Abstract
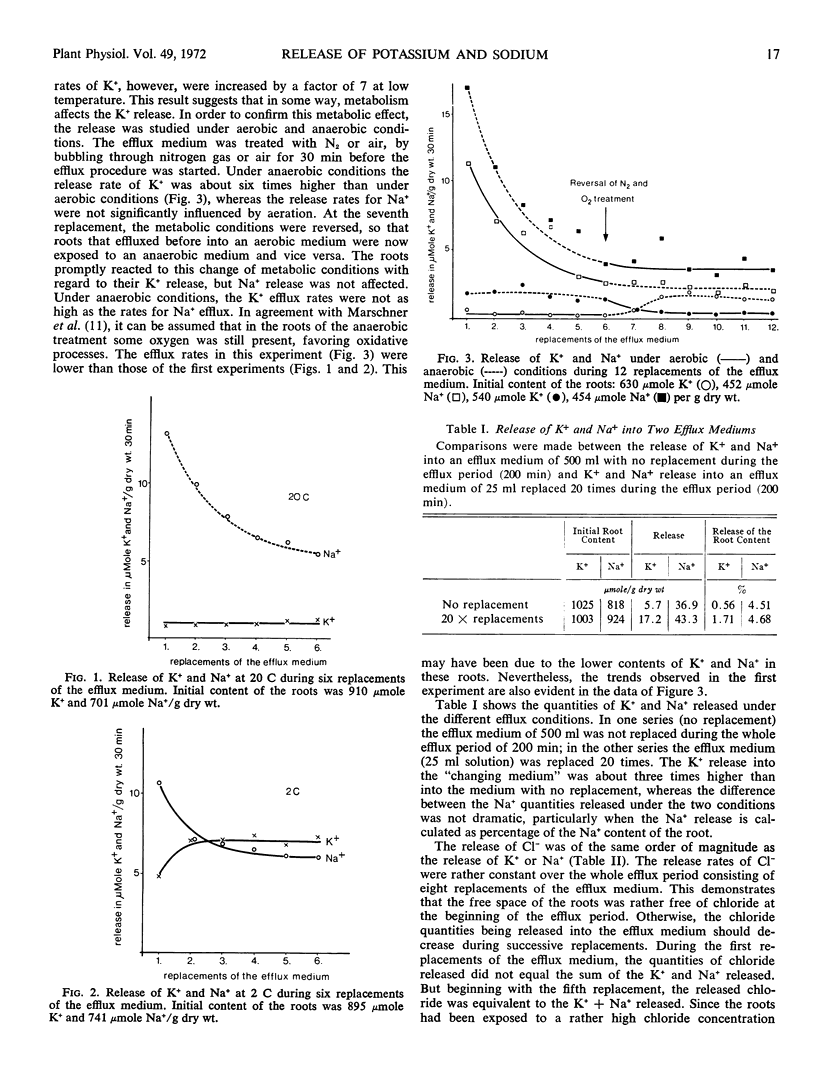
The release of potassium and sodium from excised roots of Zea mays having similar contents of potassium and sodium was studied. At low temperature (2 C) the efflux rates of both cations were very similar, but at higher temperature (20 C) the potassium release was reduced considerably, whereas the sodium release was hardly affected. Also, under anaerobic conditions the potassium efflux rate was nearly as high as the sodium efflux rate, but with normal O2 supply the potassium release was reduced to about one-fifth. Since a changing efflux medium compared with a constant efflux medium had no great influence upon the sodium release but influenced the potassium release very much, it is assumed that the low potassium release under normal metabolic conditions is due to a reabsorption of effluxed potassium from free space. For sodium this reabsorption is of minor significance, as the uptake potential of maize roots for sodium is very poor. It is concluded that the release of potassium and sodium is a diffusion process and that the cell membranes have rather similar diffusivities for these two cations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOUNT R. W., LEVEDAHL B. H. Active sodium and chloride transport in the single celled marine alga Halicystis ovalis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1960 May 25;49:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1960.tb01922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. The essential role of calcium in selective cation transport by plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1961 Jul;36(4):437–444. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton B. Relationship of Cell Transmembrane Electropotential to Potassium and Sodium Accumulation Ratios in Oat and Pea Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1963 Sep;38(5):581–585. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.5.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton B. Steady State Sodium and Rubidium Effluxes in Pisum sativum Roots. Plant Physiol. 1967 May;42(5):685–690. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.5.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiatt A. J., Lowe R. H. Loss of organic acids, amino acids, k, and cl from barley roots treated anaerobically and with metabolic inhibitors. Plant Physiol. 1967 Dec;42(12):1731–1736. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.12.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higinbotham N., Etherton B., Foster R. J. Mineral ion contents and cell transmembrane electropotentials of pea and oat seedling tissue. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jan;42(1):37–46. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe A. G. Enzyme mechanism for the active transport of sodium and potassium ions in animal cells. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):934–936. doi: 10.1038/219934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marschner H., Handley R., Overstreet R. Potassium Loss and Changes in the Fine Structure of Corn Root Tips Induced by H-ion. Plant Physiol. 1966 Dec;41(10):1725–1735. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.10.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., MERRITT C. R., KINSOLVING C. R., ALBRIGHT C. D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G. Adaptation of barley roots to low oxygen supply and its relation to potassium and sodium uptake. Plant Physiol. 1969 Sep;44(9):1233–1240. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.9.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. J. Carrier-mediated Potassium Efflux Across the Cell Membrane of Red Beet. Plant Physiol. 1969 Apr;44(4):485–490. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viets F. G. CALCIUM AND OTHER POLYVALENT CATIONS AS ACCELERATORS OF ION ACCUMULATION BY EXCISED BARLEY ROOTS. Plant Physiol. 1944 Jul;19(3):466–480. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


