Abstract
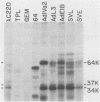
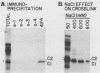
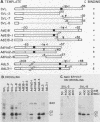
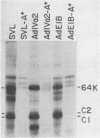
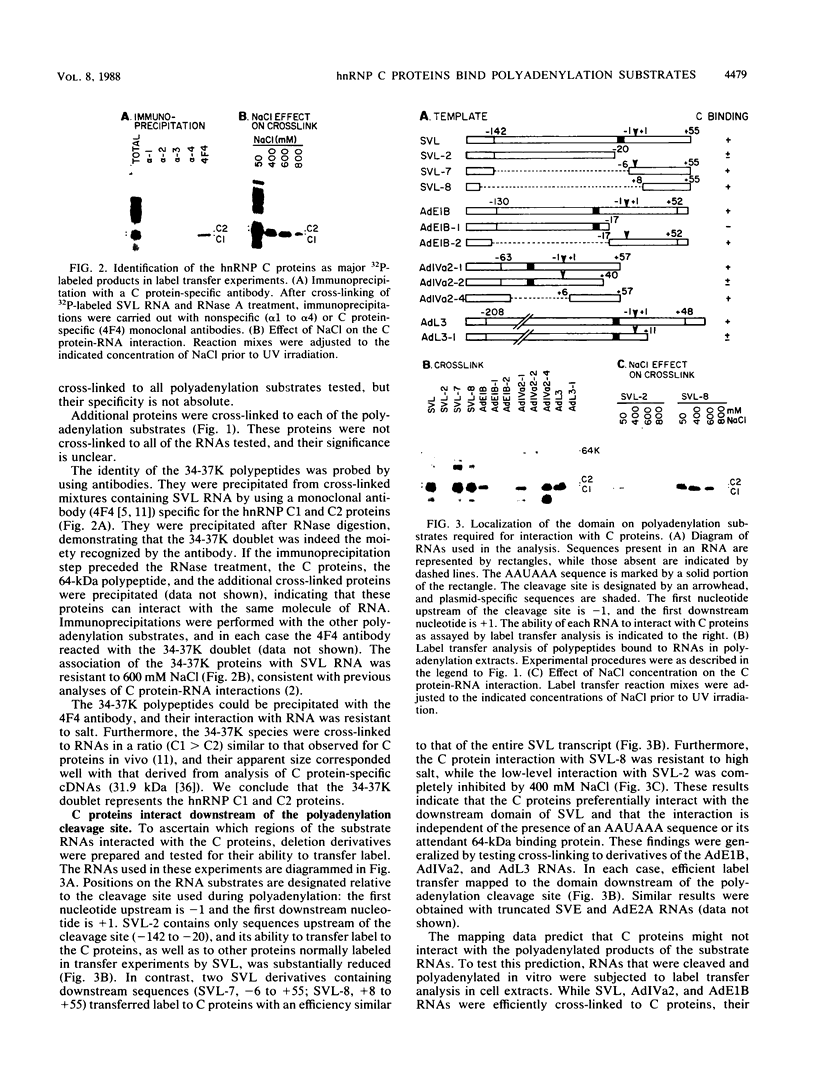
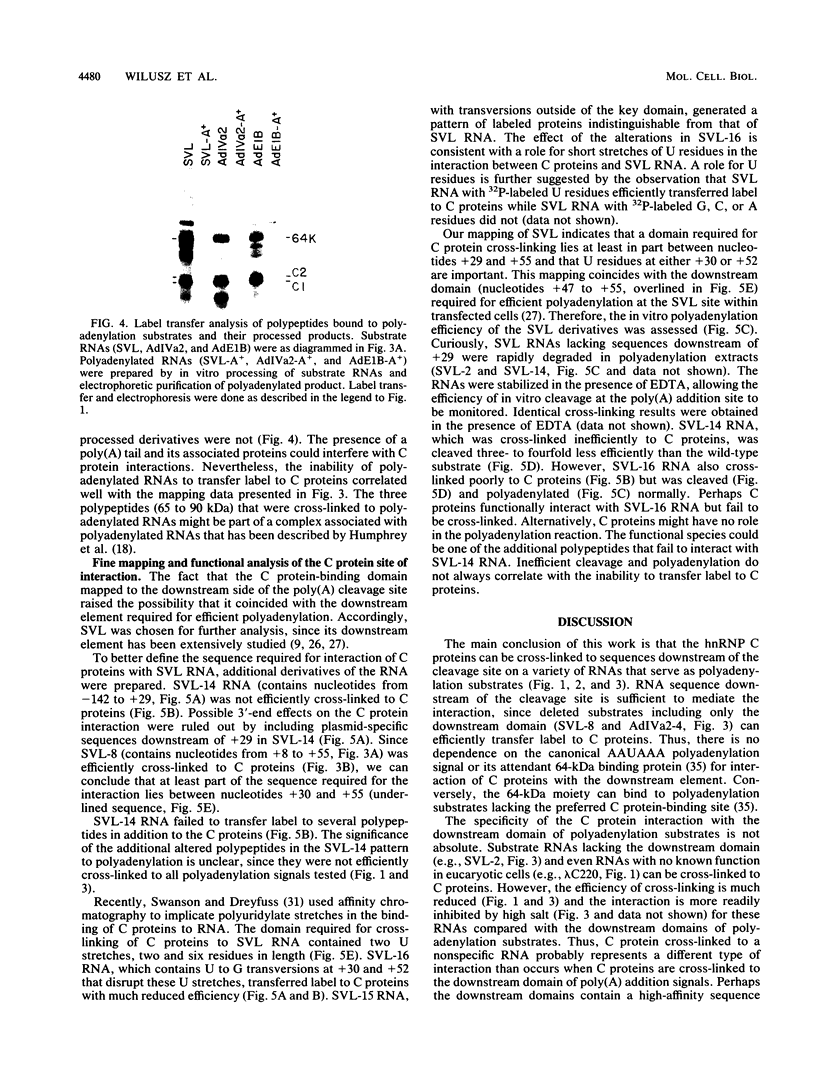
The heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C1 and C2 proteins were preferentially cross-linked by treatment with UV light in nuclear extracts to RNAs containing six different polyadenylation signals. The domain required for the interaction was located downstream of the poly(A) cleavage site, since deletion of this segment from several polyadenylation substrate RNAs greatly reduced cross-linking efficiency. In addition, RNAs containing only downstream sequences were efficiently cross-linked to C proteins, while fully processed, polyadenylated RNAs were not. Analysis of mutated variants of the simian virus 40 late polyadenylation signal showed that uridylate-rich sequences located in the region between 30 and 55 nucleotides downstream of the cleavage site were required for efficient cross-linking of C proteins. This downstream domain of the simian virus 40 late poly(A) addition signal has been shown to influence the efficiency of the polyadenylation reaction. However, there was not a strict correlation between cross-linking of C proteins and the efficiency of polyadenylation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification and characterization of the packaging proteins of core 40S hnRNP particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Isolation of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA-ribonucleoprotein complex (hnRNP): a unique supramolecular assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7471–7475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Monoclonal antibody characterization of the C proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes in vertebrate cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1997–1204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Stacy T. P. Identification of sequences in the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene required for efficient processing and polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2104–2113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. A sequence downstream of A-A-U-A-A-A is required for formation of simian virus 40 late mRNA 3' termini in frog oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Choi Y. D., Adam S. A. Characterization of heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein complexes in vivo with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Definition of essential sequences and functional equivalence of elements downstream of the adenovirus E2A and the early simian virus 40 polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2975–2983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein associates with the AAUAAA polyadenylation signal in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Lamb J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Proudfoot N. J. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a polyadenylation signal mutation. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):398–400. doi: 10.1038/306398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T., Christofori G., Lucijanic V., Keller W. Cleavage and polyadenylation of messenger RNA precursors in vitro occurs within large and specific 3' processing complexes. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4159–4168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02762.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Inhibition of RNA cleavage but not polyadenylation by a point mutation in mRNA 3' consensus sequence AAUAAA. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):600–605. doi: 10.1038/305600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Site-specific polyadenylation in a cell-free reaction. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Skolnik-David H., Sharp P. A. Sedimentation analysis of polyadenylation-specific complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Alwine J. C. Sequences on the 3' side of hexanucleotide AAUAAA affect efficiency of cleavage at the polyadenylation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Connelly S., Manley J. L., Alwine J. C. Identification of a sequence element on the 3' side of AAUAAA which is necessary for simian virus 40 late mRNA 3'-end processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2713–2719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Analysis of processing and polyadenylation signals of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene by using simian virus 40-hepatitis B virus chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2250–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of polyadenylation-specific complexes. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):672–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Nakagawa T. Y., LeVan K., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure of human nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle C proteins: conservation of sequence and domain structures in heterogeneous nuclear RNA, mRNA, and pre-rRNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Separation and characterization of a poly(A) polymerase and a cleavage/specificity factor required for pre-mRNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90411-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T. A 64 kd nuclear protein binds to RNA segments that include the AAUAAA polyadenylation motif. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain S., Sambrook J., Roberts R. J., Keller W., Fried M., Dunn A. R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the leader segments in a cloned copy of adenovirus 2 fiber mRNA. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):851–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Wickens M. Formation of mRNA 3' termini: stability and dissociation of a complex involving the AAUAAA sequence. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):177–186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Cole C. N. Identification of a complex associated with processing and polyadenylation in vitro of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase precursor RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3277–3286. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]