Abstract
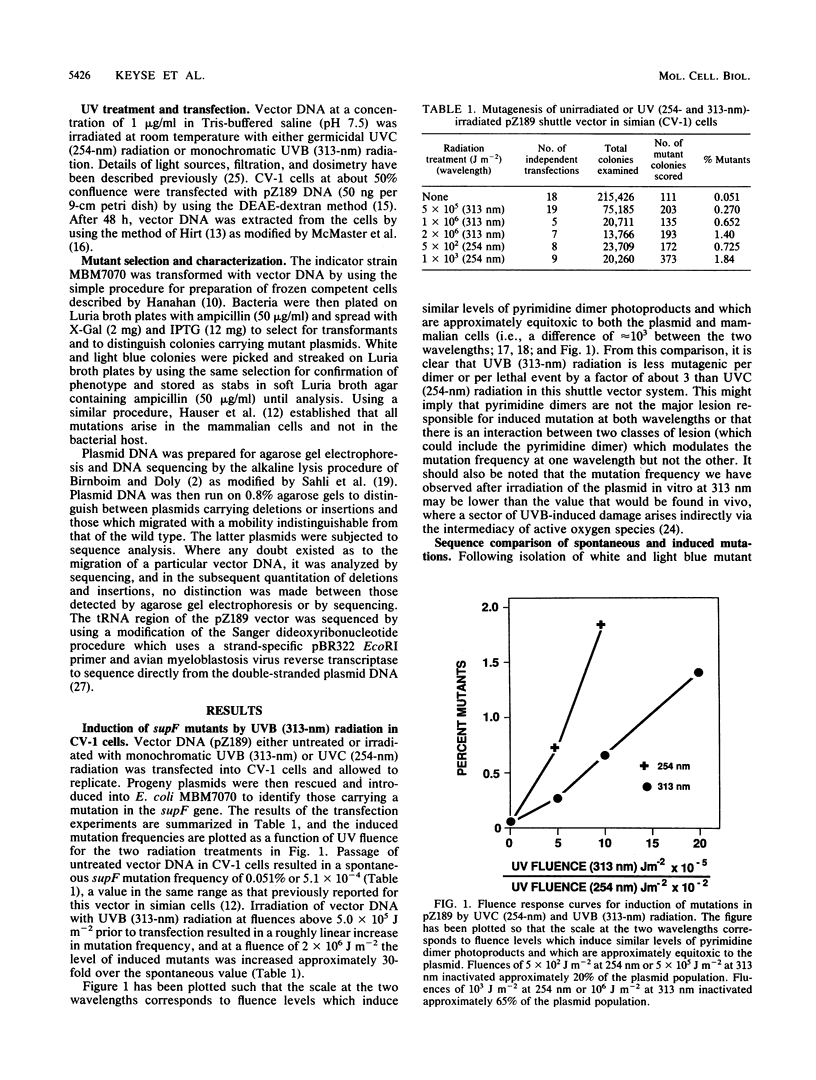
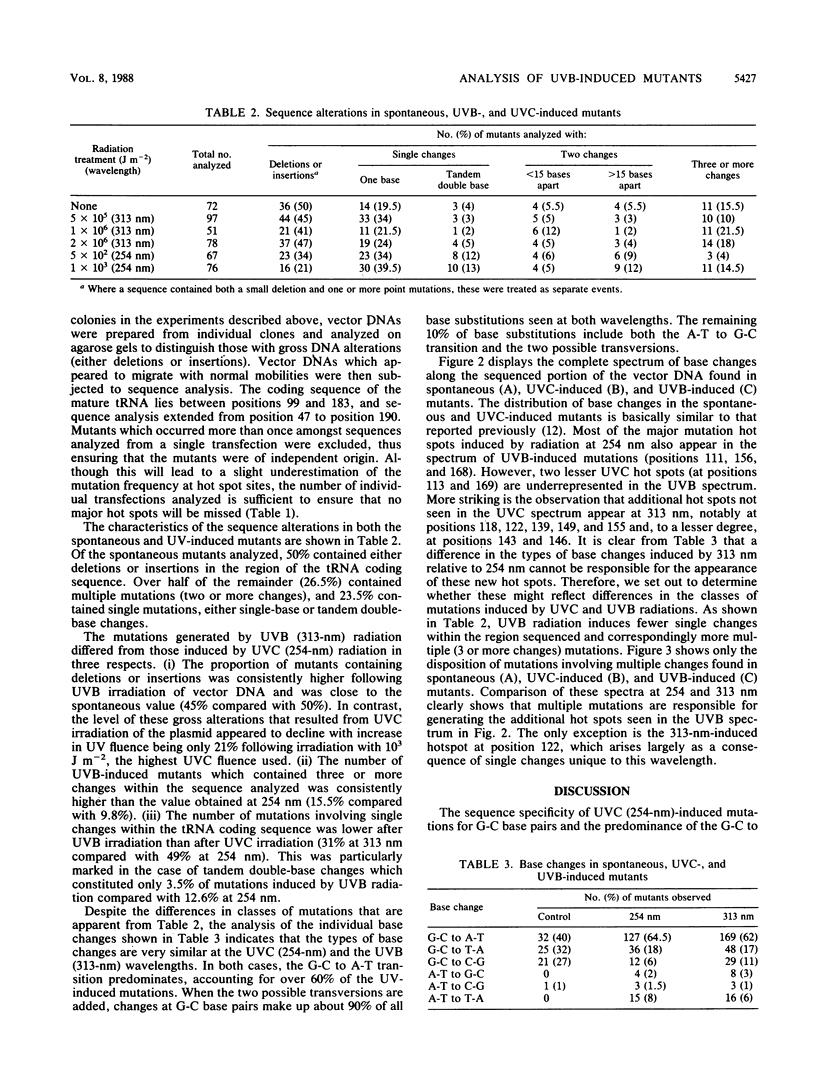
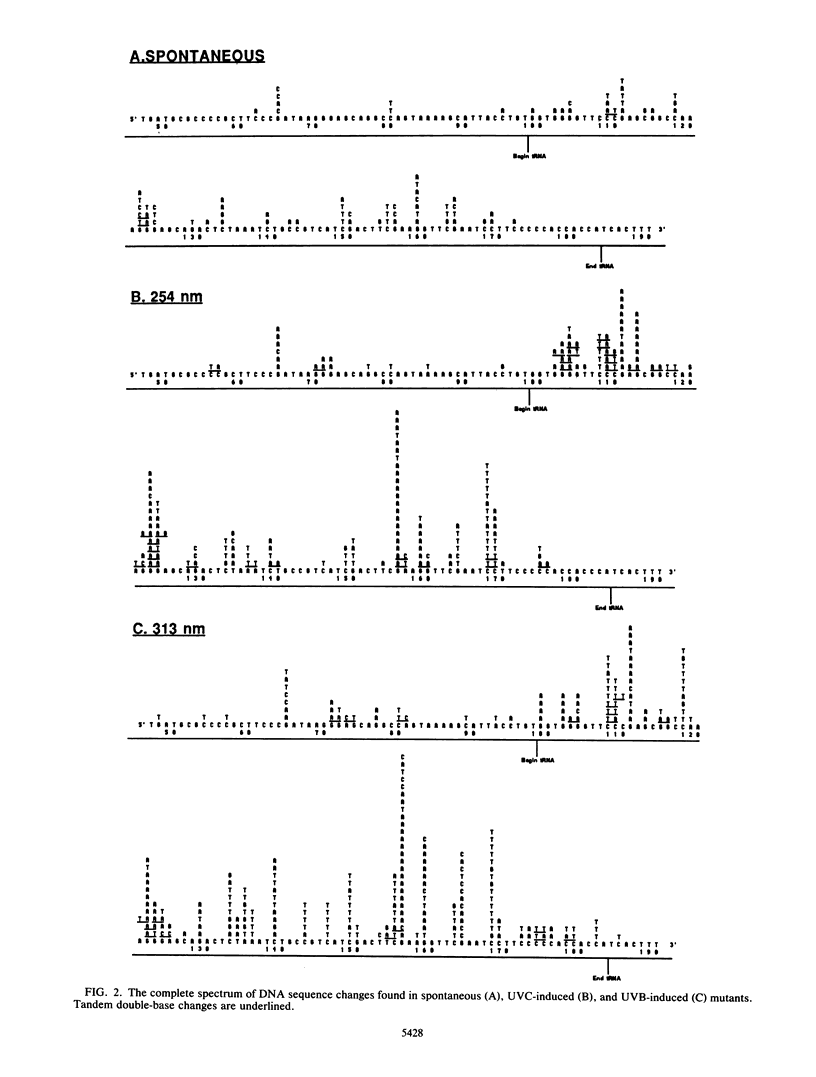
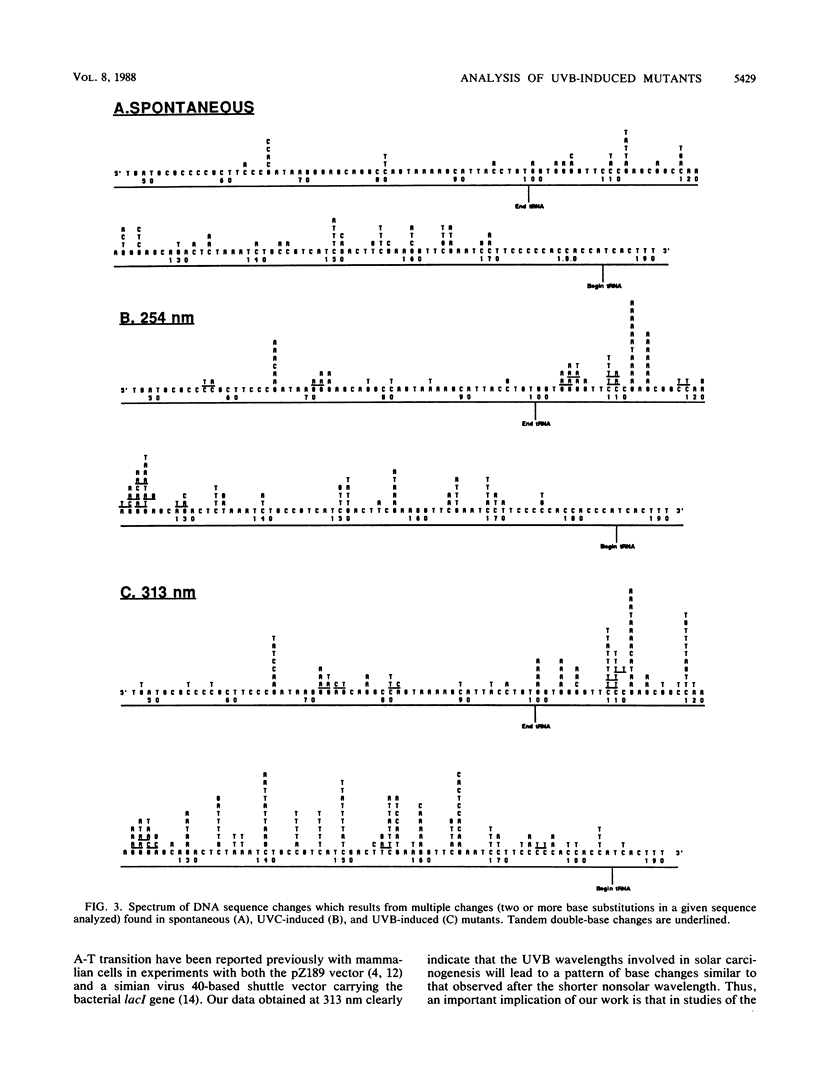
Mutations induced by UVB (313-nm) radiation, a wavelength in the region of peak effectiveness for sunlight-induced skin cancer in humans, have been analyzed at the sequence level in simian cells by using a plasmid shuttle vector (pZ189). We find that significant differences exist between the types of mutations induced by this solar wavelength and those induced by nonsolar UVC (254-nm) radiation. Compared with 254-nm radiation, 313-nm radiation induces more deletions and insertions in the region sequenced. In addition, although the types of base substitutions induced by the two wavelengths are broadly similar (in both cases, the majority of changes occur at G-C base pairs and the G-C to A-T transition is predominant), an analysis of the distribution of these base changes within the supF gene following irradiation at 313 nm reveals additional hot spots for mutation not seen after irradiation at 254 nm. These hot spots are shown to arise predominantly at sites of mutations involving multiple base changes, a class of mutations which arises more frequently at the longer solar wavelength. Lastly, we observed that most of the sites at which mutational hot spots arise after both UVC and UVB irradiation of the shuttle vector are also sites at which mutations arise spontaneously. Thus, a common mechanism may be involved in determining the site specificity of mutations, in which the DNA structure may be a more important determinant than the positions of DNA photoproducts.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balmain A., Ramsden M., Bowden G. T., Smith J. Activation of the mouse cellular Harvey-ras gene in chemically induced benign skin papillomas. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):658–660. doi: 10.1038/307658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Seetharam S., Kraemer K. H., Seidman M. M., Bredberg A. Photoproduct frequency is not the major determinant of UV base substitution hot spots or cold spots in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredberg A., Kraemer K. H., Seidman M. M. Restricted ultraviolet mutational spectrum in a shuttle vector propagated in xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8273–8277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. IV. Mutagenic specificity in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):577–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drobetsky E. A., Grosovsky A. J., Glickman B. W. The specificity of UV-induced mutations at an endogenous locus in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9103–9107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison M. J., Childs J. D. Pyrimidine dimers induced in Escherichia coli DNA by ultraviolet radiation present in sunlight. Photochem Photobiol. 1981 Oct;34(4):465–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser J., Levine A. S., Dixon K. Unique pattern of point mutations arising after gene transfer into mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):63–67. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser J., Seidman M. M., Sidur K., Dixon K. Sequence specificity of point mutations induced during passage of a UV-irradiated shuttle vector plasmid in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):277–285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Clancy S., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. The lacI shuttle: rapid analysis of the mutagenic specificity of ultraviolet light in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8606–8610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Beard P., Engers H. D., Hirt B. Characterization of an immunosuppressive parvovirus related to the minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):317–326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.317-326.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miguel A. G., Tyrrell R. M. Induction of oxygen-dependent lethal damage by monochromatic UVB (313 nm) radiation: strand breakage, repair and cell death. Carcinogenesis. 1983;4(4):375–380. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.4.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli H. J., Cerutti P. A. Cyclobutane-type pyrimidine photodimer formation and excision in human skin fibroblasts after irradiation with 313-nm ultraviolet light. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 15;22(6):1390–1395. doi: 10.1021/bi00275a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahli R., McMaster G. K., Hirt B. DNA sequence comparison between two tissue-specific variants of the autonomous parvovirus, minute virus of mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3617–3633. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M., Bredberg A., Seetharam S., Kraemer K. H. Multiple point mutations in a shuttle vector propagated in human cells: evidence for an error-prone DNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4944–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M., Dixon K., Razzaque A., Zagursky R. J., Berman M. L. A shuttle vector plasmid for studying carcinogen-induced point mutations in mammalian cells. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90222-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B. The wavelengths in sunlight effective in producing skin cancer: a theoretical analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3363–3366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell R. M. Mutagenic action of monochromatic UV radiation in the solar range on human cells. Mutat Res. 1984 Oct;129(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(84)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell R. M., Pidoux M. Endogenous glutathione protects human skin fibroblasts against the cytotoxic action of UVB, UVA and near-visible radiations. Photochem Photobiol. 1986 Nov;44(5):561–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1986.tb04709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell R. M., Werfelli P., Moraes E. C. Lethal action of ultraviolet and visible (blue-violet) radiations at defined wavelengths on human lymphoblastoid cells: action spectra and interaction sites. Photochem Photobiol. 1984 Feb;39(2):183–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1984.tb03426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldren C., Correll L., Sognier M. A., Puck T. T. Measurement of low levels of x-ray mutagenesis in relation to human disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4839–4843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarbl H., Sukumar S., Arthur A. V., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Direct mutagenesis of Ha-ras-1 oncogenes by N-nitroso-N-methylurea during initiation of mammary carcinogenesis in rats. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):382–385. doi: 10.1038/315382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong P. J., Grosovsky A. J., Glickman B. W. Spectrum of spontaneous mutation at the APRT locus of Chinese hamster ovary cells: an analysis at the DNA sequence level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



