Abstract
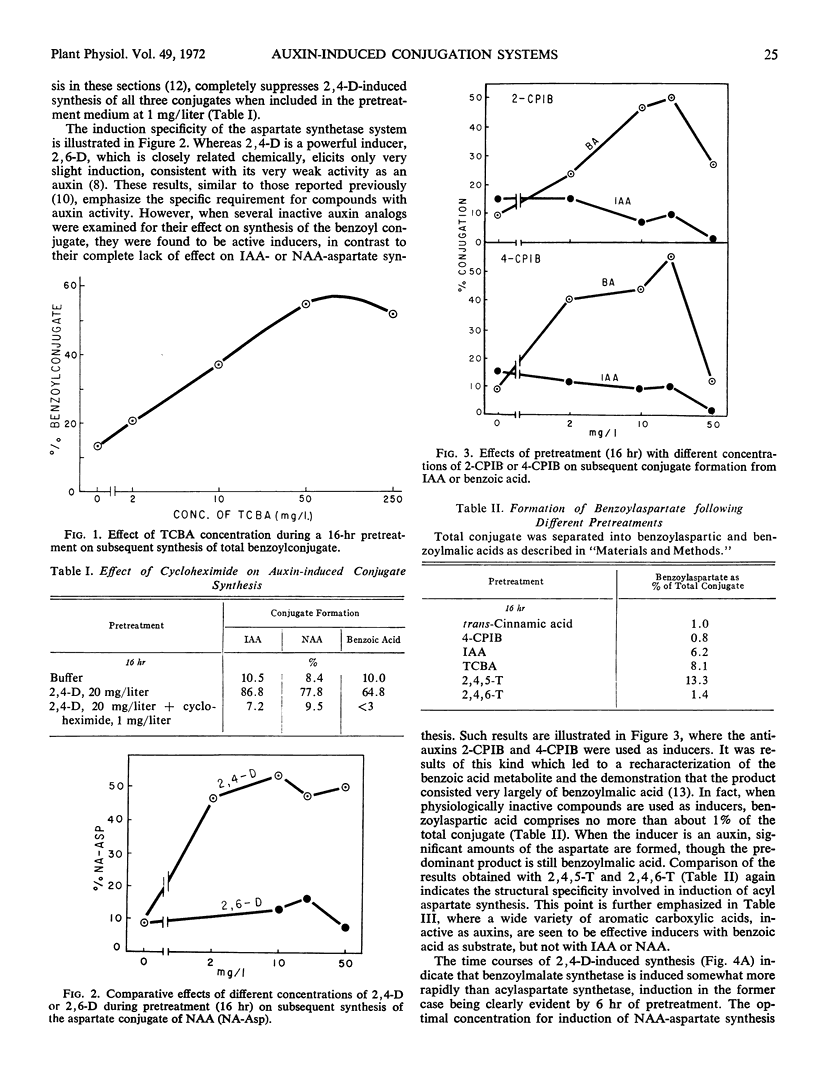
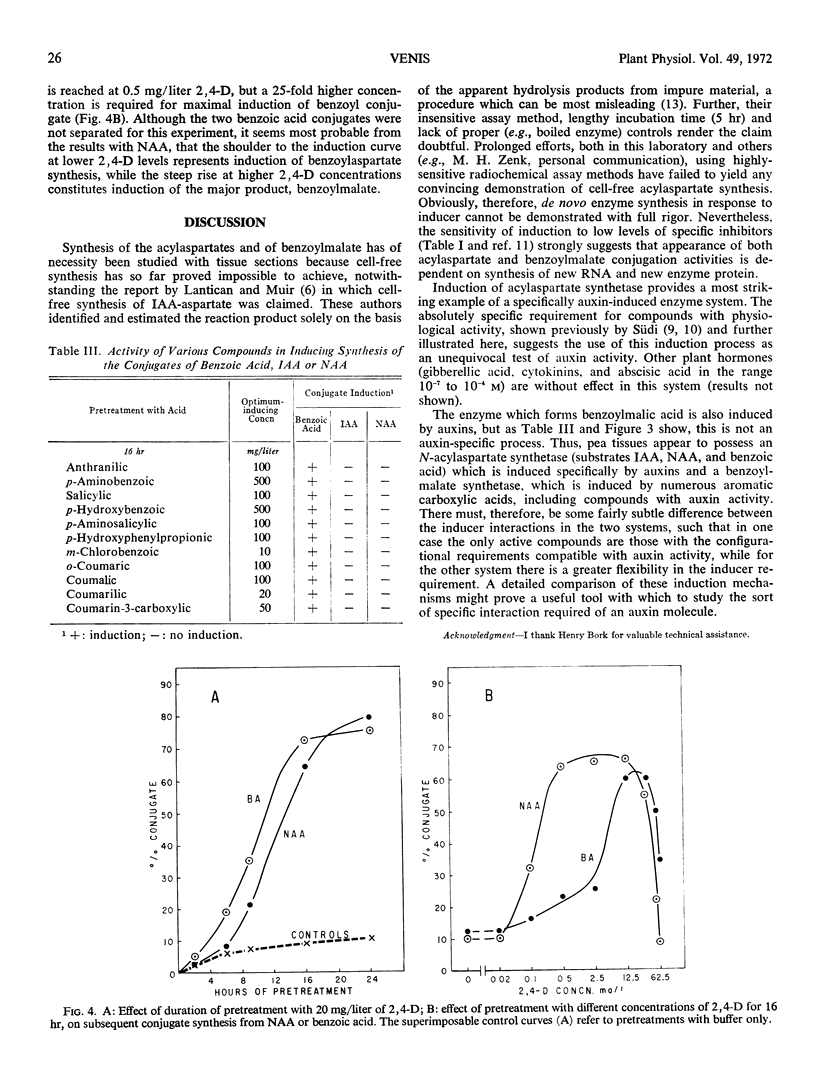
Pretreatment of pea (Pisum sativum var. Alaska) sections with any active auxin induces an enzyme which forms aspartate conjugates of exogenously supplied indoleacetic acid, naphthaleneacetic acid, or benzoic acid. Whereas induction of this system is an absolutely auxin-specific process, another enzyme, which forms benzoylmalic acid, is induced both by auxins and by physiologically inactive aromatic carboxylic acids. Induction of both enzymes is abolished by low levels of RNA and protein synthesis inhibitors. The induction specificities and other characteristics of the two systems are compared.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Datta A., Sen S. P., Datta A. G. The effect of indole-3-acetic acid on the synthesis in vitro of isocitrate lyase (EC 4.1.3.1) in potato tuber. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 6;108(1):147–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filner P., Varner J. E., Wray J. L. Environmental or developmental changes cause many enzyme activities of higher plants to rise or fall. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):358–367. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venis M. A., Stoessl A. Auxin-induced conjugates of benzoic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 7;36(1):54–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90648-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



