Abstract
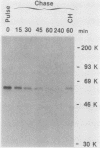
The human ets-2 gene is a homolog of the v-ets oncogene of the E26 virus and codes for a 56-kilodalton nuclear protein. The ets-2 protein is phosphorylated and has a rapid turnover, with a half-life of 20 min. When human lymphocytic CEM cells were treated with the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), the level of the ets-2 protein was quickly elevated 5- to 20-fold. This effect of TPA was mimicked by a synthetic diacylglycerol, 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl glycerol, and was blocked by the protein kinase C inhibitor H7, indicating that protein kinase C is involved in the induction. The increase in the ets-2 protein was due to stabilization of the protein, because the protein had a half-life of more than 2 h in the presence of TPA and the ets-2 mRNA level did not increase significantly upon TPA treatment. The protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide enhanced the effect of TPA on the ets-2 protein and could itself slow turnover of the protein. Properties of the ets-2 protein, such as nuclear localization, phosphorylation, rapid turnover, and response to protein kinase C, indicate that this protein belongs to a group of oncogene proteins which are generally thought to have regulatory functions in the nucleus (e.g., myc, fos, myb, and p53). Our results suggest that protein kinase C, either directly or indirectly, regulates the level of the ets-2 protein by posttranslational mechanisms.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat N. K., Fisher R. J., Fujiwara S., Ascione R., Papas T. S. Temporal and tissue-specific expression of mouse ets genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3161–3165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Kan N. C., Pribyl L., Lautenberger J. A., Moudrianakis E., Papas T. S. Molecular cloning of the ets proto-oncogene of the sea urchin and analysis of its developmental expression. Dev Biol. 1988 Feb;125(2):432–440. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. C., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Matsumoto-Kobayashi M., Kay R. M., Kaufman R. J., Brown E. L., Shoemaker C., Copeland T., Oroszlan S. Human T-cell growth factor: partial amino acid sequence, cDNA cloning, and organization and expression in normal and leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2543–2547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Morgan J. I. Superinduction of c-fos by nerve growth factor in the presence of peripherally active benzodiazepines. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.4035354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Thompson C. B. Oncogenes with potential nuclear function: myc, myb and fos. Cancer Surv. 1986;5(2):309–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Fisher R. J., Seth A., Bhat N. K., Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Papas T. S. Characterization and localization of the products of the human homologs of the v-ets oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysdael J., Gegonne A., Pognonec P., Boulukos K., Leprince D., Dernis D., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. Identification in chicken macrophages of a set of proteins related to, but distinct from, the chicken cellular c-ets-encoded protein p54c-ets. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2251–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by the human c-myc oncogene: differential expression in neoplastic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2486–2497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Hoshijima M., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Phosphatidylinositol turnover in platelet activation; calcium mobilization and protein phosphorylation. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11442–11445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Bishop J. M. Neoplastic transformation by E26 leukemia virus is mediated by a single protein containing domains of gag and myb genes. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):280–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.280-283.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Symonds G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. Subcellular localization of proteins encoded by oncogenes of avian myeloblastosis virus and avian leukemia virus E26 and by chicken c-myb gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Gegonne A., Coll J., de Taisne C., Schneeberger A., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):395–397. doi: 10.1038/306395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. The SV40 A gene product is required for the production of a 54,000 MW cellular tumor antigen. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90554-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Müller D., Guilbert L. Differential expression of c-fos in hematopoietic cells: correlation with differentiation of monomyelocytic cells in vitro. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1887–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. G., Simsiman R. C., Boutwell R. K. Induction of the polyamine-biosynthetic enzymes in mouse epidermis by tumor-promoting agents. Cancer Res. 1975 Jul;35(7):1662–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl L. J., Watson D. K., McWilliams M. J., Ascione R., Papas T. S. The Drosophila ets-2 gene: molecular structure, chromosomal localization, and developmental expression. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoyama C., Frunzio R., Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Transcriptional activation encoded by the v-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford D. A., Trowbridge I. S. Induction of expression and phosphorylation of the human interleukin 2 receptor by a phorbol diester. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11706–11712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P. D., Fukuda M. Induction of cytoskeletal vimentin and actin gene expression by a tumor-promoting phorbol ester in the human leukemic cell line K562. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3868–3874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Vogt P. K. DNA related to the transforming gene(s) of avian sarcoma viruses is present in normal avian DNA. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):170–173. doi: 10.1038/260170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torelli G., Selleri L., Donelli A., Ferrari S., Emilia G., Venturelli D., Moretti L., Torelli U. Activation of c-myb expression by phytohemagglutinin stimulation in normal human T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2874–2877. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Kozak C., Reeves R., Gearhart J., Nunn M. F., Nash W., Fowle J. R., 3rd, Duesberg P., Papas T. S. Conserved chromosomal positions of dual domains of the ets protooncogene in cats, mice, and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1792–1796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Nunn M. F., Duesberg P. H., O'Brien S. J., Papas T. S. The ets sequence from the transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus, E26, has unique domains on human chromosomes 11 and 21: both loci are transcriptionally active. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7294–7298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]