Abstract
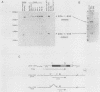
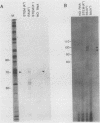
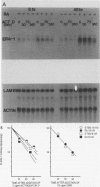
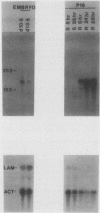
Retinoic acid (RA), the natural acidic derivative of vitamin A, can modulate the expression of specific genes and can induce some cell types, such as the murine F9 teratocarcinoma stem cell line, to differentiate in culture. As an initial step toward understanding the molecular mechanism(s) by which RA exerts these effects, we previously isolated cDNA clones for a gene, ERA-1, which has the characteristics of an early, direct target for RA. We demonstrated that RA causes a rapid, dose-dependent, and protein synthesis-independent expression of the ERA-1 gene (G. J. LaRosa and L. J. Gudas, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:329-333, 1988). We now report the full-length cDNA sequence and the further characterization of this gene. The data indicate that the RA-induced 2.2- to 2.4-kilobase ERA-1 RNA species that we previously detected consists of two alternately spliced messages. One mRNA encodes a protein with a predicted mass of about 36 kilodaltons (kDa) that possesses the Hox 1.6 homeobox domain. The other mRNA encodes a truncated protein of about 15 kDa which is identical to the 36-kDa protein for 114 amino acids at the amino-terminal end but which lacks the homeobox amino acid sequence. The RA-associated increase in the ERA-1 mRNA level does not appear to be due to message stabilization, suggesting that the response is at the level of transcription. By Northern (RNA) blot analysis, the usual 2.2- to 2.4-kilobase mRNA species was also rapidly expressed in P19 teratocarcinoma cells during their differentiation to fibroblastic cells in response to RA and was detected in day 10.5 and day 13.5 mouse embryos. This result indicates that the expression of this gene is not limited to the endodermal differentiation of F9 cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awgulewitsch A., Utset M. F., Hart C. P., McGinnis W., Ruddle F. H. Spatial restriction in expression of a mouse homoeo box locus within the central nervous system. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):328–335. doi: 10.1038/320328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron A., Featherstone M. S., Hill R. E., Hall A., Galliot B., Duboule D. Hox-1.6: a mouse homeo-box-containing gene member of the Hox-1 complex. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2977–2986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breier G., Bućan M., Francke U., Colberg-Poley A. M., Gruss P. Sequential expression of murine homeo box genes during F9 EC cell differentiation. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2209–2215. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Scott M. P. Localization of the fushi tarazu protein during Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F., Ong D. E. Cellular vitamin A binding proteins. Vitam Horm. 1978;36:1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60980-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Voss S. D., Chowdhury K., Stewart C. L., Wagner E. F., Gruss P. Clustered homeo boxes are differentially expressed during murine development. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Huebner K., Parnes J. R., Margulies D. H., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Control of expression of histocompatibility antigens (H-2) and beta 2-microglobulin in F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5754–5758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The Drosophila developmental gene, engrailed, encodes a sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):630–635. doi: 10.1038/318630a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Kuner J. M., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. Development of embryonic pattern in D. melanogaster as revealed by accumulation of the nuclear engrailed protein. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90012-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duboule D., Baron A., Mähl P., Galliot B. A new homeo-box is present in overlapping cosmid clones which define the mouse Hox-1 locus. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1973–1980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duprey P., Morello D., Vasseur M., Babinet C., Condamine H., Brûlet P., Jacob F. Expression of the cytokeratin endo A gene during early mouse embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainsod A., Bogarad L. D., Ruusala T., Lubin M., Crothers D. M., Ruddle F. H. The homeo domain of a murine protein binds 5' to its own homeo box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9532–9536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haff L. A., Bogorad L. Poly(adenylic acid)-containing RNA from plastids of maize. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):4110–4115. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Doyle H. J., Harding K., Wedeen C., Levine M. Homeo box gene expression in anterior and posterior regions of the Drosophila embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4809–4813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Schulze F., Fibi M., Gruss P. Primary structure and nuclear localization of a murine homeodomain protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5306–5310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Holland P. W., McVey J. H., Hogan B. L. Developmental and spatial patterns of expression of the mouse homeobox gene, Hox 2.1. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):603–617. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurkinen M., Barlow D. P., Helfman D. M., Williams J. G., Hogan B. L. Isolation of cDNA clones for basal lamina components: type IV procollagen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6199–6209. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
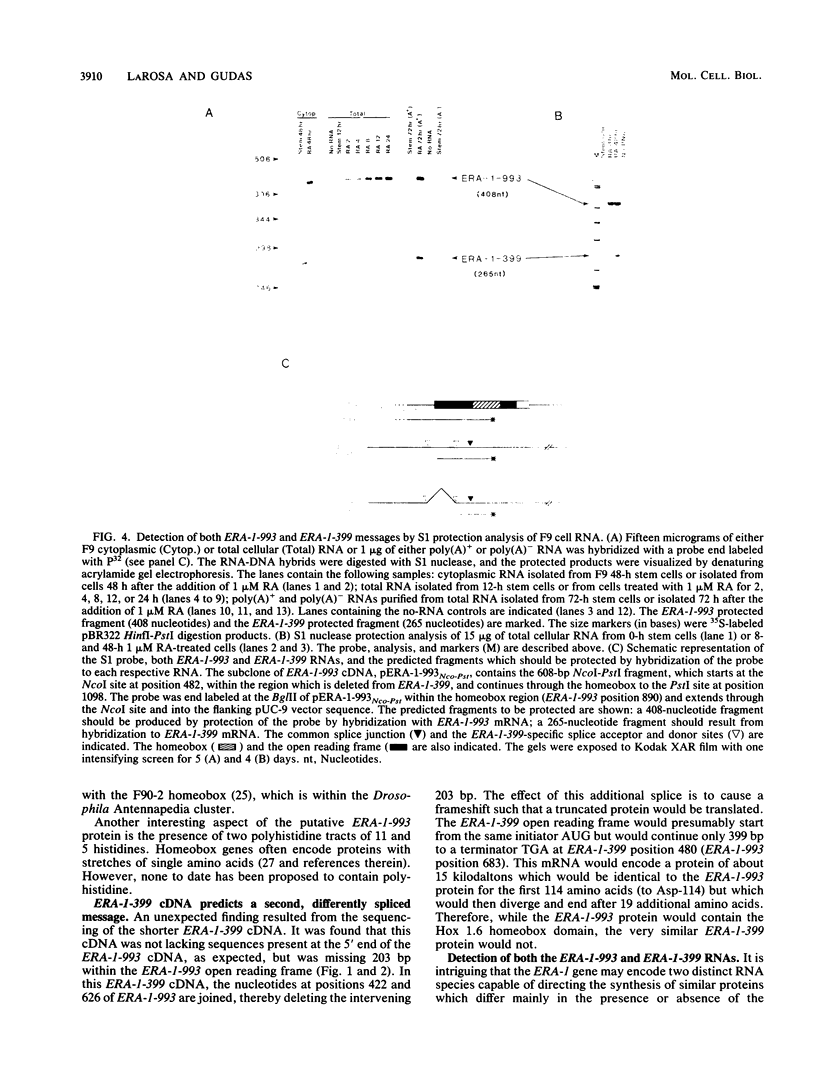
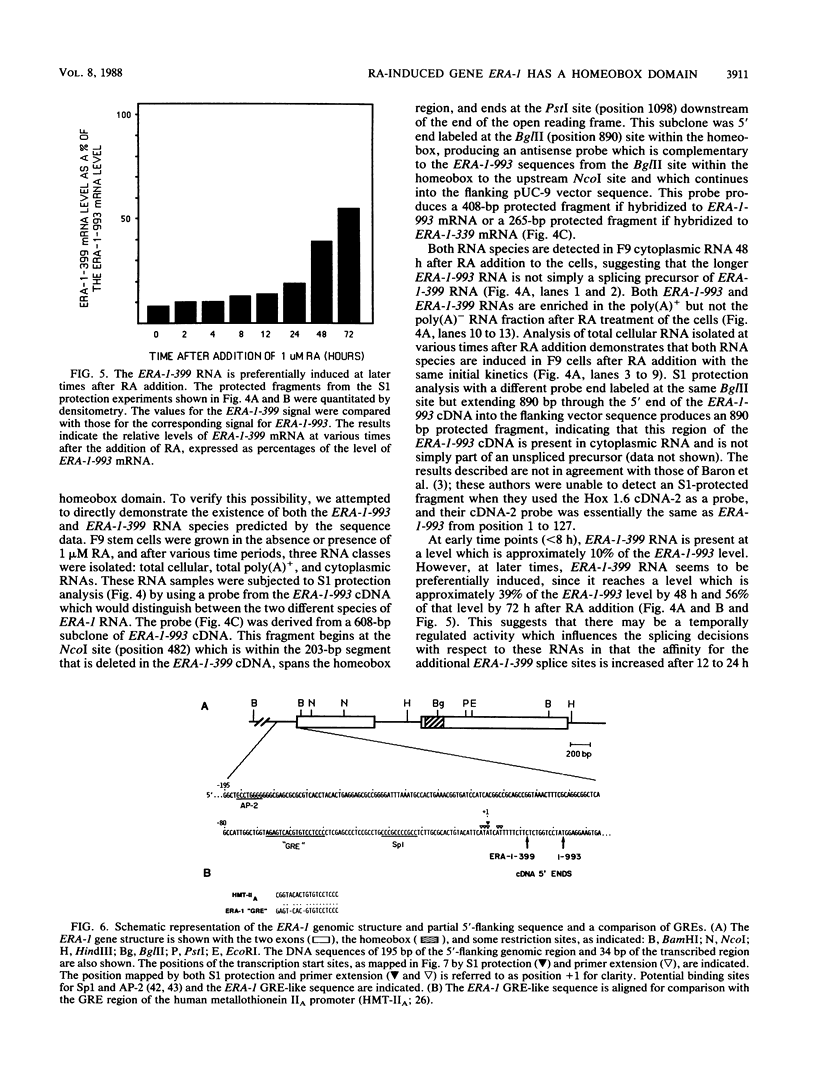
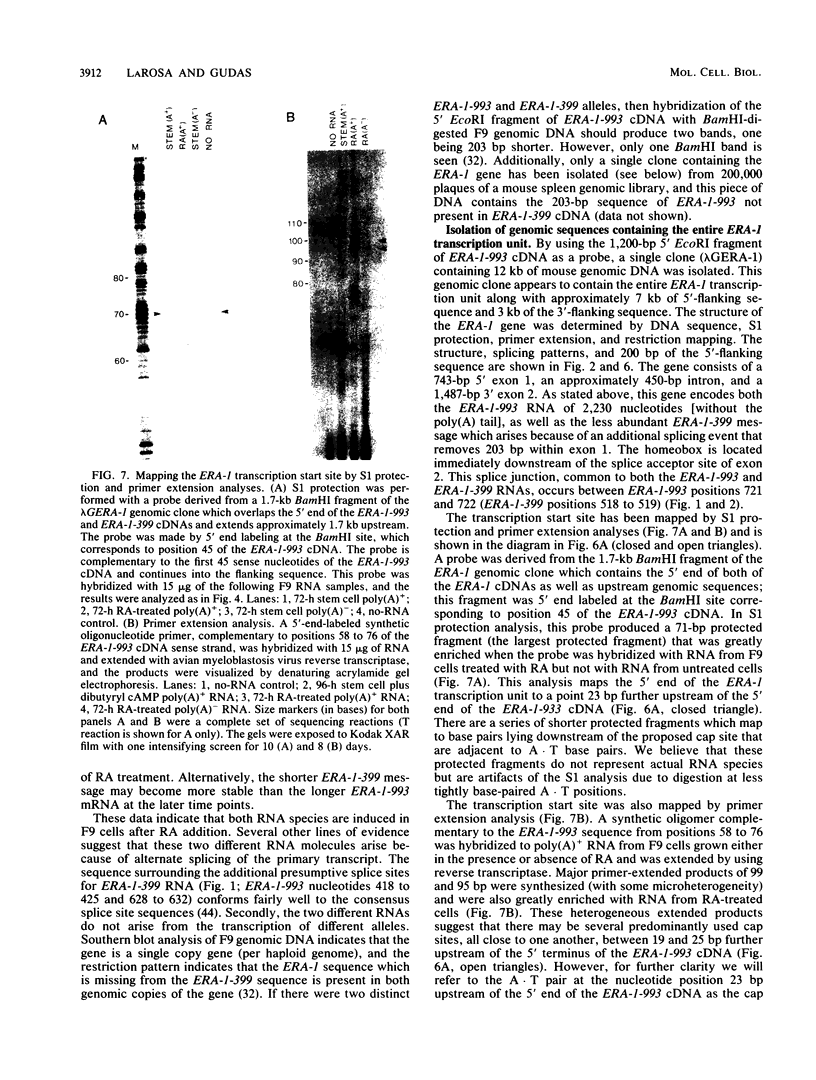
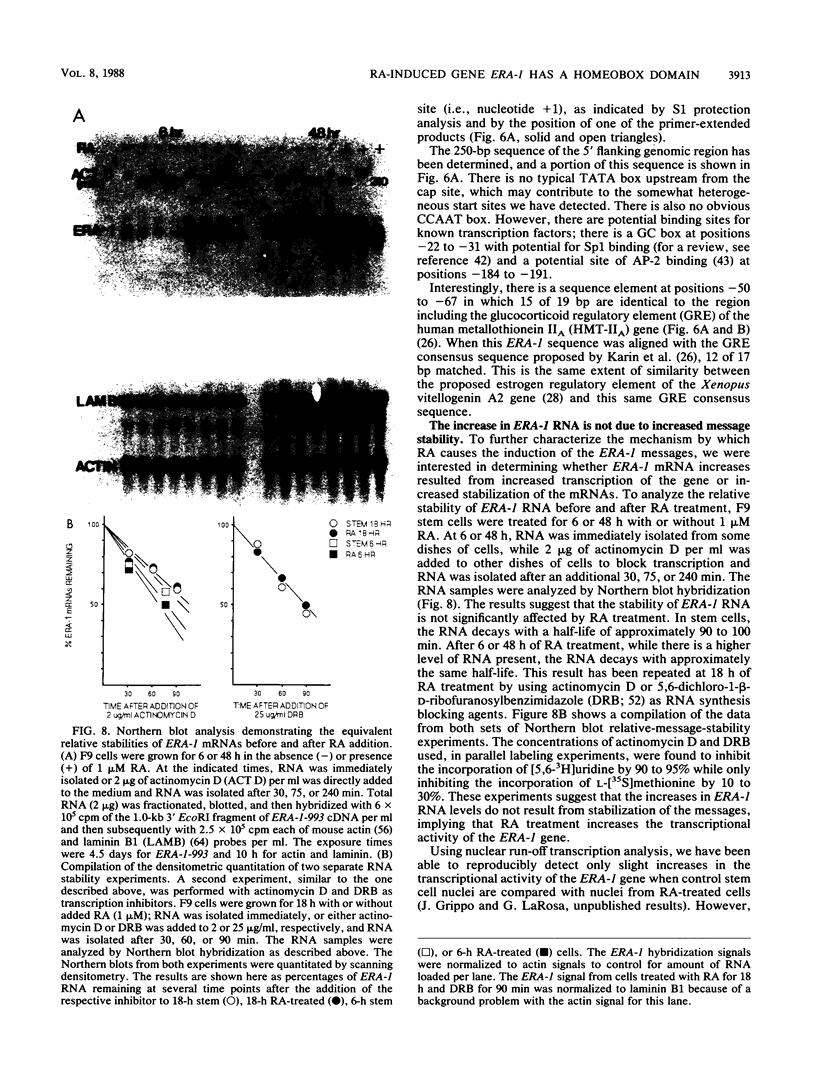
- LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. An early effect of retinoic acid: cloning of an mRNA (Era-1) exhibiting rapid and protein synthesis-independent induction during teratocarcinoma stem cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):329–333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Scott M. P. Sequence of a Drosophila segmentation gene: protein structure homology with DNA-binding proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):25–31. doi: 10.1038/310025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Nomenclature for homoeobox-containing genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):21–22. doi: 10.1038/325021b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas and mammalian embryogenesis. Science. 1980 Aug 15;209(4458):768–776. doi: 10.1126/science.6250214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason I. J., Taylor A., Williams J. G., Sage H., Hogan B. L. Evidence from molecular cloning that SPARC, a major product of mouse embryo parietal endoderm, is related to an endothelial cell 'culture shock' glycoprotein of Mr 43,000. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1465–1472. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Edwards M. K., Anderson P. J. Control of muscle and neuronal differentiation in a cultured embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):165–167. doi: 10.1038/299165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Garber R. L., Wirz J., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. A homologous protein-coding sequence in Drosophila homeotic genes and its conservation in other metazoans. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Hart C. P., Gehring W. J., Ruddle F. H. Molecular cloning and chromosome mapping of a mouse DNA sequence homologous to homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Levine M. S., Hafen E., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. A conserved DNA sequence in homoeotic genes of the Drosophila Antennapedia and bithorax complexes. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):428–433. doi: 10.1038/308428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Female steroid hormones and target cell nuclei. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):610–620. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Taylor C. F., Palmer-Hill F. J., Friedrich V., Jr, Tani M., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a homeo domain protein in noncontact-inhibited cultured cells and postmitotic neurons. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):482–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. R., Toth L. E., Patel M. D., D'Eustachio P., Nguyen-Huu M. C. A mouse homeo box gene is expressed in spermatocytes and embryos. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):663–667. doi: 10.1126/science.3726554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Weiner A. J. Structural relationships among genes that control development: sequence homology between the Antennapedia, Ultrabithorax, and fushi tarazu loci of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4115–4119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Darnell J. E., Jr, Tamm I. The inhibition by DRB (5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole) of hnRNA and mRNA production in HeLa cells. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. A., Trevor K., Oshima R. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the Endo B cytokeratin expressed in preimplantation mouse embryos. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):538–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Frank M., Green H. Molecular cloning of mRNA from 3T3 adipocytes. Regulation of mRNA content for glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and other differentiation-dependent proteins during adipocyte development. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10083–10089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Role of retinoids in differentiation and carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3034–3040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohman R. C., Moss P. S., Micou-Eastwood J., Spector D., Przybyla A., Paterson B. Messenger RNA for myosin polypeptides: isolation from single myogenic cell cultures. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):625–628. doi: 10.1038/327625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Alberts B., Wolpert L., Lee J. Local application of retinoic acid to the limb bond mimics the action of the polarizing region. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):564–566. doi: 10.1038/296564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tickle C., Lee J., Eichele G. A quantitative analysis of the effect of all-trans-retinoic acid on the pattern of chick wing development. Dev Biol. 1985 May;109(1):82–95. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Gudas L. J. Isolation of cDNA clones specific for collagen IV and laminin from mouse teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5880–5884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Molecular cloning of gene sequences transcriptionally regulated by retinoic acid and dibutyryl cyclic AMP in cultured mouse teratocarcinoma cells. Dev Biol. 1985 Jan;107(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Wilcox M. Protein products of the bithorax complex in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Fritz A., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. A Xenopus laevis gene encodes both homeobox-containing and homeobox-less transcripts. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4083–4094. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02754.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]