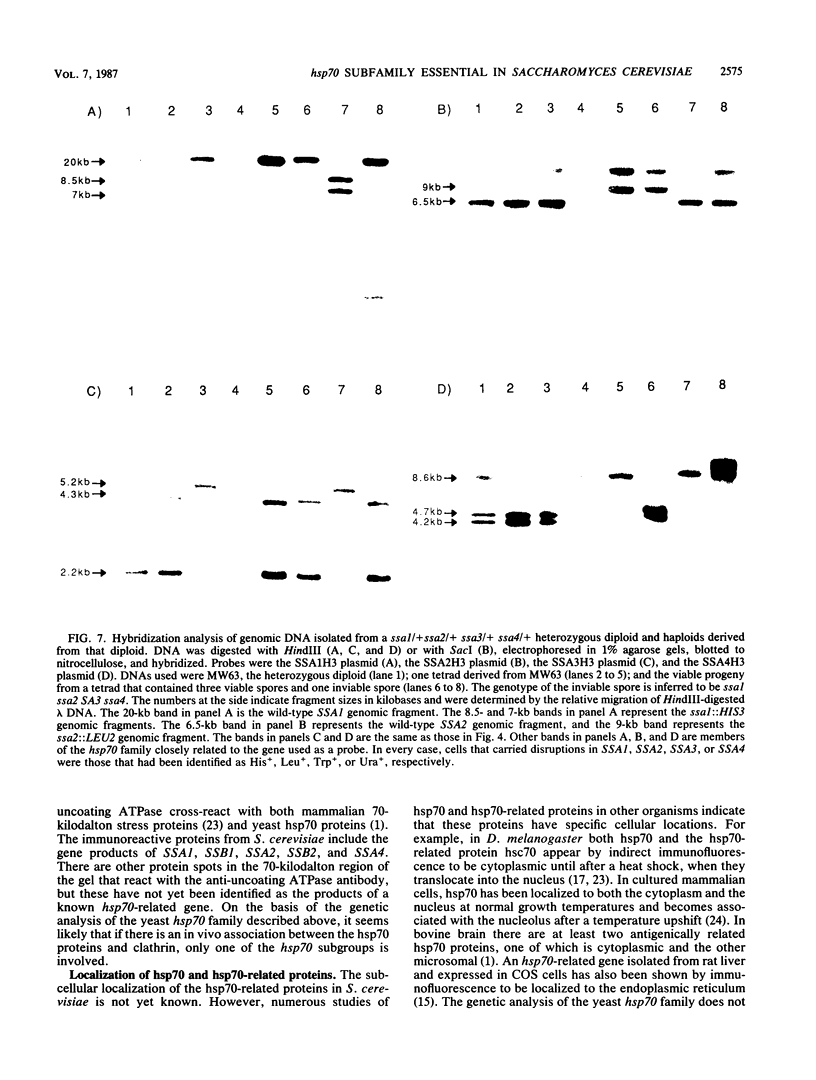
Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains a large family of genes related to hsp70, the major heat shock-inducible gene of Drosophila melanogaster. One subfamily, identified by sequence homology, contains four genes, SSA1, SSA2, SSA3, and SSA4 (formerly YG100, YG102, YG106, and YG107, respectively). Previous studies showed that strains containing mutations in SSA1 and SSA2 are temperature sensitive for growth. SSA4, which is normally heat inducible and not expressed during vegetative growth, is expressed at high levels in ssa1 ssa2 strains at 23 degrees C. We constructed mutations in SSA3 and SSA4 and analyzed strains carrying mutations in the four genes. Strains carrying mutations in SSA3 SSA4 or SSA3 and SSA4 were indistinguishable from the wild type. However, ssa1 ssa2 ssa4 strains were inviable. SSA3, like SSA4, is a heat-inducible gene that is not normally expressed at 23 degrees C. Nevertheless, an intact copy of SSA3 regulated by the constitutive SSA2 promoter was capable of rescuing a ssa1 ssa2 ssa4 strain. This indicates that SSA3 encodes a functional protein and that the SSA1, SSA2, SSA3, and SSA4 gene products are functionally similar.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chappell T. G., Welch W. J., Schlossman D. M., Palter K. B., Schlesinger M. J., Rothman J. E. Uncoating ATPase is a member of the 70 kilodalton family of stress proteins. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Jacobsen K. Mutations in cognate genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae hsp70 result in reduced growth rates at low temperatures. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3517–3524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Jacobsen K. Mutations of the heat inducible 70 kilodalton genes of yeast confer temperature sensitive growth. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):841–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. The heat shock response. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(3):239–280. doi: 10.3109/10409238509085135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison J., Heusterspreute M., Merchez M., Brunel F. Vectors with restriction-site banks. I. pJRD158, a 3903-bp plasmid containing 28 unique cloning sites. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellwood M. S., Craig E. A. Differential regulation of the 70K heat shock gene and related genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1454–1459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains a complex multigene family related to the major heat shock-inducible gene of Drosophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Arias A. E., Casadaban M. J. Fusion of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae leu2 gene to an Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):580–586. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Xuong N. H., Geiduschek E. P. A response of protein synthesis to temperature shift in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5222–5225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mues G. I., Munn T. Z., Raese J. D. A human gene family with sequence homology to Drosophila melanogaster Hsp70 heat shock genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):874–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palter K. B., Watanabe M., Stinson L., Mahowald A. P., Craig E. A. Expression and localization of Drosophila melanogaster hsp70 cognate proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1187–1203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin D. Y., Matsumoto K., Iida H., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Heat shock response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants altered in cyclic AMP-dependent protein phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):244–250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungewickell E. The 70-kd mammalian heat shock proteins are structurally and functionally related to the uncoating protein that releases clathrin triskelia from coated vesicles. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3385–3391. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez J. M., Lindquist S. hsp70: nuclear concentration during environmental stress and cytoplasmic storage during recovery. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):655–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Nuclear and nucleolar localization of the 72,000-dalton heat shock protein in heat-shocked mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]