Abstract
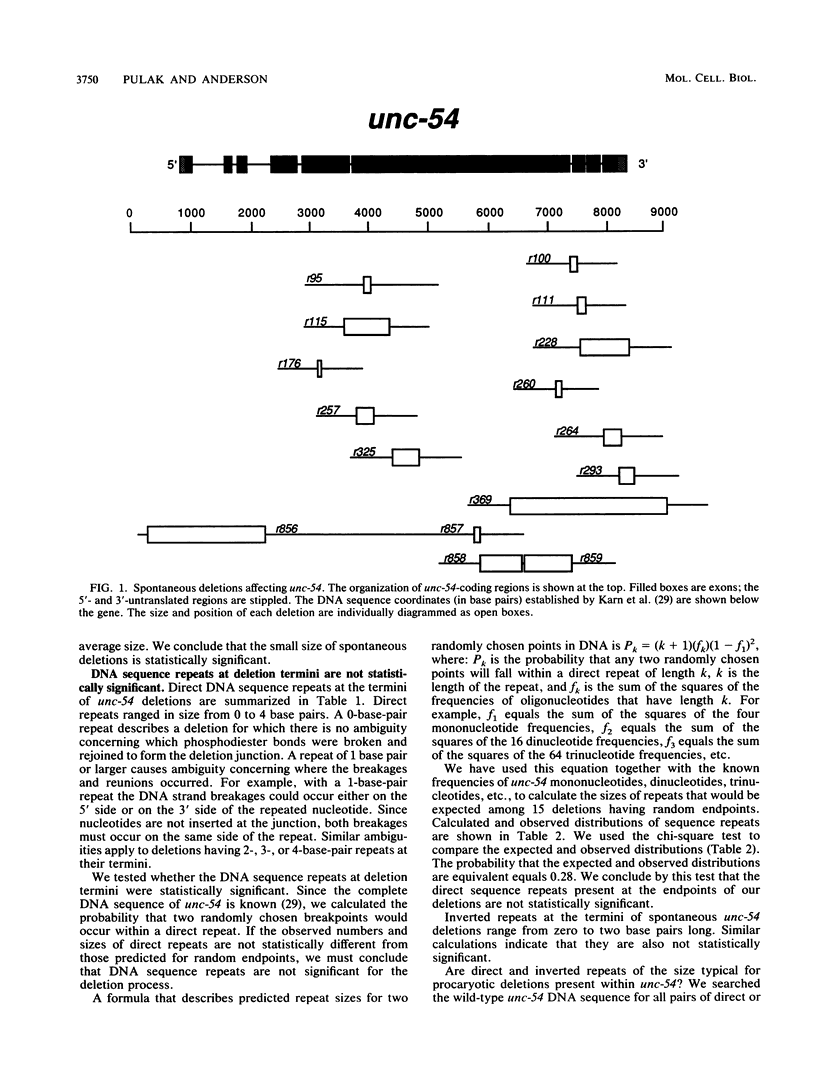
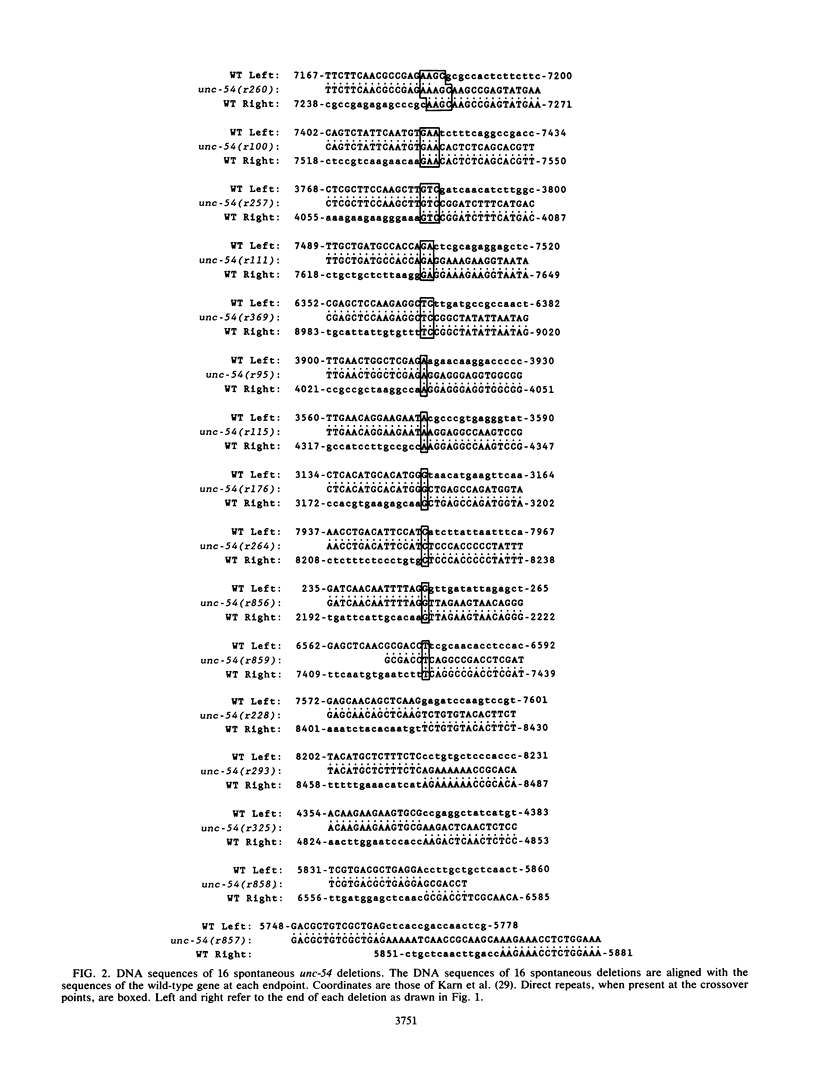
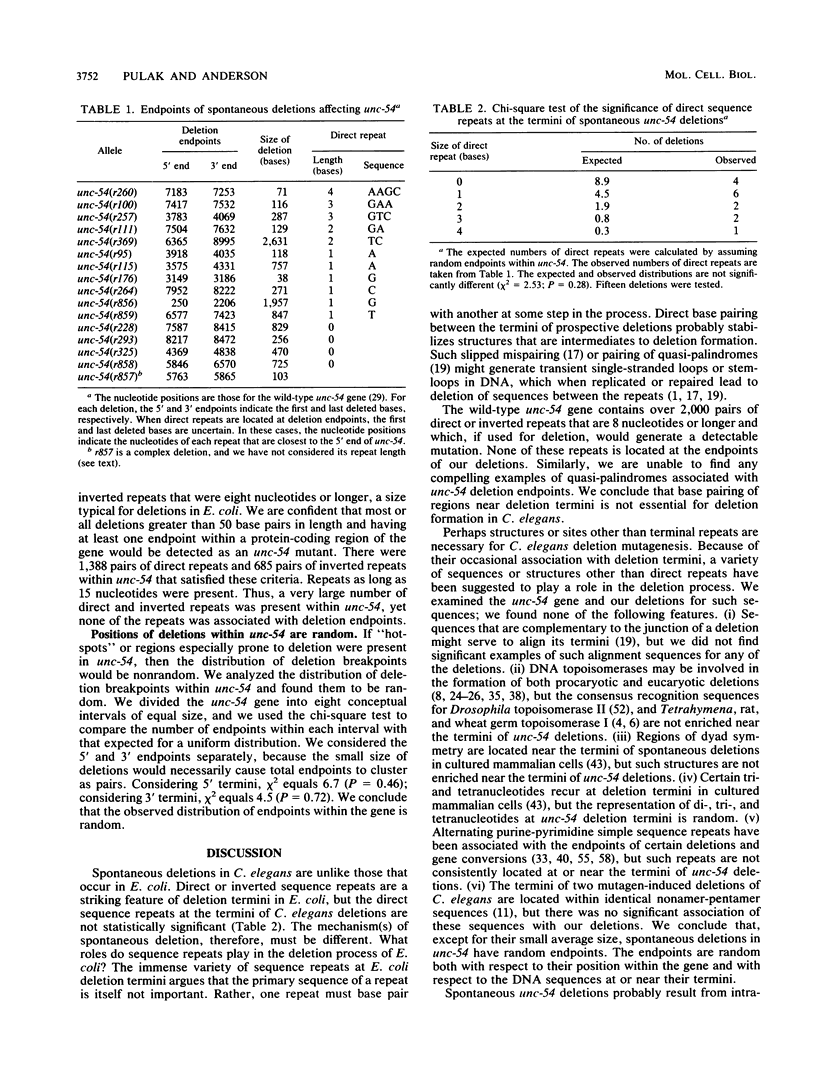
We have investigated the structural features of spontaneous deletions in Caenorhabditis elegans. We cloned and sequenced the junctions of 16 spontaneous deletions affecting the unc-54 myosin heavy-chain gene and compared their sequences with those of the wild type. We analyzed these sequences in an attempt to identify structural features of the gene that are consistently involved in the spontaneous deletion process. Most deletions (15 of 16) removed a single contiguous region of DNA, with no nucleotides inserted or rearranged at the deletion junctions; one deletion was more complex. unc-54 deletions were small, averaging 600 base pairs in length, and were randomly distributed throughout the gene. Unlike deletions that occur in Escherichia coli, spontaneous unc-54 deletions did not contain statistically significant direct or inverted repeats at or near their termini. Except for their small average size, we have not identified any distinguishing features of their sequence or structure. We discuss these results with regard to the mechanisms for spontaneous deletion in eucaryotic and procaryotic cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertson D. G., Sulston J. E., White J. G. Cell cycling and DNA replication in a mutant blocked in cell division in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1978 Mar;63(1):165–178. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Kato S., Camerini-Otero R. D. A pattern of partially homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):206–210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Burgess R. R., Champoux J. J. Nucleotide sequence preference at rat liver and wheat germ type 1 DNA topoisomerase breakage sites in duplex SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3097–3114. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonven B. J., Gocke E., Westergaard O. A high affinity topoisomerase I binding sequence is clustered at DNAase I hypersensitive sites in Tetrahymena R-chromatin. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):541–551. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P., Champoux J. J., Botchan M. Association of crossover points with topoisomerase I cleavage sites: a model for nonhomologous recombination. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.2997924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P., Forrester W., Botchan M. DNA sequence studies of simian virus 40 chromosomal excision and integration in rat cells. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):55–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang X. B., Wilson J. H. Modification of DNA ends can decrease end joining relative to homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4959–4963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibb N. J., Brown D. M., Karn J., Moerman D. G., Bolten S. L., Waterston R. H. Sequence analysis of mutations that affect the synthesis, assembly and enzymatic activity of the unc-54 myosin heavy chain of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide D., Anderson P. The gene structures of spontaneous mutations affecting a Caenorhabditis elegans myosin heavy chain gene. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):67–79. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide D., Anderson P. Transposition of Tc1 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1756–1760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Lundblad V., Hanley-Way S., Halling S. M., Kleckner N. Three Tn10-associated excision events: relationship to transposition and role of direct and inverted repeats. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C. Extraordinary recombinational events in Escherichia coli. Their independence of the rec+ function. Genetics. 1967 Apr;55(4):699–707. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman B. W., Ripley L. S. Structural intermediates of deletion mutagenesis: a role for palindromic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):512–516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. Z., Kuebbing D., Trauber D., Schafer M. P., Lewis S. E., Popp R. A., Anderson W. F. A 66-base pair insert bridges the deletion responsible for a mouse model of beta-thalassemia. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12368–12374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Mager D. L., Huisman T. H., Smithies O. A gene deletion ending within a complex array of repeated sequences 3' to the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5194–5198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsthemke B., Beisiegel U., Dunning A., Havinga J. R., Williamson R., Humphries S. Unequal crossing-over between two alu-repetitive DNA sequences in the low-density-lipoprotein-receptor gene. A possible mechanism for the defect in a patient with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 1;164(1):77–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Aoki K., Naito A. Illegitimate recombination mediated in vitro by DNA gyrase of Escherichia coli: structure of recombinant DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3724–3728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H. Bacteriophage T4 DNA topoisomerase mediates illegitimate recombination in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):922–926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Moriya K., Matsumoto T. In vitro study of illegitimate recombination: involvement of DNA gyrase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):399–408. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J. Formation of deletion mutations in recombination-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1266–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1266-1267.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. W., Jones R. W., Wood W. G., Weatherall D. J. Analysis of an inversion within the human beta globin gene cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2897–2906. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. Protein structural domains in the Caenorhabditis elegans unc-54 myosin heavy chain gene are not separated by introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopchick J. J., Stacey D. W. Differences in intracellular DNA ligation after microinjection and transfection. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):240–246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Alu-Alu recombination deletes splice acceptor sites and produces secreted low density lipoprotein receptor in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3354–3361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):140–146. doi: 10.1126/science.3155573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Henthorn P. S., Smithies O. A Chinese G gamma + (A gamma delta beta)zero thalassemia deletion: comparison to other deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster and sequence analysis of the breakpoints. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6559–6575. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvo S. L., King S. R., Jaskunas S. R. Role of short regions of homology in intermolecular illegitimate recombination events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2452–2456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Stability of Broken Ends of Chromosomes in Zea Mays. Genetics. 1941 Mar;26(2):234–282. doi: 10.1093/genetics/26.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B., Ehrlich S. D. Illegitimate recombination at the replication origin of bacteriophage M13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3386–3390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. K., Temin H. M. High-efficiency ligation and recombination of DNA fragments by vertebrate cells. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):606–609. doi: 10.1126/science.6301012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molineaux S. M., Engh H., de Ferra F., Hudson L., Lazzarini R. A. Recombination within the myelin basic protein gene created the dysmyelinating shiverer mouse mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7542–7546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Hogikyan N. D. A deletion involving Alu sequences in the beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain gene of French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15396–15399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B., Kania J. Lac repressor can be fused to beta-galactosidase. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):561–563. doi: 10.1038/249561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Hartley D., Phear G., Tear G., Meuth M. Spontaneous deletion formation at the aprt locus of hamster cells: the presence of short sequence homologies and dyad symmetries at deletion termini. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1199–1204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04347.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Phear G., Meuth M. DNA sequence analysis of spontaneous mutations at the aprt locus of hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1445–1449. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Higgs D. R. Recombination at the human alpha-globin gene cluster: sequence features and topological constraints. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. C., Horvitz H. R. C. elegans unc-105 mutations affect muscle and are suppressed by other mutations that affect muscle. Genetics. 1986 Aug;113(4):853–867. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Relative rates of homologous and nonhomologous recombination in transfected DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3355–3359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R., Helms C., Rosenberg N. Concerted deletions and inversions are caused by mitotic recombination between delta sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1198–1207. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Danforth B. N., Glickman B. W. Mechanisms of spontaneous mutagenesis: an analysis of the spectrum of spontaneous mutation in the Escherichia coli lacI gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 20;189(2):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90509-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Orkin S. H. Duplication followed by deletion accounts for the structure of an Indian deletion beta (0)-thalassemia gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8025–8029. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Horn V., Yanofsky C. On the production of deletions in the chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):49–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R. Recombination between poly[d(GT).d(CA)] sequences in simian virus 40-infected cultured cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1247–1259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J. E., Brenner S. The DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):95–104. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Henthorn P. S., Kioussis D., Grosveld F., Smithies O. Unexpected relationships between four large deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Fried M. Inverted duplication-transposition event in mammalian cells at an illegitimate recombination join. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2179–2184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


