Abstract
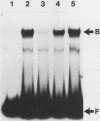
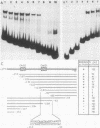
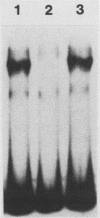
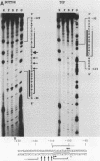
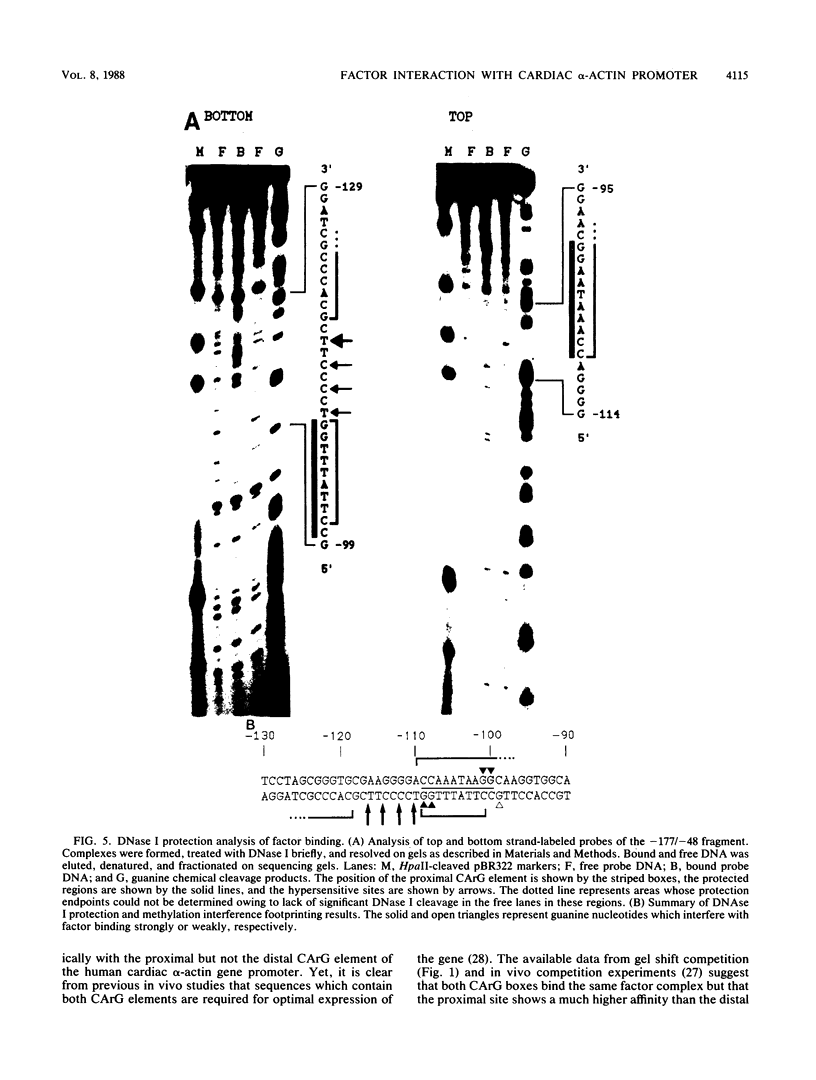
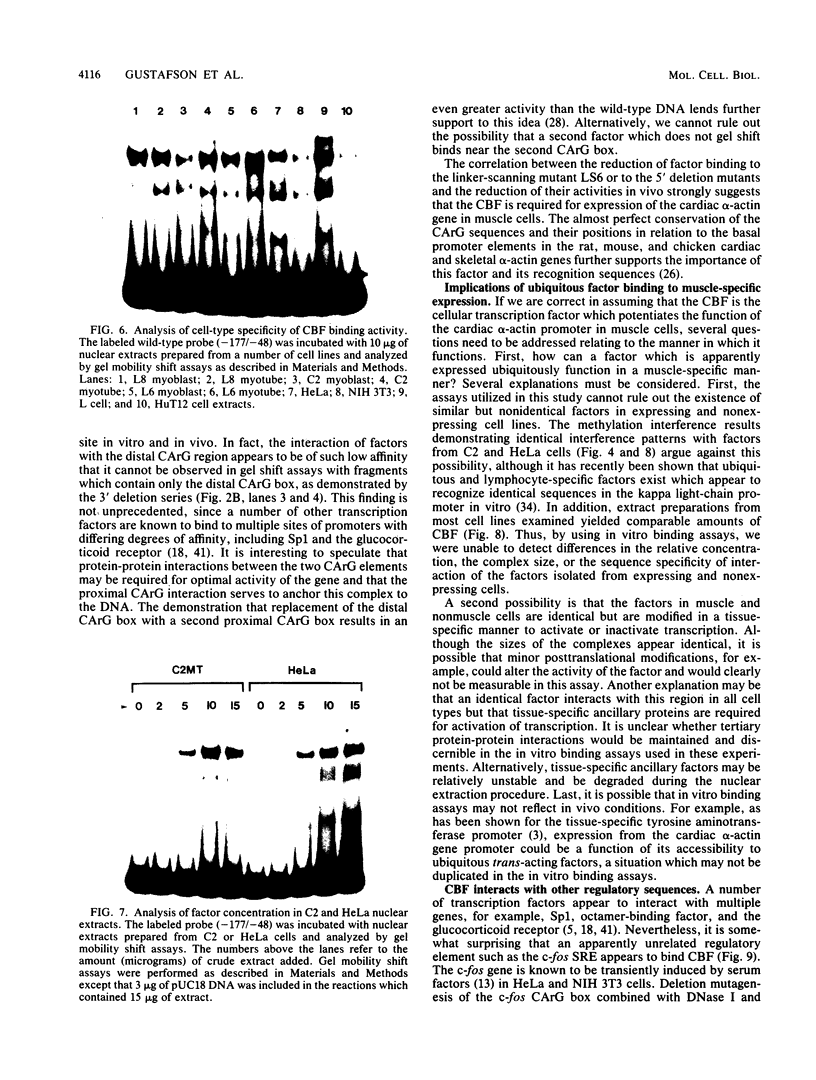
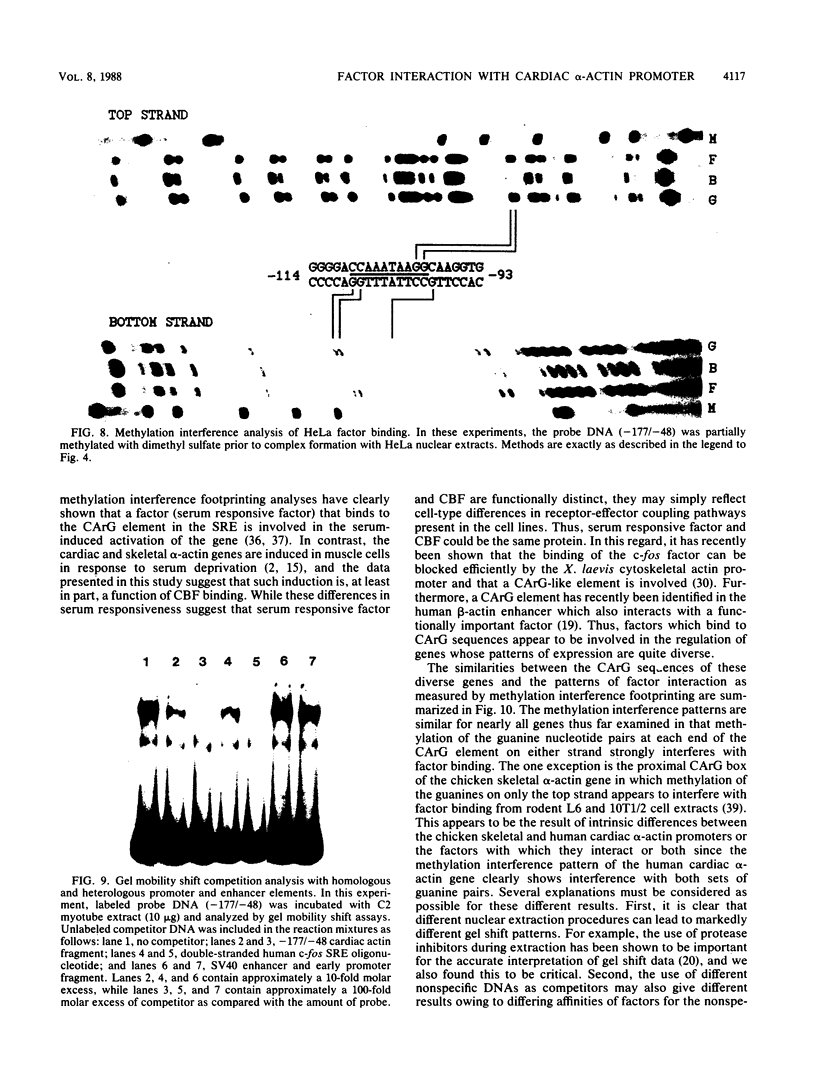
The human cardiac alpha-actin promoter is involved in the muscle-specific transcriptional regulation of the gene. In this study, we utilized gel mobility shift, methylation interference, and DNase I protection assays to examine protein factor interaction with the promoter in vitro. All assays demonstrated specific interaction of nuclear factors with a region of the promoter encompassed by nucleotides -93 to -113 base pairs from the transcriptional start site. This region contains a CC(A + T-rich)6GG element, termed a CArG box, which has previously been implicated in the muscle-specific transcriptional regulation of the gene by functional assays. Although the gene is only expressed in muscle cells, identical binding activity was present in nuclear extracts of all cell types examined, including those of muscle (C2, L8, and L6 cells) and nonmuscle (HeLa, NIH 3T3, HuT12, and L cells) origin. Furthermore, methylation interference assays showed that identical nucleotides interacted with factors isolated from C2 and HeLa cells. Competition studies showed that the CArG-binding factor, designated as CBF, also interacts with the c-fos serum responsive element, which contains a CArG element, but not with the simian virus 40 enhancer and early promoter. Thus, a region of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter known to be functionally involved in muscle-specific regulation of the gene appears to interact in vitro, and in an identical manner, with a factor(s) which is neither muscle nor gene specific, suggesting a more complex mode of regulation than previously envisioned.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F., Ohlendorf D. H., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Structure of the cro repressor from bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):754–758. doi: 10.1038/290754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Grichnik J. M., Gossett L. M., Schwartz R. J. Delimitation and characterization of cis-acting DNA sequences required for the regulated expression and transcriptional control of the chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2462–2475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Keller W., Dale T., Schöler H. R., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. A transcription factor which binds to the enhancers of SV40, immunoglobulin heavy chain and U2 snRNA genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):268–272. doi: 10.1038/325268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Blau H., Kedes L. alpha-skeletal and alpha-cardiac actin genes are coexpressed in adult human skeletal muscle and heart. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):1985–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey R., Skoultchi A., Gunning P., Kedes L. Regulation of a human cardiac actin gene introduced into rat L6 myoblasts suggests a defect in their myogenic program. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3287–3290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachimiak A., Kelley R. L., Gunsalus R. P., Yanofsky C., Sigler P. B. Purification and characterization of trp aporepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):668–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Makino K., Niwa H., Sugiyama H., Kimura S., Amemura M., Nakata A., Kakunaga T. Identification of the human beta-actin enhancer and its binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L. DNA-binding factors of B lymphoid cells are susceptible to limited proteolytic cleavage during nuclear extract preparation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1812–1815. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer Y., Czosnek H., Zeelon P. E., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Expression of the genes coding for the skeletal muscle and cardiac actions in the heart. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1087–1100. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B., Steitz T. A. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 A resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloul D., Aloni B., Calvo J., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Developmentally regulated expression of chimeric genes containing muscle actin DNA sequences in transfected myogenic cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):983–990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Blau H., Kedes L. Two-level regulation of cardiac actin gene transcription: muscle-specific modulating factors can accumulate before gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Boxer L. M., Kedes L. CArG boxes in the human cardiac alpha-actin gene are core binding sites for positive trans-acting regulatory factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6702–6706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Kedes L. Duplicated CArG box domains have positive and mutually dependent regulatory roles in expression of the human alpha-cardiac actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2803–2813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. Upstream sequences required for tissue-specific activation of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus laevis embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3185–3193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T., Garrett N., Treisman R. Xenopus cytoskeletal actin and human c-fos gene promoters share a conserved protein-binding site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):667–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Multiple 5'-flanking regions of the human alpha-skeletal actin gene synergistically modulate muscle-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Yaniv M. Two different factors bind to the alpha-domain of the polyoma virus enhancer, one of which also interacts with the SV40 and c-fos enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1331–1337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02372.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Bugaisky G., Buckingham M. Simultaneous expression of skeletal muscle and heart actin proteins in various striated muscle tissues and cells. A quantitative determination of the two actin isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1838–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Schimmel P. Two nuclear factors compete for the skeletal muscle actin promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9429–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]