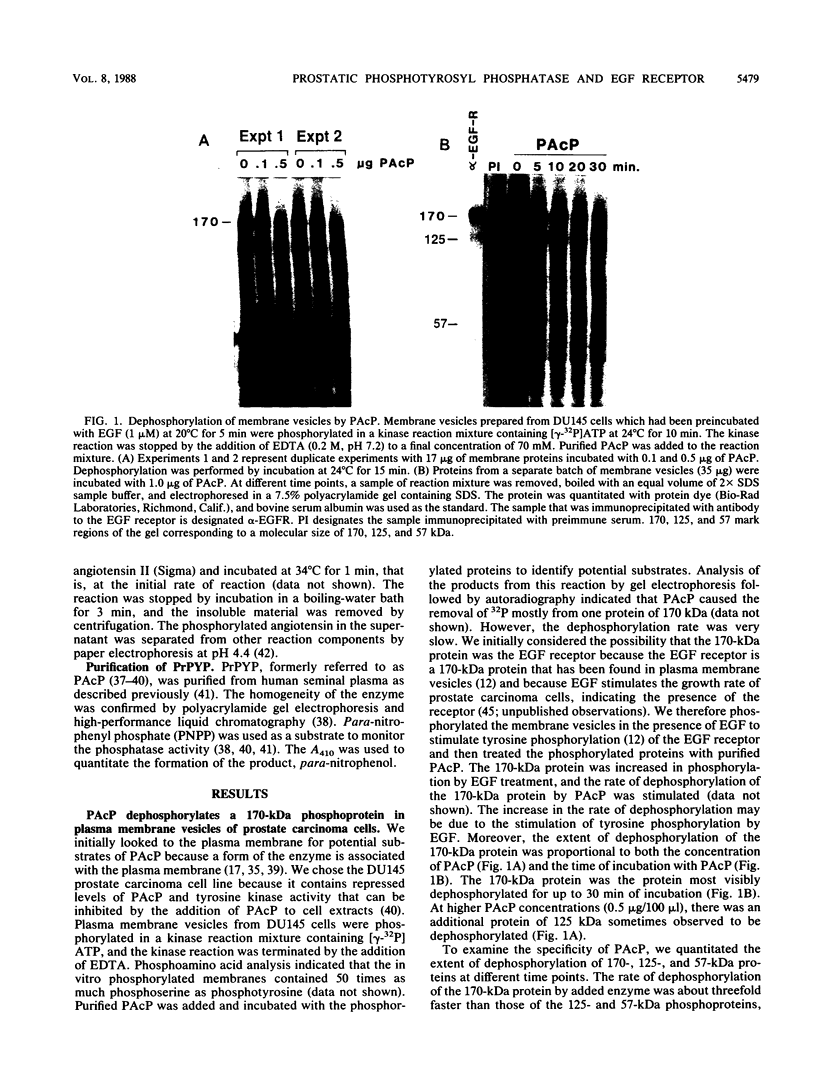
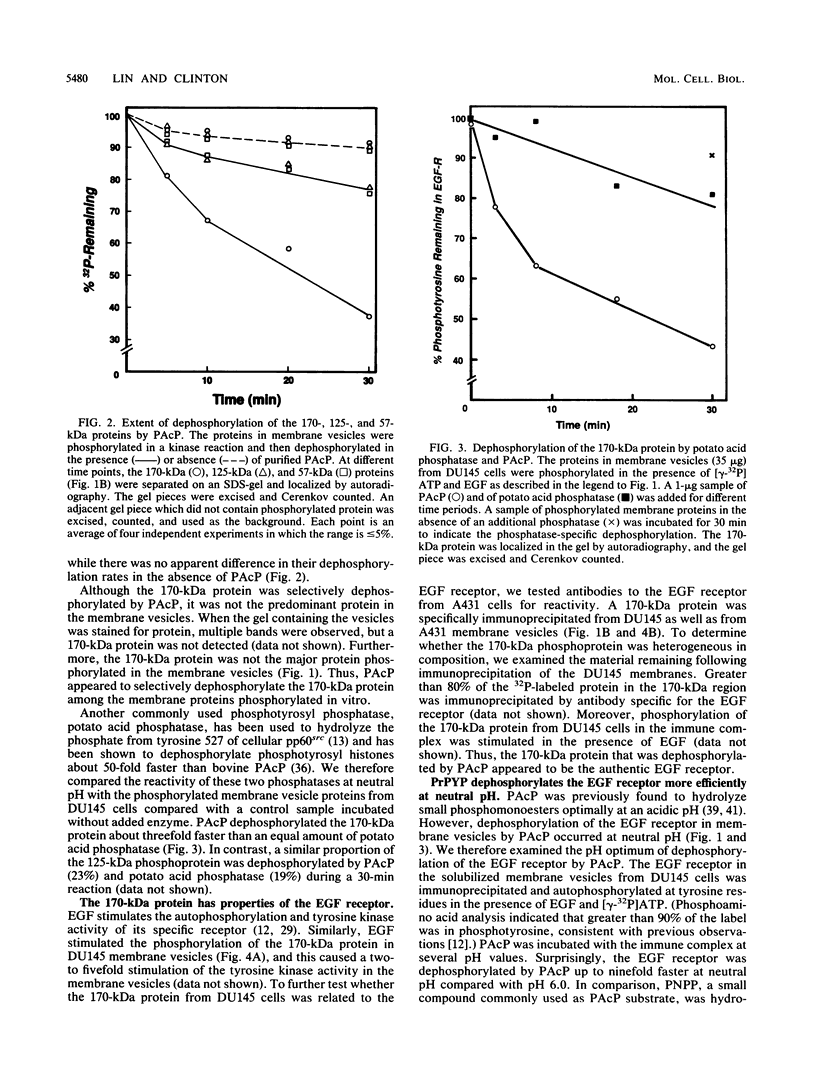
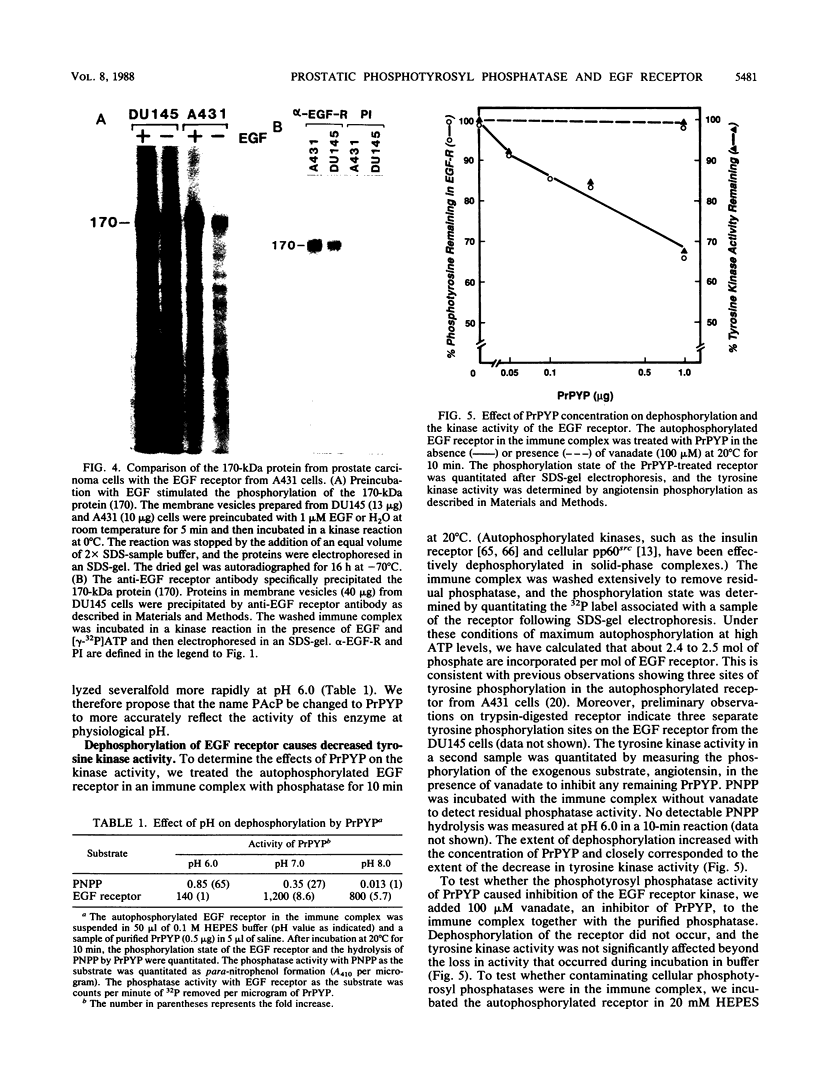
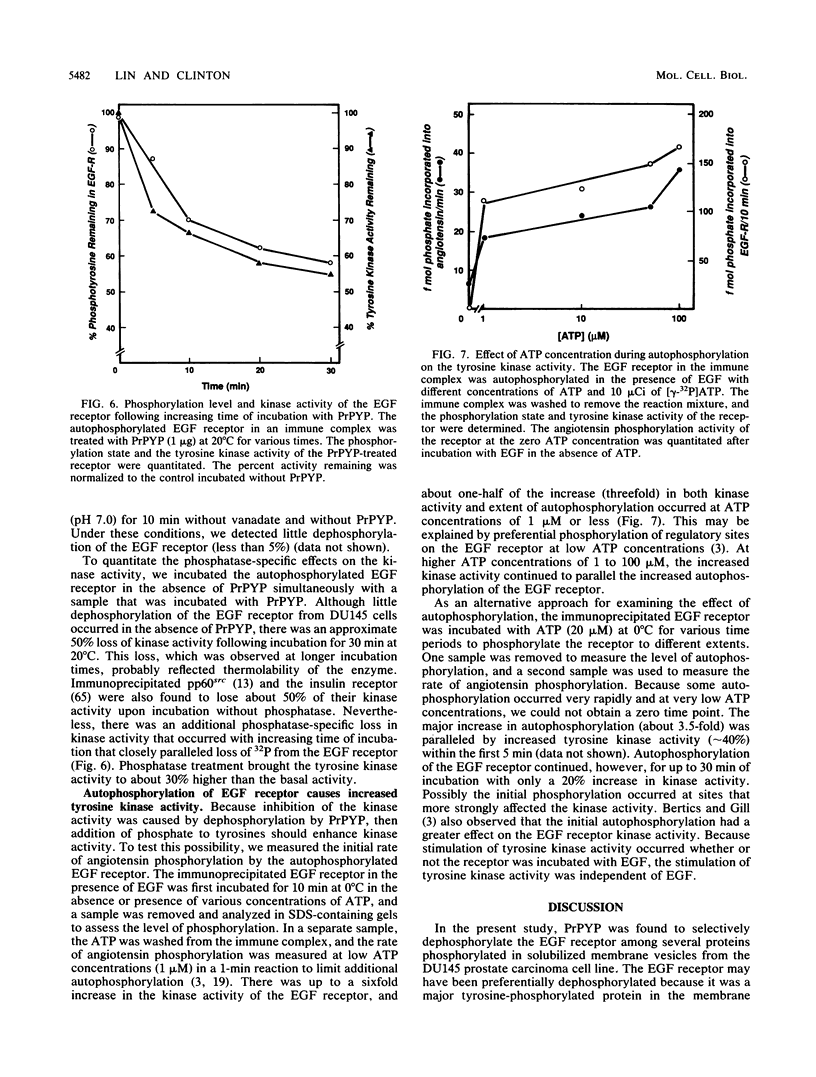
Abstract
Human prostatic acid phosphatase (PAcP) has been found to have phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity (H. C. Li, J. Chernoff, L. B. Chen, and A. Kirschonbaun, Eur. J. Biochem. 138:45-51, 1984; M.-F. Lin and G. M. Clinton, Biochem. J. 235:351-357, 1986) and has been suggested to negatively regulate phosphotyrosine levels, at least in part, by inhibition of tyrosine protein kinase activity (M.-F. Lin and G. M. Clinton, Adv. Protein Phosphatases 4:199-228, 1987; M.-F. Lin, C. L. Lee, and G. M. Clinton, Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:4753-4757, 1986). We investigated the molecular interaction of PAcP with a specific tyrosine kinase, the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor, from prostate carcinoma cells. Of several proteins phosphorylated in membrane vesicles from prostate carcinoma cells, PAcP selectively dephosphorylated the EGF receptor. The prostate EGF receptor was more efficiently dephosphorylated by PAcP than by another phosphotyrosyl phosphatase, potato acid phosphatase. Further characterization of the interaction of PAcP with the EGF receptor revealed that the optimal rate of dephosphorylation occurred at neutral rather than at acid pH. Thus, the enzyme that we formerly referred to as PAcP we now call prostatic phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase. Hydrolysis of phosphate from tyrosine residues in the immunoprecipitated EGF receptor catalyzed by purified prostatic phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase caused a 40 to 50% decrease in the receptor tyrosine kinase activity with angiotensin as the substrate. In contrast, autophosphorylation of the receptor was associated with an increase in tyrosine kinase activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertics P. J., Chen W. S., Hubler L., Lazar C. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N. Alteration of epidermal growth factor receptor activity by mutation of its primary carboxyl-terminal site of tyrosine self-phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3610–3617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertics P. J., Gill G. N. Self-phosphorylation enhances the protein-tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14642–14647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boivin P., Galand C. The human red cell acid phosphatase is a phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase which dephosphorylates the membrane protein band 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):557–564. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Rosen N., Israel M. A. Increased pp60c-src tyrosyl kinase activity in human neuroblastomas is associated with amino-terminal tyrosine phosphorylation of the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7275–7279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Bornstein P., Gallis B. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase. Specific inhibition by Zn. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6519–6522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. J., Gordon J. A. The stimulation of pp60v-src kinase activity by vanadate in intact cells accompanies a new phosphorylation state of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9580–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Brugge J. S. Characterization of structural domains of the human epidermal growth factor receptor obtained by partial proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11534–11542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Van Beveren C., Smith D., Chen E., Mitchell R. L., Isacke C. M., Verma I. M., Ullrich A. Structural alteration of viral homologue of receptor proto-oncogene fms at carboxyl terminus. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):277–280. doi: 10.1038/320277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Chu T. M., Leong S. S., Horoszewicz J. S., Lee C. L. Effect of methotrexate-monoclonal anti-prostatic acid phosphatase antibody conjugate on human prostate tumor. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):3751–3755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Fleming T. P., Hazan R., Ullrich A., King C. R., Schlessinger J., Aaronson S. A. Overexpression of the human EGF receptor confers an EGF-dependent transformed phenotype to NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Autophosphorylation and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Effect on tyrosine kinase activity and ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14538–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foti A. G., Herschman H., Cooper J. F. Isozymes of acid phosphatase in normal and cancerous human prostatic tissue. Cancer Res. 1977 Nov;37(11):4120–4124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Separation of multiple phosphotyrosyl-and phosphoseryl-protein phosphatases from chicken brain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:163–180. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69075-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Downward J., Waterfield M. D. Antibodies to the autophosphorylation sites of the epidermal growth factor receptor protein-tyrosine kinase as probes of structure and function. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2869–2877. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horoszewicz J. S., Leong S. S., Kawinski E., Karr J. P., Rosenthal H., Chu T. M., Mirand E. A., Murphy G. P. LNCaP model of human prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1809–1818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Fox C. F. Epidermal growth factor and potent phorbol tumor promoters induce epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation in a similar but distinctively different manner in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2559–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund J. K. Transformation of cells by an inhibitor of phosphatases acting on phosphotyrosine in proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau K. H., Freeman T. K., Baylink D. J. Purification and characterization of an acid phosphatase that displays phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity from bovine cortical bone matrix. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1389–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. F., Kaplan N. O. An acid phosphatase in the plasma membranes of human astrocytoma showing marked specificity toward phosphotyrosine protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. C., Chernoff J., Chen L. B., Kirschonbaum A. A phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity associated with acid phosphatase from human prostate gland. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. F., Clinton G. M. Human prostatic acid phosphatase has phosphotyrosyl protein phosphatase activity. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):351–357. doi: 10.1042/bj2350351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. F., Lee C. L., Clinton G. M. Tyrosyl kinase activity is inversely related to prostatic acid phosphatase activity in two human prostate carcinoma cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4753–4757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. F., Lee C. L., Li S. S., Chu T. M. Purification and characterization of a new human prostatic acid phosphatase isoenzyme. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1055–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. F., Lee P. L., Clinton G. M. Characterization of tyrosyl kinase activity in human serum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1582–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loor R., Wang M. C., Valenzuela L., Chu T. M. Expression of prostatic acid phosphatase in human prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 1981 Oct;14(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(81)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. L., Branton P. E. Identification, purification, and characterization of phosphotyrosine-specific protein phosphatases from cultured chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1003–1012. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peehl D. M., Stamey T. A. Serum-free growth of adult human prostatic epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1986 Feb;22(2):82–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02623537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchio A. F., Wells S. K., Collett M. S. Increase in the phosphotransferase specific activity of purified Rous sarcoma virus pp60v-src protein after incubation with ATP plus Mg2+. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1589–1597. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif A. E., Schlesinger R. M., Fish C. A., Robinson C. M. Acid phosphatase isozymes in cancer of the prostate. Cancer. 1973 Mar;31(3):689–699. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197303)31:3<689::aid-cncr2820310331>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotenberg S. A., Brautigan D. L. Membrane protein phosphotyrosine phosphatase in rabbit kidney. Proteolysis activates the enzyme and generates soluble catalytic fragments. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):747–754. doi: 10.1042/bj2430747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Dull T. J., Rettenmier C. W., Ralph P., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J. Transforming potential of the c-fms proto-oncogene (CSF-1 receptor). Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):549–552. doi: 10.1038/325549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M. The viral tyrosine protein kinases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;123:39–72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70810-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shriner C. L., Brautigan D. L. Cytosolic protein phosphotyrosine phosphatases from rabbit kidney. Purification of two distinct enzymes that bind to Zn2+-iminodiacetate agarose. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11383–11390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks J. W., Brautigan D. L. Specificity of protein phosphotyrosine phosphatases. Comparison with mammalian alkaline phosphatase using polypeptide substrates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2042–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. R., Mickey D. D., Wunderli H., Mickey G. H., Paulson D. F. Isolation of a human prostate carcinoma cell line (DU 145). Int J Cancer. 1978 Mar 15;21(3):274–281. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Brown T. A., Whipple J. H., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Dubler R. E., Cheng K., Larner J. A novel mechanism for the insulin-like effect of vanadate on glycogen synthase in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6650–6658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M., Gill G. N. The EGF receptor: structure, regulation and potential role in malignancy. Cancer Surv. 1985;4(4):767–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velu T. J., Beguinot L., Vass W. C., Willingham M. C., Merlino G. T., Pastan I., Lowy D. R. Epidermal-growth-factor-dependent transformation by a human EGF receptor proto-oncogene. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1408–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.3500513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Zoller M. J., Smith M., Hinze E., Pawson T. Mutagenesis of Fujinami sarcoma virus: evidence that tyrosine phosphorylation of P130gag-fps modulates its biological activity. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T. Clinical significance of the human acid phosphatases: a review. Am J Med. 1974 May;56(5):604–616. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90630-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto W., Filson A. J., Queral-Lustig A. E., Wang J. Y., Brugge J. S. Detection of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins in polyomavirus middle tumor antigen-transformed cells after treatment with a phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):905–913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor beta subunit activates the receptor tyrosine kinase in intact H-35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4715–4722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor beta subunit activates the receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5277–5286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]