Abstract
Achieving transgene integration into preselected genomic sites is currently one of the central tasks in stem cell gene therapy. A strategy to mediate such targeted integration involves site specific endonucleases. Two genomic sites within the MBS85 and CCR5 genes [AAVS1 and CCR5 zinc finger nuclease (CCR5-ZFN) site, respectively] have recently been suggested as potential target regions for integration as their disruption has no functional consequence. We hypothesized that efficient transgene integration maybe affected by DNA accessibility of endonucleases and therefore studied the transcriptional and chromatin status of the AAVS1 and CCR5 sites in eight human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell lines and pooled CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. Matrixchromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays demonstrated that the CCR5 site and surrounding regions possessed a predominantly closed chromatin configuration consistent with its transcriptionally inactivity in these cell types. In contrast, the AAVS1 site was located within a transcriptionally active region and exhibited an open chromatin configuration in both iPS cells and hematopoietic stem cells. To show that the AAVS1 site is readily amendable to genome modification, we expressed Rep78, an AAV2-derived protein with AAVS1-specific endonuclease activity, in iPS cells after adenoviral gene transfer. We showed that Rep78 efficiently associated with the AAVS1 site and triggered genome modifications within this site. On the other hand, binding to and modification of the CCR5-ZFN site by a zinc-finger nuclease was relatively inefficient. Our data suggest a critical influence of chromatin structure on efficacy of site-specific endonucleases used for genome editing.
Introduction
Gene therapy requires the permanent integration of transgenes into chromosomes of target cells. Optimally transgene integration should occur into defined genomic sites. This would simultaneously ensure the appropriate expression of the transgene, and prevent side-effects due to insertional mutagenesis of cellular genes. None of the gene transfer vector systems currently used display DNA sequence preferences specific enough for targeted insertion into a defined location in the target cell genome 1, 2. A new concept to increase targeted integration involves the placement of site-a specific double stranded DNA break (DSB) which has been shown to increase the frequency of gene addition of transgenes delivered in the context of AAV vectors 3, 4, non-integrating lentivirus vectors 5, helper-dependent adenoviruses 6–9, or plasmids 10. Site-specific DSBs can be catalyzed by meganucleases, transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs), or zinc-finger nucleases (ZFN) 2, 11. ZFNs are fusion constructs between zinc-finger DNA binding domains and the nuclease domain of the type II restriction enzyme FokI. Upon binding to specific sites in the genome, ZFNs cause DSBs. Two sites for targeted gene addition have been explored in the past in the context of gene therapy. These “safe harbors” fulfill a number of criteria: i) tolerability of mono-and bi-allelic disruption of the target locus; ii) no activation of proto-oncogenes upon integration into this site; iii) transcriptional competence across cell types to maintain expression from an inserted gene cassette(s); and iv) the existence of a moiety to facilitate integration at that site.
One potential “safe harbor” site is located within the chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 (CCR5) gene on human chromosome 3. CCR5 is predominantly expressed on T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells and microglia. CCR5 is a co-receptor for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A homozygous Δ32 deletion in the CCR5 gene, found in about 1% of Caucasians, confers a natural resistance to HIV-1 12. Individuals carrying this mutation are healthy, most likely due to the redundant nature of the chemokine system. In a recent pivotal study it was shown that the transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from a donor who was homozygous for CCR5Δ32 into a patient with acute myeloid leukemia and AIDS resulted in long-term control of HIV 13. Importantly, it has been shown that CCR5-specific ZFNs can mediate efficient and permanent disruption of the CCR5 in primary human CD4+ T lymphocytes 14 and primary CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells 10, thus conferring robust protection against HIV-1 infection both in vitro and in an in vivo mouse model of HIV-1 infection. In these cases, CCR5 gene disruption is the result of DSB repair by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) leading to an interruption of the reading frame. In the context of gene addition, CCR5-specific ZFNs have been used in several studies 15–17.
Another genomic site that is thought to fulfill the criteria of a “safe harbor” is the site preferentially used by wild-type adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype 2 for integration, i.e. AAVS1 18. The AAVS1 site is located within the promoter region of the protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit 12C (PPP1R12C) gene, a.k.a. the myosin-binding subunit 85 (MBS85) gene, on human chromosome 19. The MBS85 protein is thought to be involved in the regulation of actin–myosin fiber assembly, and its translation initiation start codon is located only 17 nucleotides downstream of the AAV Rep78 binding site (RBS). Notably, AAV integration/infection is not associated with a known disease. Furthermore, both human embryonic stem (ES) cells 19 and human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells 20 with a disruption of MBS85 retain their pluripotency. Mouse embryonic stem cells with AAV integrated into the mouse orthologue of AAVS1 contributed successfully to mouse development when injected into blastocysts 21. AAV integration into AAVS1 is catalyzed by the AAV Rep68/78 proteins. The large Rep proteins can simultaneously bind to the RBS within the incoming viral genome and to the RBS within the chromosomal AAVS1. AAV integration is then facilitated by Rep-mediated site-specific DNA breaks within the AAVS1 terminal resolution site (trs). A 33 kb sequence comprising the RBS and trs site were sufficient to mediate site-specific integration 22. Expression of Rep68/78 has been used to achieve targeted integration of gene therapy vectors 6, 8, 23, 24.
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and, recently, embryonic stem (ES) cells and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells are mainly used for targeted gene addition. The epigenetic status of embryonic stem (ES) cells and iPS cells differs from that of differentiated cells in several features: i) ES and iPS cells maintain a globally open chromatin state, i.e. display less repressive histone marks (H3K9m3 and H3K27m3) than differentiated somatic cells 25, 26. This “transcription-ready” chromatin status might enable rapid gene activation during differentiation. ii) The ES cell genome is transcriptionally hyperactive, with widespread transcription in both coding and noncoding regions, including sporadic low-level expression of tissue-specific genes 27. iii) CpGs found within heterochromatic regions are hypomethylated in ES cell genomes. iv) Chromatin remodeling factors are over-represented in the ES cells 28.
Recently it has been suggested that the chromatin accessibility of preselected target sites might affect the efficacy of DSB generation and gene addition 1. This is in line with findings that the chromatin structure plays a role of integration site selection in lentivirus and AAV vector integration 29, 30. Due to the unknown chromatin status in iPS cells, we performed a detailed analysis of the chromatin marks within the AAVS1 and the CCR5-ZFN sitesin eight iPS cell lines derived from 5 different sources as a well as in human CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. Strikingly, we found that the AAVS1 site possesses an active chromatin configuration in both iPS cells and in CD34+ cells. By contrast, a predominantly inactive chromatin configuration was found for the CCR5-ZFN site reflecting the immune cell-restricted expression of the CCR5 gene. Support for these findings was garnered from the presence or absence of RNA polymerase II at the AAVS1 and CCR5 sites, respectively, as well as mRNA analyses in these lines. These results suggest that the AAVS1 site is potentially the preferred site for targeted gene integration in iPS cells and hematopoietic stem cells. In support of this conclusion, we show that Rep78, expressed in iPS cells after adenoviral gene transfer, efficiently associated with the AAVS1 site and triggers genome modifications within this site. In contrast, CCR5-ZFN interaction with its target site and DNA cleavage appeared to be inefficient, indicating a critical influence of chromatin accessibility on binding and/or activity of site-specific endonucleases.
Results
Quality analyses of iPS cell lines
Recent data indicate that iPS cells are not a homogeneous cell population 31. As chromatin analysis in iPS cell lines can be affected by heterogeneity, i.e. presence of cells in different differentiation and/or reprogramming stages, we first performed phenotypic and genetic quality analyses of all the iPS lines. We used eight previously generated iPS cell lines from five different sources: i) MHF2C1, MHF2C2, and MHFC3 were derived from human fetal fibroblasts (GM05387, Coriell Institute for Medical Research), ii) OI12-1, OI12-4, and OI12-7 were generated from human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the spine of a 15-year-old patient with Osteogenesis imperfecta 32, 33, iii and iv) FSHD43-1 and the FSHD83-6 lines were created from primary fibroblasts of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy patients, a male and a female patient respectively 34, and v) M83-9 was derived from primary human foreskin fibroblasts 35. All iPS cell lines were characterized and gave rise to progenies of all 3 germ layers as shown by teratoma assays in immunodeficient mice 34, 36. Upregulation of the pluripotency markers is used as a criterion to distinguish between the three types of iPS cell colonies, where type I are the least iPS-like colonies being incompletely reprogrammed or partially differentiated (SSEA-4−, TRA-1-60−). Type II iPS cells are SSEA-4+, TRA-1-60−, while type III cells are ‘bona fide’ iPS colonies (SSEA-4+, TRA-1-60+)37. All of our iPS cell lines formed tightly packed colonies and stained positive for SSEA-4 and TRA-1-60 in immunofluorescence studies (Fig. 1). Crucial for the maintenance of this phenotype was that iPS cells were cultured in TeSR™2 medium on matrigel. In contrast, our initial attempts to passage iPS in the widely used KOSR medium on MEF feeder cells yielded less homogenous cultures.
Figure 1. Immunofluorescence characterization of iPS cell lines.
All nine iPS cell lines were subcultured for a period of two days before being immunohistochemically stained with SSEA-4 (red) and TRA-1-60 (green) antibodies. SSEA-4 staining is indicative of partially and fully reprogrammed iPS cells (Type II), whereas TRA-1-60 and SSEA-4 indicates fully reprogrammed (Type III) iPS cells 37. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI Fluorescent Counterstain. The white scale bar represents 200 μm.
IPS cells are genetically unstable. We therefore analyzed the karyotype as well as the presence of the AAVS1 and CCR5 sites in the iPS cell lines. All iPS cell lines, except line MHF2-C1, had normal karyotypes (Fig. 2). MHF2-C1 contained an isochromosome abnormality of chromosome 19 p10. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis revealed the presence of two signals for each of the AAVS1 and the CCR5 site, indicating that both sites were intact in all iPS cell lines (Fig. 3).
Figure 2. Karyotyping of iPS lines.
All iPS cell lines were grown for four passages on matrigel before being G-band karyotyped. The upper panel shows the abnormal karyotype of MHF2-C1.
Figure 3. FISH labeling of target sites.
iPS cell lines were subjected to FISH probes either targeting the CCR5-ZFN site on chromosome 3 (Red) or the AAVS1 site on Chromosome 19 (Green) (see arrows). Every genome contains only two of each target sites. DNA was counterstained with DAPI Fluorescent Counterstain.
ChIP analyses of integration sites
In addition to iPS cells, we also included into our analyses primary human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34+ cells and the CD34-positive erythroleukemia Mo7e cell line, which is often used as a HSC model.
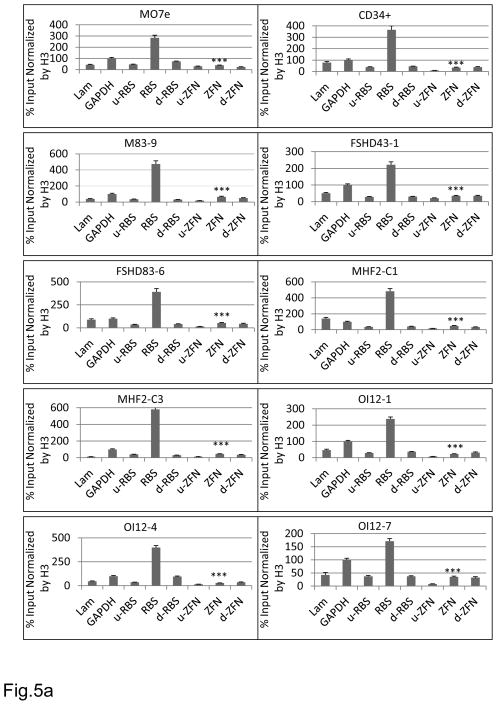
Chromosomal DNA is associated with histones where the histone tails that project out from the core can be post-translationally modified by lysine acetylation, lysine and arginine methylation, serine and threonine phosphorylation and lysine ubiquitylation or sumoylation 38. Some histone tail modifications, e.g. histone H3 K9 and K14 acetylation (H3K9/14Ac), can be recognized by several chromatin-modifying and transcription co-activator proteins and are indicative of transcriptionally active chromatin regions. On the other hand, the presence of other histone tail modifications or markers, e.g. K9 tri-methylated histone H3 (H3K9m3), recruit heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1), and is characteristic of transcriptionally inactive chromatin regions. There are several approaches to study the chromatin state. In this study we used a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay (ChIP) that measures the density of DNA binding proteins along selected DNA regions using antibodies that are specific for the above mentioned H3 modifications. Specifically, we employed a matrix ChIP protocol 39, which has been shown to have several advantages over the more traditional ChIP assay, including being high throughput and faster, with reduced variation. Throughout this study, the −20 kb LamC1 intergenic region was used as a control for a transcriptionally inactive chromatin region and the house-keeping glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) promoter was used as a control for a transcriptionally active region 40 (Fig. 4). In addition to the two sites of interest, i.e. the AAVS1 RBS site and the ZFN site in the CCR5 gene, we also examined the adjoining ~1 kb up- and ~1 kb downstream areas for each of these sites, thus forming a clearer depiction of the region (Fig. 4). The first histone mark we used to investigate the chromatin structure of the AAVS1 and the CCR5-ZFN sites was H3K9/14Ac (Fig. 5a), which is indicative of transcriptionally active chromatin state. This marker was abundantly (p < 0.001) present at the AAVS1 site for all of the iPS cell lines, as well as the MO7e cell and the CD34+ cells, varying from 1.6-fold to 6-fold higher occupancy at this site when compared to the GAPDH promoter site. The CCR5-ZFN site, however, was less varying between the lines with consistently low H3K9/14Ac levels (~0.5 fold that of the GAPDH region) – a similar trend to that of the −20 kb LamC1 intergenic silenced region. The results were inverted when a marker for transcriptionally inactive regions, H3K9m3, was used (Fig. 5b). This marker was present at significantly higher levels at the −20 kb LamC1 region and the CCR5-ZFN site when compared to the GAPDH and the AAVS1 regions, respectively, in all the tested cell lines (p < 0.001).
Figure 4. Primers used in ChIP assays.
a) Table containing all the forward (F) and reverse (R) primer sets with their genomic binding positions. b) Diagrammatic representation of the primer amplification region positions with regard to the target sites. Primers were designed to amplify a region across the target site, and approximately 1 kb up-and 1 kb downstream of the target site.
Figure 5. ChIP analyses of histone marks associated with the Rep78 binding site (RBS) and the CCR5-ZFN binding site.
RBS is the rep binding site with an additional ~1 kb upstream region (u-RBS) and a ~1 kb downstream region (d-RBS) amplified, whereas “ZFN” spans the zinc finger nuclease binding region with additional amplified regions ~1 kb up- (u-ZFN) and 1 kb downstream (d-ZFN) of the ZNF site. a) H3K9/14 acetylated marker was used to identify transcriptionally active/open chromatin regions in the various cell lines. b) H3K9m3 marker was used to identify transcriptionally inactive/closed chromatin regions. Values were expressed as a percentage of the original input values and normalized to their respective H3 values. The data in figure a) was further expressed as a percentage of the GAPDH signal (GAPDH =100%) and b) data were expressed as a percentage of the LamC1 signal (LamC1=100%). Significance was calculated between the RBS and the CCR5-1 sites, ***p < 0.001.
The results from these markers indicate that the AAVS1 site has a transcriptionally active chromatin configuration when compared to that of the CCR5-ZFN cleavage site. Further support for our findings came from ChIP analyses of the RNA polymerase II levels at the sites of interest in the same cell lines (Fig. 6). As expected, The GAPDH promoter region had a greater Pol II occupancy than the −20 kb LamC1 region. There was also a significantly greater (p < 0.001) occupancy by Pol II at the AAVS1 RBS site, when compared to the occupancy at the CCR5-ZFN site, clearly indicating that the AAVS1 region is more transcriptionally active than the CCR5-ZFN site and surrounding regions.
Figure 6. ChIP analysis of RNA Polymerase II associated with the Rep78 binding site and the zinc finger nuclease binding site.
Chromatin-PolII complexes were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Pol II antibody and the precipitate subjected to qPCR to quantify the Pol II activity in the regions of interest. The presence of PolII is indicative of a transcriptionally active chromatin region. The GAPDH promoter (GAPDH) and the −20 kb LamC1 (Lam) regions act as controls for transcriptionally active and inactive regions, respectively. Values were expressed as a percentage of the original input values and further normalized to GAPDH signal value (GAPDH=100%). Significance was calculated between the RBS and the CCR5-1 sites, ***p < 0.001.
Transcriptional activity of AAVS1 and CCR5-ZFN sites
Transcriptionally active genes are characterized by an overall active chromatin structure. To assess a correlation between the ChIP data of the AAVS1 and the CCR5-ZFN sites and transcription of the genes they are located in, we performed RT-qPCR analyses for the corresponding mRNAs relative to the expression of the GAPDH gene (Table 1). We compared CCR5, MBS85, and GAPDH mRNA levels in iPS cell lines with the levels found in HeLa-TZM-bl cells – a cell line that constitutively expresses CCR5 used in HIV research 41. While CCR5 mRNA levels in this cell line were only 8.22 fold lower than GAPDH RNA levels, in all iPS cells CCR5 mRNA levels were 21,000–40,000-fold lower than GAPDH levels, indicating that CCR5 is poorly transcribed in these cells. MBS85 mRNA levels in HeLa-TZM-bl cells, however, were only 410-fold lower than GAPDH levels. While the MBS85 mRNA levels in iPS cells showed greater variation than CCR5 mRNA levels, they were, however, overall comparable to those in the HeLa-TZM-bl cell line. This implies that the MBS85 gene is transcribed at low levels in all cell lines, a finding that is in agreement with the ubiquitous expression of this gene 42.
Table 1. RT-PCR.
a) Table containing all the forward (F) and reverse (R) primer sets used in the RT-PCR. Given also is the primers’ genomic binding positions. b) Table with the quantitative analyses of each cell line’s mRNA transcription for the gene of interest expressed as a percentage of each respective line’s GAPDH mRNA, ± the SEM. The HeLa-TZM-bl cell line overexpresses the CCR5 gene and serves as positive control.
| A | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Amplicon | mRNA | Primer Sequence | Genome position |
| MBS85F | MBS85 | GTGGATGTGGAAGCAGCCAAG | Chr19:55614779 |
| MBS85R | MBS85 | CATCACCTCAATGTAGCCCTTG | Chr19:55614934 |
| CCR5F1 | CCR5 | CCTCCGCTCTACTCACTGGT | Chr3:46389497 |
| CCR5R1 | CCR5 | AGCATAGTGAGCCCAGAAGG | Chr3:46389667 |
| GAPDHF | GAPDH | GGCCTCCAAGGAGTAAGACC | Chr12:6647321 |
| GAPDHR | GAPDH | AGGGGTCTACATGGCAACTG | Chr12:6647467 |
| B | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | CCR5 | MBS85 | |
| Hela-TZM-bl | 100 ± 1.79 | 12.166 ± 0.2764 | 0.238 ± 0.0114 |
| M89-6 | 100 ± 1.21 | 0.0048 ± 0.0004 | 0.693 ± 0.0515 |
| FSHD43-1 | 100 ± 0.52 | 0.0023 ± 0.0001 | 0.154 ± 0.0058 |
| FSHD83-6 | 100 ± 1.28 | 0.0023 ± 0.0001 | 0.205 ± 0.0124 |
| MEF2-C1 | 100 ± 3.21 | 0.0043 ± 0.0003 | 0.284 ± 0.0475 |
| MEF2-C3 | 100 ± 0.38 | 0.0073 ± 0.001 | 0.545 ± 0.0566 |
| OI12-1 | 100 ± 3.60 | 0.0042 ± 0.0006 | 0.312 ± 0.0029 |
| OI12-4 | 100 ± 0.67 | 0.0024 ± 0.0003 | 0.262 ± 0.0129 |
| OI12-7 | 100 ± 1.29 | 0.0036 ± 0.0002 | 0.409 ± 0.048 |
Ad-mediated transgene expression
Our ChIP analyses showed that the AAVS1 site is more open than the CCR5-ZFN site, implying that genomic modification of the AAVS1 might be more efficient than approaches that target the CCR5-ZFN site. Testing this hypothesis requires the expression of site-specific endonucleases in stem cells. Here, we used adenovirus (Ad) vectors for gene transfer. In previous studies we found that Ad vectors containing fibers derived from Ad serotype 35 (Ad5/35) are superior in transducing iPS cells 43 and CD34+ cells 44. Infection of iPS cell culture with an Ad5/35 vector containing the CMV promoter resulted in GFP expression only in differentiated cells at the periphery of colonies (Fig. 7a, left panel). This is in agreement with previous studies demonstrating that the CMV promoter is not active in undifferentiated iPS cells 43, 45. In contrast, a vector that contained the GFP gene under the control of the ubiquitin promoter 46 (Ad5/35-Ub-GFP), conferred GFP expression of cells in the center and periphery of iPS cell colonies (Fig. 7a, right panel). Overall, however, the transduction efficiency of cells in the center of iPS cell colonies was inefficient, even at an MOI of 500pfu/cell (data not shown). We speculated that cells in the center of colonies are less accessible to Ad vectors. To test this, we stained iPS cell colonies for intercellular junction markers, i.e. the coxsackie-adenoviral receptor (CAR; receptor for adenovirus species C) and desmoglein 2 (DSG2; receptor for adenovirus species B), which are located in tight and desmosomal junctions, respectively (Fig. 7b). Both markers stained cells in the center of colonies, which were also positive for the stem cell markers TRA-1-60 and Tie-2. The finding that undifferentiated iPS cells have epithelial feature, such as epithelial junctions, has been reported before 47. Our findings imply that Ad receptors are trapped in junctions in undiffentiated iPS cells, which explains the relative low transduction efficiency by Ad vectors, including Ad5/35 vectors. (Notably, earlier we reported that the Ad5/35 receptor, CD46, is trapped in junctions of epithelial tumor cells 48.) We also found that another epithelial marker, E-cadherin, is less expressed in undifferentiated cells (in the center of colonies) compared to more differentiated cells at the periphery (Fig. 7b). On the other hand, undifferentiated iPS cells stained positive for the mesenchymal marker N-cadherin. Due to the inefficient transduction of iPS cells in the context of colonies, we adapted a protocol that involves the plating of single iPS cells on matrigel coated plates subsequent to the disruption of colonies with accutase. As iPS cells are prone to apoptosis as single cells 49, we incubated plated cells with an inhibitor of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) before Ad transduction. Under these conditions, 75+/−8% of iPS cells could be transduced with Ad5/35-Ub-GFP at an MOI of 20 pfu/cell (Fig. 7c). We therefore used these transduction conditions for all subsequent studies with Ad vectors.
Figure 7. Adenovirus vector transduction of iPS cells.
a) Effect of different promoters on Ad transduction of iPS cell colonies. IPS cells (line FSHD43-1) were infected with Ad5/35 vectors expressing GFP under the control of the CMV or ubiquitin promoter at an MOI of (20 pfu/cell). Representative microphotographs taken 48 hours after infection are shown. The scale bar is 40 μm. b) Expression of epithelial and stem cell markers in iPS cell colonies. Cells were grown on glass slides and stained for the indicated markers. Representative images are shown. The scale bar is 40 μm. Note that culturing iPS cells on glass slides triggers their differentiation at the periphery of colonies. In the E-cadherin/tubulin and E-cadherin panels the round cell cluster on the right represents the washed-out core of the colony on the left. c) Ad5/35 transduction of iPS cells (MOI of 20 pfu/cell) plated as single cells in the presence of Y-27632, an inhibitor of Rho-associated protein kinase (Rock). Representative microphotographs taken 48 hours after infection are shown. The scale bar is 40 μm.
The generation of Ad vectors expressing ZFNs is problematic due to off-target “genotoxicity” of ZFNs and killing of Ad producer cells. While we were able to produce Ad vectors expressing CCR5 ZFNs, we failed in several attempts to generate Ad vector that express AAVS1-specific ZFNs. Also, our attempts to use electroporation/nucleofection-based approaches for transfer of ZFN encoding plasmids into stem cells were unsuccessful due to severe cytotoxicity associated with transfection. Therefore, our attempts to achieve modification of the AAVS1 site are based on the endonuclease activity of Rep78 expressed from an Ad5/35 vector (Ad.Rep78).
Ad.Rep78-mediated genome modification in iPS cells
Rep78 inhibits adenoviral DNA replication 50. Therefore, to minimize expression of Rep78 in 293 cells during Ad amplification we placed the corresponding gene under the control of a doxycycline (Dox) inducible system (Fig. 8a). This system utilizes a tTR-KRAB repressor. Binding of DNA binding proteins fused to KRAB results in histone deacetylation and methylation, thus creating a local heterochromatin state and inactivation of promoters that are 2 to 3 kb up- or downstream of the binding site 51. It has been shown that tTR-KRAB mediated repression of cellular Pol-II and Pol-III promoters juxtaposed to the TetO can be reversibly controlled by Dox 52. Here we used this system to control Rep78 expression from the ubiquitin promoter (Ad.Rep78). We infected iPS cells (line FSHD43-1) with Ad.Rep78. Rep78 protein expression upon Dox induction was validated by Western blot (Fig. 8b). To measure Rep78 binding to the AAVS1 site in the context of native chromatin, iPS cells were infected with Ad.Rep78, chromatin was isolated 2 days later and subjected to ChIP assay with Rep78-specific antibodies and primers specific for selected genomic sites. Ad.GFP infected iPS cells served as controls. This study showed a significant higher Rep78 occupancy at the AAVS1 site in Ad.Rep78 transduced cells than in cells transduced with the control Ad.GFP vector (Fig. 8c). There was no significant difference in Rep78 occupancy signals for the GAPDH site. To assess Rep78 mediated rearrangements of the AAVS1 site, we performed Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from Ad infected cells (at day 2 after infection) using an AAVS1-specific probe and a probe for a gene that is not targeted by Rep78 (HPRT1). In control virus infected cells, a single band, reflecting the native AAVS1 site, was visible (Fig. 8e). Analysis of DNA from Ad.Rep infected cells showed a >70% decrease in the intensity of the AAVS1-specific band while the HPRT1-specific band was unchanged. Rep78 cleaves within the AAVS1 site and triggers genomic rearrangements that involve deletions/translocations/replications varying in length in different cells 21, 53. This implies that rearranged AAV1 sites do not appear as discrete bands in Southern blot of cell populations but rather as a smear of signals that cannot be quantified by phosphoimager analysis. Overall, these studies suggest that the AAVS1 site in iPS cells is readily accessible and amendable to Rep78 mediated genome modification.
Figure 8. Ad.Rep78-mediated gene editing in iPS cells.
a) Schematic of Dox inducible expression cassettes in first-generation Ad5/35 vectors. The vectors contained a fusion between the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) domain and the tetracycline repressor (TetR). In this system, tTR-KRAB-mediated repression of an ubiquitin (Ub) promoter, juxtaposed to Tet operator sequences can be reversibly controlled by Dox. The bicistronic expression cassette is flanked by two different polyadenylation signals to avoid read-through from adjacent Ad promoters and unspecific activation of transgene expression without Dox. b) Western blot for Rep 78. iPS cells were infected with Ad.Rep at an MOI of 10 in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml Dox. Rep expression was analyzed 48 hours later by Western blot using Rep78 specific antibodies. Antibodies against GAPDH were used to show equal protein loading. c) Rep78 occupancy of CCR5 site. IPS cells were infected with Ad5/35 vectors expressing GFP or Rep78 under the control of the ubiquitin promoter at an MOI of 20 pfu/cell. Chromatin was isolated 2 days later and occupancy of selected sites by Rep78 was analyzed by ChIP assay using anti-Rep antibodies: rabbit polyclonal anti-Rep78 (N208 antibody clone MSMC111) provided by Dr. Linden, Oxford Univ. 64 (left panel) and a rabbit polyclonal anti-Rep78 provided by Dr. Trempe, NIDDK 65 (right panel). The amplified RBS region spans the Rep Binding Site. p<0.001 for Ad.GFP vs Ad.Rep78. d) ChIP analysis of the GAPDH promoter region using anti-Rep78 (N208 antibody clone MSMC111). We have performed the experiments in four iPS lines (FSHD83-6, FSHD43-1, OI12-4, and MHF2-C2) with similar outcomes. Shown are the data with FSHD43-1. e) Southern blot analysis of the AAVS1 and HPRT1 sites: A total of 15 μg genomic DNA of Ad.ZFN and Ad.GFP transduced iPS cells was digested and subjected to Southern blotting. Filters were simultaneously hybridized with AAVS1-specific and HPRT-specific probes. Signals were quantitated using a phophoimager. The AAVS1 and HPRT specific signals are marked by arrows.
Ad.ZFN-mediated genome modification in HSCs and iPS cells
The same Dox inducible system was used to express CCR5-ZFNs (Fig. 9a). Expression of CCR5 ZFN was confirmed in transduction studies with CD34+ cells (Fig. 9b). Functional activity of CCR5 ZFN expressed from Ad.ZFN was tested in HeLa-TZM-bl cells using a surveyor nuclease-based PCR assay 54 (Fig. 9c). This assay reveals gene modification by the appearance of rearranged products, which can be quantified to yield the % gene modification. Two days after infection of HeLa-TZM-bl cells with Ad.ZFN at a MOI of 50 pfu/cell, 2.4% and 12.1% of CCR5 alleles were found to be modified, in the absence and presence of Dox, respectively (Fig. 9c, left panel). CCR5 gene knockout is also reflected in flow cytometry analysis of surface CCR5 protein (Fig. 9c, right panel). The percentage of CCR5-positive cells was 16+/−4% less in Ad.ZFN+Dox than in mock-infected cells. The relative CCR5 expression level decreased 31+/−7% in HeLa-TZM-bl cells that expressed CCR5 ZFN (N = 3). For functional studies, we first used CD34+ cells, isolated from peripheral blood cells of G-CSF mobilized donors. CD34+ cells were infected with the CCR5 ZFN-expressing Ad5/35 vector in the presence of Dox under conditions that minimize CD34+ proliferation and differentiation 44. Two days later, genomic rearrangements within the CCR5 target site were analyzed by surveyor nuclease-based PCR. Regardless of the MOI used for infection, CCR5-ZFN rearrangements in CCD34+ cells was less than 1% (which is the lower detection limit of the surveyor nuclease-based PCR assay) (data not shown). Infection with an Ad5/35-GFP vector carrying the GFP gene instead of the ZFN gene at an MOI of 100pfu/cell resulted in transgene expression in >70% of cells (data not shown). Transduction of CD34+ cells at higher MOI was associated with cytotoxicity. Because we found high occupancy of markers for inactive chromatin around the CCR5-ZFN cleavage site in CD34+ cells (see Fig. 5), we therefore tested whether chromatin modifiers can increase CCR5 ZFN cleavage. We incubated CD34+ cells with the histone deacetylase inhibitors sodium butyrate (NaBu), valproic acid (VPA), and trichostain A (TSA) and analyzed 24 hour later the occupancy of H3K9/14Ac, a marker for open chromatin for the CCR5-ZFN site and for the ubiquitously expressed gene GAPDH (Fig. 9d). This study showed that VPA+TSA (Fig. 9d) and TSA+NaBu (not shown) significantly increased H3K9/14Ac occupancy of the CCR5-ZFN site in CD34+ cells. Based on this, we included the chromatin modifiers in transduction studies with Ad.ZFN. Overnight pre-incubation of CD34+ cells with VPA+TSA, or TSA+ NaBu stimulated Ad.ZFN mediated rearrangements of the CCR5-ZFN site, with 2.9, 4.9, and 4.6% CCR5 gene modification respectively (Fig. 9e). However, treatment of CD34+ cells with histone deacetylase inhibitors at the indicated concentrations causes also significant cell deaths (<20% viability). Lower concentrations of the inhibitors did not result in detectable CCR5 gene modification upon Ad.ZFN infection. A similar study was performed with iPS cells. Infection with Ad.ZFN and analysis of genomic DNA 2 days later revealed 1.3% and 1.2% CCR5 gene modification at MOIs 100 and 200 pfu/cell, respectively, in Dox induced cells (Fig. 9f). Ad.ZFN infection at higher MOIs was associated with severe cytotoxicity, most likely due to leaky expression of viral genes from first-generation vectors in transduced cells 55. Similar cytotoxicity was seen when iPS cells were infected with Ad5/35.GFP at equal MOIs. No CCR5 gene rearrangement was detectable if transduced cells were incubated without Dox. Exposure of iPS cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors resulted in >90% cell death. We also used a ChIP assay with antibodies specific to the FokI-endonuclease domain of the CCR5-ZFNs to measure ZFN binding to the CCR5-ZFN site (Fig. 9g). In this study we did not find a significant difference in FokI signals in Ad.GFP and Ad.ZFN infected iPS cells. This indicates that ZFN binding is inefficient and most likely blocked by inactive chromatin.
Figure 9. Ad.ZFN mediated rearrangements within the CCR5-ZFN site.
a) Schematic of Dox inducible expression CCR5-ZFN expression cassette in a first-generation Ad5/35 vector. b) Immunofluorescence analysis of ZFN expression. CD34+ cells were infected with Ad.ZFN at an MOI of 5 and stained for Fok I expression 48 hours later using FokI-specific antibodies (red). In the lower panel, cells were also stained with DAPI (blue) to visualize nuclei. c) HeLa-TZM-bl cells were infected with Ad.ZFN at MOI of 5 and 50 pfu/cell in the presence or absence of Dox. Cells were harvested 48 hours later. Left panel: Genomic DNA was subjected to a PCR assay based on the mismatch-sensitive Surveyor nuclease. PCR products were separated by PAA gel electrophoresis. Bands that correspond to rearranged CCR5 sites are marked by arrows. The numbers indicate the % of rearranged CCR5 alleles. Right panel: Flow cytometry for surface CCR5 was performed using anti-CCR5 monoclonal antibodies 2D7 (Becton Dickinson). Shown are representative data of cells infected at an MOI of 5 and 50 and incubated in the presence of Dox for 48 hours. d) Chromatin status of CCR5 site in CD34+ cells. CD34+ cells were incubated with either PBS or chromatin modifiers valproic acid (VPA) (1 mM) plus tichostatin A (TSA) (48ng/ml) for 24 hours and then analyzed by ChIP assay with GAPDH specific primers and primers specific to the CCR5-ZFN site, as well as additional amplified regions ~1 kb up- (u-ZFN) and 1 kb downstream (d-ZFN) of the ZNF site. The H3K9/14 acetylated marker was used to identify transcriptionally active/open chromatin regions. Values were expressed as a percentage of the original input values and normalized to their respective H3 values. Each treatment group was further expressed as a percentage of its respective GAPDH signal. (GAPDH=100%) N = 3 e) Ad.ZFN induced rearrangements in CD34+ cells incubated with chromatin modifiers. Cells were infected at an MOI of 100pfu/cell in the presence of Dox. TSA and and VPA concentrations were as in d). Sodium butyrate concentrations were 0.5 mM. f and g) Studies in iPS cells. We have performed the experiments in four iPS lines (FSHD83-6, FSHD43-1, OI12-4, and MHF2-C2) with similar outcomes. Shown are the data with FSHD43-1. f) Rearrangements within the CCR5-ZFN site. iPS cells were infected with Ad.ZFN at the indicated MOI in the presence or absence of Dox and genomic DNA was harvested 48 hours later and analyzed by Surveyor nuclease-based PCR assay. The numbers indicate the % of rearranged CCR5 alleles. g) ZFN occupancy of CCR5-ZFN site (left panel) and control-GAPDH site (right panel). IPS cells were infected with Ad5/35 vectors expressing GFP or CCR5 ZFN under the control of the ubiquitin promoter at an MOI of 20 pfu/cell. Chromatin was isolated 48 hours later and occupancy of selected sited by CCR5 ZFN was analyzed by ChIP assay using anti-Fok antibody. As before, the amplified ZFN region spans the zinc finger nuclease binding region and the amplified GAPDH region spans the GAPDH promoter region.
Discussion
The potential importance of chromatin structure for targeted transgene integration is illustrated by a study that showed that HIV integration frequency is associated with epigenetic modifications where strong positive associations were seen with markers of transcriptionally active chromatin, including H3K9/14Ac, H3 K4 mono-, di-, and tri-methylation, and H4 acetylation, and integration was negatively associated with H3 K27 tri-methylation, a histone mark known to be associated with heterochromatin 29. Furthermore, a recent study emphasized the critical influence of chromatin accessibility on binding of DNA interacting proteins, specifically glucocorticoid receptors 56. This study showed that the chromatin landscape of glucocorticoid receptor recognition sequences predetermines receptor binding and differential effects of corticosteroids on different cell types. We therefore speculated that chromatin will play a similar critical role on the binding/activity of DNA-sequence specific enzymes used for genome editing, e.g. ZFNs and Rep78.
The AAVS1 and CCR5-ZFN sites were chosen because they fulfill the criteria of a “safe harbor” for transgene integration. While the AAVS1 site is located in a ubiquitously expressed gene, the CCR5-ZFN site is within a gene whose expression is restricted to T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells and microglia. The transcriptional activity of any given gene, however, does not always predict its chromatin status. For instance, changes in the mRNA levels of the inducible egr-1 gene did not correlate with changes in either open chromatin marks, like di- and trimethylated H3 lysine 4 (H3K4m2 and H3K4m3), or closed chromatin marks, like histone H3 K27 40. The egr-1 mRNA levels did, however, correlate with some open histone marks, e.g. H3K9/14Ac, and Pol II presence. The chromatin status of the CCR5-ZFN and AAVS1 sites in iPS cells were therefore unknown. Pluripotent stem cells maintain a globally open chromatin state, possibly so that genes are readily available for activation during tissue specification 25. ES cells, for instance, have low levels of dense, compacted chromatin (heterochromatin) and the ES cell genome is transcriptionally hyperactive, with widespread transcription in both coding and noncoding regions, including sporadic low-level expression of tissue specific genes 25. In addition, a recent study showed that the distribution of repressive marks, e.g. H3K9m3, is significantly expanded in somatic cells relative to pluripotent stem cells 57.
Previous studies by Stadtfeld and colleagues showed that even minimal variables between clonal iPS cell lines can result in chromatin differences between lines 58. We therefore analyzed the chromatin structures in eight iPS cell lines as well as CD34+ and Mo7e cells. All the iPS cell lines stained positive for TRA-1-60 and SSEA-4, indicating that these cells remained fully reprogrammed in our feeder-free cultures with TeSR2 medium – a necessity as the chromatin from the feeders would interfere with the ChIP assays. Seven out of eight iPS cell lines had a normal karyotype. All lines contained two alleles of the CCR5 and AAVS1 site. Matrix ChIP analysis of the ZFN cleavage site in the CCR5 gene and the surrounding regions were indicative of a predominantly inactive chromatin configuration in iPS cells and peripheral blood CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. This is supported by the relatively high occupancy of H3K9m3 and the relatively low occupancy of H3K9/14Ac and Pol II. Furthermore, we found that the CCR5 gene is transcriptionally inactive in all iPS cell lines. In contrast, the AAVS1 site was within a transcriptionally active region and possessed an active chromatin configuration in both iPS cells and hematopoietic stem cells. Characteristic for this was the relatively low occupancy of the H3K9m3 marker and high occupancy of the H3K14Ac marker and Pol II. In agreement with our studies in stem cells, Lombardo et al. recently showed in untreated lymphoblastoid cells (cells which did not express CCR5) the presence of open histone marks around the AAVS1 site, whereas repressive histone marks were found around the CCR5-ZFN site 61. Lombardo’s and our study indicate that the target site for ZFNs must be located in a transcriptionally active gene or region that is not associated with closed chromatin.
To demonstrate that the AAVS1 site is readily accessible to site-specific endonucleases, we expressed Rep78 in iPS cells using first-generation Ad5/35 vectors and the ubiquitin promoter. Transgene expression was controlled by Dox to prevent interference of Rep78 and CCR5 ZFN with Ad replication/production in 293 cells. Ad transduction of iPS cell colonies was relatively inefficient due to undifferentiated iPS cells maintaining epithelial feature that created physical barriers for Ad vectors. The presence of epithelial features in iPS cells is not surprising as the reprogramming of somatic cells into iPS cells involves elements of a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition 47. All Ad transduction studies in iPS cells were therefore performed on single cell cultures in the presence of a ROCK inhibitor that supports the survival of iPS cells in a single cell state. Another problem associated with Ad-mediated gene transfer into both iPS and CD34+ cells is dose-dependent toxicity, which is most likely due to leaky expression of viral genes in cells transduced with first-generation Ad vectors 55, 62. Although, we showed Rep78 binding to the AAVS1 site in the context of intact chromatin as well as efficient Rep78-mediated AAVS1 site modification at day 2 after Ad.Rep78 infection, we were unable to obtain colonies from transduced iPS cells due to Ad-mediated toxicity. This problem also precluded potential transgene integration analyses upon co-infection with a transgene-donor Ad vector. These studies require the use of Dox-controlled helper-dependent-Ad5/35 vectors, i.e. vectors that are devoid of all viral genes, expressing Rep78 only for ashort time period.
In contrast to Rep78-mediated AAVS1 site modification, CCR5-ZFN site modification by ZFNs was inefficient in HSCs and iPS cells. We excluded the possibility that this is primarily due to the lack of i) Ad5/35 transduction, because a corresponding GFP vector allowed for transgene expression in >70% of iPS and CD34+ cells, ii) ZFN expression because ZFN was detected by immunofluorescence analyses, or iii) activity of ZFN, because the same vector resulted in efficient CCR5-ZFN site modification in HeLa-TZM-bl cells, i.e. cells in which the CCR5 gene is actively expressed and in which the ZFN site is open with regards to chromatin structure. A number of reasons could account for inefficient CCR5-ZFN site modification i) the ZFN expression level in CD34+ cells was not high enough to trigger efficient cleavage, ii) non-homologous end-joining repair mechanism/enzymes (required to repair the ZFN mediated DNA double strand break) are absent or not active in quiescent stem cells, and/or iii) the CCR5-ZFN site is not accessible to ZFN binding and/or cleavage. The latter speculation is supported by our ChIP studies, which revealed high occupancy of markers for inactive chromatin around the CCR5-ZFN cleavage site in CD34+ and iPS cells and inefficient binding of CCR5-ZFN in the context of native chromatin (see Figs. 5 and 9g). We have tried to address the problem of chromatin accessibility of the CCR5-ZFN site in stem cells by using chromatin-modifying drugs, but found, however, that a significant amount of cytotoxicity is associated with this approach. Histone-deacetylase inhibitors also act globally on the whole genome which most likely affects the phenotype of stem cells. The use of chromatin modifiers is therefore not a viable approach to achieve CCR5 knockout by ZFNs in stem cells.
Our conclusion that the CCR5-ZFN site is blocked by inactive chromatin in CD34+ cells is in conflict with a recent study reporting CCR5 gene disruption in fetal liver-derived CD34+ cells at a mean frequency of 17% after electroporation of cells with a plasmid expressing the ZFN under the control of the CMV promoter 10. At this point, we are unable to reconcile this conflict. It is possible that fetal liver derived CD34+ cells are more amenable to gene transfer and genome modification.
Overall, our study sheds light on chromatin-related problems of genome editing in stem cells and opens potential ways to address these problems.
Material and Methods
Cells
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM), Iscove’s modified Dulbecco’s medium (IMDM), and RPMI 1640 were purchased from Invitrogen. Fetal calf serum (FCS) was bought from HyClone. The HeLa-TZM-bl (TZM) cell line was obtained from the National Institutes of Health acquired immunodeficiency syndrome Research and Reagent Program and was maintained in DMEM, supplemented with 10% FCS, 2 mM L-glutamine, and 1X penicillin–streptomycin solution (Pen-Strep) (Invitrogen). Mo7e cells 63 were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% FCS, 2 mM L-glutamine, Pen-Strep, and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (0.1 ng/ml) (Amgen). Primary human CD34+-enriched cells were obtained from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. CD34+ cells were recovered from frozen stocks and incubated overnight in IMDM, supplemented with 20% FCS, 0.1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, stem cell factor (50 ng/ml), DNase I (100 μg/ml), 2 mM L-glutamine, Flt3 ligand (Flt3L, 50 ng/ml), interleukin (IL)-3 (10 U/ml), and thrombopoietin (10 ng/ml).
All iPS cell lines were grown in TeSR™2 (StemCell Technologies) on matrigel (BD Biosciences) coated dishes and passaged as needed. The creation of the three iPS-MHF2 cell lines, the three iPS-OI12 cell lines, the iPS-M83-9 cell line, and the two iPS-FSHD cell lines were described elsewhere 32, 34–36.
Immunofluorescence analyses
Cells were grown with TeSR™2 medium on coverslips coated with matrigel before being fixed with cold acetone:methanol (1:1 v/v) for 15 min at room temperature (RT). The cells were permeabilized for antibody staining with 0.1% Trition X-100, incubated for 5 min at RT, and washed twice with PBS. Blocking occurred with 2% non-fat dry milk for 20 min at RT. Samples were incubated with the primary antibody, either the mouse anti-human TRA-1-60 or the mouse anti-SSEA-4 (BD Pharmingen) at a dilution of 1:50 for 1 hour at RT prior to washing with PBS. Samples were incubated with their corresponding secondary antibody, goat anti-mouse alexafluor 488 for the TRA-1-60 staining and goat anti-mouse alexafluor 568 for the SSEA-4 staining (both from Invitrogen), at a dilution of 1:200 for a periodof 30 min at RT. In addition, the following antibodies were used for analysis of iPS cells: FITC-conjugated anti-E-cadherin (Abcam, Cambridge, MA), mouse monoclonal anti-N-cadherin (Gene Tex, Inc, Irvine, CA), mouse monoclonal anti-α-tubulin (Sigma), goat anti-Tie2 (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, goat-anti-DSG2 (R&D Systems), and mouse monoclonal anti-CAR (RmcB) (ATCC). Samples were washed again and counterstained with DAPI before being mounted on the slides with Vectastain mounting solution (Vector Labs).
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
The fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) procedure utilized two probes: the Satellite probe for chromosome 3 (Cytocell Technology) targeted at chromosome region 3p11.1-q11.1, and the AAVS1 FISH probe which was made with the Nick Translation Kit (Abbott Molecular Inc.) in combination with green dUTP (Abbott Molecular Inc.) according to the manufacturer’s specifications, using the plasmid DNA from a human BAC clone (RP11-463M24) containing the AAVS1 and surrounding sequences, as template 24. Cells were cultured and were, upon reaching approximately 70% confluence, incubated in the presence of 100 ng/ml colcemid (Invitrogen) for a period of 3 hours before being harvested and washed twice with PBS. Cells were gently resuspended in 75 mM KCl and incubated for 15 min at 37 °C. Samples were centrifuged and the supernatant removed before resuspending the cells in ice cold fixative (3:1 v:v methanol:glacial acetic acid). Samples were washed three times with the cold fixative before finally being stored at 4 °C at approximately 5×106 cells/ml of the fixative. Of this cell suspension, 10 μl was dropped from 6 inches high unto a clean microscope slide and air dried before the sample was dehydrated by 5 min incubation in an EtOH series (70%, 90% and 100%) and air dried. 2 μl of each probe diluted with 6 μl In Situ Hybridization Buffer (Enzo Life Science, Inc) was added to each slide, covered with a coverslip and sealed. Samples were denatured at 75 °C for 2 min on a hotplate before being incubated in a humidity chamber at 37 °C overnight. Subsequent to incubation, the coverslip was removed and the slide washed with pre-warmed 0.25xSSC at 72 °C for 2 min. Samples were washed with 2xSSC containing 0.05% Tween20 (Fisher Scientific) at RT for 30 seconds. Samples were air dried and counterstained with DAPI before being mounted on the slides with Vectastain mounting solution. Photographs were taken with a Leica DFC300FX digital camera using a 100x oil lens.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
Approximately 5×106 cells were washed with PBS before cross-linking by the addition of formaldehyde to a final concentration of 1.0% for 15 minutes at room temperature with gentle agitation before the addition of glycine to a final concentration of 125 mM and incubation for another 5 min. Samples were harvested and centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 3 min, 4°C and the supernatant removed. Cells were washed twice with PBS containing 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin (BSA) before being resuspended in immunoprecipitation (IP) buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 5 mM EDTA, NP-40 (0.5% v/v), Triton X-100 (1.0% v/v), with the addition of Protease Inhibitor Cocktail III (Calbiochem). Cells were sonicated using a Bioruptor (Diagenode) for 30 min at 4°C on the high setting. Samples were centrifuged for 10 min at 10 000 rpm at 4 °C and the supernatant collected, aliquoted, and frozen in liquid nitrogen.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed in 96-well plates as previously described 39. The following antibodies were utilized in this procedure at 1 μg/well: rabbit polyclonal histone H3 antibody (H3) (Abcam #ab1791), rabbit polyclonal histone H3 tri methyl K9 antibody (H3K9m3) (Abcam #ab8898), mouse monoclonal histone H3 tri methyl K27 antibody (H3K27m3) (Abcam #ab6002), rabbit polyclonal anti-acetyl-histone H3 (H3K9/14Ac) (Upstate #06-599), mouse monoclonal to Pol II CTD (4H8) (Santa Cruz # sc-47701), rabbit polyclonal anti-Rep78 (N208 antibody clone MSMC111)(provided by Dr. Linden, Oxford Univ.) 64, and a rabbit polyclonal anti-Rep78 provided by Dr. Trempe (NIDDK) 65.
Surveyor nuclease assay
This assay is based on the “Surveyor mutation detection kit” (Transgenomic). This assay efficiently and specifically cleaves DNA duplexes at the sites of distortions created by either bulges or mismatches. The assay is sensitive enough to detect single-nucleotide changes induced by NHEJ and has a detection limit of ~1%. The detailed protocol is described elsewhere 54.
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)
qPCR was performed in triplicate with an ABI 7900 instrument (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) in 384-well plates. All the primers used for the qPCR of ChIP samples are listed in Fig. 4. 2.7 μl of template DNA recovered from ChIP was supplemented with 200 nM primers, 2X Kappa MasterMix (Kappa Biosystems, Woburn, MA), and 5X Enhancer to a total reaction volume of 6.2 μl. Specificity of the reaction was assessed by inspection of the denaturation curves obtained from the PCR instrument.
RNA isolation, reverse transcription and qPCR
Extraction of mRNA from cells was performed according to the Qiagen RNAeasy kit protocol. RNA samples were frozen at −20°C or processed directly for Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR). All primers used for qPCR are listed in Table 1. qPCR was performed in an ABI 7900 instrument in 384-well plates in triplicates. 2 μl Template cDNA was supplemented 7.5 μl SYBR green 2x MasterMix (Quantace), 200 nM primers, and water to a total reaction volume of 15 μl. Specificity of the reaction was assessed by inspection of dissociation curves obtained from the PCR instrument.
Karyotyping
iPS cells were grown for four passages on matrigel before being karyotyped by the Department of Pathology, Cytogenetics and Genomics Division at the University of Washington (Seattle, WA).
Adenovirus vectors
All Ad vectors used in this study are deleted for E1 and E3 and contain Ad35 fibers 44. Ad.CMV-GFP and Ad.Ub-GFP contain the CMV and ubiquitin promoter, respectively. The Doxycycline (Dox) inducible vectors for Rep78 and CCR5 ZFN expression (Ad.Rep and Ad.ZFN contained a fusion between the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) domain and the tetracycline repressor (TetR). In this system, tTR-KRAB-mediated repression of a heterologous promoter, juxtaposed to Tet operator sequences can be reversibly controlled by Doxycycline 52. The Ub promoter and the Rep78 gene were synthesized by DNA 2.0 (Menlo Park, CA). The expression cassette was inserted into the BamHI/EcoRV site of pHVAd2 66. The CCR5 ZFN genes were obtained by PCR from pVax-8267-ELD/2A/8196z-KKR 14. The expression cassettes were inserted into the BamHI/EcoRV site of pHVAd2 66. Ad.GFP contains the GFP gene instead of the Rep78 or ZFN genes. Ad5/35 virus vectors were generated and tested as described elsewhere 44.
Transduction of iPS cells
iPS cell line FSHD43-1 was divided with accutase (StemCell Technologies) and seeded as single cells on matrigel coated dishes in TeSR™2 medium containing 10 μM of an inhibitor of Rho-associated protein kinase, Y-27632 dihydrochloride (Tocris Bioscience), for a period of 24 hours. Subsequent to this, cells were counted and infected with an Ad vector at the appropriate multiplicity of infection (MOI) and incubated for a further 48 hours prior to analyses.
Treatment with histone deacetylase inhibitors
CD34+ cells were incubated for a period of 48 hours with histone deacytelase (HDAC) inhibitors; either 1 mM sodium butyrate (NaBu) (Sigma-Aldrich), or 2 mM valproic acid sodium salt (VPA) (Sigma-Aldrich) with 80 nM trichostatin A (Sigma-Aldrich), prior to fixing for ChIP assay.
Western blot
Cultured cells were washed twice with ice-cold PBS and then lysed on ice for 30 min in protein lysis buffer [20 mM Hepes (pH 7.5), 2 mM EDTA, 10% glycine, 1% TritonX100, 150 mM NaCl (all from Sigma-Aldrich), and protease inhibitors (Complete Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Roche)]. Samples were pelleted (10 min, 4 °C, 15,000 RPM, and the protein containing supernatant stored at −80 °C. A total of 15 μg of total protein was used for the Western blot procedure. Protein samples were boiled (5 min at 95 °C) and separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) using 4–15% gradient gels (BioRad), followed by transfer onto nitrocellulose membranes according to the supplier’s protocol (Mini ProteanIII, BioRad). Membranes were blocked in PBS containing 0.1% Tween20 (PBS-T, Sigma) and 5% dry milk powder. Incubation times for primary and secondary antibodies were 2 hours and 1 hour at room temperature, respectively. Rabbit polyclonal anti-Rep78 65 antibody was diluted 1:200 in PBS-T and 2% dry-milk powder. Membranes were washed 5 times in PBS-T between antibody incubations, and films were developed using ECL plus (Amersham).
Southern blot
Total cellular DNA was extracted from cultured cells by pronase digestion followed by phenol/chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation. 15 μg of total DNA was subjected to Southern blot analysis as described before 67. 32P-labeled DNA probes were used for hybridization. The AAVS1 probe was a 1.6 kb EcoRI/BamHI fragment from pRE2 68. The HPRT1 probe has been described previously 69.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH grants R21HL094994 (AL), R01 HLA078836 (AL), R01CA136487 (AL), R01CA141018 (KB), R01DK083310 (KB), R37DK45978 (KB), and NIH/NIDDK DK grant R37-45978. We thank Drs. Linden and Trempe for providing Rep78 antibodies. We a grateful to Carol Ware and the members of the Ellison Stem Cell Core Laboratory of the Institute of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Voigt K, Izsvak Z, Ivics Z. Targeted gene insertion for molecular medicine. J Mol Med. 2008;86 (11):1205–19. doi: 10.1007/s00109-008-0381-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kramer O, Klausing S, Noll T. Methods in mammalian cell line engineering: from random mutagenesis to sequence-specific approaches. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2798-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Miller DG, Petek LM, Russell DW. Adeno-associated virus vectors integrate at chromosome breakage sites. Nat Genet. 2004;36(7):767–73. doi: 10.1038/ng1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Li H, Haurigot V, Doyon Y, Li T, Wong SY, Bhagwat AS, et al. In vivo genome editing restores haemostasis in a mouse model of haemophilia. Nature. 2011;475(7355):217–21. doi: 10.1038/nature10177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lombardo A, Genovese P, Beausejour CM, Colleoni S, Lee YL, Kim KA, et al. Gene editing in human stem cells using zinc finger nucleases and integrase-defective lentiviral vector delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(11):1298–306. doi: 10.1038/nbt1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang H, Lieber A. A helper-dependent capsid-modified adenovirus vector expressing adeno-associated virus rep78 mediates site-specific integration of a 27-kilobase transgene cassette. J Virol. 2006;80(23):11699–709. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00779-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang H, Shayakhmetov DM, Leege T, Harkey M, Li Q, Papayannopoulou T, et al. A capsid-modified helper-dependent adenovirus vector containing the beta-globin locus control region displays a nonrandom integration pattern and allows stable, erythroid-specific gene expression. J Virol. 2005;79(17):10999–1013. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.10999-11013.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Recchia A, Perani L, Sartori D, Olgiati C, Mavilio F. Site-specific integration of functional transgenes into the human genome by adeno/AAV hybrid vectors. Mol Ther. 2004;10(4):660–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Suzuki K, Mitsui K, Aizawa E, Hasegawa K, Kawase E, Yamagishi T, et al. Highly efficient transient gene expression and gene targeting in primate embryonic stem cells with helper-dependent adenoviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37):13781–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806976105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Holt N, Wang J, Kim K, Friedman G, Wang X, Taupin V, et al. Human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells modified by zinc-finger nucleases targeted to CCR5 control HIV-1 in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(8):839–47. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hockemeyer D, Wang H, Kiani S, Lai CS, Gao Q, Cassady JP, et al. Genetic engineering of human pluripotent cells using TALE nucleases. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(8):731–4. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liu R, Paxton WA, Choe S, Ceradini D, Martin SR, Horuk R, et al. Homozygous defect in HIV-1 coreceptor accounts for resistance of some multiply-exposed individuals to HIV-1 infection. Cell. 1996;86(3):367–77. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hutter G, Nowak D, Mossner M, Ganepola S, Mussig A, Allers K, et al. Long-term control of HIV by CCR5 Delta32/Delta32 stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(7):692–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0802905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Perez EE, Wang J, Miller JC, Jouvenot Y, Kim KA, Liu O, et al. Establishment of HIV-1 resistance in CD4+ T cells by genome editing using zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(7):808–16. doi: 10.1038/nbt1410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Benabdallah BF, Allard E, Yao S, Friedman G, Gregory PD, Eliopoulos N, et al. Targeted gene addition to human mesenchymal stromal cells as a cell-based plasma-soluble protein delivery platform. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(3):394–9. doi: 10.3109/14653240903583803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kandavelou K, Ramalingam S, London V, Mani M, Wu J, Alexeev V, et al. Targeted manipulation of mammalian genomes using designed zinc finger nucleases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;388(1):56–61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.07.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kim HJ, Lee HJ, Kim H, Cho SW, Kim JS. Targeted genome editing in human cells with zinc finger nucleases constructed via modular assembly. Genome Res. 2009;19(7):1279–88. doi: 10.1101/gr.089417.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kotin RM, Linden RM, Berns KI. Characterization of a preferred site on human chromosome 19q for integration of adeno-associated virus DNA by non-homologous recombination. EMBO J. 1992;11 (13):5071–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Smith JR, Maguire S, Davis LA, Alexander M, Yang F, Chandran S, et al. Robust, persistent transgene expression in human embryonic stem cells is achieved with AAVS1-targeted integration. Stem Cells. 2008;26(2):496–504. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hockemeyer D, Soldner F, Beard C, Gao Q, Mitalipova M, DeKelver RC, et al. Efficient targeting of expressed and silent genes in human ESCs and iPSCs using zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27(9):851–7. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Henckaerts E, Dutheil N, Zeltner N, Kattman S, Kohlbrenner E, Ward P, et al. Site-specific integration of adeno-associated virus involves partial duplication of the target locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U SA. 2009;106(18):7571–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806821106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Meneses P, Berns KI, Winocour E. DNA sequence motifs which direct adeno-associated virus site-specific integration in a model system. J Virol. 2000;74(13):6213–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.13.6213-6216.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cortes ML, Oehmig A, Saydam O, Sanford JD, Perry KF, Fraefel C, et al. Targeted integration of functional human ATM cDNA into genome mediated by HSV/AAV hybrid amplicon vector. Mol Ther. 2008;16(1):81–8. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Howden SE, Voullaire L, Wardan H, Williamson R, Vadolas J. Site-specific, Rep-mediated integration of the intact beta-globin locus in the human erythroleukaemic cell line K562. Gene Ther. 2008;15(20):1372–83. doi: 10.1038/gt.2008.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Efroni S, Duttagupta R, Cheng J, Dehghani H, Hoeppner DJ, Dash C, et al. Global transcription in pluripotent embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(5):437–47. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.03.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Meshorer E, Yellajoshula D, George E, Scambler PJ, Brown DT, Misteli T. Hyperdynamic plasticity of chromatin proteins in pluripotent embryonic stem cells. Dev Cell. 2006;10(1):105–16. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.10.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Carter MG, Sharov AA, VanBuren V, Dudekula DB, Carmack CE, Nelson C, et al. Transcript copy number estimation using a mouse whole-genome oligonucleotide microarray. Genome Biol. 2005;6(7):R61. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-7-r61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gaspar-Maia A, Alajem A, Polesso F, Sridharan R, Mason MJ, Heidersbach A, et al. Chd1 regulates open chromatin and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2009;460(7257):863–8. doi: 10.1038/nature08212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang GP, Ciuffi A, Leipzig J, Berry CC, Bushman FD. HIV integration site selection: analysis by massively parallel pyrosequencing reveals association with epigenetic modifications. Genome Res. 2007;17(8):1186–94. doi: 10.1101/gr.6286907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huser D, Gogol-Doring A, Lutter T, Weger S, Winter K, Hammer EM, et al. Integration preferences of wildtype AAV-2 for consensus rep-binding sites at numerous loci in the human genome. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6(7):e1000985. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Djuric U, Ellis J. Epigenetics of induced pluripotency, the seven-headed dragon. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(1):3. doi: 10.1186/scrt3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chamberlain JR, Deyle DR, Schwarze U, Wang P, Hirata RK, Li Y, et al. Gene targeting of mutant COL1A2 alleles in mesenchymal stem cells from individuals with osteogenesis imperfecta. Mol Ther. 2008;16(1):187–93. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Deyle DR, Khan IF, Raen G, Wang P, Kho J, Schwarze U, et al. Normal Collagen and Bone Production by Gene-Targeted Human Osteogenesis Imperfecta iPSCs. Molecular Therapy. 2011 doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.209. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Snider L, Geng LN, Lemmers RJ, Kyba M, Ware CB, Nelson AM, et al. Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy: incomplete suppression of a retrotransposed gene. PLoS Genet. 2010;6(10):e1001181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stadler B, Ivanovska I, Mehta K, Song S, Nelson A, Tan Y, et al. Characterization of microRNAs involved in embryonic stem cell states. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(7):935–50. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chang KH, Huang A, Hirata RK, Wang PR, Russell DW, Papayannopoulou T. Globin phenotype of erythroid cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Blood. 2010;115(12):2553–4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-252650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chan EM, Ratanasirintrawoot S, Park IH, Manos PD, Loh YH, Huo H, et al. Live cell imaging distinguishes bona fide human iPS cells from partially reprogrammed cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27 (11):1033–7. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lieberman PM. Chromatin regulation of virus infection. Trends Microbiol. 2006;14(3):132–40. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Flanagin S, Nelson JD, Castner DG, Denisenko O, Bomsztyk K. Microplate-based chromatin immunoprecipitation method, Matrix ChIP: a platform to study signaling of complex genomic events. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(3):e17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nelson JD, Denisenko O, Bomsztyk K. Protocol for the fast chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) method. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(1):179–85. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Taylor JA, Vojtech L, Bahner I, Kohn DB, Laer DV, Russell DW, et al. Foamy virus vectors expressing anti-HIV transgenes efficiently block HIV-1 replication. Mol Ther. 2008;16(1):46–51. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dutheil N, Henckaerts E, Kohlbrenner E, Linden RM. Transcriptional analysis of the adeno-associated virus integration site. J Virol. 2009;83(23):12512–25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01754-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tuve S, Wang H, Ware C, Liu Y, Gaggar A, Bernt K, et al. A new group B adenovirus receptor is expressed at high levels on human stem and tumor cells. J Virol. 2006;80(24):12109–20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01370-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shayakhmetov DM, Papayannopoulou T, Stamatoyannopoulos G, Lieber A. Efficient gene transfer into human CD34(+) cells by a retargeted adenovirus vector. J Virol. 2000;74(6):2567–83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.6.2567-2583.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tashiro K, Kawabata K, Inamura M, Takayama K, Furukawa N, Sakurai F, et al. Adenovirus vector-mediated efficient transduction into human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Reprogram. 2010;12(5):501–7. doi: 10.1089/cell.2010.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rufaihah AJ, Huang NF, Jame S, Lee J, Nguyen HN, Byers B, et al. Endothelial Cells Derived From Human iPSCS Increase Capillary Density and Improve Perfusion in A Mouse Model of Peripheral Arterial Disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.230938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Golipour A, David L, Sung H-k, Beyer TA, Datti A, et al. Functional Genomics Reveals a BMP-Driven Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition in the Initiation of Somatic Cell Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(1):64–77. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang H, Li ZY, Liu Y, Persson J, Beyer I, Moller T, et al. Desmoglein 2 is a receptor for adenovirus serotypes 3, 7, 11 and 14. Nat Med. 2011;17(1):96–104. doi: 10.1038/nm.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ohgushi M, Matsumura M, Eiraku M, Murakami K, Aramaki T, Nishiyama A, et al. Molecular pathway and cell state responsible for dissociation-induced apoptosis in human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(2):225–39. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Casto BC, Armstrong JA, Atchison RW, Hammon WM. Studies on the relationship between adeno-associated virus type 1 (AAV-1) and adenoviruses. II. Inhibition of adenovirus plaques by AAV; its nature and specificity. Virology. 1967;33(3):452–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Moosmann P, Georgiev O, Thiesen HJ, Hagmann M, Schaffner W. Silencing of RNA polymerases II and III-dependent transcription by the KRAB protein domain of KOX1, a Kruppel-type zinc finger factor. Biol Chem. 1997;378(7):669–77. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1997.378.7.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Szulc J, Wiznerowicz M, Sauvain MO, Trono D, Aebischer P. A versatile tool for conditional gene expression and knockdown. Nat Methods. 2006;3(2):109–16. doi: 10.1038/nmeth846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Drew HR, Lockett LJ, Both GW. Increased complexity of wild-type adeno-associated virus-chromosomal junctions as determined by analysis of unselected cellular genomes. J Gen Virol. 2007;88(Pt 6):1722–32. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.82880-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Miller JC, Holmes MC, Wang J, Guschin DY, Lee YL, Rupniewski I, et al. An improved zinc-finger nuclease architecture for highly specific genome editing. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(7):778–85. doi: 10.1038/nbt1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shimizu K, Sakurai F, Machitani M, Katayama K, Mizuguchi H. Quantitative analysis of the leaky expression of adenovirus genes in cells transduced with a replication-incompetent adenovirus vector. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(4):1430–5. doi: 10.1021/mp200121z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.John S, Sabo PJ, Thurman RE, Sung MH, Biddie SC, Johnson TA, et al. Chromatin accessibility predetermines glucocorticoid receptor binding patterns. Nat Genet. 2011;43(3):264–8. doi: 10.1038/ng.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hawkins RD, Hon GC, Lee LK, Ngo Q, Lister R, Pelizzola M, et al. Distinct epigenomic landscapes of pluripotent and lineage-committed human cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6(5):479–91. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Stadtfeld M, Hochedlinger K. Induced pluripotency: history, mechanisms, and applications. Genes Dev. 2010;24(20):2239–63. doi: 10.1101/gad.1963910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kolasinska-Zwierz P, Down T, Latorre I, Liu T, Liu XS, Ahringer J. Differential chromatin marking of introns and expressed exons by H3K36me3. Nat Genet. 2009;41(3):376–81. doi: 10.1038/ng.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Barrand S, Andersen IS, Collas P. Promoter-exon relationship of H3 lysine 9, 27, 36 and 79 methylation on pluripotency-associated genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;401(4):611–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.09.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lombardo A, Cesana D, Genovese P, Di Stefano B, Provasi E, Colombo DF, et al. Site-specific integration and tailoring of cassette design for sustainable gene transfer. Nat Methods. 2011 doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lieber A, He CY, Kirillova I, Kay MA. Recombinant adenoviruses with large deletions generated by Cre-mediated excision exhibit different biological properties compared with first-generation vectors in vitro and in vivo. J Virol. 1996;70(12):8944–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.12.8944-8960.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Avanzi GC, Lista P, Giovinazzo B, Miniero R, Saglio G, Benetton G, et al. Selective growth response to IL-3 of a human leukaemic cell line with megakaryoblastic features. Br J Haematol. 1988;69 (3):359–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yoon-Robarts M, Linden RM. Identification of active site residues of the adeno-associated virus type 2 Rep endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(7):4912–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209750200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Trempe JP, Mendelson E, Carter BJ. Characterization of adeno-associated virus rep proteins in human cells by antibodies raised against rep expressed in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1987;161(1):18–28. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Shayakhmetov DM, Lieber A. Dependence of adenovirus infectivity on length of the fiber shaft domain. J Virol. 2000;74(22):10274–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10274-10286.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wang H, Shayakhmetov DM, Leege T, Harkey M, Li Q, Papayannopoulou T, et al. A Capsid-Modified Helper-Dependent Adenovirus Vector Containing the {beta}-Globin Locus Control Region Displays a Nonrandom Integration Pattern and Allows Stable, Erythroid-Specific Gene Expression. J Virol. 2005;79(17):10999–1013. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.10999-11013.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Samulski RJ, Zhu X, Xiao X, Brook JD, Housman DE, Epstein N, et al. Targeted integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) into human chromosome 19 [published erratum appears in EMBO J 1992 Mar;11(3):1228] Embo J. 1991;10(12):3941–50. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Khan IF, Hirata RK, Wang PR, Li Y, Kho J, Nelson A, et al. Engineering of human pluripotent stem cells by AAV-mediated gene targeting. Mol Ther. 2010;18(6):1192–9. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]