Abstract
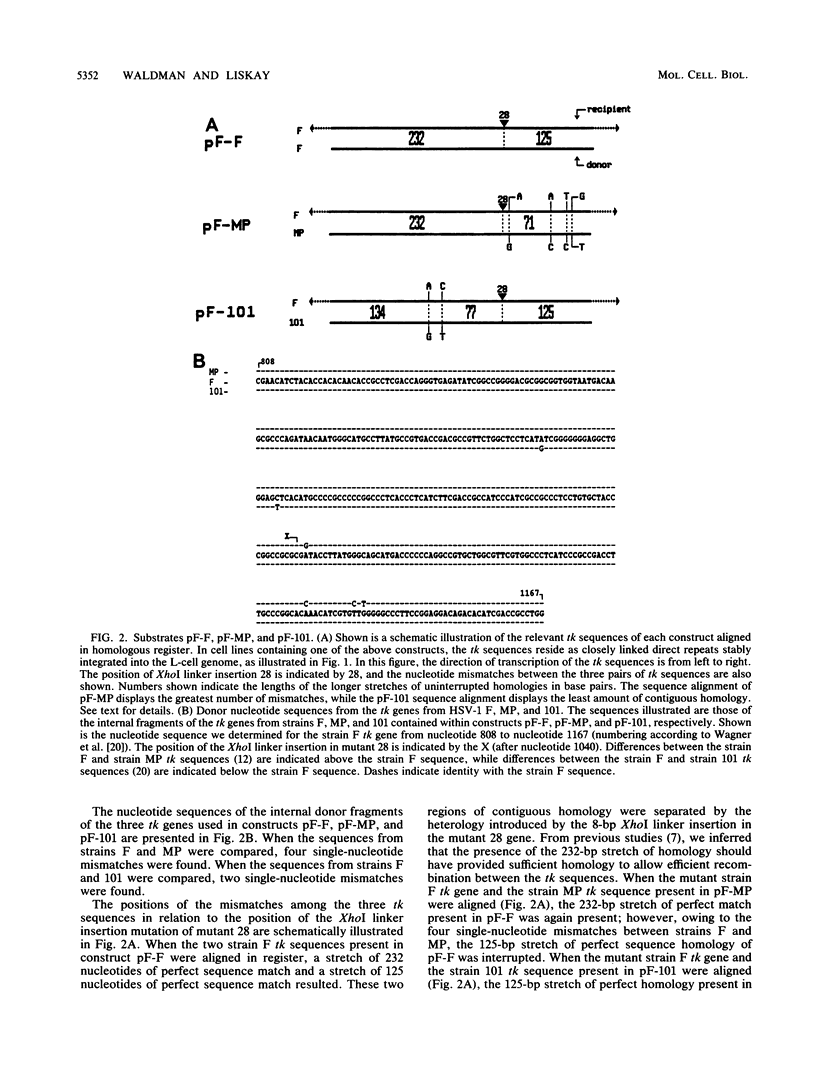
Recombination between a 360-base-pair (bp) segment of a wild-type thymidine kinase gene (tk) from each of three different strains (F, MP, and 101) of herpes simplex virus type one and a complete herpes simplex virus type 1 (strain F) tk gene containing an 8-bp insertion mutation was studied. The pairs of tk sequences resided as closely linked repeats within the genome of mouse LTK- cells. The frequency of recombination between sequences exhibiting 232 bp of uninterrupted homology and containing no mismatches other than the insertion mutation was comparable to the frequency of recombination between two sequences exhibiting four additional nucleotide mismatches distributed in such a way to preserve the 232-bp stretch of contiguous homology. In contrast, the placement of only two single-nucleotide mismatches (in addition to the insertion mutation) in such a manner to reduce the longest uninterrupted homology to 134 bp resulted in a 20-fold reduction in recombination. We conclude that the rate of intrachromosomal recombination in mammalian cells is determined by the amount of uninterrupted homology available and not by the total number of mismatches within a given interval of DNA. Furthermore, efficient recombination appears to require between 134 and 232 bp of uninterrupted homology; single-nucleotide heterologies are most likely sufficient to disrupt the minimal efficient recombination target. We also observed that if recombination was allowed to initiate within sequences exhibiting perfect homology, the event could propagate through and terminate within adjacent sequences exhibiting 19% base pair mismatch. We interpret this to mean that heterology exerts most of its impact on early rather than late steps of intrachromosomal recombination in mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayares D., Chekuri L., Song K. Y., Kucherlapati R. Sequence homology requirements for intermolecular recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5199–5203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld O. O., Smith A. J., Moulds J. J. Membrane glycophorins of Dantu blood group erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11864–11870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag R. J., Liskay R. M. Conservative intrachromosomal recombination between inverted repeats in mouse cells: association between reciprocal exchange and gene conversion. Genetics. 1988 May;119(1):161–169. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., Smigocki A. C., Camerini-Otero R. D. Effect of insertions, deletions, and double-strand breaks on homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):684–691. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Kit M., Qavi H., Trkula D., Otsuka H. Nucleotide sequence of the herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) thymidine kinase gene and predicted amino acid sequence of thymidine kinase polypeptide and its comparison with the HSV-1 thymidine kinase gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 17;741(2):158–170. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Homology-dependent interactions in phage lambda site-specific recombination. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):346–348. doi: 10.1038/329346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M., Letsou A., Stachelek J. L. Homology requirement for efficient gene conversion between duplicated chromosomal sequences in mammalian cells. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):161–167. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M., Stachelek J. L. Evidence for intrachromosomal gene conversion in cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M., Stachelek J. L. Information transfer between duplicated chromosomal sequences in mammalian cells involves contiguous regions of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1802–1806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskay R. M., Stachelek J. L., Letsou A. Homologous recombination between repeated chromosomal sequences in mouse cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:183–189. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. The nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubnitz J., Subramani S. The minimum amount of homology required for homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2253–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P., Huang H. V. Homologous recombination in Escherichia coli: dependence on substrate length and homology. Genetics. 1986 Mar;112(3):441–457. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. S., Gold L., Gauss P., Doherty D. H. Determination of the amount of homology required for recombination in bacteriophage T4. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain M. A., Galloway D. A. Nucleotide sequence of the herpes simplex virus type 2 thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1045-1050.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman A. S., Liskay R. M. Differential effects of base-pair mismatch on intrachromosomal versus extrachromosomal recombination in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5340–5344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. B. Sequence-dependent gene conversion: can duplicated genes diverge fast enough to escape conversion? Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):543–557. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt V. M., Ingles C. J., Urdea M. S., Rutter W. J. Homology requirements for recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4768–4772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]