Abstract
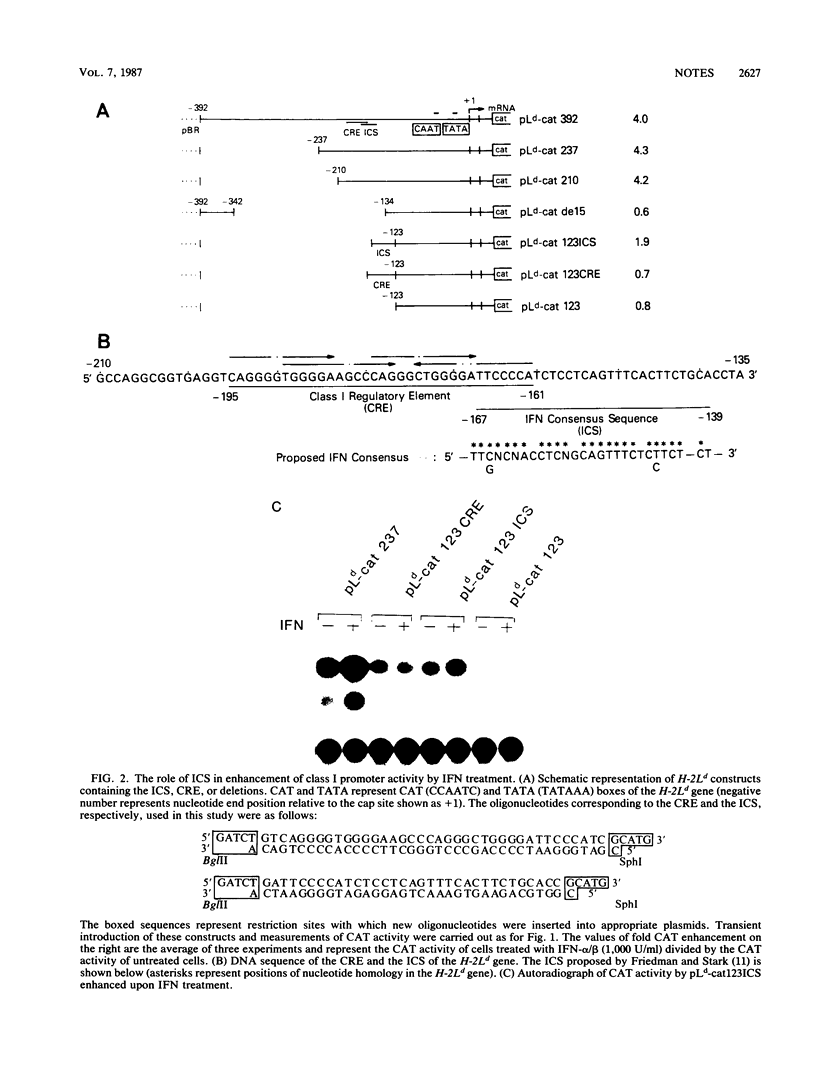
Interferons (IFNs) augment expression of major histocompatibility class I genes in many cells. To study the effect of IFNs on transcription of class I genes, we prepared and tested activity of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) hybrid genes in which the cat gene is under the control of the 5' flanking region of the murine H-2Ld gene. NIH 3T3 cells transiently transfected with a cat construct having the sequence from position -210 to -134 showed a four- to fivefold increase in CAT activity when treated with IFN-alpha/beta. This sequence contains the IFN consensus sequence (ICS) shared among IFN-inducible genes, as well as the class I regulatory element (CRE) that controls up and down regulation of class I gene expression. To determine the precise sequence requirement for the IFN action, the ICS and CRE were independently placed upstream of the class I or a heterologous simian virus 40 promoter, and CAT activity was tested. The ICS, but not the CRE, enhanced activity of both promoters by about twofold upon exposure to IFN-alpha/beta, although greater responses were noted when the ICS and CRE were combined. These results demonstrate that the ICS alone is capable of enhancing promoter activity in response to IFN-alpha/beta treatment and that the CRE exerts a synergistic effect. Further, we show that the ICS functions as an inducible enhancer since it acts regardless of its orientation and distance in the simian virus 40 promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Bourgeade M. F., Creasey A. A., Merigan T. C. Interferon increases HLA synthesis in melanoma cells: interferon-resistant and -sensitive cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Regulation of a transfected human class II major histocompatibility complex gene in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Merlin G., Metz R., Benech P., Revel M. Interferon-induced 56,000 Mr protein and its mRNA in human cells: molecular cloning and partial sequence of the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1213–1226. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Margulies D. H., Shykind B., Seidman J. G., Ozato K. Exon shuffling: mapping polymorphic determinants on hybrid mouse transplantation antigens. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):755–757. doi: 10.1038/300755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Nir U., Wallach D., Merlin G., Rubinstein M., Revel M. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA for the major histocompatibility antigens in human fibroblasts and lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. Transformation of rat cells by DNA of human adenovirus 5. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):536–539. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Differential regulation of interferon-induced mRNAs and c-myc mRNA by alpha- and gamma-interferons. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 2;153(2):367–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Jonak G., Cheng Y. S., Korant B., Knight E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction of two genes in human cells by beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6733–6737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Mulligan R., Berg P., Ringold G. Glucocorticoids regulate expression of dihydrofolate reductase cDNA in mouse mammary tumour virus chimaeric plasmids. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):228–232. doi: 10.1038/294228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D., Larner A., Chaudhuri A., Babiss L. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-stimulated transcription: isolation of an inducible gene and identification of its regulatory region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8929–8933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Negative regulation of the major histocompatibility class I gene in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9537–9541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Wan Y. J., Orrison B. M. Mouse major histocompatibility class I gene expression begins at midsomite stage and is inducible in earlier-stage embryos by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashidbaigi A., Langer J. A., Jung V., Jones C., Morse H. G., Tischfield J. A., Trill J. J., Kung H. F., Pestka S. The gene for the human immune interferon receptor is located on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):384–388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Le Bouteiller P. P., Abadie A., Mishal Z., Lemonnier F. A., Bourrel D., Lamotte M., Kalil J., Jordan B., Fellous M. HLA class I genes integrated into murine cells are inducible by interferon. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jun;13(6):495–499. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Gupta S. L. Differential efficacies of human type I and type II interferons as antiviral and antiproliferative agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5928–5932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satz M. L., Singer D. S. Effect of mouse interferon on the expression of a porcine major histocompatibility gene introduced into mouse L cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Setoyama C., de Crombrugghe B. Regulation of a collagen gene promoter by the product of viral mos oncogene. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):286–289. doi: 10.1038/314286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Danielson P., Haller O., Sutcliffe J. G. Transcriptional activation of the mouse Mx gene by type I interferon. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4770–4774. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli P., Haller O., Boll W., Lindenmann J., Weissmann C. Mx protein: constitutive expression in 3T3 cells transformed with cloned Mx cDNA confers selective resistance to influenza virus. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia antigen expression by a lymphokine with immune interferon activity. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C., Felber B. K., Carter A. D., Hamer D. H. Competition for cellular factors that activate metallothionein gene transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):781–785. doi: 10.1038/312781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J., Kress M., Khoury G., Jay G. A transcriptional enhancer and an interferon-responsive sequence in major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3550–3554. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Fellous M., Revel M. Preferential effect of gamma interferon on the synthesis of HLA antigens and their mRNAs in human cells. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):833–836. doi: 10.1038/299833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B., Sedmak J. J., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. A unique set of polypeptides is induced by gamma interferon in addition to those induced in common with alpha and beta interferons. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):437–439. doi: 10.1038/301437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Bartlett P. F., Clark-Lewis I., Battye F., Schrader J. W. Inducible expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):688–691. doi: 10.1038/310688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Kawade Y. Antigenicity of mouse interferons: distinct antigenicity of the two L cell interferon species. Virology. 1980 May;103(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Schmidt H., Reddy E. S., Weissman S., Lengyel P. Mouse interferons enhance the accumulation of a human HLA RNA and protein in transfected mouse and hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13169–13172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]