Abstract
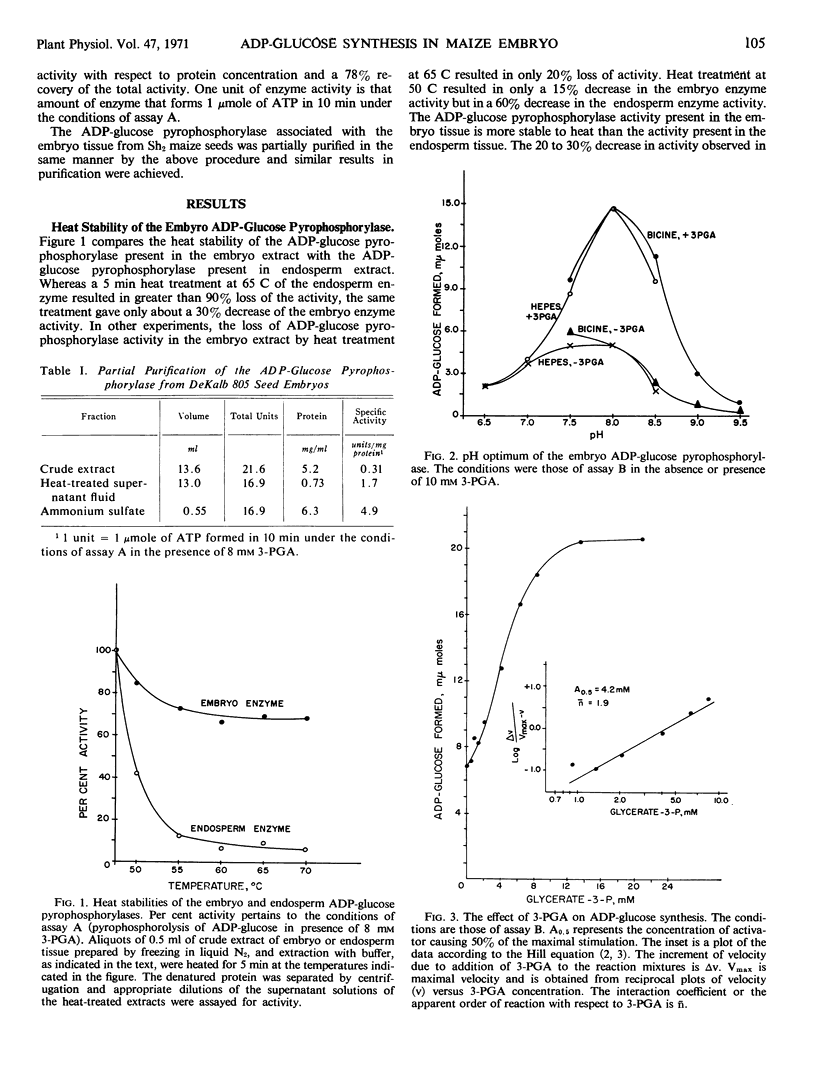
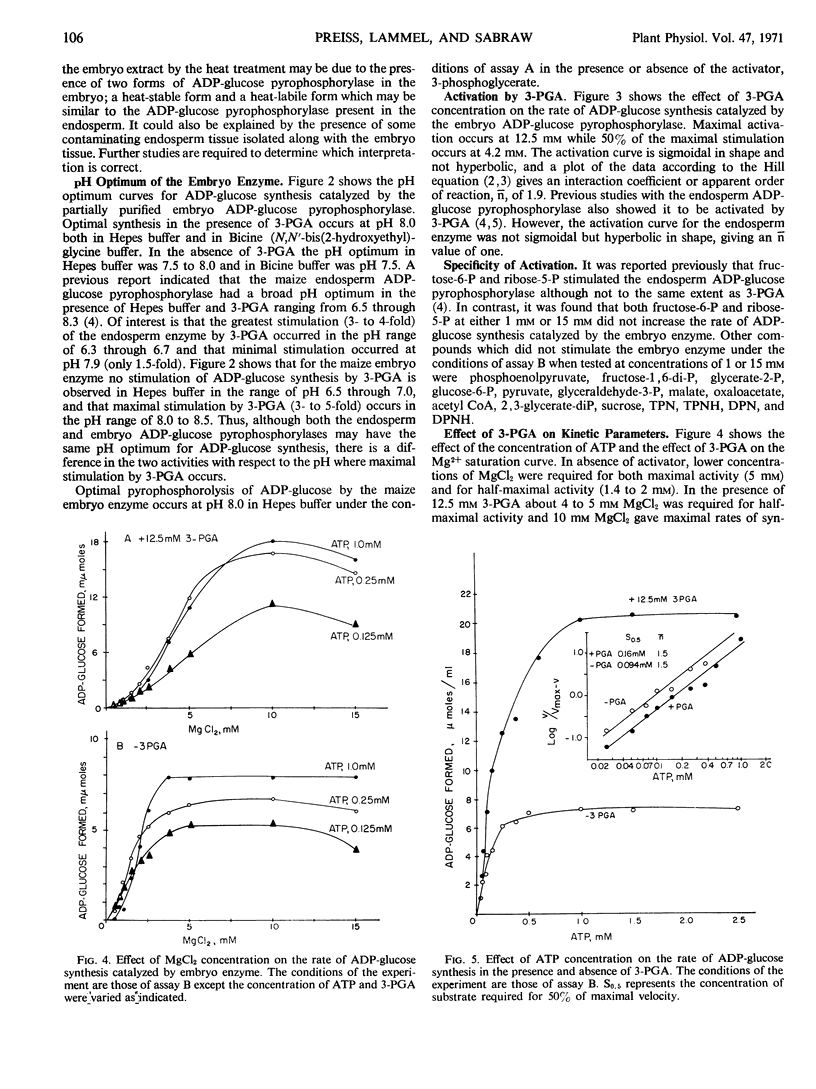
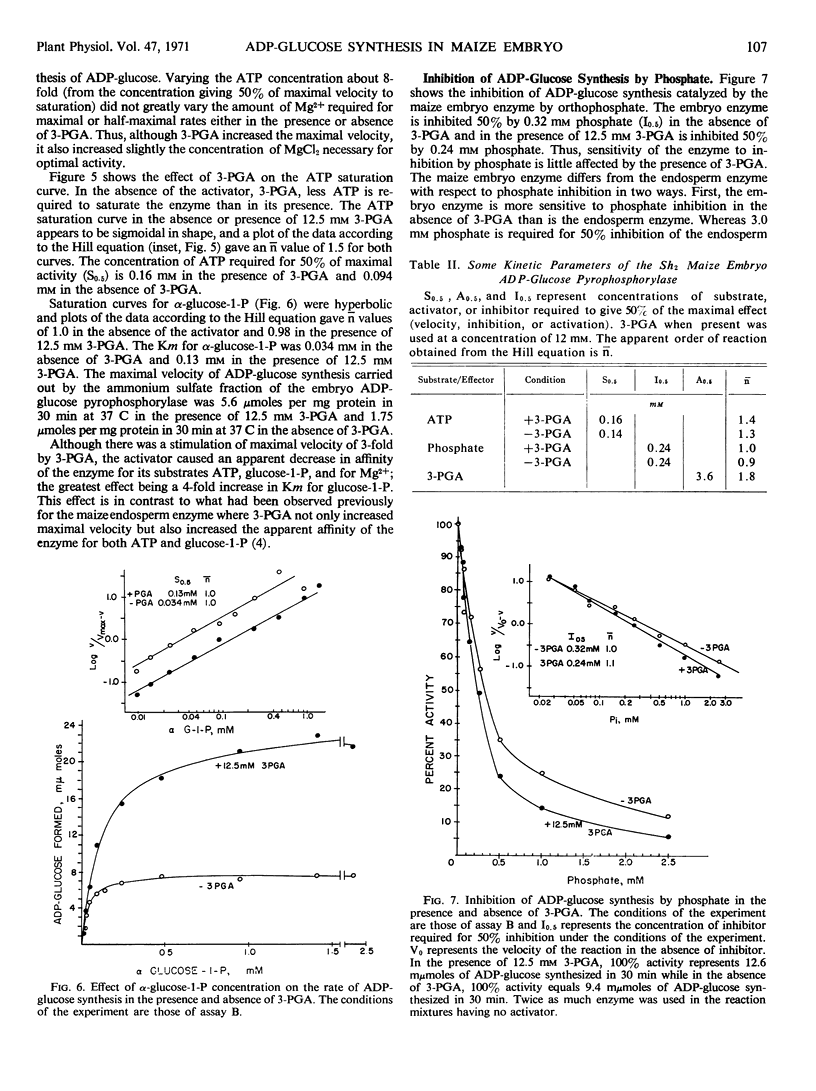
A comparison of heat stabilities and various kinetic properties between the adenosine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylases isolated from endosperm and embryo tissues from starchy maize seeds indicates that the adenosine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase associated with the embryo is distinct from the enzyme isolated from the endosperm. The embryo enzyme is more stable to incubation for 5 minutes at 60 C while the endosperm enzyme is labile to this treatment. Both enzymes are activated by glycerate-3-P. The embryo enzyme is more sensitive to inhibition by phosphate than is the endosperm enzyme. Glycerate-3-P, which reverses the inhibition of the endosperm enzyme by phosphate, has little effect on the phosphate inhibition of the embryo enzyme. Other kinetic studies distinguish the two enzymes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINSON D. E., HATHAWAY J. A., SMITH E. C. KINETICS OF REGULATORY ENZYMES. KINETIC ORDER OF THE YEAST DIPHOSPHOPYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE ISOCITRATE DEHYDROGENASE REACTION AND A MODEL FOR THE REACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2682–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akatsuka T., Nelson O. E. Starch granule-bound adenosine diphosphate glucose-starch glucosyltransferases of maize seeds. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2280–2285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. B., Preiss J. ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase from maize endosperm. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. B., Preiss J. Presence of ADP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase in Shrunken-2 and Brittle-2 Mutants of Maize Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jul;44(7):1058–1062. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.7.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. P., Preiss J. Adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase. A regulatory enzyme in the biosynthesis of starch in spinach leaf chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4491–4504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEN L., PREISS J. BIOSYNTHESIS OF BACTERIAL GLYCOGEN. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHOGLUCOSE PYROPHOSPHORYLASE OF ARTHROBACTER SPECIES NRRL B1973. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2334–2340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal G. G., Preiss J. Biosynthesis of starch in Chlorella pyrenoidosa. II. Regulation of ATP: alpha-D-glucose 1-phosphate adenyl transferase (ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase) by inorganic phosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):454–469. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90477-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Nelson O. E. Two additional phosphorylases in developing maize seeds. Plant Physiol. 1969 Feb;44(2):159–167. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


