Abstract
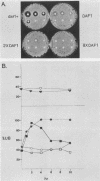
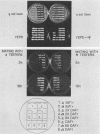
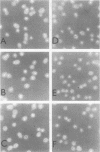
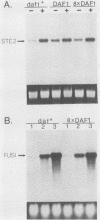
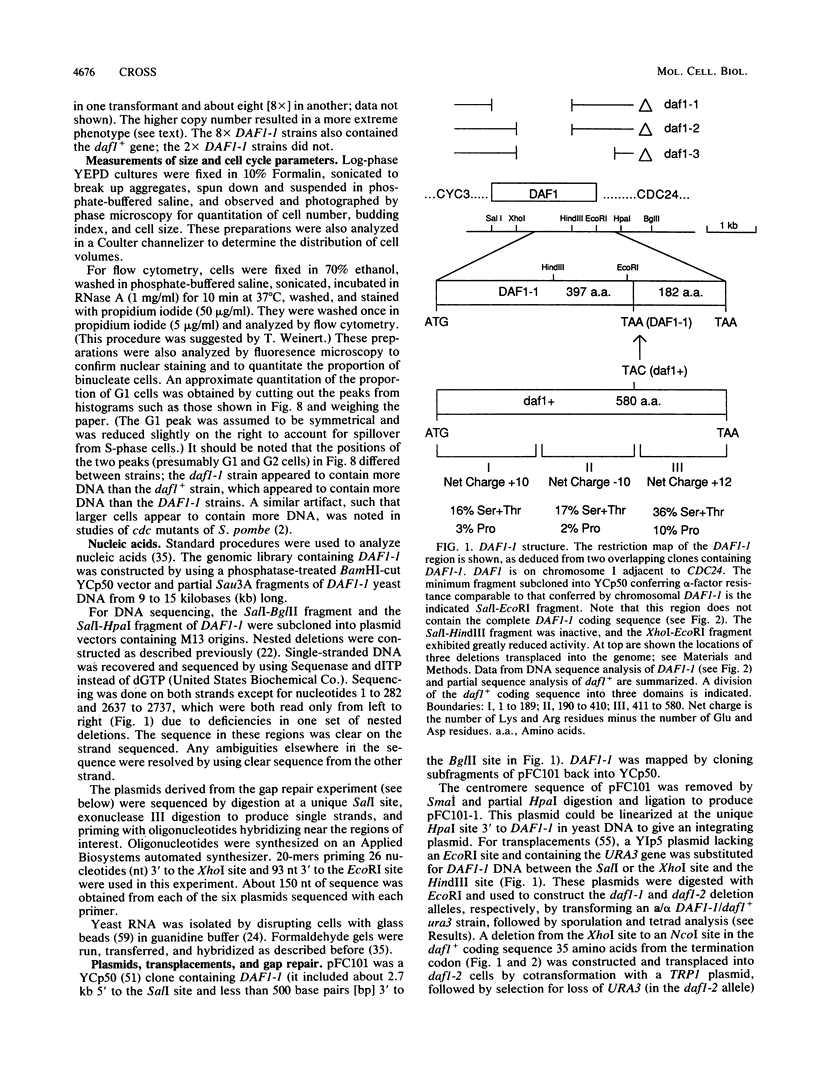
The mating pheromone alpha-factor arrests Saccharomyces cerevisiae MATa cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Size control is also exerted in G1, since cells do not exit G1 until they have attained a critical size. A dominant mutation (DAF1-1) which causes both alpha-factor resistance and small cell size (volume about 0.6-fold that of the wild type) has been isolated and characterized genetically and by molecular cloning. Several alpha-factor-induced mRNAs were induced equivalently in daf1+ and DAF1-1 cells. The DAF1-1 mutation consisted of a termination codon two-thirds of the way through the daf1+ coding sequence. A chromosomal deletion of DAF1 produced by gene transplacement increased cell volume about 1.5-fold; thus, DAF1-1 may be a hyperactive or deregulated allele of a nonessential gene involved in G1 size control. Multiple copies of DAF1-1 also greatly reduced the duration of the G1 phase of the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF


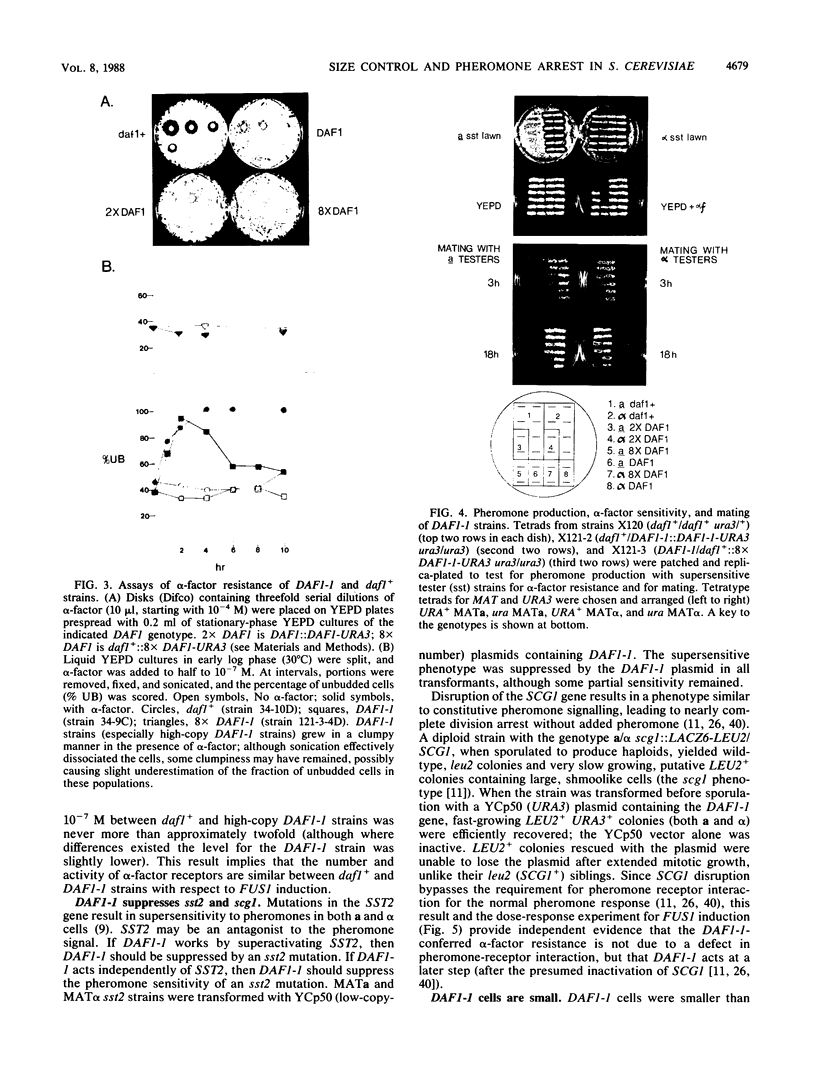



Images in this article
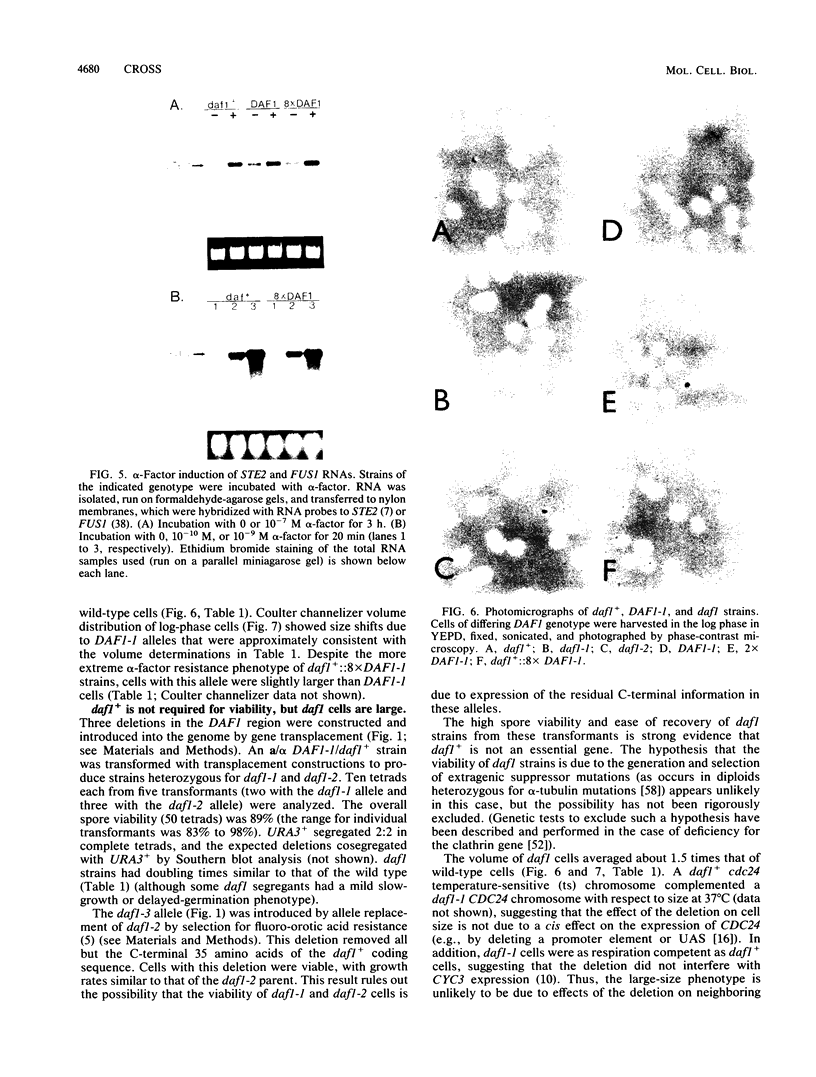
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
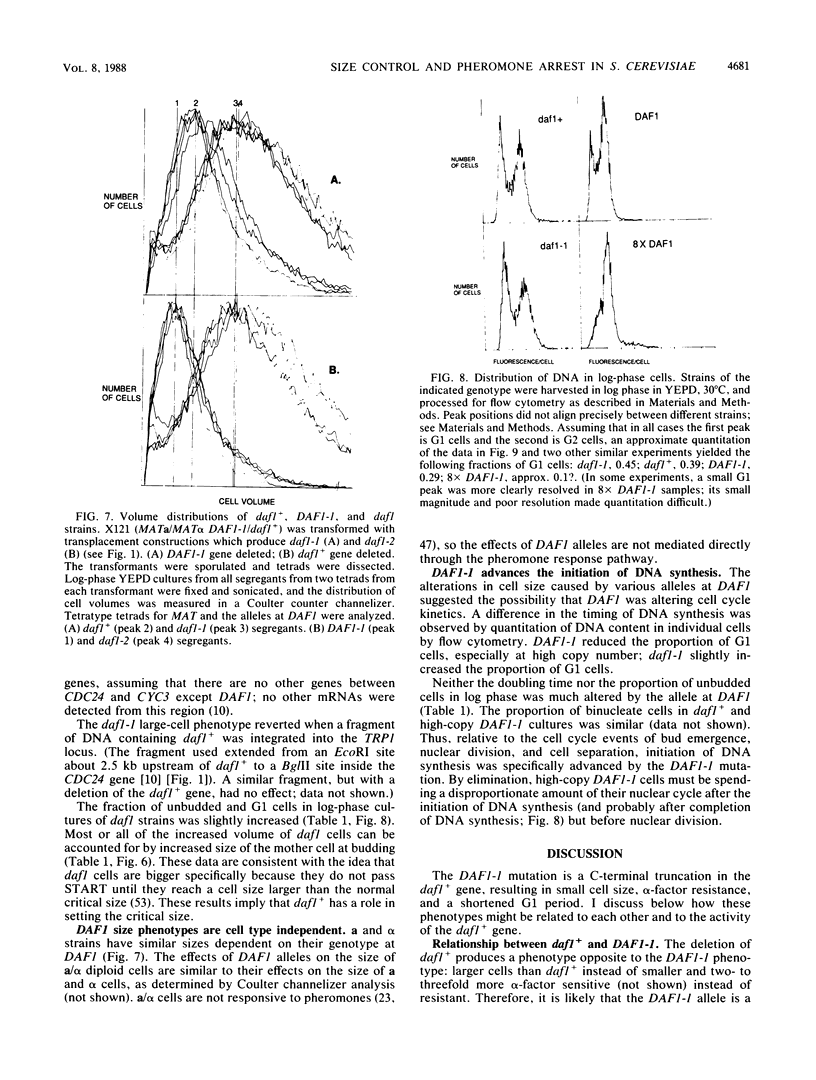
- Beach D., Durkacz B., Nurse P. Functionally homologous cell cycle control genes in budding and fission yeast. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):706–709. doi: 10.1038/300706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach D., Rodgers L., Gould J. ran1+ controls the transition from mitotic division to meiosis in fission yeast. Curr Genet. 1985;10(4):297–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00365626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast peptide pheromones, a-factor and alpha-factor, activate a common response mechanism in their target cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90808-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bücking-Throm E., Duntze W., Hartwell L. H., Manney T. R. Reversible arrest of haploid yeast cells in the initiation of DNA synthesis by a diffusible sex factor. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jan;76(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. L., Sudbery P. E. Small-sized mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):561–566. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Otte C. A. Isolation and genetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):11–20. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K. G., Steensma H. Y., Kaback D. B., Pringle J. R. Molecular cloning of chromosome I DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and characterization of the CDC24 gene and adjacent regions of the chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4516–4525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes P. A. Control of timing of cell cycle events in fission yeast by the wee 1+ gene. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):153–155. doi: 10.1038/302153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes P., Nurse P. Control of cell size at division in fission yeast by a growth-modulated size control over nuclear division. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jul;107(2):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Chaleff D. T., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast STE7, STE11, and STE12 genes are required for expression of cell-type-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):551–556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Herskowitz I. The yeast STE12 product is required for expression of two sets of cell-type specific genes. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Evidence the yeast STE3 gene encodes a receptor for the peptide pheromone a factor: gene sequence and implications for the structure of the presumed receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Sprague G. F., Jr Induction of the yeast alpha-specific STE3 gene by the peptide pheromone a-factor. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):835–852. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig A., Holly J., Saari G., MacKay V. L. Multiple regulation of STE2, a mating-type-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2106–2114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae unresponsive to cell division control by polypeptide mating hormone. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Unger M. W. Unequal division in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its implications for the control of cell division. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):422–435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Meeks-Wagner D. W., Fangman W. L., Botstein D. A rapid, efficient method for isolating DNA from yeast. Gene. 1986;42(2):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadish M. N., Carter B. L. Genetic control of cell division in yeast cultured at different growth rates. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):145–147. doi: 10.1038/269145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahng K. Y., Ferguson J., Reed S. I. Mutations in a gene encoding the alpha subunit of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae G protein indicate a role in mating pheromone signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2484–2493. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. Binding of alpha-factor pheromone to Saccharomyces cerevisiae a cells: dissociation constant and number of binding sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):318–320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. Binding of alpha-factor pheromone to yeast a cells: chemical and genetic evidence for an alpha-factor receptor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90186-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Goldman B. S., Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants unresponsive to alpha-factor pheromone: alpha-factor binding and extragenic suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Spatrick P. Down regulation of the alpha-factor pheromone receptor in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):345–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90655-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. C., Pringle J. R., Hartwell L. H. Coordination of growth with cell division in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 1;105(1):79–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Holly J. A., MacKay V. L. A yeast operator overlaps an upstream activation site. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunes S., Ma H., Overbye K., Fox M. S., Botstein D. Fine structure recombinational analysis of cloned genes using yeast transformation. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):73–81. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay V., Manney T. R. Mutations affecting sexual conjugation and related processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Isolation and phenotypic characterization of nonmating mutants. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):255–271. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manney T. R. Expression of the BAR1 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: induction by the alpha mating pheromone of an activity associated with a secreted protein. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):291–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.291-301.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Control of cell division in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants defective in adenylate cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jun;146(1):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey G., Clay F. J., Kelsay K., Sprague G. F., Jr Identification and regulation of a gene required for cell fusion during mating of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2680–2690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D., Jones C. A., Reed S. I. Dual regulation of the yeast CDC28-p40 protein kinase complex: cell cycle, pheromone, and nutrient limitation effects. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):927–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. A. Comparison of dose-response curves for alpha factor-induced cell division arrest, agglutination, and projection formation of yeast cells. Implication for the mechanism of alpha factor action. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13849–13856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. A. Yeast cells recover from mating pheromone alpha factor-induced division arrest by desensitization in the absence of alpha factor destruction. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1004–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, edition 9. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):181–213. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.181-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Nucleotide sequences of STE2 and STE3, cell type-specific sterile genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. A control acting over the initiation of DNA replication in the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci. 1979 Apr;36:155–168. doi: 10.1242/jcs.36.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Shore D. Transcriptional regulation in the yeast life cycle. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1162–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.3306917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Thuriaux P. Controls over the timing of DNA replication during the cell cycle of fission yeast. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jul;107(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Genetic applications of yeast transformation with linear and gapped plasmids. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:228–245. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent S. A., Fenimore C. M., Bostian K. A. Vector systems for the expression, analysis and cloning of DNA sequences in S. cerevisiae. Yeast. 1985 Dec;1(2):83–138. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Hasson T. B., Hasson M. S., Schekman R. Genetic and biochemical characterization of clathrin-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3888–3898. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The selection of S. cerevisiae mutants defective in the start event of cell division. Genetics. 1980 Jul;95(3):561–577. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. The mitotic inducer nim1+ functions in a regulatory network of protein kinase homologs controlling the initiation of mitosis. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Solomon F., Botstein D. Genetically essential and nonessential alpha-tubulin genes specify functionally interchangeable proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3722–3733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler G. L., Thorner J. Molecular cloning of hormone-responsive genes from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1144–1148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Abraham J. A., Ivy J. M., Nasmyth K. A., McGill C. Homothallic switching of yeast mating type cassettes is initiated by a double-stranded cut in the MAT locus. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strazdis J. R., MacKay V. L. Induction of yeast mating pheromone a-factor by alpha cells. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):543–545. doi: 10.1038/305543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Naturally occurring poly(dA-dT) sequences are upstream promoter elements for constitutive transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8419–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudbery P. E., Goodey A. R., Carter B. L. Genes which control cell proliferation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):401–404. doi: 10.1038/288401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuriaux P., Nurse P., Carter B. Mutants altered in the control co-ordinating cell division with cell growth in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 May 3;161(2):215–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00274190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueheart J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Two genes required for cell fusion during yeast conjugation: evidence for a pheromone-induced surface protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2316–2328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheals A. E. Size control models of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):361–368. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]