Abstract
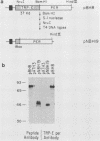
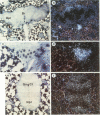
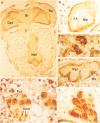
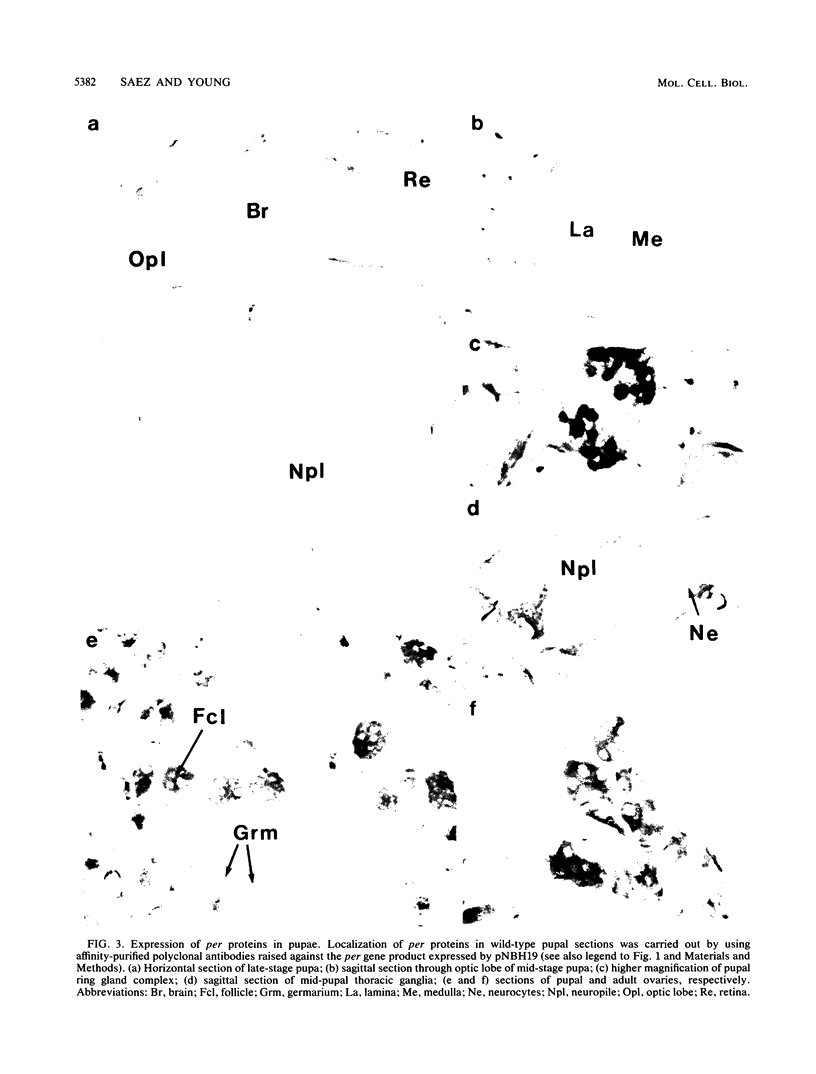
The per locus influences biological rhythms in Drosophila melanogaster. In this study, per transcripts and proteins were localized in situ in pupae and adults. Earlier genetic studies have demonstrated that per expression is required in the brain for circadian locomotor activity rhythms and in the thorax for ultradian rhythmicity of the Drosophila courtship song. per RNA and proteins were detected in a restricted group of cells in the eyes and optic lobes of the adult brain and in many cell bodies in the adult and pupal thoracic ganglia. per products were also found in the pupal ring gland complex, a tissue involved in rhythmic aspects of Drosophila development. Abundant expression was seen in gonadal tissue. No biological clock phenotypes have been reported for this tissue in any of the per mutants, per protein mapped to different subcellular locations in different tissues. The protein accumulated in or around nuclei in some cells and appeared to be cytoplasmic in others.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargiello T. A., Saez L., Baylies M. K., Gasic G., Young M. W., Spray D. C. The Drosophila clock gene per affects intercellular junctional communication. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):686–691. doi: 10.1038/328686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargiello T. A., Young M. W. Molecular genetics of a biological clock in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2142–2146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylies M. K., Bargiello T. A., Jackson F. R., Young M. W. Changes in abundance or structure of the per gene product can alter periodicity of the Drosophila clock. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):390–392. doi: 10.1038/326390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Genetic and molecular analysis of biological rhythms. J Biol Rhythms. 1987 Fall;2(3):153–178. doi: 10.1177/074873048700200301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler A. M., Konopka R. J. Transplantation of a circadian pacemaker in Drosophila. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):236–238. doi: 10.1038/279236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich C. Role of the optic lobes in the regulation of the locomotor activity rhythm of Drosophila melanogaster: behavioral analysis of neural mutants. J Neurogenet. 1986 Nov;3(6):321–343. doi: 10.3109/01677068609106857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. R., Bargiello T. A., Yun S. H., Young M. W. Product of per locus of Drosophila shares homology with proteoglycans. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):185–188. doi: 10.1038/320185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. A., Ewer J., Reddy P., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Embryonic expression of the period clock gene in the central nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2313–2320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Lorenz L., Yu Q. N., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Spatial and temporal expression of the period gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):228–238. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page T. L., Caldarola P. C., Pittendrigh C. S. Mutual entrainment of bilaterally distributed circadian pacemaker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1277–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page T. L. Transplantation of the cockroach circadian pacemaker. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):73–75. doi: 10.1126/science.216.4541.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Jacquier A. C., Abovich N., Petersen G., Rosbash M. The period clock locus of D. melanogaster codes for a proteoglycan. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90859-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Zehring W. A., Wheeler D. A., Pirrotta V., Hadfield C., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Molecular analysis of the period locus in Drosophila melanogaster and identification of a transcript involved in biological rhythms. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Tanese N., Goff S. P. Purification and characterization of murine retroviral reverse transcriptase expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9326–9335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siwicki K. K., Eastman C., Petersen G., Rosbash M., Hall J. C. Antibodies to the period gene product of Drosophila reveal diverse tissue distribution and rhythmic changes in the visual system. Neuron. 1988 Apr;1(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. W., Jackson F. R., Shin H. S., Bargiello T. A. A biological clock in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:865–875. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]