Abstract
We examined the expression of a nucleus-encoded mitochondrial protein, cytochrome c, during the life cycle of Trypanosoma brucei. The bloodstream forms of T. brucei, the long slender and short stumpy trypanosomes, have inactive mitochondria with no detectable cytochrome-mediated respiration. The insect form of T. brucei, the procyclic trypanosomes, has fully functional mitochondria. Cytochrome c is spectrally undetectable in the bloodstream forms of trypanosomes, but during differentiation to the procyclic form, spectrally detected holo-cytochrome c accumulates rapidly. We have purified T. brucei cytochrome c and raised antibodies that react to both holo- and apo-cytochrome c. In addition, we isolated a partial cDNA to trypanosome cytochrome c. An examination of protein expression and steady-state mRNA levels in T. brucei indicated that bloodstream trypanosomes did not express cytochrome c but maintained significant steady-state levels of cytochrome c mRNA. The results suggest that in T. brucei, cytochrome c is developmentally regulated by a posttranscriptional mechanism which prevents either translation or accumulation of cytochrome c in the bloodstream trypanosomes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Wynn M. The amino acid sequences of cytochromes c-551 from three species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):485–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1310485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baim S. B., Sherman F. mRNA structures influencing translation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1591–1601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Van den Burg J., Brakenhoff J. P., Sloof P., Van Boom J. H., Tromp M. C. Major transcript of the frameshifted coxII gene from trypanosome mitochondria contains four nucleotides that are not encoded in the DNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):819–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienen E. J., Hammadi E., Hill G. C. Trypanosoma brucei: biochemical and morphological changes during in vitro transformation of bloodstream- to procyclic-trypomastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Jun;51(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienen E. J., Hill G. C., Shin K. O. Elaboration of mitochondrial function during Trypanosoma brucei differentiation. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Jan;7(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P. Discontinuous transcription and antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:701–732. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. C., Evans D. A., Vickerman K. Changes in oxidative metabolism and ultrastructure accompanying differentiation of the mitochondrion in Trypanosoma brucei. Int J Parasitol. 1973 Sep;3(5):691–704. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(73)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., Thornton D. A., Boothroyd J. C. Apparent discontinuous transcription of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface antigen genes. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):350–355. doi: 10.1038/311350a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham I. New culture medium for maintenance of tsetse tissues and growth of trypanosomatids. J Protozool. 1977 May;24(2):325–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb00987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T., Hajduk S. L., Marini J. C. The molecular biology of trypanosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Jasmer D. P., Stuart K. Developmentally regulated addition of nucleotides within apocytochrome b transcripts in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Shaw J. M., Simpson L., Stuart K. Creation of AUG initiation codons by addition of uridines within cytochrome b transcripts of kinetoplastids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):539–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Stuart K. Developmental aspects of uridine addition within mitochondrial transcripts of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1259–1265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig B. Change of cytochrome c structure during development of the mouse. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):167–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig B., Koehler H., Neupert W. Receptor sites involved in posttranslational transport of apocytochrome c into mitochondria: specificity, affinity, and number of sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4963–4967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig B., Neupert W. Biogenesis of cytochrome c in Neurospora crassa. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:261–274. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. C. Electron transport systems in kinetoplastida. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 27;456(2):149–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(76)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadenbach B. Biosynthesis of cytochrome c. The sites of synthesis of apoprotein and holoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Feb;12(2):392–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooter J. M., De Lange T., Borst P. Discontinuous synthesis of mRNA in trypanosomes. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2387–2392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura S., Arpin M., Hannum C., Margoliash E., Sabatini D. D., Morimoto T. In vitro synthesis and posttranslational uptake of cytochrome c into isolated mitochondria: role of a specific addressing signal in the apocytochrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4368–4372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
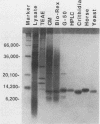
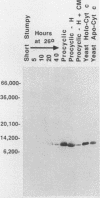
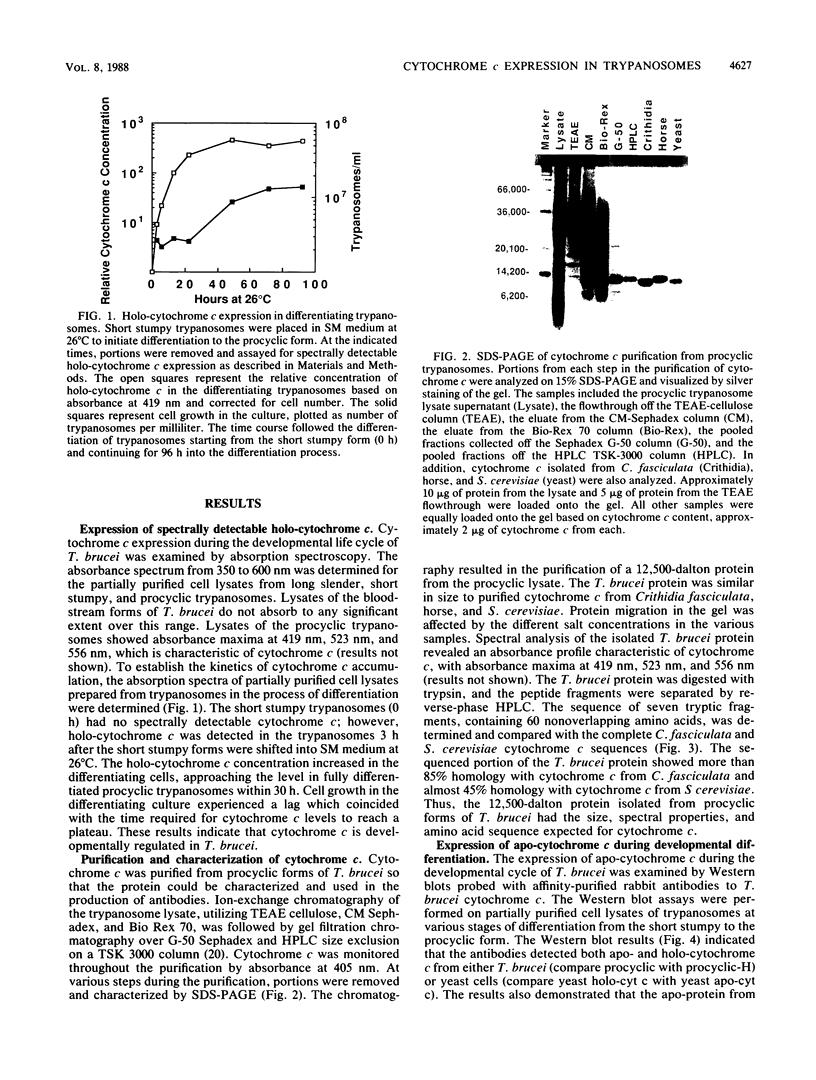
- Michelotti E. F., Hajduk S. L. Developmental regulation of trypanosome mitochondrial gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):927–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison P. R., Montgomery J. A., Wong T. S., Booth F. W. Cytochrome c protein-synthesis rates and mRNA contents during atrophy and recovery in skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):257–263. doi: 10.1042/bj2410257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowatt M. R., Clayton C. E. Developmental regulation of a novel repetitive protein of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2838–2844. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller D. M., Getz G. S. Transcriptional regulation of the mitochondrial genome of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11756–11764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. G., Lukins H. B., Linnane A. W., Nagley P. Biogenesis of mitochondria: a mutation in the 5'-untranslated region of yeast mitochondrial oli1 mRNA leading to impairment in translation of subunit 9 of the mitochondrial ATPase complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):1965–1977. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons M., Nelson R. G., Stuart K., Agabian N. Variant antigen genes of Trypanosoma brucei: genomic alteration of a spliced leader orphon and retention of expression-linked copies during differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):684–688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Fogel S., Nisonoff A., Margoliash E. Antibodies against cytochromes c from vertebrates. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):251–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer S. P., Michelotti E. F., Torri A. F., Hajduk S. L. Transcription of kinetoplast DNA minicircles. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Elledge S., Sweetser D., Young R. A., Davis R. W. Lambda gt 11: gene isolation with antibody probes and other applications. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:107–128. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Zieminn S. M., Miller D. D., Garber E. A., Margoliash E. Developmental expression of nuclear genes that encode mitochondrial proteins: insect cytochromes c. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1964–1968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Milhausen M., Rutter W. J., Agabian N. Tubulin genes are tandemly linked and clustered in the genome of trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Developmental cycles and biology of pathogenic trypanosomes. Br Med Bull. 1985 Apr;41(2):105–114. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Polymorphism and mitochondrial activity in sleeping sickness trypanosomes. Nature. 1965 Nov 20;208(5012):762–766. doi: 10.1038/208762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L. A sensitive and rapid method for recombinant phage screening. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:389–395. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]