Abstract
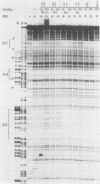
The glucagon gene is expressed specifically in the alpha cells of the pancreatic islets. We show here that 300 base pairs of the 5'-flanking region of the rat glucagon gene, linked to a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter plasmid transfected into islet cell lines of different hormone-producing phenotypes, directs transcription only in glucagon-producing islet cells. Deletional and linker-scanning mutations and DNase I footprinting assays identify three transcriptional control elements within these 300 base pairs. Two of these elements (G2 and G3) independently display enhancerlike functions on both homologous and heterologous promoters in glucagon (alpha) cells, but only on heterologous promoters in insulin- (beta) and somatostatin- (delta) expressing cells, and not in non-islet cells. The proximal promoter element (G1), characterized by low intrinsic transcriptional activity, is critical for specific expression of the glucagon gene in alpha cells. However, nuclear extracts prepared from all three islet cell phenotypes give similar protection to the three control elements of the glucagon 5'-flanking sequence. We conclude that these phenotypically distinct islet cell lines all contain regulatory DNA-binding proteins interacting with the three control elements of the glucagon gene, but that factors interacting with the glucagon promoter result in transcriptional activation only in alpha cells, to restrict glucagon gene expression to these cells. These observations suggest that interactions of nuclear proteins with cis-control elements are involved in the programmed developmental expression of the islet polypeptide hormone genes.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cells and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. A 3' enhancer is required for temporal and tissue-specific transcriptional activation of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):731–734. doi: 10.1038/323731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Ciliberto G., Hardon E., Paonessa G., Palla F., Lundberg L., Cortese R. Cis- and trans-acting elements responsible for the cell-specific expression of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2759–2766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP responsiveness of human gonadotropin-alpha gene transcription is directed by a repeated 18-base pair enhancer. Alpha-promoter receptivity to the enhancer confers cell-preferential expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12169–12174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drucker D. J., Philippe J., Jepeal L., Habener J. F. Glucagon gene 5'-flanking sequences promote islet cell-specific gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15659–15665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Bich-Thuy L. T., Stafford J., Queen C. Synergism between immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):383–385. doi: 10.1038/322383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Gros P., Habener J. F. Glucagon gene sequence. Four of six exons encode separate functional domains of rat pre-proglucagon. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14082–14087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Deutsch P. J., Gallagher G. D., Jaffe R. C., Habener J. F. trans-acting factors interact with a cyclic AMP response element to modulate expression of the human gonadotropin alpha gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3032–3040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Martinson H. G. Nucleosomes will not form on double-stranded RNa or over poly(dA).poly(dT) tracts in recombinant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6869–6888. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. A bent helix in kinetoplast DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):279–283. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojsov S., Heinrich G., Wilson I. B., Ravazzola M., Orci L., Habener J. F. Preproglucagon gene expression in pancreas and intestine diversifies at the level of post-translational processing. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11880–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musti A. M., Ursini V. M., Avvedimento E. V., Zimarino V., Di Lauro R. A cell type specific factor recognizes the rat thyroglobulin promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8149–8166. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Albert V. R., Elsholtz H. P., Lu L. I., Rosenfeld M. G. Activation of cell-specific expression of rat growth hormone and prolactin genes by a common transcription factor. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1400–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2831625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):841–845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Hammer R. E., Davison B. L., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Promoter and enhancer elements from the rat elastase I gene function independently of each other and of heterologous enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3466–3472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov C., Holst J. J., Knuhtsen S., Baldissera F. G., Poulsen S. S., Nielsen O. V. Glucagon-like peptides GLP-1 and GLP-2, predicted products of the glucagon gene, are secreted separately from pig small intestine but not pancreas. Endocrinology. 1986 Oct;119(4):1467–1475. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-4-1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippe J., Chick W. L., Habener J. F. Multipotential phenotypic expression of genes encoding peptide hormones in rat insulinoma cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):351–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI112819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pictet R. L., Rall L. B., Phelps P., Rutter W. J. The neural crest and the origin of the insulin-producing and other gastrointestinal hormone-producing cells. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):191–192. doi: 10.1126/science.1108195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost E., Moore D. D. CAT vectors for analysis of eukaryotic promoters and enhancers. Gene. 1986;45(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Sequence-dependent helical periodicity of DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):378–380. doi: 10.1038/292378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki R., Ono J., Nakamura M., Yokogawa Y., Kumae S., Hiraoka T., Yamaguchi K., Hamaguchi K., Uchida S. Isolation of glucagon-secreting cell lines by cloning insulinoma cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;22(3 Pt 1):120–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02623498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. Glucagon and the A cell: physiology and pathophysiology (first two parts). N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 18;304(25):1518–1524. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106183042504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. W., Saunders G. F. Structure of the human glucagon gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4719–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]