Abstract
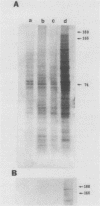
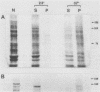
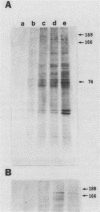
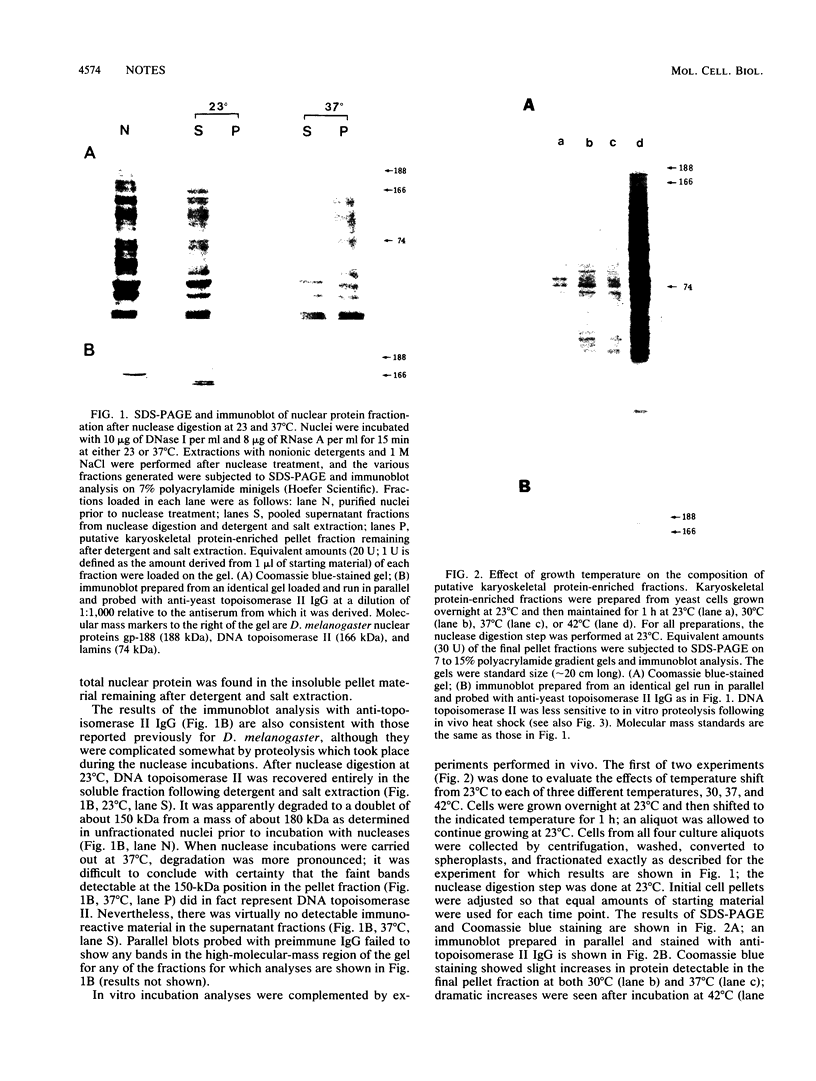
Elevated growth temperature (heat shock) promoted the structural stability of karyoskeletal protein-enriched fractions isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Similar stabilization could be induced by brief incubation of nuclei at 37 degrees C in vitro. These results are similar to those reported for higher eucaryotes and have practical implications for investigation of the karyoskeleton in S. cerevisiae.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton B. M., Berrios S., Fisher P. A. p75, a polypeptide component of karyoskeletal protein-enriched fractions associated with transcriptionally active loci of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1877–1886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Hancock D. C. Studies on the interaction of the human c-myc protein with cell nuclei: p62c-myc as a member of a discrete subset of nuclear proteins. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Berrios M., Blobel G. Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous subnuclear fraction composed of nuclear matrix, peripheral lamina, and nuclear pore complexes from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):674–686. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell M., Whalen A. M., Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Heat shock-induced changes in the structural stability of proteinaceous karyoskeletal elements in vitro and morphological effects in situ. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1087–1098. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potashkin J. A., Zeigel R. F., Huberman J. A. Isolation and initial characterization of residual nuclear structures from yeast. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Aug;153(2):374–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90607-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. C., Fisher P. A., Broach J. R. A yeast plasmid partitioning protein is a karyoskeletal component. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):883–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]