Stem cell therapy holds promise as a treatment for muscular dystrophy by providing cells that can both deliver functional muscle proteins and replenish the stem cell pool. This article reviews the current state of research on myogenic stem cells and identifies the important challenges that must be addressed as stem cell therapy is brought to the clinic.
Keywords: Stem cell, Embryonic stem cells, Myogenesis, Muscular dystrophy, Tissue regeneration
Abstract
Muscular dystrophy comprises a group of genetic diseases that cause progressive weakness and degeneration of skeletal muscle resulting from defective proteins critical to muscle structure and function. This leads to premature exhaustion of the muscle stem cell pool that maintains muscle integrity during normal use and exercise. Stem cell therapy holds promise as a treatment for muscular dystrophy by providing cells that can both deliver functional muscle proteins and replenish the stem cell pool. Here, we review the current state of research on myogenic stem cells and identify the important challenges that must be addressed as stem cell therapy is brought to the clinic.
Introduction
Muscle wasting diseases affect millions of people worldwide. Among these, the various types of muscular dystrophy (MD) caused by mutations in structural proteins are characterized by loss of functional muscle due to muscle fiber damage, inflammation, and deposition of fibrotic tissue [1]. With Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in particular, muscle tissue begins to deteriorate early in childhood, pushing the resident muscle stem cell pool to its limit, leading to the exhaustion of normal muscle repair mechanisms [2, 3]. Current treatments are palliative and primarily target the inflammatory response. Cell therapy has the potential to replace damaged tissue by fusion of healthy cells with damaged fibers while replenishing the adult stem cell pool for long-term muscle maintenance. In the 1990s, several moderately successful clinical trials with isolated myoblasts demonstrated the feasibility of cell therapy for DMD while also highlighting the limitations [4–8]. Transplanted myoblasts were able to fuse with host myofibers and deliver normal proteins; however, long-term engraftment was limited because of low cell survival, the inability of myoblasts to migrate throughout the damaged tissue, and failure to restore the stem cell pool.
In this review, we describe the aspects of embryonic and postnatal myogenesis that have informed recent work with myogenic stem cells, the identification and evaluation of various stem-like cells shown to have myogenic properties in vitro and in vivo, current work being done to drive pluripotent stem cells toward muscle progenitors for therapeutic purposes, and advances in biomaterials research and tissue engineering that leverage new information about the role of the tissue environment in controlling myogenic cell fate.
Primary Myogenesis During Embryonic Development
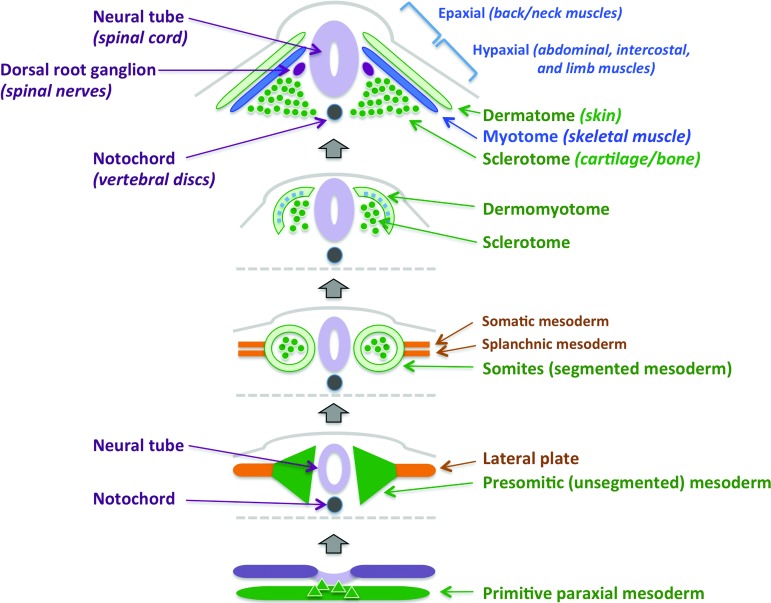
Investigations with muscle stem cells have proceeded from an understanding of embryonic myogenesis developed over the past two decades (Fig. 1). In vertebrates, skeletal muscle development begins in the embryo with the formation of presomitic mesoderm from primitive paraxial mesoderm flanking the notochord [9]. At embryonic day 8, somitogenesis occurs in an anterior-posterior sequence as signals from the surrounding tissues further organize the somites in a dorsal-ventral direction. The origins of skeletal muscles corresponding to various parts of the body are diverse. The facial muscles are derived from unsegmented paraxial head and prechordial mesoderm [10, 11], whereas the dermomyotome formed at the dorsal part of the somite contributes to skin and skeletal muscle formation of the body and limbs [9]. The ventral part of the somites gives rise to the sclerotome, the foundation for cartilage and bone tissue [12]. Delamination of cells from the hypaxial myotome results in a sheet that gives rise to precursor cells forming the intercostal and ventral body wall musculature [13–15]. Muscle precursors similarly have distinct origins, including the ventrolateral (hypaxial) region of the epithelial dermomyotome (trunk and limb muscles), rostral somites (tongue, tracheal, pharyngeal muscles), unsegmented head paraxial mesoderm (mastication, facial expression, eye movement), and lateral splanchnic mesoderm (lower jaw and head) [16–20].
Figure 1.
Embryonic myogenesis in vertebrates. Bottom to top: Paraxial mesoderm is generated during gastrulation and forms symmetrical bodies of presomitic mesoderm surrounding the neural tube prior to segmentation. Soon after segmentation, dermomyotome and sclerotome emerge, followed by differentiation of the myotome between them. The sclerotome ultimately gives rise to cartilage and bone, whereas the dermatome forms the structures of the skin. The myotome further specifies into epaxial myotome, which will form the muscles of the back and neck, adjacent to the dorsal root ganglia, and the hypaxial myotome, which will give rise to the muscles of the ventral body wall, the intercostal muscles, and the limb muscles.
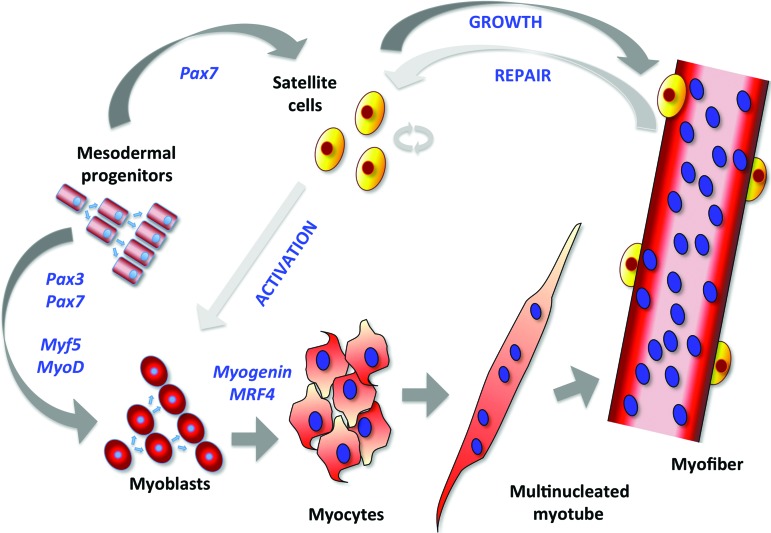
The molecular development of skeletal muscle involves a diverse set of transcriptional networks (Fig. 2). At the center of the dermomyotome, a proliferating cell population arises to form the myotome that expresses the paired-box transcription factors Pax3 and Pax7. This forms an uncommitted reservoir of cells that support muscle growth during embryogenesis. Pax3+ cells that coexpress the basic helix-loop-helix muscle regulatory factors Myf5 and MyoD arise from the borders of the dermomyotome and coordinate myogenesis [21, 22]. Pax3 is typically expressed first and initiates expression of Pax7, a marker of adult muscle stem cells, or satellite cells. The Pax proteins are upstream regulators of Myf5, MyoD, and muscle-specific regulatory factor 4 (MRF4), which act as determination genes directing progenitor cells into the myogenic program. Progenitor cells that express MyoD and/or Myf5 are considered myoblasts, which differentiate with expression of myogenin into postmitotic myocytes that fuse to form multinucleated myotubes.
Figure 2.
Transcriptional regulation of skeletal muscle cell differentiation. Mesodermal progenitor cells expressing Pax3 and Pax7 proliferate and differentiate into proliferating myoblasts, which express the myogenic transcription factors Myf5 and MyoD. With the expression of myogenin and MRF4, myoblasts further differentiate into myocytes, which cease proliferation and fuse to form multinucleated myotubes. Myotubes undergo further maturation and innervation as they bundle together in myofibers, where Pax7-expressing satellite cells, also derived from mesodermal progenitors, localize beneath the basal lamina and remain quiescent until activated in adult muscle to differentiate into proliferating myoblasts. In adult muscle, activated satellite cells undergo asymmetrical division to both repopulate the quiescent satellite cell pool and give rise to proliferating myoblasts.
Defects in Pax gene expression have profound effects on skeletal muscle formation. Pax3 is essential for migration of muscle progenitor cells, whereas Pax7 directs myogenic specification [23–25]. Pax3 mutant mice are characterized by the loss of hypaxial dermomyotome. The ensuing lack of myogenic progenitor cells results in the absence of limb musculature [26]. Pax7 mutant mice show a reduction in the number of satellite cells, but fiber size and quantity is normal in adult mice [27]. However, secondary myogenesis in response to injury, as discussed below, is compromised. This suggests a specific role for Pax7 in satellite cell self-renewal and maintenance of the muscle stem cell pool.
The roles of Myf5 and MyoD have also been studied in vivo. Although mice lacking either Myf5 or MyoD alone are capable of primary myogenesis, Myf5−/MyoD− mice demonstrate a complete lack of skeletal muscle [21, 28, 29]. Myogenin knockout mice contain myoblasts, but muscle fiber formation is affected, indicating that myogenin is critical for myotube formation and myofiber maturation [30, 31].
Secondary Myogenesis: The Response to Muscle Injury
Satellite Cells
During embryogenesis, the dermomyotome is a transient structure and therefore produces a limited number of muscle progenitor cells. Prior to birth, some of these precursors migrate into position between the sarcolemma (plasma membrane) and basement membrane of the muscle fiber [32]. These resident satellite cells constitute the stem cell pool in adult muscle tissue and are characterized by Pax7 expression (Fig. 2) [22, 33]. Satellite cells remain quiescent until regular maintenance, muscle injury, or disease triggers their activation and subsequent proliferation. Upon activation, these cells express Myf5 and MyoD, which initiate differentiation into fusible myoblasts. Myogenin controls terminal differentiation by orchestrating fusion of postmitotic, mononucleated myocytes into myotubes or fusion of myoblasts with existing myofibers (Fig. 2) [21, 28, 34–41].
Heterogeneity has been observed within the satellite cell population based on age and body location [42]. After birth, satellite cells proliferate to support growth and repair in response to environmental signals. As such, the satellite cell niche plays an essential role in maintaining muscle homeostasis. However, in aged muscle the niche diminishes in its capacity to activate satellite cells, affecting their function and proliferative capacity. In addition to age-dependent differences, the function and anatomic localization of satellite cells vary according to the embryonic origins of the adult muscle; this includes variation in vascularization, innervation, fiber composition, and gene expression. Satellite cells also vary in their degree of myogenic commitment. Recently, Rocheteau et al. identified subpopulations of proliferating satellite cells with high Pax7 expression levels (Pax7high) exhibiting lower metabolic activity that appear less mature with respect to myogenic commitment compared with satellite cells with low levels of Pax7 expression (Pax7low) [43]. This diversity is based on template DNA strand segregation, where Pax7low cells inheriting the daughter DNA strand upregulate differentiation genes and Pax7high cells inheriting the parental DNA strand become dormant with respect to differentiation [43].
Asymmetric Cell Division During Secondary Myogenesis
With satellite cell activation and expansion, asymmetric division occurs where both satellite cells and differentiating myoblasts are formed. This maintains the population of resident satellite cells while repairing damaged muscle and is determined by cell polarity with respect to the tissue niche [44, 45]. During asymmetric division, the mitotic spindle is oriented perpendicularly with respect to the muscle fiber axis. Two different cell types are formed: a Pax7high cell apposing the basal lamina that will become a satellite cell capable of self-renewal, and a Pax7+/Myf5+ cell with apical orientation toward the surface of the host fiber that will continue to differentiate along the myogenic lineage. Activated satellite cells where the mitotic spindle remains parallel to the muscle fiber axis give rise to two Pax7+/Myf5+ cells through symmetric division [44].
During embryonic and early fetal development, symmetric division plays a dominant role in populating the stem cell pool. During wound repair, symmetric cell division is critical to the restoration of damaged tissues [46]. Under steady-state conditions, however, satellite cells divide asymmetrically, in order to maintain the resident stem cell pool [44].
Genetic Muscle Disease: Muscular Dystrophies
MD refers to a group of destructive inherited muscle-wasting diseases that lead to skeletal muscle weakening and degeneration caused by defective proteins essential to muscle integrity [1]. The absence of these critical proteins leads to loss of tissue, hampering normal muscle activity and, more critically, causing premature exhaustion of the reservoir of muscle stem cells that contribute to muscle maintenance and integrity during daily activity and exercise [2, 3]. MD occurs in several different forms. Duchenne MD and Becker MD are caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene [47], although Becker MD appears later in childhood or adolescence and demonstrates much slower progression. Emery-Dreifus MD, which is caused by mutations in genes encoding emerin, lamin A and C, nesprin, and “four and a half LIM domains protein 1, ” affects similar types of muscle, but it usually manifests later in life with more variability in phenotype; inheritance patterns depend on the affected gene [48, 49]. Limb-girdle MD manifests as weakness and atrophy of the muscles of the hips and shoulders and results from pleiotropic molecular defects in a number of genes encoding muscle structural proteins, including myotilin, lamin, calpain, dysferlin, and titin [50].
DMD is the most severe and prevalent form of dystrophy affecting the body's striated muscle tissue. Therefore, DMD has been the most broadly studied form of muscle disease and is the focus of this review. DMD is an X-linked recessive disease that occurs worldwide, affecting approximately one in 3,500 male births of all races [1]. One-third of DMD cases are caused by a new mutation [1, 47, 51]. The disease onset is early, with observable difficulty with walking as early as 2 years of age in some patients. Muscle failure begins in the lower extremities and progresses to the upper extremities, where multiple rounds of regeneration result in fibrosis and fixation of muscles. Eventually, distal muscle disease leads to asymmetric spinal deformities and respiratory insufficiency. By adolescence, DMD patients are confined to wheelchairs, and death occurs by the fourth decade because of respiratory failure and/or dilated cardiomyopathy.
DMD is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene [52], which encodes a cytoskeletal protein found in skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac myofibers, and brain [53]. Dystrophin deficiency primarily leads to the pathologic perturbation of myofibers; however, the disease also is associated with absence of several glycoproteins that interact with dystrophin. Although the precise sequence of the events is incompletely understood, the mechanical weakness leading to sarcolemmal lesions causes abnormal calcium influx and inflammation, which in turn alter the composition of structural glycoproteins in the extracellular matrix (ECM). This disruption of the ECM causes resident muscle stem cells to undergo fibrogenesis, rather than myogenesis, leading to abnormal collagen deposition and subsequent necrosis; multiple cycles of fibrosis and necrosis result in exhaustion of the stem cell pool [54, 55].
Progressive telomere shortening also has been associated with exhaustion of the muscle stem cell pool. Shorter telomeres have been reported in muscle cells from DMD patients compared with those of healthy individuals [56, 57]. Interestingly, human telomeres are shorter then mouse telomeres, which may explain why the X-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) mouse model of DMD exhibits a less severe degenerative phenotype compared with the human disease. To test this, Sacco et al. engineered the mdx/mTR mouse strain, which lacks the RNA component of telomerase as well as dystrophin, and showed that muscle wasting and a decline in muscle stem cells parallels human DMD when telomerase function is disturbed in the mouse [57].
Human Clinical Trials
In the 1990s, promising results of preclinical studies in mdx mice led to human clinical trials of stem cell therapy for DMD at six institutions in the United States, Canada, and Italy [4–7, 58] (Table 1). Huard et al. demonstrated the feasibility of cell transplantation by injecting myoblasts isolated from 11 normal, unrelated donors into the tibialis anterior muscle of 4 human leukocyte antigen (HLA) I- and HLA II-DR-matched recipients with DMD [7]. Variable numbers of dystrophin-positive myofibers were detected in three recipients, with an immune reaction in only one patient. Gussoni et al. demonstrated the molecular efficacy of myoblast transplant by injecting HLA I/II-matched donor myoblasts from family members into eight DMD recipients [6]. Three recipients had evidence of engraftment after 1 month, as determined by polymerase chain reaction analysis of normal dystrophin in muscle biopsies. The subsequent use of fluorescent in situ hybridization improved the sensitivity of donor nuclei detection in transplant recipients. A later study showed that donor nuclei could be detected in almost all recipients and that these were fused to recipient myofibers [59]. However, very low cell retention rates were seen, and not all donor cells produced dystrophin.
Table 1.
Intramuscular myoblast transplant studies in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients
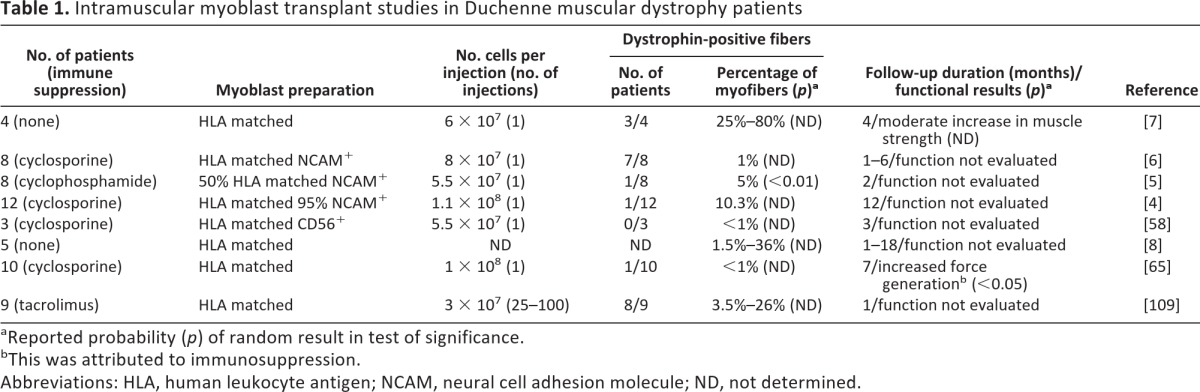
aReported probability (p) of random result in test of significance.
bThis was attributed to immunosuppression.
Abbreviations: HLA, human leukocyte antigen; NCAM, neural cell adhesion molecule; ND, not determined.
Although these early clinical studies varied with respect to transplanted cell numbers, diversity of patient populations, and evaluation of tissue response and muscle function, the combined clinical outcomes were encouraging: they showed that donor myoblasts could deliver normal muscle protein to dystrophic myofibers. However, they also uncovered the limitations of cell therapy at the time [4, 7, 8, 59–65]. These included the inability of transplanted myoblasts to self-renew and repopulate the stem cell pool, poor myoblast survival, and the lack of myoblast migration within the musculature, which limits their usefulness for systemic MD therapy. To address these, the focus of the research community turned toward the derivation of muscle stem cell candidates that might overcome these obstacles.
Therapeutic Potential of Resident Myogenic Cells
The limitations encountered with myoblast transplantation have led many groups to pursue the identification of other populations of stem-like cells with myogenic properties for potential therapeutic application (Table 2). These various progenitor cells differ in anatomical location, self-renewal, and differentiation potential, as well as cell surface marker expression [66]. Whether these are derived from muscle resident satellite cells or other remnants of primary myogenesis is unclear. Some progenitor cells are associated with the circulatory system, suggesting that they may have the advantage of easy access to the vascular network throughout the muscle tissue, whereas others are in closer contact with myofibers. The phenotypes of these various resident stem cells have suggested specific modes of delivery to which they might be best suited.
Table 2.
Cell transplant studies with resident myogenic cells
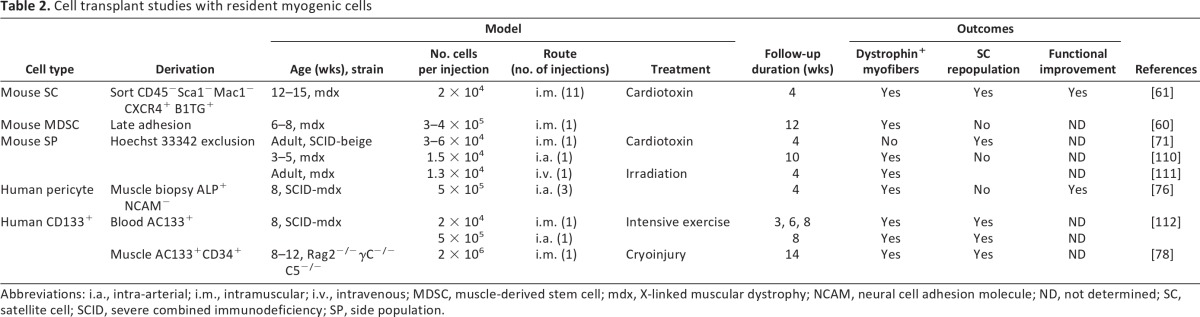
Abbreviations: i.a., intra-arterial; i.m., intramuscular; i.v., intravenous; MDSC, muscle-derived stem cell; mdx, X-linked muscular dystrophy; NCAM, neural cell adhesion molecule; ND, not determined; SC, satellite cell; SCID, severe combined immunodeficiency; SP, side population.
Cells Amenable to Intramuscular Delivery
A population of resident cells known as muscle-derived stem cells (MDSCs) can be distinguished from satellite cells by their broad multilineage differentiation potential. In addition to their myogenic potential, they are capable of differentiating into osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic, hematopoietic, cardiac, endothelial, smooth muscle, and neural lineages, both in vitro and in vivo [67–69]. MDSCs have higher survival rates than satellite cells and myoblasts in transplant studies, likely because of their resistance to oxidative stress and in vivo proliferation capacity. MDSCs also release high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, which promotes vascularization and thus facilitates tissue restoration in vivo [70].
Side population (SP) cells, which reside in skeletal muscle as well as in bone marrow, are characterized by their ability to exclude Hoechst 33342 [71]. The ATP-binding cassette G subfamily transporter responsible for dye efflux is not characteristic of standard satellite cells but is present in up to 3% of resident muscle stem cells [72]. Furthermore, SP cells are found in Pax7 knockout mice that lack satellite cells, providing evidence that SP cells are distinct from the satellite cell population [25]. SP cells localize outside the muscle fiber and have the capacity to regenerate tissue and to engraft in skeletal muscle [71, 73].
A subset of satellite cells in adult muscle that coexpress markers associated with the vascular system have been identified as myoendothelial cells [66, 74]. These are capable of long-term expansion in vitro and appear to support muscle regeneration at rates superior to myoblasts [75]. Myoendothelial cells represent ∼0.4% of resident muscle stem cells and, on the basis of cell surface marker expression, share myogenic as well as endothelial features [66]. The myoendothelial cell population (CD56+, CD34+, CD144+) can be purified from myogenic (CD56+, CD34−, CD144+) and endothelial (CD56−, CD34+, CD144+) cell populations on the basis of surface marker expression [66].
Cells Amenable to Systemic Delivery
Other blood vessel-associated cells called pericytes, located beneath the basal lamina of small vessels [74, 76], lack endothelial markers but express NG2 proteoglycan, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)-β, and CD146. They can be derived by outgrowth from tissue explants and purified by sorting for alkaline phosphatase expression in the absence of CD56 expression. Although pericytes lack expression of myogenic markers (Pax7, Myf5, MyoD), they differentiate into multinucleated myotubes when exposed to myogenic differentiation medium. Pericytes injected intra-arterially into immunodeficient mdx mice after in vitro expansion have led to formation of large numbers of new dystrophin-expressing muscle fibers [76].
A circulating subpopulation of CD133+ muscle progenitor cells also has been found in human peripheral blood that expresses a variety of adhesion molecules, including CD34, very late antigen-4 (VLA-4), and l-selectin. These cells also express muscle-specific transcription factors such as Pax7, Myf5, MyoD, and myogenin [24, 77, 78]. Coculture with C2C12 mouse myoblasts prior to intramuscular or intra-arterial injection resulted in cellular muscle regeneration and satellite cell replenishment in mdx mice [77]. Specific homing of CD133+ cells to muscle tissue was seen in these experiments, presumably directed by expression of l-selectin and VLA-4 on their surface, both of which serve as chemoattractant receptors expressed in response to exercise-induced muscle inflammation and damage [78].
Directed Differentiation of Pluripotent Stem Cells
Studies in animals and humans have demonstrated both the feasibility and the potential effectiveness of cell therapy for MD [4, 7, 8, 59–65]. However, few available stem cell sources are capable of ex vivo expansion to provide cell numbers sufficient to treat a systemic disease. In fact, only one therapeutic trial for MD listed on ClinicalTrials.gov uses cell replacement as an approach to treating myopathic disease: a trial to treat dysphagia in patients with oculopharyngeal MD by transplanting autologous myoblasts isolated from unaffected limb muscles into pharyngeal muscle [79]. This emphasizes the need for continuing the search for an expandable source of cultured cells with myogenic properties in order to approach MDs affecting larger muscle groups, such as DMD.
Pluripotent stem cells provide an alternative therapeutic agent to treat MD that affects large muscle groups because of their capacity for migration and self-renewal. Pluripotent stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from somatic cells, differentiate into tissue precursors arising from all three embryonic germ layers. As such, they have the potential to both repair existing damaged muscle and regenerate healthy muscle from a pool of muscle stem cells.
Several groups have reported the derivation of myogenic progenitor cells from human ESCs (hESCs) (Table 3). Zheng et al. showed that exposure of hESC-derived embryoid bodies to serum in the presence of epithelial growth factor directed their differentiation toward myogenic precursors [80]. The differentiated cells were characterized by cMet, Pax7, and MyoD expression but lacked other muscle proteins, such as neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), Myf5, and desmin. Subsequent exposure to the DNA demethylating agent 5-azacytidine further directed the cells toward a myogenic fate, with diminished expression of the satellite cell marker cMet and increased MyoD expression. Although terminal differentiation and fusion into myotubes was not observed in vitro, hESC-derived cells transplanted into injured tibialis anterior muscle underwent terminal differentiation to form new muscle and localized into the satellite cell compartment as well.
Table 3.
Evaluation of pluripotent stem cell derivatives
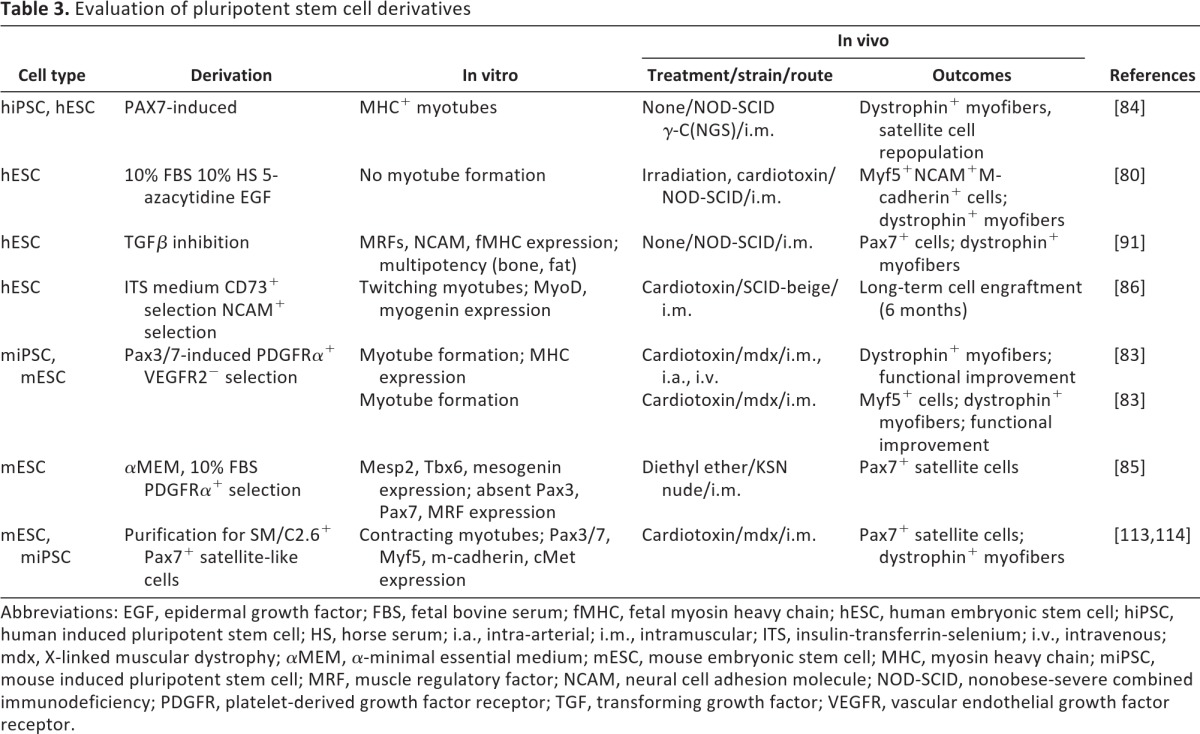
Abbreviations: EGF, epidermal growth factor; FBS, fetal bovine serum; fMHC, fetal myosin heavy chain; hESC, human embryonic stem cell; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cell; HS, horse serum; i.a., intra-arterial; i.m., intramuscular; ITS, insulin-transferrin-selenium; i.v., intravenous; mdx, X-linked muscular dystrophy; αMEM, α-minimal essential medium; mESC, mouse embryonic stem cell; MHC, myosin heavy chain; miPSC, mouse induced pluripotent stem cell; MRF, muscle regulatory factor; NCAM, neural cell adhesion molecule; NOD-SCID, nonobese-severe combined immunodeficiency; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; TGF, transforming growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
Darabi et al. used inducible Pax7- and Pax3-overexpressing mouse ESC (mESC) lines to direct myogenic commitment [81]. Myogenic progenitor cells produced by Pax7 or Pax3 overexpression were identified on the basis of Myf5, MyoD, and myosin heavy chain expression. Pax3-overexpressing mESCs were then sorted for expression of the mesodermal marker PDGFRα and depletion of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), which is downregulated in paraxial mesoderm. The therapeutic potential of these mESC-derived PDGFRα+VEGFR2− cells was shown by intramuscular injection or systemic intravascular delivery in mdx mice, which resulted in engraftment with dystrophin-expressing myofibers and improved muscle function. Similar results were obtained in mice with a more severe form of facioscapulohumeral MD [82]. Although these experiments confirmed the regenerative potential of mESC-derived muscle progenitors, tissue maintenance by resident stem cells is critical for long-term treatment of dystrophic muscle. To address this, these investigators evaluated whether mESC-derived myogenic cells could repopulate the satellite cell compartment. In transplanted animals, single fiber staining showed colocalization of the satellite cell marker M-cadherin with green fluorescent protein expressed by the mESC-derived cells in cells localized beneath the basal lamina of recipient myofibers. Serial transplantation of reisolated mESC-derived cells confirmed subsequent engraftment, as well as satellite cell compartmentalization [83]. Next, they derived Pax7-induced satellite cells from hESCs and human iPSCs using a doxycycline-inducible lentiviral vector encoding Pax7 [84]. EB differentiation over 7 days and monolayer outgrowth allowed them to purify highly engraftable cells for injection into dystrophic muscle. Functional improvement, as well as dystrophin restoration, validated this stem cell population. Engraftment of ESC-derived muscle progenitors was confirmed by detection of Pax7 and human laminin in cells localized to the satellite cell compartment.
Another approach taken to direct the differentiation of mESCs toward paraxial mesoderm has been the selection of PDGFRα+VEGFR2− cell populations from cultured mESC monolayers [85]. Sakurai et al. found that VEGFR2 expression was excluded from paraxial mesoderm, whereas PDGFRα+VEGFR2+ cells were committed to lateral mesoderm [85]. Although PDGFRα+VEGFR2− cells did not express Pax3, Pax7, Myf5, or MyoD, transplantation into damaged muscle tissue resulted in engraftment, localization adjacent to myofibers, and subsequent expression of the satellite cell-associated markers Pax7 and CD34.
Barberi et al. enriched for a myogenic progenitor cell fraction from hESC-derived mesenchymal precursors [86]. To induce mesenchymal lineage differentiation, single hESCs were plated at low density on mouse embryonic feeder cells in serum-rich medium containing insulin, transferrin, and selenium. Following enrichment for CD73 expression, mesenchymal cells were sorted for myogenic affiliation on the basis of NCAM expression. NCAM is involved in neuromuscular development and has been widely used to identify myoblasts [87–90]. Transplantation of the CD73+NCAM+ cells to hind limb muscle of immunodeficient mice resulted in long-term survival and myofiber commitment.
Other groups have taken advantage of known molecular cues to guide the differentiation of myogenic cells from hESCs. Activation of the transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ)/activin/nodal pathway through activin A and serum enhances endodermal specification of hESCs [91]. In the early stages of hESC differentiation, inhibition of TGFβ signaling with the small molecule SMAD2/3 inhibitor SB431542 directs mesoendodermal induction and blocks neuroectodermal differentiation. Mahmood et al. blocked the TGFβ pathway with SB431542 to obtain hESC-derived mesenchymal progenitors [92]. Embryoid body outgrowths subsequently cultured on fibronectin-coated plates in the presence of lower concentrations of SB431542 differentiated into myotubes. Cell transplantation into immunodeficient mice showed muscle differentiation; however, the transplanted cells did not fuse to the host muscle tissue.
Preliminary experiments have been performed with several pluripotent stem cell-derived myogenic cells, and these have shown their ability to form muscle in vivo, but the next steps are clear. Long-term integration into adult muscle and functional improvement need to be evaluated. Repopulation of the depleted muscle stem cell compartment needs to be demonstrated. Methods to mitigate the host immune response to donor cells need to be refined. Large-scale production of these cells using good manufacturing practice needs to be demonstrated.
The Use of Synthetic Biomaterials
The satellite cell niche is a unique microenvironment that supports communication between the plasma membrane of the cell and the adjacent basal lamina of the muscle fiber. The niche contains an ECM consisting of laminin, type IV collagen, fibronectin, heparan sulfate, and other proteoglycans [93, 94]. The muscle cells initially secrete the ECM, with subsequent binding of cell surface integrins to the assembled network of niche proteins. The ECM also binds growth factors (basic fibroblast growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor, insulin-like growth factor 1, epidermal growth factor) and ligands (e.g., Wnts) through covalently attached heparin sulfates present in the matrix. These growth factors are known to play an important role in controlling muscle stem cell fate [95, 96].
In diseased tissue, overexpression of ECM components may occur in response to inflammation, altering the rigidity of the microenvironment. This has been seen in muscular dystrophies, as well as arthritis, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, and fibrotic diseases of the heart, liver, kidney, and lung [97]. Such changes in the tissue environment can have a negative impact on stem cell engraftment and differentiation, as has been shown specifically in cardiac muscle [98].
Matrix structure and organization influence focal-adhesion and interactions between the ECM with the intracellular cytoskeleton through integrin signaling. These interactions are affected by the structural rigidity, or stiffness, of the tissue. In fact, recent work has shown that ECM stiffness plays a major role in directing cell differentiation [99–101]. Synthetic ECM that mimics the elasticity of muscle tissue (∼12 kPa) can maintain satellite cell self-renewal in vitro; this has been accomplished with inert polyacrylamide gels in which the concentration of bis-acrylamide cross-linker sets the elasticity [102]. Tissue rigidity also has been shown to drive myogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells; muscle proteins are expressed when mesenchymal stem cells are cultured on substrate with stiffness of 11 kPa, mimicking the in vivo muscle environment [100]. Engler et al. demonstrated that more elastic matrices (0.1–1 kPa) commit the cells to a neurogenic lineage, whereas a more rigid environment (25–40 kPa) promotes osteogenic differentiation [100].
Transplantation of stem cells alone may not be practical for traumatic injury that requires regeneration of larger tissue volumes. For these situations, tissue engineering efforts have focused on generating large tissue grafts to be transplanted into the injured tissue. This has been advanced by hydrogel technology using synthetic polymers that contain biological factors to support cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation [103]. Porous, biodegradable scaffolds have been shown to support myogenic cell alignment and subsequent myotube formation together with the formation of a vascular network formed by endothelial cells [104]. These could potentially support a satellite cell niche as well, by creating a three-dimensional matrix with specific stiffness and cell adhesion properties. Synthetic ECM containing type 1 collagen has been shown to support myogenic and osteogenic differentiation [105, 106], whereas Matrigel (BD Biosciences, San Diego, CA, http://www.bdbiosciences.com), a protein mixture secreted by mouse sarcoma cells resembling the complex extracellular milieu found in some tissues, promotes robust myogenic differentiation [107, 108].
Conclusion
Although palliative therapies have been used to treat patients with MD, no curative treatment currently exists for these patients. Many criteria must be met to achieve restorative therapy with stem cells. Depending on the nature of the specific MD phenotype, its age of onset, course of degeneration, and distribution of affected muscles, muscle progenitors stratified by specific stage of development may be needed. Clearly, one cellular reagent may not suffice for all diseases. Several general goals have been identified, however, in developing stem cell therapy for skeletal muscle disease. Efficient fusion of donor cells to existing myofibers will be necessary to deliver normal muscle proteins into affected fibers and to contribute healthy muscle mass by new fiber formation. Large quantities of potent myogenic cells will have to be delivered to affected muscles, either through large-scale culture in vitro or in vivo expansion and dissemination. Normal myogenic cells will have to repopulate the stem cell reservoir residing in the muscle fiber and self-renew to achieve long-term muscle homeostasis. Immune rejection will need to be addressed, through either immunosuppression or patient-specific cell reagents, to sustain long-term survival of donor cells. In addition, secondary organ failure, such as MD-associated cardiomyopathy, will need to be addressed, since the requirements for other organs may not be met by skeletal muscle stem cells. Although these aims may seem daunting, the process of basic discovery informing clinical translation, as well as clinical studies in animals and humans guiding subsequent experiments at the bench, has already led to significant progress.
Acknowledgments
The authors apologize to colleagues whose work could not be cited because of space limitations. H.S.B. is supported by grants from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine and the Muscular Dystrophy Association.
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Author Contributions
K.J.W.: conception and design, manuscript writing; V.B.L.: manuscript writing; H.S.B.: conception and design, financial support, manuscript writing, final approval of manuscript.
References
- 1.Emery AE. The muscular dystrophies. Lancet. 2002;359:687–695. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07815-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Matsumura K, Campbell KP. Dystrophin-glycoprotein complex: Its role in the molecular pathogenesis of muscular dystrophies. Muscle Nerve. 1994;17:2–15. doi: 10.1002/mus.880170103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Decary S, Hamida CB, Mouly V, et al. Shorter telomeres in dystrophic muscle consistent with extensive regeneration in young children. Neuromuscul Disord. 2000;10:113–120. doi: 10.1016/s0960-8966(99)00093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mendell JR, Kissel JT, Amato AA, et al. Myoblast transfer in the treatment of Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:832–838. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199509283331303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Karpati G, Ajdukovic D, Arnold D, et al. Myoblast transfer in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 1993;34:8–17. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gussoni E, Pavlath GK, Lanctot AM, et al. Normal dystrophin transcripts detected in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients after myoblast transplantation. Nature. 1992;356:435–438. doi: 10.1038/356435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Huard J, Bouchard JP, Roy R, et al. Human myoblast transplantation: Preliminary results of 4 cases. Muscle Nerve. 1992;15:550–560. doi: 10.1002/mus.880150504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tremblay JP, Malouin F, Roy R, et al. Results of a triple blind clinical study of myoblast transplantations without immunosuppressive treatment in young boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cell Transplant. 1993;2:99–112. doi: 10.1177/096368979300200203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Buckingham M. Skeletal muscle formation in vertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001;11:440–448. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(00)00215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Christ B, Ordahl CP. Early stages of chick somite development. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1995;191:381–396. doi: 10.1007/BF00304424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Noden DM, Marcucio R, Borycki AG, et al. Differentiation of avian craniofacial muscles: I. Patterns of early regulatory gene expression and myosin heavy chain synthesis. Dev Dyn. 1999;216:96–112. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199910)216:2<96::AID-DVDY2>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Buckingham M, Bajard L, Chang T, et al. The formation of skeletal muscle: From somite to limb. J Anat. 2003;202:59–68. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cinnamon Y, Kahane N, Kalcheim C. Characterization of the early development of specific hypaxial muscles from the ventrolateral myotome. Development. 1999;126:4305–4315. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.19.4305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kalcheim C, Cinnamon Y, Kahane N. Myotome formation: A multistage process. Cell Tissue Res. 1999;296:161–173. doi: 10.1007/s004410051277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Denetclaw WF, Ordahl CP. The growth of the dermomyotome and formation of early myotome lineages in thoracolumbar somites of chicken embryos. Development. 2000;127:893–905. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.4.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Parker MH, Seale P, Rudnicki MA. Looking back to the embryo: Defining transcriptional networks in adult myogenesis. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:497–507. doi: 10.1038/nrg1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nathan E, Monovich A, Tirosh-Finkel L, et al. The contribution of Islet1-expressing splanchnic mesoderm cells to distinct branchiomeric muscles reveals significant heterogeneity in head muscle development. Development. 2008;135:647–657. doi: 10.1242/dev.007989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Harel I, Nathan E, Tirosh-Finkel L, et al. Distinct origins and genetic programs of head muscle satellite cells. Dev Cell. 2009;16:822–832. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tajbakhsh S, Rocancourt D, Cossu G, et al. Redefining the genetic hierarchies controlling skeletal myogenesis: Pax-3 and Myf-5 act upstream of MyoD. Cell. 1997;89:127–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80189-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sambasivan R, Gayraud-Morel B, Dumas G, et al. Distinct regulatory cascades govern extraocular and pharyngeal arch muscle progenitor cell fates. Dev Cell. 2009;16:810–821. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Relaix F, Rocancourt D, Mansouri A, et al. A Pax3/Pax7-dependent population of skeletal muscle progenitor cells. Nature. 2005;435:948–953. doi: 10.1038/nature03594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kassar-Duchossoy L, Giacone E, Gayraud-Morel B, et al. Pax3/Pax7 mark a novel population of primitive myogenic cells during development. Genes Dev. 2005;19:1426–1431. doi: 10.1101/gad.345505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Patruno M, Caliaro F, Martinello T, et al. Expression of the paired box domain Pax7 protein in myogenic cells isolated from the porcine semitendinosus muscle after birth. Tissue Cell. 2008;40:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2007.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Péault B, Rudnicki M, Torrente Y, et al. Stem and progenitor cells in skeletal muscle development, maintenance, and therapy. Mol Ther. 2007;15:867–877. doi: 10.1038/mt.sj.6300145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Seale P, Sabourin LA, Girgis-Gabardo A, et al. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell. 2000;102:777–786. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tajbakhsh S, Buckingham M. The birth of muscle progenitor cells in the mouse: Spatiotemporal considerations. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2000;48:225–268. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60758-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Oustanina S, Hause G, Braun T. Pax7 directs postnatal renewal and propagation of myogenic satellite cells but not their specification. EMBO J. 2004;23:3430–3439. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kassar-Duchossoy L, Gayraud-Morel B, Gomes D, et al. Mrf4 determines skeletal muscle identity in Myf5:Myod double-mutant mice. Nature. 2004;431:466–471. doi: 10.1038/nature02876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rudnicki MA, Schnegelsberg PN, Stead RH, et al. MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 1993;75:1351–1359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90621-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hasty P, Bradley A, Morris JH, et al. Muscle deficiency and neonatal death in mice with a targeted mutation in the myogenin gene. Nature. 1993;364:501–506. doi: 10.1038/364501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nabeshima Y, Hanaoka K, Hayasaka M, et al. Myogenin gene disruption results in perinatal lethality because of severe muscle defect. Nature. 1993;364:532–535. doi: 10.1038/364532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mauro A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961;9:493–495. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schienda J, Engleka KA, Jun S, et al. Somitic origin of limb muscle satellite and side population cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:945–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510164103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bajanca F, Luz M, Raymond K, et al. Integrin alpha6beta1-laminin interactions regulate early myotome formation in the mouse embryo. Development. 2006;133:1635–1644. doi: 10.1242/dev.02336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Carvajal JJ, Rigby PW. Regulation of gene expression in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316:3014–3018. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bismuth K, Relaix F. Genetic regulation of skeletal muscle development. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316:3081–3086. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pownall ME, Gustafsson MK, Emerson CP., Jr Myogenic regulatory factors and the specification of muscle progenitors in vertebrate embryos. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002;18:747–783. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.18.012502.105758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cornelison DD, Wold BJ. Single-cell analysis of regulatory gene expression in quiescent and activated mouse skeletal muscle satellite cells. Dev Biol. 1997;191:270–283. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen JC, Goldhamer DJ. The core enhancer is essential for proper timing of MyoD activation in limb buds and branchial arches. Dev Biol. 2004;265:502–512. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.09.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dhawan J, Rando TA. Stem cells in postnatal myogenesis: Molecular mechanisms of satellite cell quiescence, activation and replenishment. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:666–673. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Horsley V, Pavlath GK. Forming a multinucleated cell: Molecules that regulate myoblast fusion. Cells Tissues Organs. 2004;176:67–78. doi: 10.1159/000075028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Biressi S, Rando TA. Heterogeneity in the muscle satellite cell population. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010;21:845–854. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rocheteau P, Gayraud-Morel B, Siegl-Cachedenier I, et al. A subpopulation of adult skeletal muscle stem cells retains all template DNA strands after cell division. Cell. 2012;148:112–125. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kuang S, Kuroda K, Le Grand F, et al. Asymmetric self-renewal and commitment of satellite stem cells in muscle. Cell. 2007;129:999–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cossu G, Tajbakhsh S. Oriented cell divisions and muscle satellite cell heterogeneity. Cell. 2007;129:859–861. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Morrison SJ, Kimble J. Asymmetric and symmetric stem-cell divisions in development and cancer. Nature. 2006;441:1068–1074. doi: 10.1038/nature04956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Prior TW, Bridgeman SJ. Experience and strategy for the molecular testing of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Mol Diagn. 2005;7:317–326. doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60560-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Brown SC, Piercy RJ, Muntoni F, et al. Investigating the pathology of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:1335–1338. doi: 10.1042/BST0361335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wheeler MA, Ellis JA. Molecular signatures of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:1354–1358. doi: 10.1042/BST0361354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Nigro V, Aurino S, Piluso G. Limb girdle muscular dystrophies: Update on genetic diagnosis and therapeutic approaches. Curr Opin Neurol. 2011;24:429–436. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e32834aa38d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Moser H. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Pathogenetic aspects and genetic prevention. Hum Genet. 1984;66:17–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00275183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hoffman EP, Knudson CM, Campbell KP, et al. Subcellular fractionation of dystrophin to the triads of skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987;330:754–758. doi: 10.1038/330754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Durbeej M, Campbell KP. Muscular dystrophies involving the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex: An overview of current mouse models. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12:349–361. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Heslop L, Morgan JE, Partridge TA. Evidence for a myogenic stem cell that is exhausted in dystrophic muscle. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:2299–2308. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.12.2299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Grounds MD. Two-tiered hypotheses for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008;65:1621–1625. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-7574-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mouly V, Aamiri A, Perie S, et al. Myoblast transfer therapy: Is there any light at the end of the tunnel? Acta Myol. 2005;24:128–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sacco A, Mourkioti F, Tran R, et al. Short telomeres and stem cell exhaustion model Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mdx/mTR mice. Cell. 2010;143:1059–1071. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Morandi L, Bernasconi P, Gebbia M, et al. Lack of mRNA and dystrophin expression in DMD patients three months after myoblast transfer. Neuromuscul Disord. 1995;5:291–295. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(94)00070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gussoni E, Blau HM, Kunkel LM. The fate of individual myoblasts after transplantation into muscles of DMD patients. Nat Med. 1997;3:970–977. doi: 10.1038/nm0997-970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Qu-Petersen Z, Deasy B, Jankowski R, et al. Identification of a novel population of muscle stem cells in mice: Potential for muscle regeneration. J Cell Biol. 2002;157:851–864. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200108150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Cerletti M, Jurga S, Witczak CA, et al. Highly efficient, functional engraftment of skeletal muscle stem cells in dystrophic muscles. Cell. 2008;134:37–47. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Montarras D, Morgan J, Collins C, et al. Direct isolation of satellite cells for skeletal muscle regeneration. Science. 2005;309:2064–2067. doi: 10.1126/science.1114758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Brussee V, Tardif F, Roy B, et al. Successful myoblast transplantation in fibrotic muscles: No increased impairment by the connective tissue. Transplantation. 1999;67:1618–1622. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199906270-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Partridge TA, Morgan JE, Coulton GR, et al. Conversion of mdx myofibres from dystrophin-negative to -positive by injection of normal myoblasts. Nature. 1989;337:176–179. doi: 10.1038/337176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Miller RG, Sharma KR, Pavlath GK, et al. Myoblast implantation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: The San Francisco study. Muscle Nerve. 1997;20:469–478. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199704)20:4<469::aid-mus10>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zheng B, Cao B, Crisan M, et al. Prospective identification of myogenic endothelial cells in human skeletal muscle. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1025–1034. doi: 10.1038/nbt1334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Cao B, Zheng B, Jankowski RJ, et al. Muscle stem cells differentiate into haematopoietic lineages but retain myogenic potential. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:640–646. doi: 10.1038/ncb1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Huard J, Cao B, Qu-Petersen Z. Muscle-derived stem cells: Potential for muscle regeneration. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2003;69:230–237. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.10020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Deasy BM, Gharaibeh BM, Pollett JB, et al. Long-term self-renewal of postnatal muscle-derived stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:3323–3333. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-02-0169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Payne TR, Oshima H, Sakai T, et al. Regeneration of dystrophin-expressing myocytes in the mdx heart by skeletal muscle stem cells. Gene Ther. 2005;12:1264–1274. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Asakura A, Seale P, Girgis-Gabardo A, et al. Myogenic specification of side population cells in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 2002;159:123–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200202092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Doyle MJ, Zhou S, Tanaka KK, et al. Abcg2 labels multiple cell types in skeletal muscle and participates in muscle regeneration. J Cell Biol. 2011;195:147–163. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201103159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bachrach E, Li S, Perez AL, et al. Systemic delivery of human microdystrophin to regenerating mouse dystrophic muscle by muscle progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:3581–3586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400373101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Crisan M, Huard J, Zheng B, et al. Purification and culture of human blood vessel-associated progenitor cells. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2008 doi: 10.1002/9780470151808.sc02b02s4. Chapter 2:Unit 2B.2.1–2B.2.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Tamaki T, Akatsuka A, Ando K, et al. Identification of myogenic-endothelial progenitor cells in the interstitial spaces of skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 2002;157:571–577. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200112106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Dellavalle A, Sampaolesi M, Tonlorenzi R, et al. Pericytes of human skeletal muscle are myogenic precursors distinct from satellite cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:255–267. doi: 10.1038/ncb1542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Torrente Y, Belicchi M, Sampaolesi M, et al. Human circulating AC133(+) stem cells restore dystrophin expression and ameliorate function in dystrophic skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:182–195. doi: 10.1172/JCI20325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Negroni E, Riederer I, Chaouch S, et al. In vivo myogenic potential of human CD133+ muscle-derived stem cells: A quantitative study. Mol Ther. 2009;17:1771–1778. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.National Institutes of Health. Treatment of dysphagia in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy by autologous transplantation of myoblasts (OPMD) [Accessed April 20, 2012]. Available at: http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00773227.
- 80.Zheng JK, Wang Y, Karandikar A, et al. Skeletal myogenesis by human embryonic stem cells. Cell Res. 2006;16:713–722. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Darabi R, Gehlbach K, Bachoo RM, et al. Functional skeletal muscle regeneration from differentiating embryonic stem cells. Nat Med. 2008;14:134–143. doi: 10.1038/nm1705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Darabi R, Baik J, Clee M, et al. Engraftment of embryonic stem cell-derived myogenic progenitors in a dominant model of muscular dystrophy. Exp Neurol. 2009;220:212–216. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.08.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Darabi R, Santos FN, Filareto A, et al. Assessment of the myogenic stem cell compartment following transplantation of Pax3/Pax7-induced embryonic stem cell-derived progenitors. Stem Cells. 2011;29:777–790. doi: 10.1002/stem.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Darabi R, Arpke RW, Irion S, et al. Human ES- and iPS-derived myogenic progenitors restore dystrophin and improve contractility upon transplantation in dystrophic mice. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10:610–619. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.02.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Sakurai H, Okawa Y, Inami Y, et al. Paraxial mesodermal progenitors derived from mouse embryonic stem cells contribute to muscle regeneration via differentiation into muscle satellite cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26:1865–1873. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2008-0173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Barberi T, Bradbury M, Dincer Z, et al. Derivation of engraftable skeletal myoblasts from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Med. 2007;13:642–648. doi: 10.1038/nm1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Mesires NT, Doumit ME. Satellite cell proliferation and differentiation during postnatal growth of porcine skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;282:C899–C906. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00341.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Capkovic KL, Stevenson S, Johnson MC, et al. Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) marks adult myogenic cells committed to differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314:1553–1565. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.01.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Covault J, Sanes JR. Distribution of N-CAM in synaptic and extrasynaptic portions of developing and adult skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1986;102:716–730. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Charlton CA, Mohler WA, Blau HM. Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) and myoblast fusion. Dev Biol. 2000;221:112–119. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.D'Amour KA, Agulnick AD, Eliazer S, et al. Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1534–1541. doi: 10.1038/nbt1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Mahmood A, Harkness L, Schroder HD, et al. Enhanced differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to mesenchymal progenitors by inhibition of TGF-beta/activin/nodal signaling using SB-431542. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25:1216–1233. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sanes JR. The basement membrane/basal lamina of skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:12601–12604. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R200027200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Boonen KJ, Post MJ. The muscle stem cell niche: Regulation of satellite cells during regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2008;14:419–431. doi: 10.1089/ten.teb.2008.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ten Broek RW, Grefte S, Von den Hoff JW. Regulatory factors and cell populations involved in skeletal muscle regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2010;224:7–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Brack AS, Conboy MJ, Roy S, et al. Increased Wnt signaling during aging alters muscle stem cell fate and increases fibrosis. Science. 2007;317:807–810. doi: 10.1126/science.1144090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Moore SW, Roca-Cusachs P, Sheetz MP. Stretchy proteins on stretchy substrates: The important elements of integrin-mediated rigidity sensing. Dev Cell. 2010;19:194–206. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.07.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Laflamme MA, Murry CE. Regenerating the heart. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:845–856. doi: 10.1038/nbt1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Reilly GC, Engler AJ. Intrinsic extracellular matrix properties regulate stem cell differentiation. J Biomech. 2010;43:55–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, et al. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126:677–689. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.McBeath R, Pirone DM, Nelson CM, et al. Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev Cell. 2004;6:483–495. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(04)00075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Pelham RJ, Jr., Wang Y. Cell locomotion and focal adhesions are regulated by substrate flexibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:13661–13665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.25.13661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Fedorovich NE, Alblas J, de Wijn JR, et al. Hydrogels as extracellular matrices for skeletal tissue engineering: State-of-the-art and novel application in organ printing. Tissue Eng. 2007;13:1905–1925. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.0175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Levenberg S, Rouwkema J, Macdonald M, et al. Engineering vascularized skeletal muscle tissue. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:879–884. doi: 10.1038/nbt1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Engler AJ, Griffin MA, Sen S, et al. Myotubes differentiate optimally on substrates with tissue-like stiffness: Pathological implications for soft or stiff microenvironments. J Cell Biol. 2004;166:877–887. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200405004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.García AJ, Reyes CD. Bio-adhesive surfaces to promote osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Dent Res. 2005;84:407–413. doi: 10.1177/154405910508400502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Powell CA, Smiley BL, Mills J, et al. Mechanical stimulation improves tissue-engineered human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;283:C1557–C1565. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00595.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Wilschut KJ, Haagsman HP, Roelen BA. Extracellular matrix components direct porcine muscle stem cell behavior. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316:341–352. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Skuk D, Goulet M, Roy B, et al. Dystrophin expression in muscles of Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients after high-density injections of normal myogenic cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006;65:371–386. doi: 10.1097/01.jnen.0000218443.45782.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Bachrach E, Perez AL, Choi YH, et al. Muscle engraftment of myogenic progenitor cells following intraarterial transplantation. Muscle Nerve. 2006;34:44–52. doi: 10.1002/mus.20560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Gussoni E, Soneoka Y, Strickland CD, et al. Dystrophin expression in the mdx mouse restored by stem cell transplantation. Nature. 1999;401:390–394. doi: 10.1038/43919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Torrente Y, Tremblay JP, Pisati F, et al. Intraarterial injection of muscle-derived CD34(+)Sca-1(+) stem cells restores dystrophin in mdx mice. J Cell Biol. 2001;152:335–348. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Chang H, Yoshimoto M, Umeda K, et al. Generation of transplantable, functional satellite-like cells from mouse embryonic stem cells. FASEB J. 2009;23:1907–1919. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-123661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Mizuno Y, Chang H, Umeda K, et al. Generation of skeletal muscle stem/progenitor cells from murine induced pluripotent stem cells. FASEB J. 2010;24:2245–2253. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-137174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]