Abstract
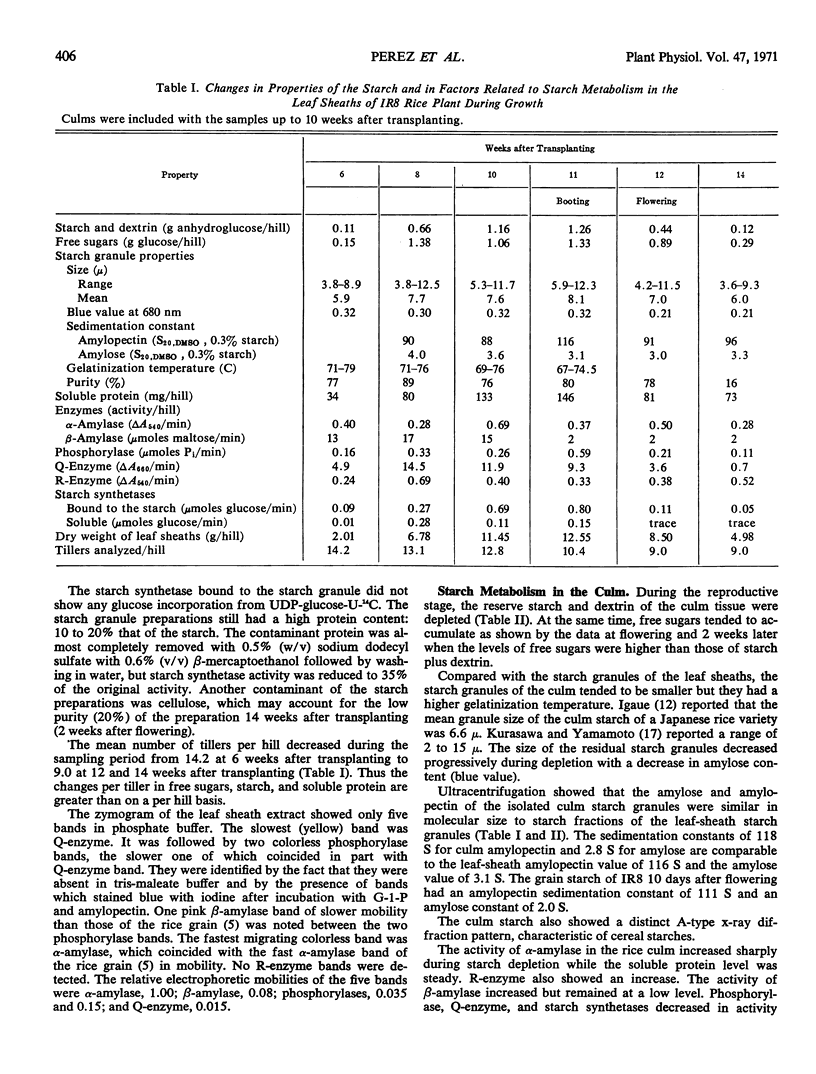
The levels of starch and dextrin, free sugars, soluble protein, and enzymes involved in starch metabolism—α-amylase, β-amylase, phosphorylase, Q-enzyme, R-enzyme, and ADP-glucose starch synthetases—were assayed in the leaf sheaths and culm of the rice plant (Oryza sativa L., variety IR8) during growth.
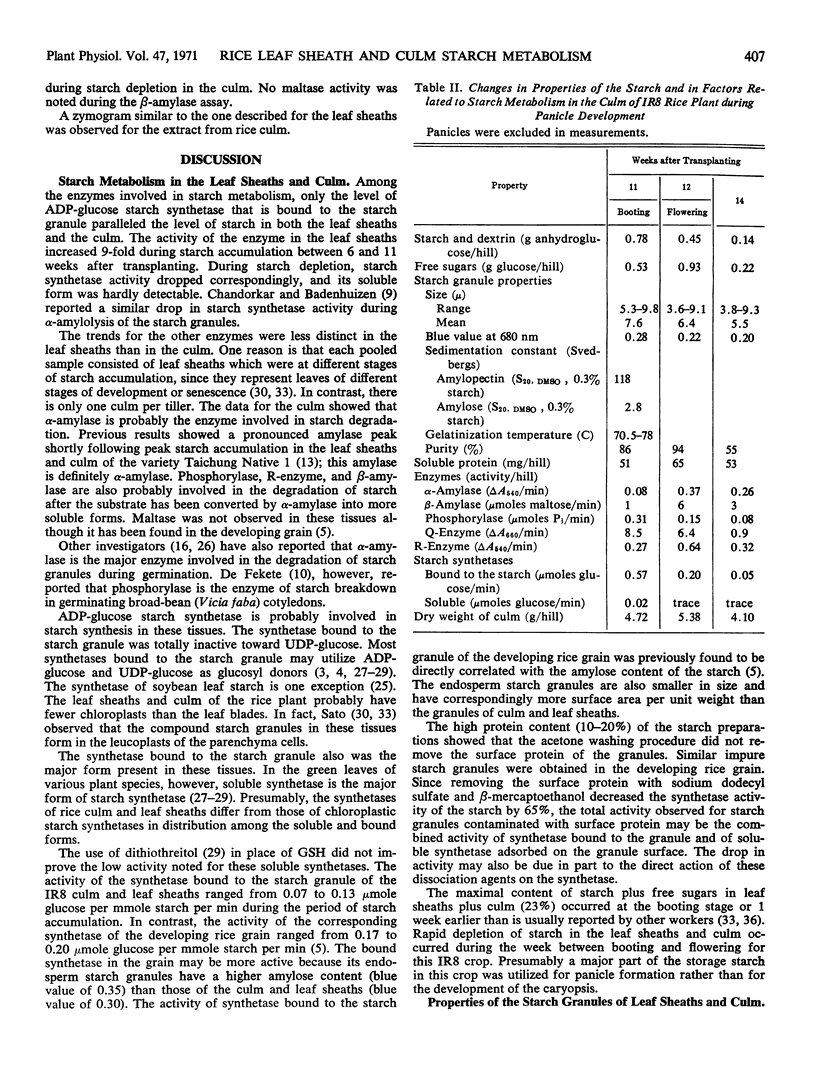
Starch accumulation in the leaf sheaths reached a maximum 10 to 11 weeks after transplanting, the time of development of the rice panicle. Maximal concentration of free sugars occurred earlier. Starch and sugars in the leaf sheaths and culm decreased rapidly during grain development.
During starch accumulation, the starch granules of the leaf sheaths increased slightly in size and its gelatinization temperature decreased. The molecular size of amylose and amylopectin and amylose content of the starch were similar in both culm and leaf sheaths.
Changes in the level of soluble protein paralleled changes in starch level in the leaf sheaths. Among the enzymes, only synthetase bound to the starch granule paralleled the level of starch in the leaf sheaths and in the culm. ADP-glucose, but not UDP-glucose, was utilized as a glucosyl donor by these starch synthetases. Zymograms of these extracts showed only one α-amylase band, one β-amylase band, two phosphorylase bands, and one Q-enzyme band.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baun L. C., Palmiano E. P., Perez C. M., Juliano B. O. Enzymes of starch metabolism in the developing rice grain. Plant Physiol. 1970 Sep;46(3):429–434. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano B. O., Varner J. E. Enzymic degradiation of starch granules in the cotyledons of germinating peas. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jun;44(6):886–892. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.6.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F., DE FEKETE M. A., CARDINI C. E. Starch and oligosaccharide synthesis from uridine diphosphate glucose. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Akazawa T. The role of adenosine diphosphate glucose in leaf starch formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 May 22;16(1):6–11. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T. Enzymic mechanism of starch breakdown in germinating rice seeds I. An analytical study. Plant Physiol. 1968 Dec;43(12):1899–1905. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.12.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura T., Nakayama N., Murata T., Akazawa T. Biosynthesis of starch in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1967 Mar;42(3):327–332. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal G. G., Greenberg E., Hardie J., Cameron E. C., Preiss J. Regulation of starch biosynthesis in plant leaves: activation and inhibition of ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 1968 Mar;43(3):417–427. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER D. H., TURNER J. F. The hydrolysis of glucose monophosphates by a phosphatase preparation from pea seeds. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:486–491. doi: 10.1042/bj0740486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


