Abstract
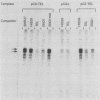
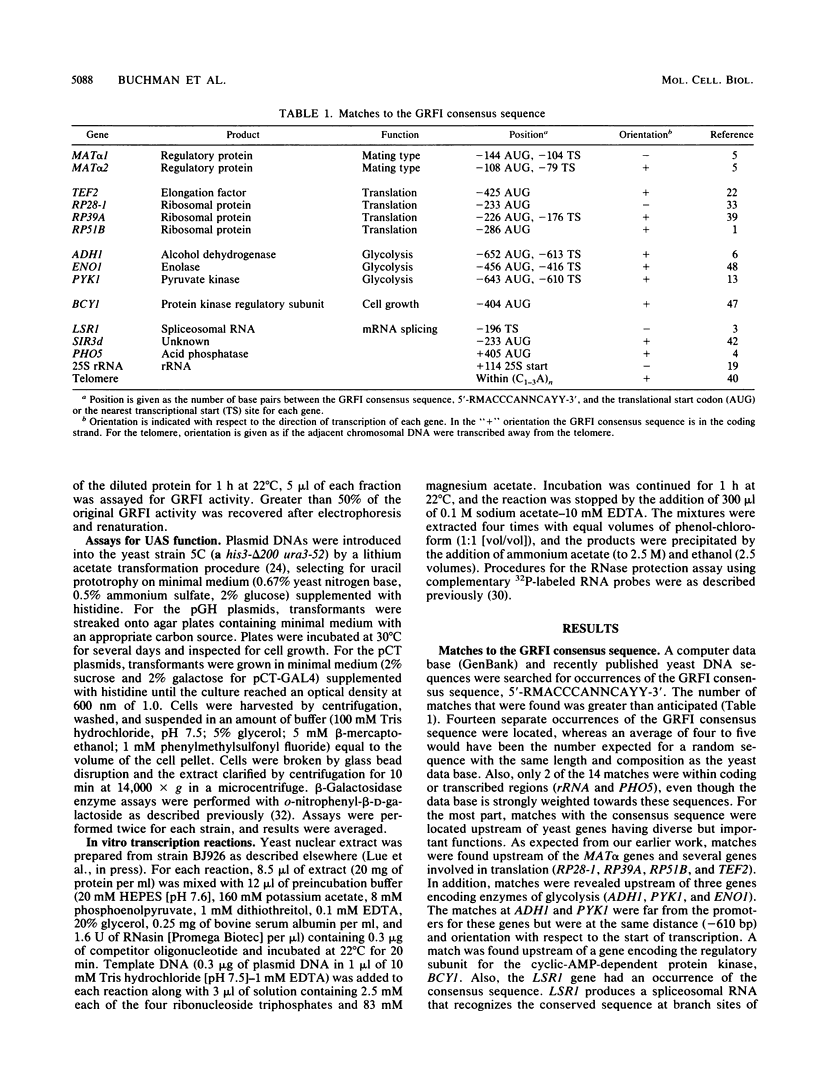
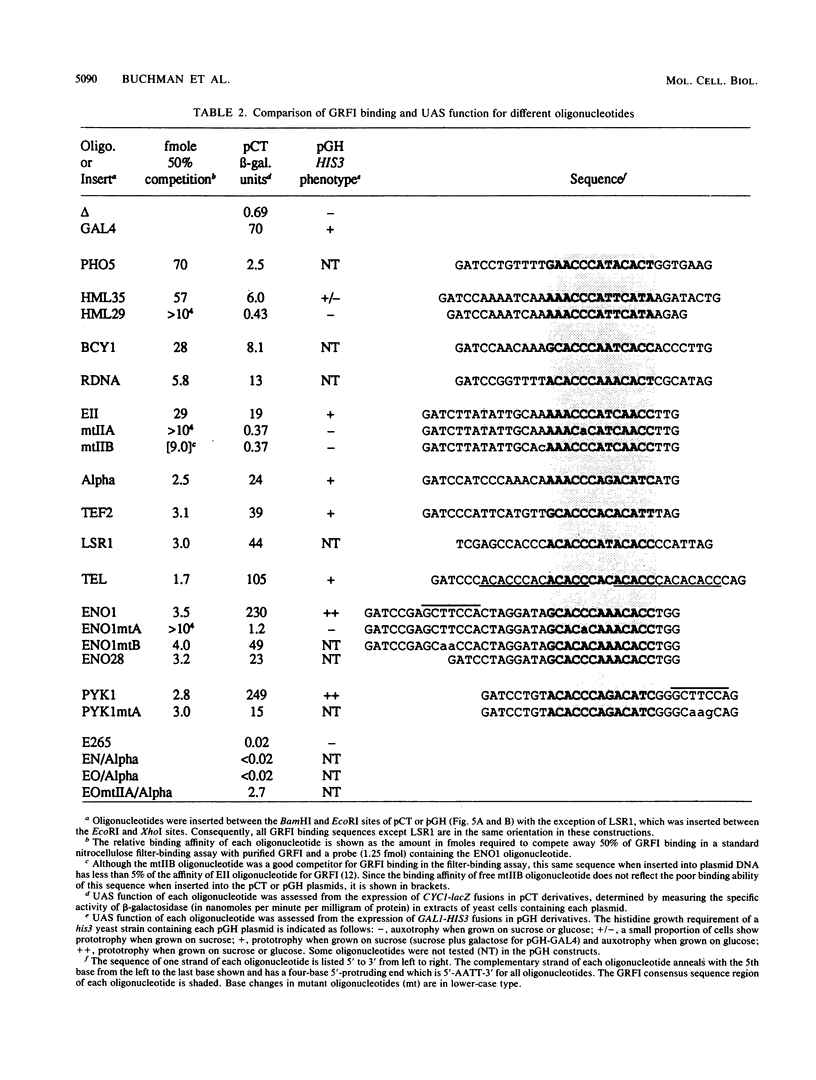
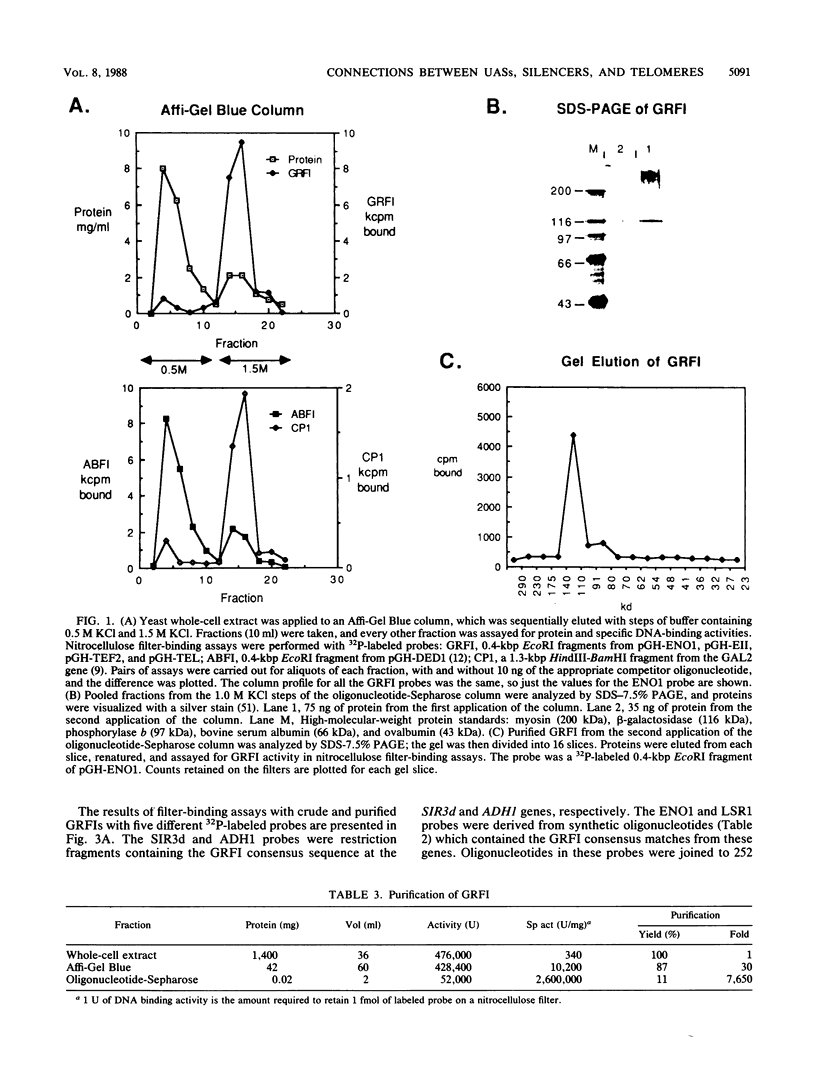
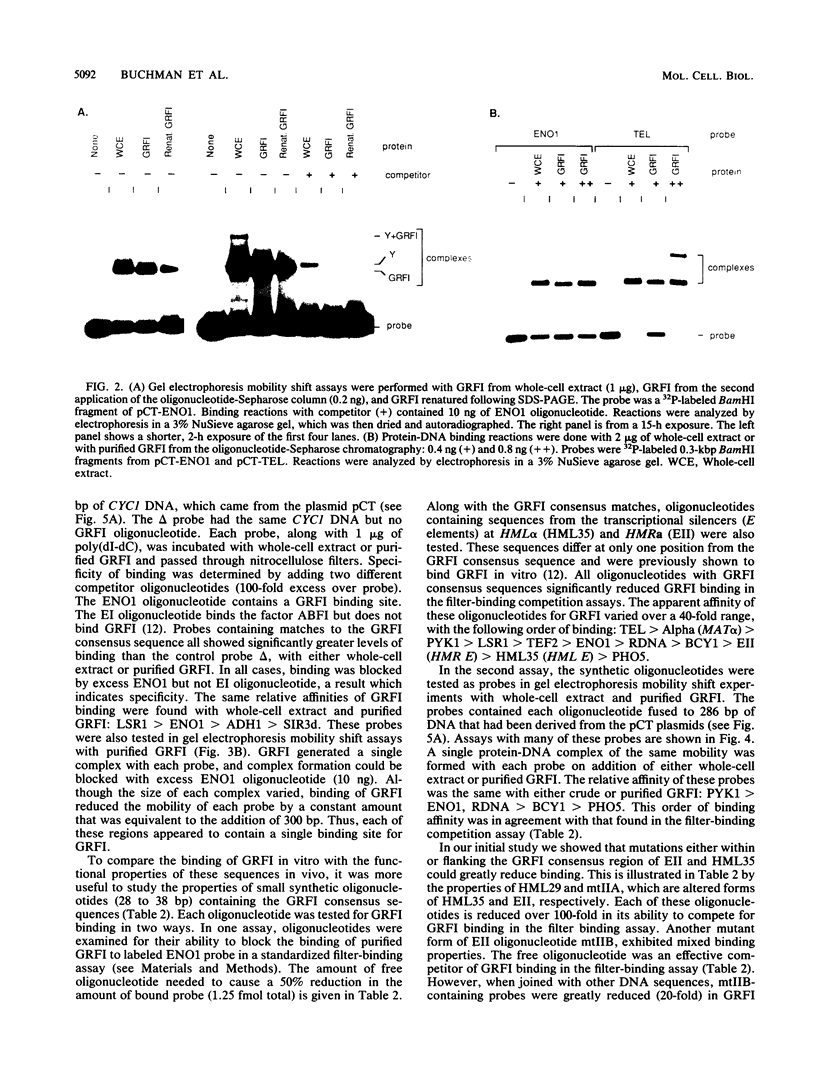
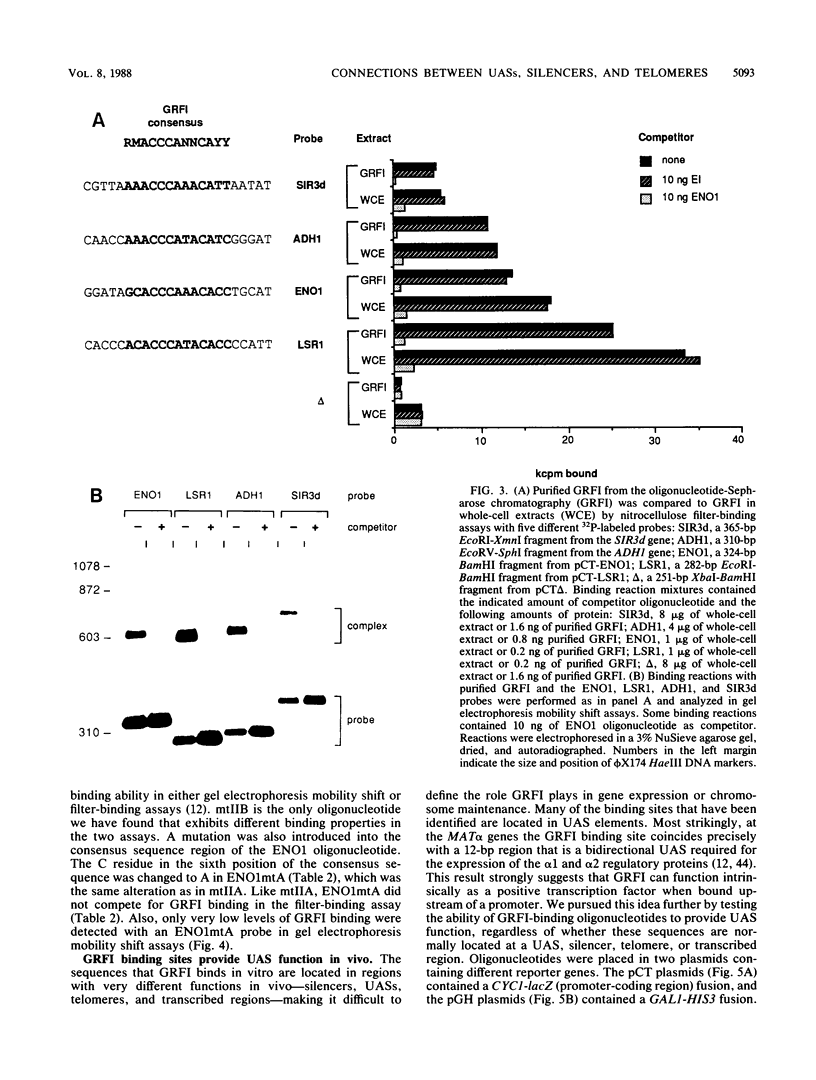
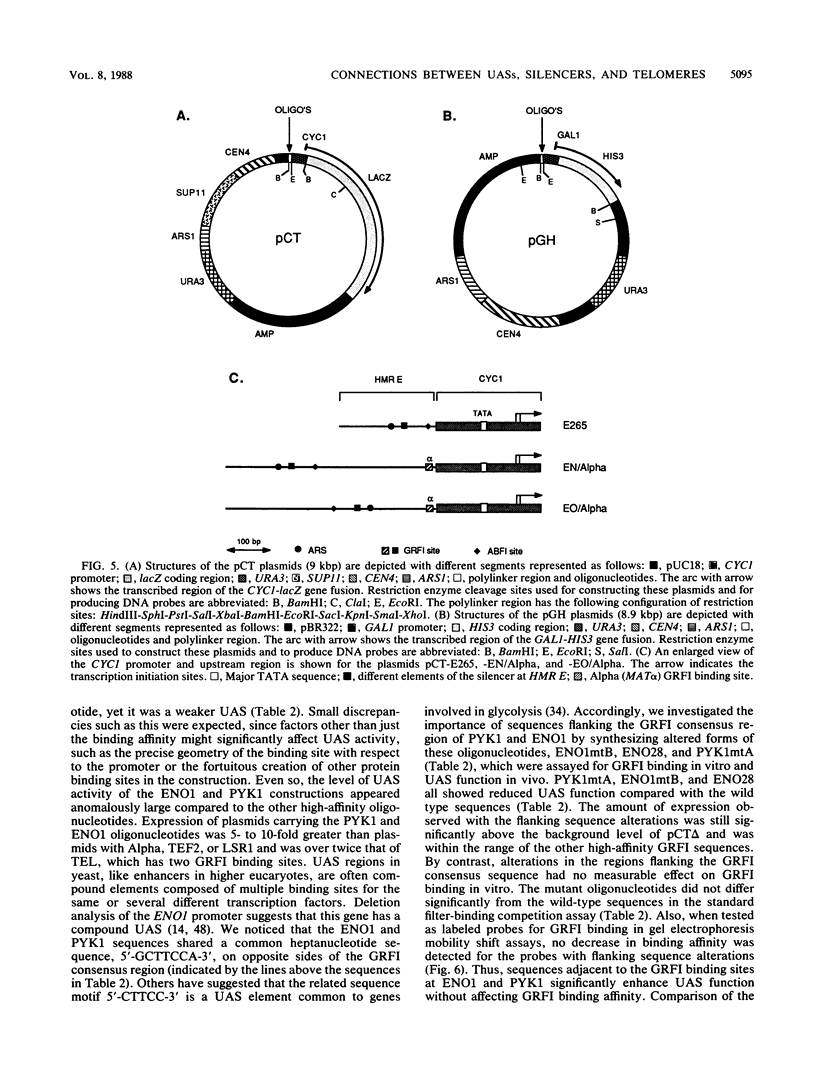
General regulatory factor I (GRFI) is a yeast protein that binds in vitro to specific DNA sequences at diverse genetic elements. A strategy was pursued to test whether GRFI functions in vivo at the sequences bound by the factor in vitro. Matches to a consensus sequence for GRFI binding were found in a variety of locations: upstream activating sequences (UASs), silencers, telomeres, and transcribed regions. All occurrences of the consensus sequence bound both crude and purified GRFI in vitro. All binding sites for GRFI, regardless of origin, provided UAS function in test plasmids. Also, GRFI binding sites specifically stimulated transcription in a yeast in vitro system, indicating that GRFI can function as a positive transcription factor. The stimulatory effect of GRFI binding sites at UASs for the PYK1 and ENO1 genes is significantly enhanced by flanking DNA elements. By contrast, regulatory sequences that flank the GRFI binding site at HMR E convert this region to a transcriptional silencer.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abovich N., Rosbash M. Two genes for ribosomal protein 51 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae complement and contribute to the ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1871–1879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Negative control requiring sequences both 5' and 3' to the regulated region. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):307–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr U2 RNA from yeast is unexpectedly large and contains homology to vertebrate U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear RNAs. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90365-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arima K., Oshima T., Kubota I., Nakamura N., Mizunaga T., Toh-e A. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast PHO5 gene: a putative precursor of repressible acid phosphatase contains a signal peptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1657–1672. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Ahlstrom-Jonasson L., Smith M., Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D. The sequence of the DNAs coding for the mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Isolation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere DNA-binding protein, its human homolog, and its possible role as a transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):403–409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Tekamp-Olson P., Najarian R. The isolation, characterization, and sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2193–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R., Yokoi T., Holland J. P., Pepper A. E., Holland M. J. Transcription of the constitutively expressed yeast enolase gene ENO1 is mediated by positive and negative cis-acting regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2753–2761. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. B., Hicks J. B., Broach J. R. Identification of sites required for repression of a silent mating type locus in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):815–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O. I., Nikolaev N., Hadjiolov A. A., Skryabin K. G., Zakharyev V. M., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. 4. Complete sequence of the 25 S rRNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6953–6958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A. TUF, the yeast DNA-binding factor specific for UASrpg upstream activating sequences: identification of the protein and its DNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3648–3652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy J. M., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Cloning and characterization of four SIR genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):688–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmerly W., Buchman A., Kornberg R., Rine J. Roles of two DNA-binding factors in replication, segregation and transcriptional repression mediated by a yeast silencer. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2241–2253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., Van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Conserved sequences upstream of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Curr Genet. 1985;9(4):273–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00419955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., Kornberg R. D. A region flanking the GAL7 gene and a binding site for GAL4 protein as upstream activating sequences in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):821–824. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90400-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Accurate initiation at RNA polymerase II promoters in extracts from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8839–8843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar C. M., Woudt L. P., Jansen A. E., Mager W. H., Planta R. J., Donovan D. M., Pearson N. J. Structure and organization of two linked ribosomal protein genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7345–7358. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. E., Stanway C., Kim S., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PGK gene depends on an upstream activation sequence but does not require TATA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4335–4343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen J., Hatamochi A., de Crombrugghe B. Separate binding sites for nuclear factor 1 and a CCAAT DNA binding factor in the mouse alpha 2(I) collagen promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11064–11070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J., Herskowitz I. Four genes responsible for a position effect on expression from HML and HMR in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1987 May;116(1):9–22. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. In vitro binding of cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the octamer motif of the SV40 enhancer and related motifs present in other promoters and enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3015–3025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotenberg M. O., Woolford J. L., Jr Tripartite upstream promoter element essential for expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):674–687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):154–157. doi: 10.1038/310154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Squire M., Nasmyth K. A. Characterization of two genes required for the position-effect control of yeast mating-type genes. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2817–2823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Stillman D. J., Brand A. H., Nasmyth K. A. Identification of silencer binding proteins from yeast: possible roles in SIR control and DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):461–467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Abovich N., Kaufer N. F., Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R., Levy A., Woolford J., Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H. A comparison of yeast ribosomal protein gene DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8295–8312. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Scott J. D., McMullen B., Hurwitz M., Krebs E. G., Wigler M. Cloning and characterization of BCY1, a locus encoding a regulatory subunit of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1371–1377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura H., Shiba T., Paterson M., Jigami Y., Tanaka H. Identification of a sequence containing the positive regulatory region of Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene ENO1. Gene. 1986;45(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Woudt L. P., Wassenaar G. M., Mager W. H., Sentenac A., Planta R. J. Specific binding of TUF factor to upstream activation sites of yeast ribosomal protein genes. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1451–1457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudt L. P., Smit A. B., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Conserved sequence elements upstream of the gene encoding yeast ribosomal protein L25 are involved in transcription activation. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1037–1040. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]