Abstract
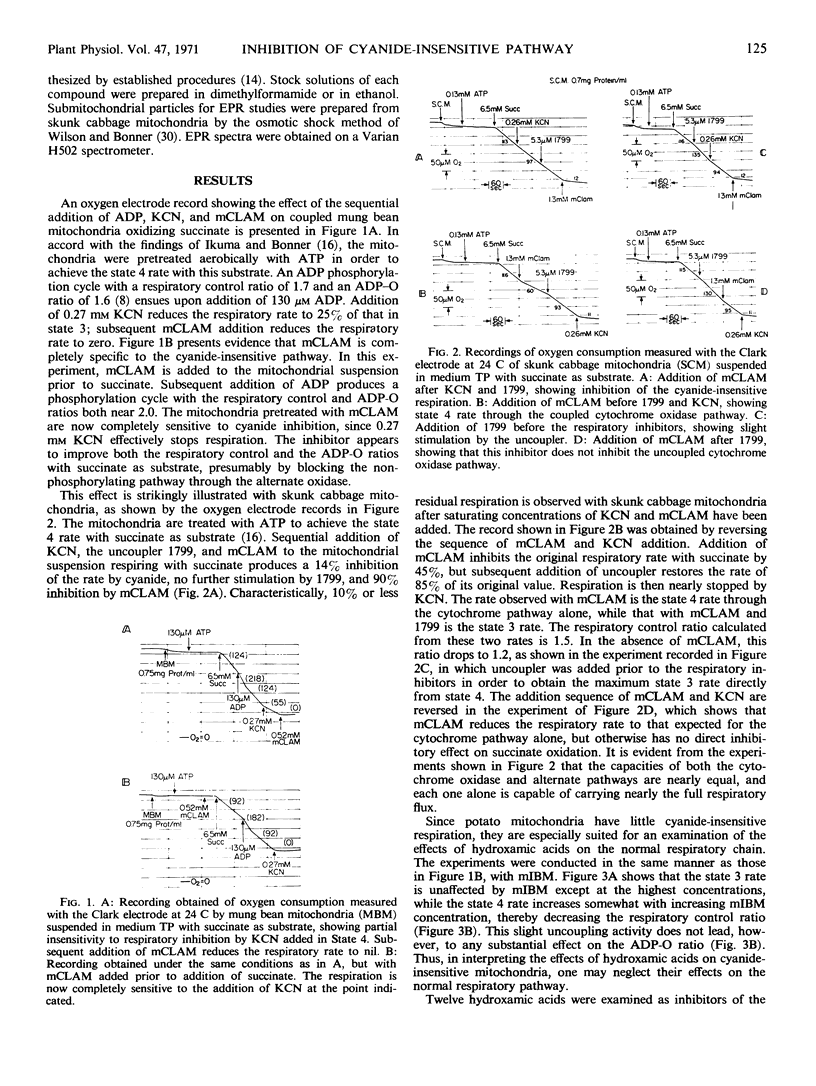
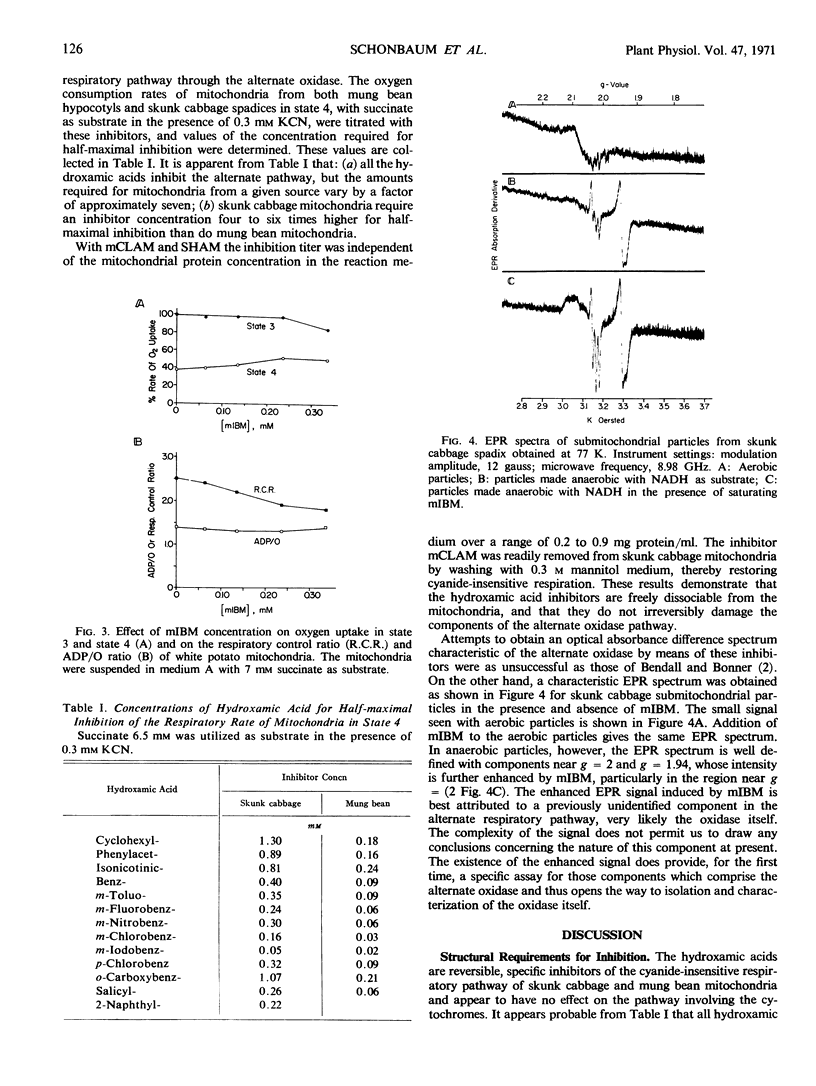
Hydroxamic acids, R-CONHOH, are inhibitors specific to the respiratory pathway through the alternate, cyanide-insensitive terminal oxidase of plant mitochondria. The nature of the R group in these compounds affects the concentration at which the hydroxamic acids are effective, but it appears that all hydroxamic acids inhibit if high enough concentrations are used. The benzhydroxamic acids are effective at relatively low concentrations; of these, the most effective are m-chlorobenzhydroxamic acid and m-iodobenzhydroxamic acid. The concentrations required for half-maximal inhibition of the alternate oxidase pathway in mung bean (Phaseolus aureus) mitochondria are 0.03 mm for m-chlorobenzhydroxamic acid and 0.02 mm for m-iodobenzhydroxamic acid. With skunk cabbage (Symplocarpus foetidus) mitochondria, the required concentrations are 0.16 for m-chlorobenzhydroxamic acid and 0.05 for m-iodobenzhydroxamic acid. At concentrations which inhibit completely the alternate oxidase pathway, these two compounds have no discernible effect on either the respiratory pathway through cytochrome oxidase, or on the energy coupling reactions of these mitochondria. These inhibitors make it possible to isolate the two respiratory pathways and study their mode of action separately. These inhibitors also enhance an electron paramagnetic resonance signal near g = 2 in anaerobic, submitochondrial particles from skunk cabbage, which appears to be specific to the alternate oxidase and thus provides a means for its assay.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENDALL D. S. Cytochromes and some respiratory enzymes in mitochondria from the spadix of Arum maculatum. Biochem J. 1958 Nov;70(3):381–390. doi: 10.1042/bj0700381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B., WILLIAMS G. R. The respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1956;17:65–134. doi: 10.1002/9780470122624.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecinska M., Storey B. T. The Respiratory Chain of Plant Mitochondria: VII. Kinetics of Flavoprotein Oxidation in Skunk Cabbage Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1970 Oct;46(4):618–624. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.4.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett D. P., Haas D. W. Oxidative Phosphorylation and Functional Cytochromes in Skunk Cabbage Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1958 Jan;33(1):27–32. doi: 10.1104/pp.33.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuma H., Bonner W. D. Properties of Higher Plant Mitochondria. I. Isolation and Some Characteristics of Tightly-coupled Mitochondria from Dark-grown Mung Bean Hypocotyls. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jan;42(1):67–75. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuma H., Bonner W. D. Properties of Higher Plant Mitochondria. III. Effects of Respiratory Inhibitors. Plant Physiol. 1967 Nov;42(11):1535–1544. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.11.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff E., Klingenberg M., Heldt H. W. Unspecific permeation and specific exchange of adenine nucleotides in liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 15;104(1):312–315. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey B. T., Bahr J. T. The respiratory chain of plant mitochondria. I. Electron transport between succinate and oxygen in skunk cabbage mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jan;44(1):115–125. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey B. T., Bahr J. T. The respiratory chain of plant mitochondria. II. Oxidative phosphorylation in skunk cabbage mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jan;44(1):126–134. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey B. T. The Respiratory Chain of Plant Mitochondria: VI. Flavoprotein Components of the Respiratory Chain of Mung Bean Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1970 Jul;46(1):13–20. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais P. V., Duée E. D., Colomb M., Reboul A., Cheruy A., Bârzu O., Vignais P. M. Transfert d'adénine-nucléotides a travers les membranes mitochondriales au cours de la phosphorylation oxydative. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1970 Jun;52(5):471–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. K., Saris N. E. Effect of hydroxylamine on respiration and oxidative phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):160–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. F., Brooks E. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by hydroxylamine and its relation to energy conservation. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 3;9(5):1090–1094. doi: 10.1021/bi00807a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. B., Bonner W. D. Preparation and some properties of submitochondrial particles from tightly coupled mung bean mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1970 Jul;46(1):25–30. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum C. S., Hackett D. P. Participation of Cytochromes in the Respiration of the Aroid Spadix. Plant Physiol. 1957 May;32(3):186–191. doi: 10.1104/pp.32.3.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


