Abstract
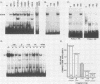
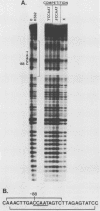
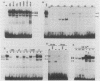
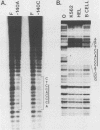
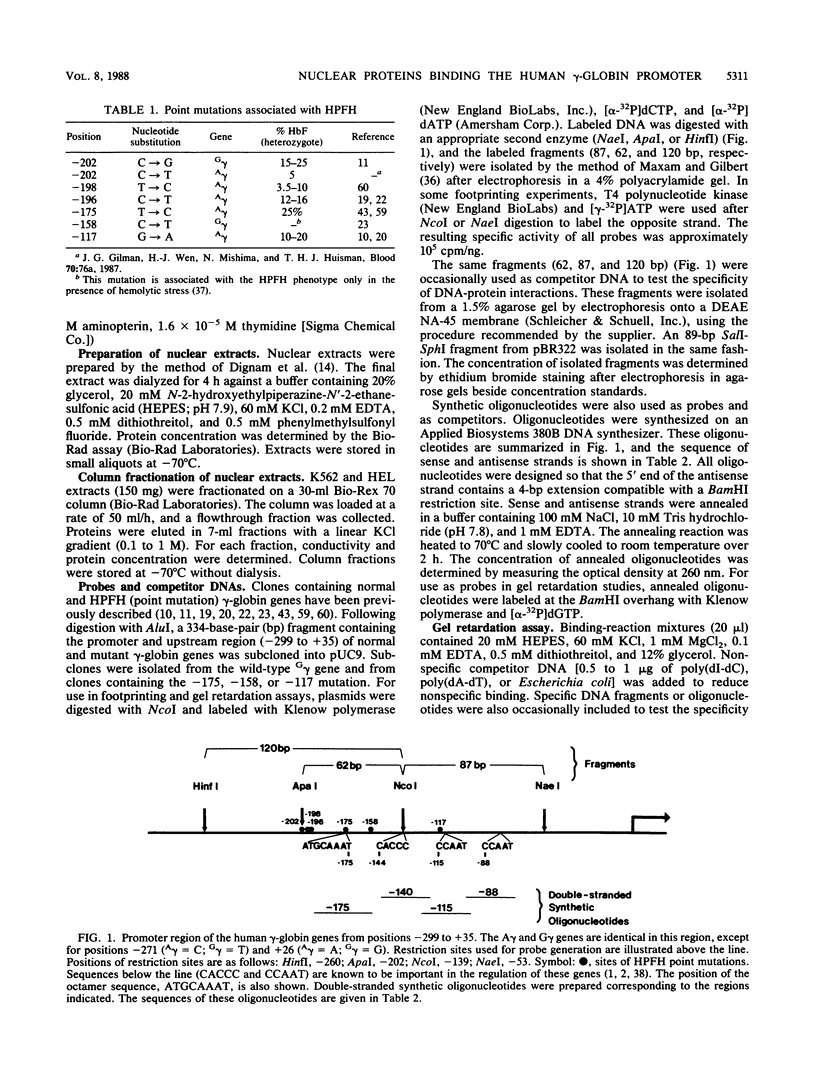
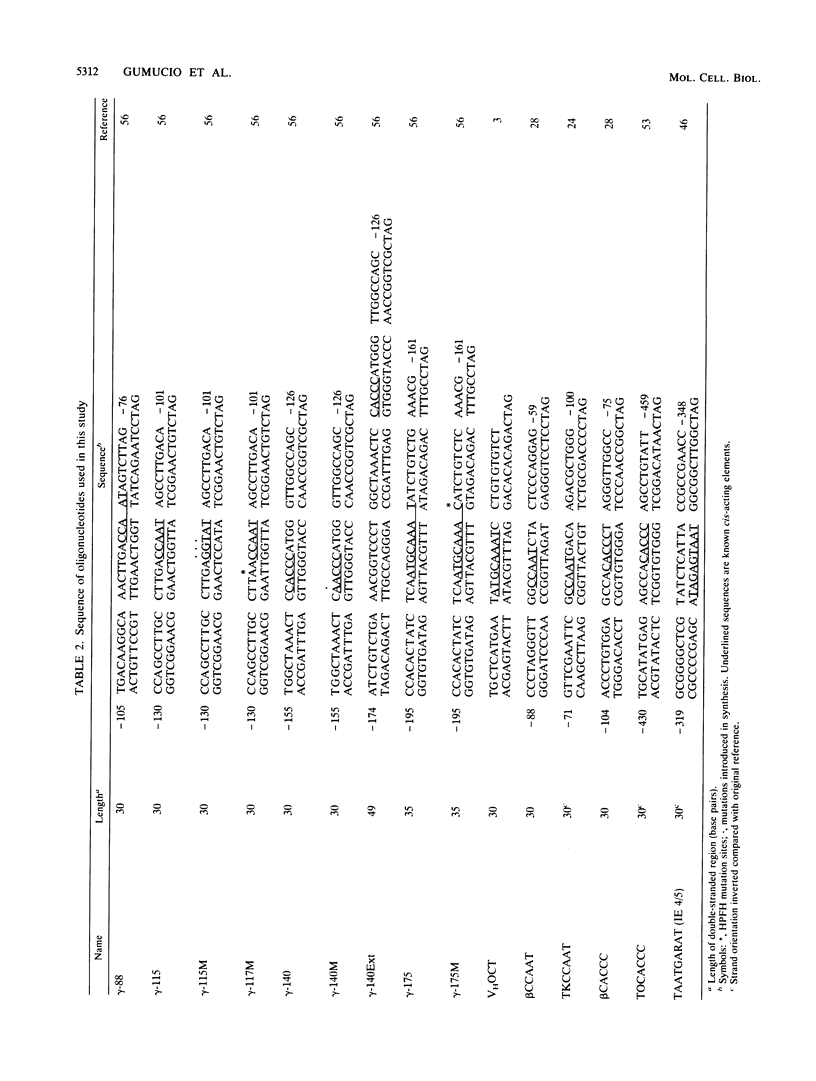
The molecular mechanisms responsible for the human fetal-to-adult hemoglobin switch have not yet been elucidated. Point mutations identified in the promoter regions of gamma-globin genes from individuals with nondeletion hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH) may mark cis-acting sequences important for this switch, and the trans-acting factors which interact with these sequences may be integral parts in the puzzle of gamma-globin gene regulation. We have used gel retardation and footprinting strategies to define nuclear proteins which bind to the normal gamma-globin promoter and to determine the effect of HPFH mutations on the binding of a subset of these proteins. We have identified five proteins in human erythroleukemia cells (K562 and HEL) which bind to the proximal promoter region of the normal gamma-globin gene. One factor, gamma CAAT, binds the duplicated CCAAT box sequences; the -117 HPFH mutation increases the affinity of interaction between gamma CAAT and its cognate site. Two proteins, gamma CAC1 and gamma CAC2, bind the CACCC sequence. These proteins require divalent cations for binding. The -175 HPFH mutation interferes with the binding of a fourth protein, gamma OBP, which binds an octamer sequence (ATGCAAAT) in the normal gamma-globin promoter. The HPFH phenotype of the -175 mutation indicates that the octamer-binding protein may play a negative regulatory role in this setting. A fifth protein, EF gamma a, binds to sequences which overlap the octamer-binding site. The erythroid-specific distribution of EF gamma a and its close approximation to an apparent repressor-binding site suggest that it may be important in gamma-globin regulation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnou N. P., Karlsson S., Moulton A. D., Keller G., Nienhuis A. W. Promoter sequences required for function of the human gamma globin gene in erythroid cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):121–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnou N. P., Moulton A. D., Keller G., Karlsson S., Papayannopoulou T., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Nienhuis A. W. Cis-acting sequences that affect the expression of the human fetal gamma-globin genes. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;191:163–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Bothwell A. Mutational analysis of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9626–9630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barberis A., Superti-Furga G., Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Yao Y. A., Rottman F. M. Hormonal regulation of the bovine prolactin promoter in rat pituitary tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12246–12251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang Y. L., Ley T. J., Sanders-Haigh L., Anderson W. F. Human globin gene expression in hybrid 2S MEL X human fibroblast cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Jul;10(4):399–407. doi: 10.1007/BF01535635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Boehm C. D., Waber P. G., Stoeckert C. J., Jr, Weissman S. M., Forget B. G., Kazazian H. H., Jr Concordance of a point mutation 5' to the G gamma globin gene with G gamma beta +. Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin in the black population. Blood. 1984 Dec;64(6):1292–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Metherall J. E., Yamakawa M., Pan J., Weissman S. M., Forget B. G. A point mutation in the A gamma-globin gene promoter in Greek hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):325–326. doi: 10.1038/313325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Stoeckert C. J., Jr, Serjeant G. R., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. G gamma beta+ hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin: cosmid cloning and identification of a specific mutation 5' to the G gamma gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4894–4898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danesch U., Gloss B., Schmid W., Schütz G., Schüle R., Renkawitz R. Glucocorticoid induction of the rat tryptophan oxygenase gene is mediated by two widely separated glucocorticoid-responsive elements. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):625–630. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Gambari R., Shaw P. A., Maniatis G., Reuben R. C., Sassa S., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Tumor promoter-mediated inhibition of cell differentiation: suppression of the expression of erythroid functions in murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend C., Scher W., Holland J. G., Sato T. Hemoglobin synthesis in murine virus-induced leukemic cells in vitro: stimulation of erythroid differentiation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):378–382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelinas R., Bender M., Lotshaw C., Waber P., Kazazian H., Jr, Stamatoyannopoulos G. Chinese A gamma fetal hemoglobin: C to T substitution at position-196 of the A gamma gene promoter. Blood. 1986 Jun;67(6):1777–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelinas R., Endlich B., Pfeiffer C., Yagi M., Stamatoyannopoulos G. G to A substitution in the distal CCAAT box of the A gamma-globin gene in Greek hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):323–325. doi: 10.1038/313323a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giglioni B., Casini C., Mantovani R., Merli S., Comi P., Ottolenghi S., Saglio G., Camaschella C., Mazza U. A molecular study of a family with Greek hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin and beta-thalassemia. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2641–2645. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman J. G., Huisman T. H. DNA sequence variation associated with elevated fetal G gamma globin production. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):783–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth M. E., Ainley W. M., Shumard D. S., Butow R. A., Grossman L. I. Location and structure of the var1 gene on yeast mitochondrial DNA: nucleotide sequence of the 40.0 allele. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):617–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson S., Nienhuis A. W. Developmental regulation of human globin genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1071–1108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight G. B., Gudas J. M., Pardee A. B. Cell-cycle-specific interaction of nuclear DNA-binding proteins with a CCAAT sequence from the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8350–8354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani R., Malgaretti N., Giglioni B., Comi P., Cappellini N., Nicolis S., Ottolenghi S. A protein factor binding to an octamer motif in the gamma-globin promoter disappears upon induction of differentiation and hemoglobin synthesis in K562 cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9349–9364. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani R., Malgaretti N., Nicolis S., Ronchi A., Giglioni B., Ottolenghi S. The effects of HPFH mutations in the human gamma-globin promoter on binding of ubiquitous and erythroid specific nuclear factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):7783–7797. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.7783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Papayannopoulou T. HEL cells: a new human erythroleukemia cell line with spontaneous and induced globin expression. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1233–1235. doi: 10.1126/science.6177045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. A., Olivieri N., Salameh M., Ahmed M., Antognetti G., Huisman T. H., Nathan D. G., Orkin S. H. Molecular analysis of the high-hemoglobin-F phenotype in Saudi Arabian sickle cell anemia. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 29;316(5):244–250. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701293160504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen J., Hatamochi A., de Crombrugghe B. Separate binding sites for nuclear factor 1 and a CCAAT DNA binding factor in the mouse alpha 2(I) collagen promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11064–11070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr Base substitution at position -88 in a beta-thalassemic globin gene. Further evidence for the role of distal promoter element ACACCC. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8679–8681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi S., Nicolis S., Taramelli R., Malgaretti N., Mantovani R., Comi P., Giglioni B., Longinotti M., Dore F., Oggiano L. Sardinian G gamma-HPFH: a T----C substitution in a conserved "octamer" sequence in the G gamma-globin promoter. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):815–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Jones S. D., Bond B., Yamamoto K. R. The immunoglobulin octanucleotide: independent activity and selective interaction with enhancers. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1498–1501. doi: 10.1126/science.3029871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pious D., Krangel M. S., Dixon L. L., Parham P., Strominger J. L. HLA antigen structural gene mutants selected with an allospecific monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7832–7836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon M. W., Gelinas R. E. A fetal globin gene mutation in A gamma nondeletion hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin increases promoter strength in a nonerythroid cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):713–721. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. In vitro binding of cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the octamer motif of the SV40 enhancer and related motifs present in other promoters and enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3015–3025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford T. R., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. K562 human leukaemic cells synthesise embryonic haemoglobin in response to haemin. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):164–165. doi: 10.1038/280164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a common factor with conserved promoter and enhancer sequences in histone H2B, immunoglobulin, and U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6382–6386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckert C. J., Jr, Metherall J. E., Yamakawa M., Eisenstadt J. M., Weissman S. M., Forget B. G. Expression of the affected A gamma globin gene associated with Greek nondeletion hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surrey S., Delgrosso K., Malladi P., Schwartz E. A single-base change at position -175 in the 5'-flanking region of the G gamma-globin gene from a black with G gamma-beta+ HPFH. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):807–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate V. E., Wood W. G., Weatherall D. J. The British form of hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin results from a single base mutation adjacent to an S1 hypersensitive site 5' to the A gamma globin gene. Blood. 1986 Dec;68(6):1389–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waber P. G., Bender M. A., Gelinas R. E., Kattamis C., Karaklis A., Sofroniadou K., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Collins F. S., Forget B. G., Kazazian H. H., Jr Concordance of a point mutation 5' to the A gamma-globin gene with A gamma beta + hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin in Greeks. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):551–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Differential 5S RNA gene expression in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Transcription fraction TFIIIC can regulate differential Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1071–1079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]