Abstract
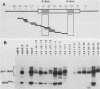
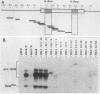
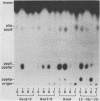
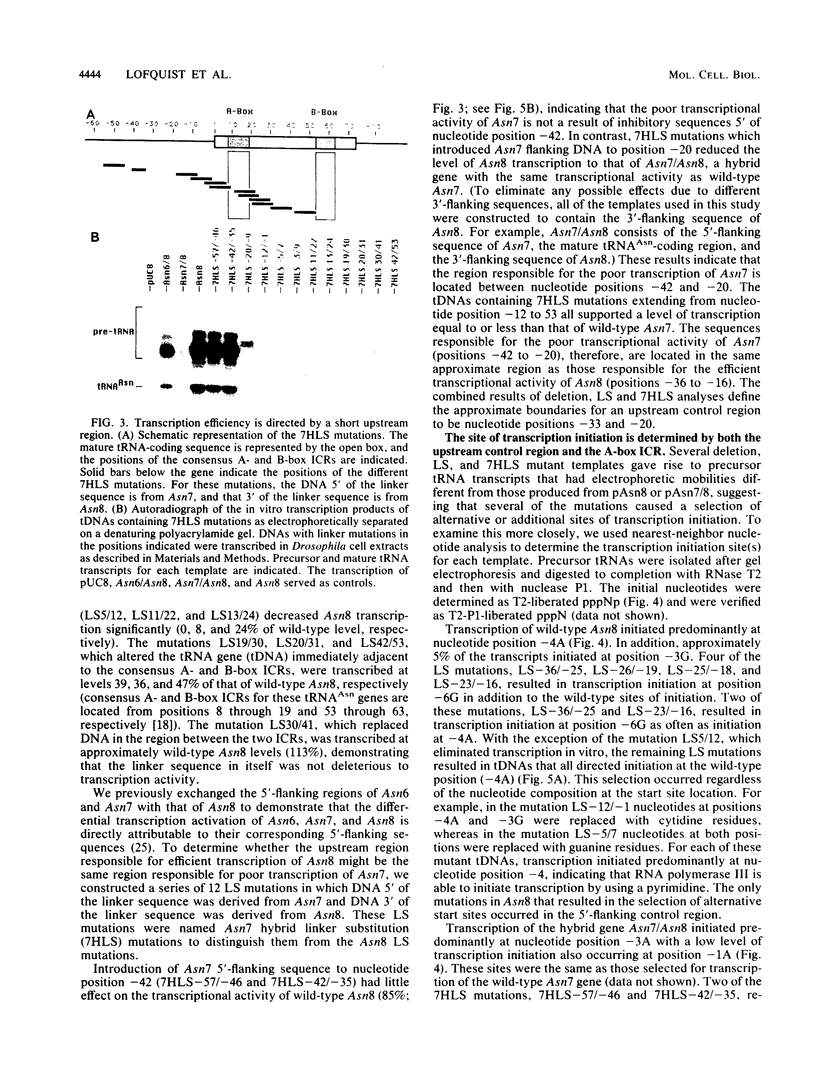
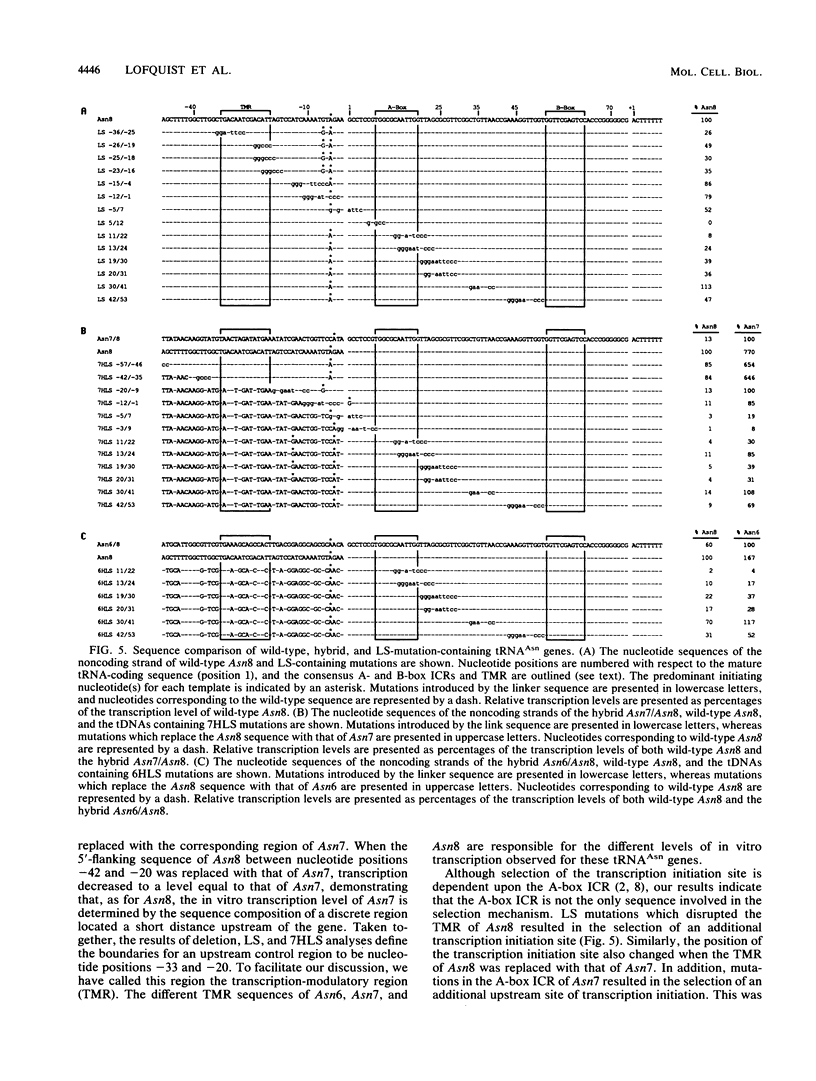
We have studied the mechanism by which 5'-flanking sequences modulate the in vitro transcription of eucaryotic tRNA genes. Using deletion and linker substitution mutagenesis, we have found that the 5'-flanking sequences responsible for the different in vitro transcription levels of three Drosophila tRNA5Asn genes are contained within a discrete region centered 22 nucleotides upstream from the transcription initiation site. In conjunction with the A-box intragenic control region, this upstream transcription-modulatory region functions in the selection mechanism for the site of transcription initiation. Since the transcription-modulatory region directs the position of the start site and the actual sequence of the transcription-modulatory region determines the level of tRNAAsn gene transcription, the possibility is raised that the transcription-modulatory region directs a transcription initiation event similar to open complex formation at procaryotic promoters.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. S., Goh S. H., Hall B. D. The promoter sequence of a yeast tRNAtyr gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Camier S., Sentenac A., Hall B. D. Gene size differentially affects the binding of yeast transcription factor tau to two intragenic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8768–8772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark C., Weller P., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. A distant enhancer element is required for polymerase III transcription of a U6 RNA gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):356–359. doi: 10.1038/328356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buc H., McClure W. R. Kinetics of open complex formation between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and the lac UV5 promoter. Evidence for a sequential mechanism involving three steps. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2712–2723. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camier S., Gabrielsen O., Baker R., Sentenac A. A split binding site for transcription factor tau on the tRNA3Glu gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):491–500. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Raugei G., Costanzo F., Dente L., Cortese R. Common and interchangeable elements in the promoters of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase iii. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Buttgereit D., Grummt I. A purified transcription factor (TIF-IB) binds to essential sequences of the mouse rDNA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):604–608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Schmidt O., Söll D. Two control regions for eukaryotic tRNA gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3365–3368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Sharp S., Söll D. Identification of regulatory sequences contained in the 5'-flanking region of Drosophila lysine tRNA2 genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12424–12429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Burke D. J., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. The 5- flanking sequences of Drosophila tRNAArg genes control their in vitro transcription in a Drosophila cell extract. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14738–14744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubendorff J. W., deHaseth P. L., Rosendahl M. S., Caruthers M. H. DNA functional groups required for formation of open complexes between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and the lambda PR promoter. Identification via base analog substitutions. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):892–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Engelke D. R., Geiduschek E. P. HeLa cell RNA polymerase III transcription factors. Functional characterization of a fraction identified by its activity in a second template rescue assay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1934–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. D., O'Connell A. M., Sharp S. J. Formation of an active transcription complex in the Drosophila melanogaster 5S RNA gene is dependent on an upstream region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2046–2051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilloud E., Clarkson S. G. A dispersed tyrosine tRNA gene from Xenopus laevis with high transcriptional activity in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):486–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Clarkson S. G. 5'-flanking sequences that inhibit in vitro transcription of a xenopus laevis tRNA gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Evans C. F., Engelke D. R. Comparison of tRNA gene transcription complexes formed in vitro and in nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3212–3220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lofquist A., Sharp S. The 5'-flanking sequences of Drosophila melanogaster tRNA5Asn genes differentially arrest RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14600–14606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morry M. J., Harding J. D. Modulation of transcriptional activity and stable complex formation by 5'-flanking regions of mouse tRNAHis genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):105–115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. G., Sprague K. U. In vitro transcription of a silkworm 5S RNA gene requires an upstream signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5519–5522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. G., Sprague K. U. Silkworm 5S RNA and alanine tRNA genes share highly conserved 5' flanking and coding sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1524–1531. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Railey J. F., 2nd, Wu G. J. Organization of multiple regulatory elements in the control region of the adenovirus type 2-specific VARNA1 gene: fine mapping with linker-scanning mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1147–1159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond K. C., Raymond G. J., Johnson J. D. In vivo modulation of yeast tRNA gene expression by 5'-flanking sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2649–2656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03983.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubacha A., Sumner W., 3rd, Richter L., Beckingham K. Conserved 5' flank homologies in dipteran 5S RNA genes that would function on 'A' form DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8193–8207. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Sharp S., Dingermann T., Burke D. J., Cooley L., Söll D. The extent of a eukaryotic tRNA gene. 5'- and 3'-flanking sequence dependence for transcription and stable complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Sharp S., Dingermann T., Söll D. Transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes in vitro. II. Formation of stable complexes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Stevens J. N., Metzenberg R. L. An upstream signal is required for in vitro transcription of Neurospora 5S RNA genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):189–192. doi: 10.1007/BF02428052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S. J., Schaack J., Cooley L., Burke D. J., Söll D. Structure and transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):107–144. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S., DeFranco D., Dingermann T., Farrell P., Söll D. Internal control regions for transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6657–6661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw K. J., Olson M. V. Effects of altered 5'-flanking sequences on the in vivo expression of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae tRNATyr gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):657–665. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B. Surprises in polymerase III transcription. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Jones N., Shenk T. A mutation which alters initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase III on the Ad5 chromosome. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. M. Transcription of Neurospora crassa 5 S rRNA genes requires a TATA box and three internal elements. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):801–811. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90406-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G. Multiple proteins bind to VA RNA genes of adenovirus type 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1021–1031. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. T., Larson D., Young L. S., Sprague K. U. A large region controls tRNA gene transcription. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Boulanger P. A., Berk A. J. Resolution of human transcription factor TFIIIC into two functional components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Takahashi N., Sprague K. U. Upstream sequences confer distinctive transcriptional properties on genes encoding silkgland-specific tRNAAla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):374–378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]