Abstract
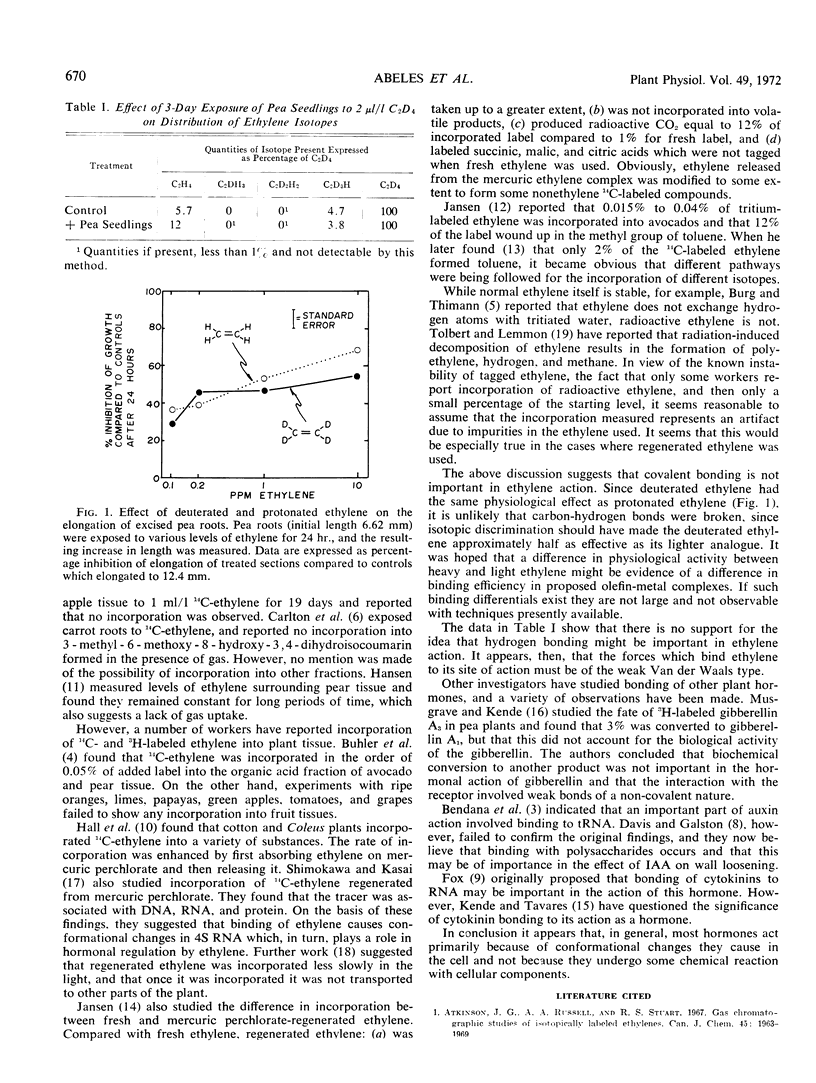
We observed no exchange between deuterated ethylene (C2D4) and the hydrogen of pea seedlings (Pisum sativum L. cv. Alaska). This suggests that bonding forces in which exchange could readily occur are not important in the physiological action of ethylene. Deuterated ethylene was just as effective as normal ethylene in inhibiting the growth of pea root sections. These results indicate that splitting carbon to hydrogen bonds did not occur during ethylene action.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendaña F. E., Galston A. W., Kaur-Sawhney R., Penny P. J. Recovery of labeled ribonucleic acid following administration of labeled auxin to green pea stem sections. Plant Physiol. 1965 Nov;40(6):977–983. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.6.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg S. P., Thimann K. V. THE PHYSIOLOGY OF ETHYLENE FORMATION IN APPLES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Mar;45(3):335–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton B. C., Peterson C. E., Tolbert N. E. Effects of ethylene & oxygen on production of a bitter compound by carrot roots. Plant Physiol. 1961 Sep;36(5):550–552. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.5.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick A. V., Burg S. P. Regulation of root growth by auxin-ethylene interaction. Plant Physiol. 1970 Feb;45(2):192–200. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.2.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. J., Galston A. W. Labeled indole-macromolecular conjugates from growing stems supplied with labeled indoleacetic Acid : I. Fractionation. Plant Physiol. 1971 Mar;47(3):435–441. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E. Incorporation of a kinin, N, 6-benzyladenine into soluble RNA. Plant Physiol. 1966 Jan;41(1):75–82. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kende H., Tavares J. E. On the significance of cytokinin incorporation into RNA. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1244–1248. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave A., Kende H. Radioactive gibberellin a(5) and its metabolism in dwarf peas. Plant Physiol. 1970 Jan;45(1):56–61. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOLBERT B. M., LEMMON R. M. Radiation decomposition of pure organic compounds. Radiat Res. 1955 Sep;3(1):52–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



