Abstract
A central goal of electronics based on correlated materials or ‘Mottronics’ is the ability to switch between distinct collective states with a control voltage. Small changes in structure and charge density near a transition can tip the balance between competing phases, leading to dramatic changes in electronic and magnetic properties. In this work, we demonstrate that an electric field induced two-step ferroelastic switching pathway in (011) oriented 0.71Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.29PbTiO3 (PMN-PT) substrates can be used to tune the Verwey metal-insulator transition in epitaxial Fe3O4 films in a stable and reversible manner. We also observe robust non-volatile resistance switching in Fe3O4 up to room temperature, driven by ferroelastic strain. These results provides a framework for realizing non-volatile and reversible tuning of order parameters coupled to lattice-strain in epitaxial oxide heterostructures over a broad range of temperatures, with potential device applications.
The central challenge in realizing electronics based on strongly correlated materials, or ‘Mottronics’1, is the ability to switch between distinct electronic and magnetic phases with a control voltage. These phases include correlated insulators and various magnetic states that result from strong electron-electron and electron-lattice interactions. Small changes in structure and charge density near a transition between competing phases can tip the balance among them, leading to large changes in electronic and magnetic properties. Devices based upon such transitions could be, in principle, both fast and energy efficient2, overcome some of the intrinsic limitations in conventional field-effect transistors3 and also provide new functionalities4,5,6. Approaches based upon the electrostatic field-effect are thought to require gate-induced charge densities in excess of 11014 carriers/cm2, too high for conventional dielectrics. In recent years, this challenge has been addressed using ferroelectric7 and ionic liquid dielectrics8,9, though in the latter electrochemical effects can play a very important role10. In principle, electrostatic gating only affects a region comparable to the Thomas Fermi/Debye screening length near the interface of the gated material with the dielectric. On the other hand, epitaxial strain imposed by a substrate can be used to tune the properties of a thin film through its entire thickness. Notably, this has been used to realize novel multiferroicity in EuTiO311,12, manipulate the metal-insulator transition in perovskite manganites13,14,15, change ferroelectric and ferromagnetic transition temperatures16,17,18,19,20,21 and enable flexoelectric rotation of polarization in PbTiO322. In these systems, a single control parameter - in-plane epitaxial strain - is used to control lattice-spin, lattice-phonon, and lattice-charge interactions to tailor properties or realize new magnetic/electronic phases. While these experiments point to a pathway for creating novel functionalities, reversible and non-volatile switching between different phases using strain has remained largely unexplored. In non-volatile switching, the electronic/magnetic states that are realized remain in a stable remnant state after the control voltage has been switched off. Furthermore, for memory applications, we need to be able to switch between these different states in a reversible manner. One of the most promising approaches for in-situ manipulation of lattice-coupled order parameters is to grow oxide films on ferroelectric/piezoelectric substrates21,23,24,25,26,27. Application of electric fields in these structures induces changes in the substrate lattice parameters, resulting in changes in the properties of the film. This has been demonstrated, for example, in La0.7Sr0.3MnO3/BaTiO325, La0.7Sr0.3CoO3/PMN-PT(001)28, and La0.7Ca0.15Sr0.15MnO3/PMN-PT(001) heterostructures29 (here, PMN-PT is an alloy of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3 (71%) and PbTiO3 (29%), and has a very large piezo response). However, in these studies non-volatile and reversible switching could not be demonstrated since the strain resulting from a piezo response decays upon removal of the control voltage, and in a purely ferroelectric reversal the strain states in the two stable polarization directions are equivalent. In our work, we use a unique ferroelastic30 switching pathway in (011) oriented PMN-PT, that allows polarization vectors to rotate from an out-of-plane to a purely in-plane direction to produce two distinct, non-volatile and reversible lattice strain states31. Using these two strain states, we demonstrate electric-field control of the Verwey metal-insulator transition, and non-volatile reversible resistive switching in epitaxial Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) heterostructures over a broad range of temperatures.
Magnetite is a conducting spin-polarized ferrimagnet with resistivity > 1 mΩ-cm at 300 K32. It undergoes a Verwey metal-insulator transition as the temperature drops below TV = 125 K, with an abrupt increase in resistivity by 2–3 orders of magnitude and a slight decrease in magnetic moment32. This transition is associated with a symmetry lowering structural transition from cubic inverse-spinel to monoclinic, and is therefore greatly sensitive to lattice or structural changes. The mechanism behind the Verwey transition is the subject of a long-standing debate between charge ordering (‘Wigner crystal’) of the Fe2+/Fe3+ cations on the octahedral sites and structural/orbital ordering, and remains an active area of research33. The transition may be suppressed with hydrostatic pressure in bulk single crystalline magnetite34, where metallization35 and subtle structural and spin-state transitions36 have been observed at low temperatures and pressures above 6 GPa. However this approach requires a large volume change induced by mechanical force, which may not be suited for device applications. In this work, we grow epitaxial Fe3O4 films on (011) oriented PMN-PT substrates. Through ferroelastic control of lattice strain, we suppressed the Verwey metal-insulator transition by up to 8 K, evidenced by large changes in resistivity, magnetization and magnetoresistance. Further, we address a critical requirement for device applications with the discovery of a reversible and non-volatile ferroelastic strain induced resistance switching in Fe3O4 that persists up to room temperature. Our approach offers new possibilities for novel electronic devices, frequency-agile microwave applications and practical realizations of non-volatile memories37,38,39,40,41,42.
Results
Ferroelastic control of the Verwey transition in epitaxial Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011)
A key aspect of our study is the ability to grow epitaxial Fe3O4 films with a sharp Verwey transition on (011) oriented PMN-PT substrates by ozone-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. The growth conditions were refined by depositing epitaxial Fe3O4 films on MgO (001), MgAl2O4 (001), PMN-PT (001), and PMN-PT (011) substrates and carrying out detailed structural, magnetic and electrical characterization (Fig S1–S4). The thicknesses of all films were determined to be around 55 nm by fitting to x-ray reflectivity spectra. A well-defined Verwey transition was observed in Fe3O4 films on all substrates as determined by resistivity and magnetization measurements (Fig. 1, Figs. S3,S4).
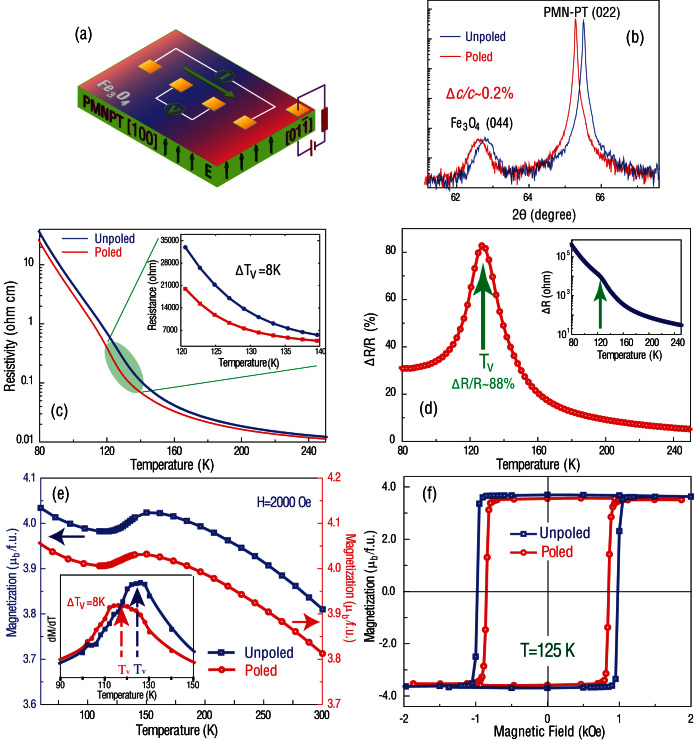
Figure 1. Ferroelastic strain control of Verwey metal-insulator transition in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011).
(a) Schematics of four-point resistance measurement. (b) X-ray diffraction patterns of Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) under unpoled and poled states. (c) Ferroelastic strain state dependence of resistivity as a function of temperature for (011) oriented Fe3O4/PMN-PT. (d) Relative resistance change at a function of temperature. The insets are absolute value of resistance change. (e) Magnetic moment as a function of temperature for poled and unpoled Fe3O4/PMN-PT(011). Inset shows the first derivative. (f) Magnetic hysteresis loops at Verwey temperature.
In order to explore ferroelastic tuning of Fe3O4 on PMN-PT (011), the electronic transport properties of magnetite were first studied under two distinct electric-field induced polarization states of the substrate. They are the initial or unpoled state denoted by P0, and the poled remnant state denoted by Pr. Figure 1(a) shows the schematic of the experimental setup. The film resistance was measured by a four-probe technique. Poling PMN-PT(011) was achieved by applying an electric field in the (011) direction, using the Fe3O4 film as the top electrode and a sputtered gold film as the bottom electrode. The top electrode was always held at ground when the poling voltage was applied.
We carried out in situ x-ray diffraction measurements on Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) heterostructures in the unpoled and poled strain states as shown in Fig. 1(b). An expansion along the out-of-plane direction associated with an effective in-plane contraction was observed as the Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) was poled. The enhanced out-of-plane lattice parameters of PMN-PT(011) and Fe3O4 are visible as a shift of Δc/c = + 0.26% and + 0.20% respectively. This difference results presumably from different Poisson's ratios of the two materials. The strain state dependence of lattice parameter in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) indicates that an electric-field-induced ferroelastic strain can be coherently transferred to the film, influencing magnetic and transport properties as discussed below.
Figure 1(c) shows the temperature dependence of the resistivity in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) under unpoled P0 and poled Pr states (note logarithmic scale for resistivity). At P0 state (blue curve), the resistivity of the film increases with reducing temperature and undergoes a metal-insulator transition at Tv = 125 K. Once the sample is poled with a DC field of 10 kV/cm, the resistivity decreases dramatically over a broad temperature range, with a visible reduction in the Verwey temperature of ~ 8 K. The large resistance change is more clearly visible in the inset of Fig. 2(c) (linear scale for resistivity). Our results reveal that an in-plane compressive strain in the poled Pr state inhibits the Verwey transition and decreases TV. Using the measured Δc/c of 0.2% and Poisson's ratio for Fe3O4, we calculated the volume change produced by in-plane strain in Fe3O4 films to be 0.3% ~ 0.4% (Fig. S5). In previous studies30 of the effects of hydrostatic pressure on bulk magnetite, an order of magnitude higher volume change of ~ 3% was required to produce an equivalent suppression of TV by ~ 8 K. Thus, electrically modulating the in-plane epitaxial strain is far more effective in manipulating the Verwey transition than would be expected from a pure volume change argument (Calculation details in Supplementary).
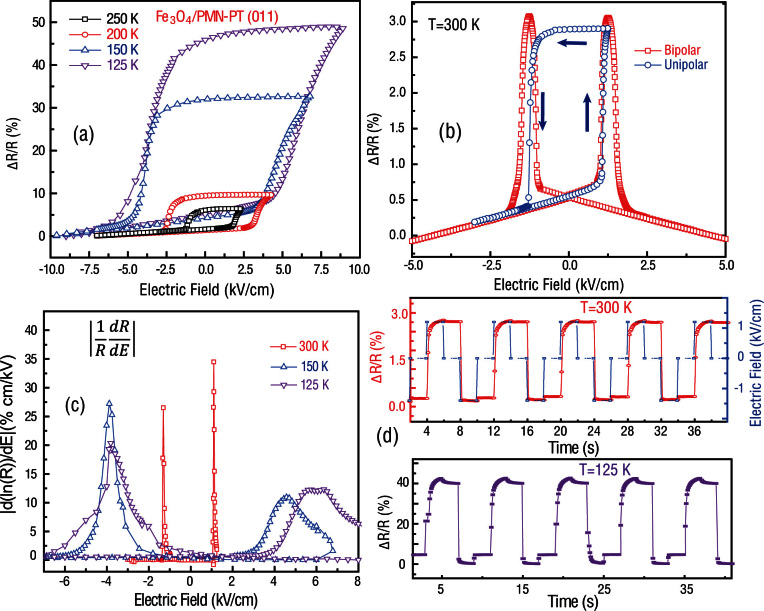
Figure 2. Non-volatile ferroelastic switching of resistivity in in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011).
(a) Resistance hysteresis loops at various temperatures. (b) Resistance response of Fe3O4/PMN-PT(011) under unipolar and bipolar sweeping of electric fields at room temperature. (c) The absolute value of the first derivative of the unipolar hysteretic resistance loop with electric field, as a function of electric field. (d) Electric-field-induced non-volatile resistance switching at T = 300 K and T = 125 K.
Figure 1(d) shows the relative resistance change between the poled and unpoled polarization states, defined as 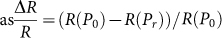 . Upon decreasing temperature, ΔR increases continuously from ~ 102 Ω at 250 K to ~ 105 Ω at 90 K (three orders of magnitude) in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011). However,
. Upon decreasing temperature, ΔR increases continuously from ~ 102 Ω at 250 K to ~ 105 Ω at 90 K (three orders of magnitude) in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011). However, 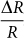 has a maximum value of 88% at 125 K, close to TV, indicating that the resistivity is maximally sensitive to structural or lattice change at the Verwey transition. In addition,
has a maximum value of 88% at 125 K, close to TV, indicating that the resistivity is maximally sensitive to structural or lattice change at the Verwey transition. In addition, 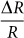 were found to be 3–5% and 30% at 300 K and 90 K, respectively. This result is in contrast to a recent report, where the resistance of a magnetite film increased near the Verwey transition by electrostatic field-effect gating in an ambipolar manner (i.e., the resistance increased for both induced holes, as well as electrons)43. This indicates that strain effects and not electrostatic charging play the dominant role in our structures, where the strain state and not the polarity of P determines the sign of resistance change.
were found to be 3–5% and 30% at 300 K and 90 K, respectively. This result is in contrast to a recent report, where the resistance of a magnetite film increased near the Verwey transition by electrostatic field-effect gating in an ambipolar manner (i.e., the resistance increased for both induced holes, as well as electrons)43. This indicates that strain effects and not electrostatic charging play the dominant role in our structures, where the strain state and not the polarity of P determines the sign of resistance change.
The polarization states in PMN-PT(011) not only affects the electronic structure but also result in magnetization change in magnetite around TV. As shown in Figure 1(e), the abrupt change in magnetization was suppressed to lower temperature, consistent with a decrease in TV. The decrease was quantitatively determined to be ~ 8 K from the first derivative of magnetization versus temperature (inset), consistent with the resistivity measurements in Fig. 1(c). Figure 1(f) shows the strain state dependence of M-H loops at TV = 125 K, exhibiting distinct changes in magnetic anisotropy and magnetization. Such effects also arise from the suppression of the structural transition at TV by electrically poling the PMN-PT (011), which leads to a change in the magneto-crystalline anisotropy as well as magnetization. Thus, we have successfully realized ferroelastic tuning of the Verwey metal-insulator transition as well as associated electronic and magnetic states.
Electrical control of non-volatile and reversible resistivity switching
Due to the stability of remnant in-plane polarization in (011) oriented PMN-PT, stable and reversible ferroelastic switching, as well as non-volatile resistance tuning can be realized in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011). Details of ferroelastic switching of PMN-PT (011) are discussed later. Figure 2(a) shows in-situ control of resistance using an applied voltage in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) at various temperatures. Hysteretic changes in resistance were observed upon applying appropriate unipolar electric fields across the PMN-PT substrate, showing a large tunability of up to 50% change in resistance near TV. The two remnant resistance states in the hysteresis loops represent two ferroelastic strain states in PMN-PT(011), which are stable and switchable. We note that the non-volatile change in resistance here is 50%, which is smaller than that observed in Fig. 1(c). We attribute this to an increase in the coercive field of PMN-PT(011) at low T, resulting in incomplete polarization switching upon poling at these temperatures44. Electrical modulation of resistance can also be achieved at room temperature, as shown in Fig. 2(b). With appropriate application of unipolar and bipolar electric fields, both a resistance hysteresis loop (blue) and ‘butterfly’ curve (red) were observed. Figure 2(c) shows the first derivatives of ln(R) with respect to the applied electric field (E) across the PMN-PT(011) substrate at various temperatures. Resistance change coefficients up to 35%-cm/kV at room temperature and 28%-cm/kV at 125 K were observed as the polarization vector was electrically switched between in-plane and out-of-plane near the coercive fields. The sharpness of the peaks in |d(ln(R))/dE| and the lower coercive fields at room temperature make these more suitable for device applications. Conversely, at low T the broad peaks and high coercive fields point to relatively difficult ferroelastic polarization switching of the PMN-PT.
Figure 2(d) shows electric-field-induced non-volatile resistance switching in Fe3O4/PMN-PT(011) at room temperature and TV ~ 125 K. The resistance was modulated when an appropriate square wave of electric field was applied across the PMN-PT (blue) to switch between out-of-plane and in-plane polarization of the PMN-PT, giving rise to two distinct non-volatile and stable strains states. As a consequence, we were able to tune the resistance by 3% and 50%, at room temperature and TVrespectively. The resistance response follows the excitation of the electric field and did not show significant decrease after being cycled for 5 hours with a cycling frequency of 0.25 Hz.
Ferroelastic switching pathway in (011) oriented PMN-PT
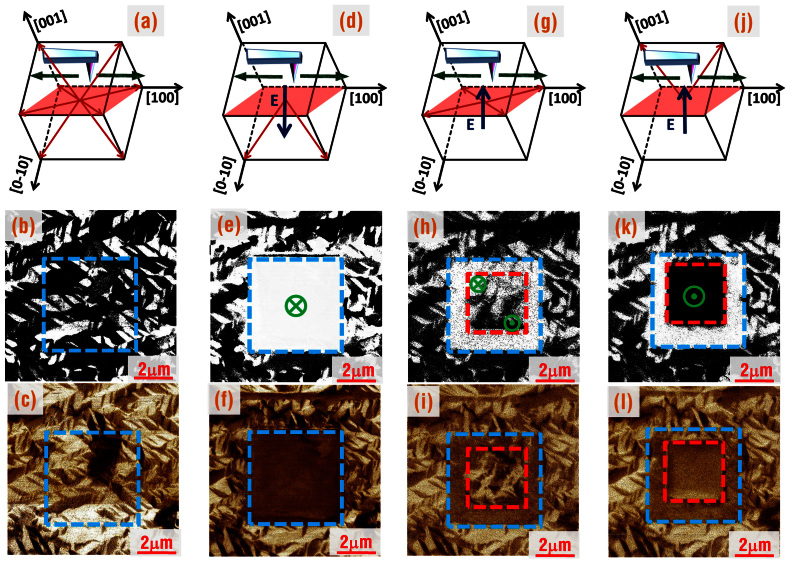
To understand the evolution of ferroelastic domains during switching in (011) oriented PMN-PT, we studied these substrates using piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM). We imaged the polarization domains using both vertical (V) and lateral (L) PFM measurements45. In VPFM, we are sensitive to the vertical piezo response, which is used to image the out-of-plane polarization component. In LPFM we measure torsional displacements that are sensitive to the in-plane component perpendicular to the cantilever, which is aligned parallel to the scanning direction (Fig. 3(a)). Thus, for a scan direction along <100>, we are sensitive to the in-plane polarization projection along the <0–11> directions. As is evident from the schematic (top row of Fig. 3), this component of polarization is non-zero only when the polarization lies in the (011) plane (parallel to the sample surface). Figure 3(a)–3(c) show schematics of polarization vectors, and domain images of the unpoled PMN-PT (011) crystal substrate. In the unpoled state at room temperature, the polarization vectors randomly point along the 8 body diagonals of the pseudocubic cell with rhombohedral symmetry, including 4 equivalent in-plane directions. This gives rise to the PFM phase images shown in Fig. 3(b) and 3 (c), showing a mixture of ferroelastic domains. When a poling voltage of +10V is applied on the tip, both ferroelectric switching (180°) and ferroelastic switching (71° and 109°) take place and all the polar vectors rotate downward in the poled area (blue box), pointing along two equivalent directions, as shown in Fig. 3(d). In this orientation, the polarization has no component along the <0–11> directions and thus there is no contrast within the blue box of the LPFM image in Fig. 3(f). Further, the average in-plane strain is compressive compared to the unpoled state, explaining the shift in lattice parameters shown in Fig. 1(b). As a subsequent DC voltage of −5V was applied, the polarization vectors change to an intermediate state with a large majority of the sample polarization lying purely in the (011) plane without any out-of-plane component, as shown in Fig. 3(g). In this orientation, domains of polarization pointing along <0–11> are clearly evident within the red box of the LPFM image in Fig. 3 (i). When the voltage was further increased to −8V, all of the out-of-plane polarization reversed as shown in Fig. 3(k) and the pure in-plane polarization completely disappeared (red box in Fig. 3(l)). Further details of switching dynamics can be seen in the supplementary section (Figs. S6–S9). These results indicate that upon increasing the poling bias gradually, a two-step 71° or 109° ferroelastic switching takes place, which first makes the polarization components completely rotate from the downward direction into (011) in-plane directions, and subsequently point in the upward direction at the end of the reversal. This is suppressed in thin film ferroelastic systems due to epitaxial clamping by the substrate. The stable and reversible in-plane and out-of-plane polarization states produced here enables non-volatile resistance tuning in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) upon applying appropriate electric fields. In this process, strain or lattice change in epitaxial Fe3O4 films arises due to ferroelastic switching in PMN-PT (011), which was determined to cover 70% of the whole poled area (Details in supplementary in Fig. S9). This highlights the extraordinary nature of poling PMN-PT (011) in comparison to PMN-PT (001)46, with dominant ferroelastic switching in PMN-PT (011) occurring due to the existence of a stable in-plane polarization state.
Figure 3. Probe-bias-dependent nanoscale switching dynamics in the (011) oriented PMN-PT crystal.
(a), (d), (g) and (j) are the schematics showing the scanning direction of the cantilever and the initial, poled, intermediate and final states of the polar vectors. The red arrows along <111> represent the spontaneous polarization vectors in the rhombohedral phase. The green arrows along <100> represent the direction of scanning of the PFM cantilever and the blue arrows in the center of cubes stand for the direction of the electric field. Panels (b), (e), (h) and (k) are the out-of-plane VPFM phase images of the above different switching states, while (c), (f), (i) and (l) are the in-plane LPFM phase images at different poling biases, respectively. These images show a switching process with the increase of tip bias, demonstrating the existence of a pure in-plane polarization at an intermediate voltage.
Role of anti-phase boundaries in ferroelastic tuning of Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011)
In epitaxial magnetite films, atomically sharp anti-phase boundaries (APBs) form as natural growth defects. Proliferation of a large number of these can strongly suppress the Verwey transition, and it is important to establish their role in ferroelastic switching of the resistance of our samples. This is particularly relevant in light of the large changes in the nanoscale ferroelastic domain patterns that we observe during switching. At the APBs, the exchange between neighboring spins is antiferromagnetic, though the regions on either side are ferromagnetically aligned. From considerations of double-exchange mediated transport and canting of spins, it can be shown that this leads to a large negative and linear magnetoresitance (MR) at high magnetic fields47,48. Thus, one way to probe the APBs is to measure the MR in epitaxial Fe3O4 films in different ferroelastic strain states. Figure 4 shows the ferroelastic strain dependence of MR, defined as MR = (R(H) − R(0))/R(0) at various temperatures with applied magnetic fields and currents along the in-plane [100] direction. In the unpoled sample, the negative MR increases in magnitude as T decreases and peaks near TV (Fig. 4(a) (blue)). Upon poling the substrate, the maximum MR peak shifts to lower temperature by up to 8 K (red), indicating the suppression of TV.. However, we note that at higher temperatures (> 180 K), there is no measurable change in the MR between the poled and unpoled states. This indicates that there were no significant changes in either the number of APBs or in their magnetic anisotropy due to ferroelastic (compressive) strain. Furthermore, at low temperature, a decrease in the magnitude of MR by 1–3% was observed at high magnetic fields for the poled sample (Fig. 4(b)). We relate this phenomenon to ferroelastic strain induced increase in the magnetic anisotropy of Fe spins in the vicinity of the APBs, which would also increase the resistance47 of the APBs. In summary, the large decrease in resistance by 88% upon poling near TV cannot be attributed to a change in the number of APBs upon poling. Changes in resistance of the APBs due to changes in magnetic anisotropy are not large enough, and also have the wrong sign, to explain the decrease in resistance upon poling.
Figure 4. The effect of ferroelastic strain on magnetoresistance in Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011).
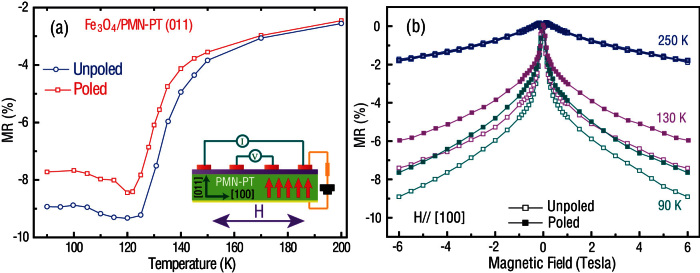
(a) The temperature dependence of magnetoresistance measured at H = 6 Tesla under poled and unpoled polarization states. (b) Ferroelastic strain dependence of magnetoresistance at various temperatures with applied magnetic fields and measured current along the in-plane [100] direction.
Discussion
In conclusion, we have demonstrated electrical tuning of the Verwey metal-insulator transition and non-volatile resistance switching at room temperature in epitaxial Fe3O4/PMN-PT (011) heterostructures. This was achieved using a unique ferroelastic switching pathway in PMN-PT (011) to maximize ferroelastic strain and realize two distinct, stable and reversible strain states. These results point to opportunities for electrical tuning of strain sensitive phase transitions and other properties of correlated oxides that may be grown on PMN-PT(011) substrates.
Methods
The Fe3O4 films were epitaxially synthesized on (011) oriented PMN-PT single crystal substrates in a MBE chamber with a base pressure in the 10−10 Torr range. A pure flow of distilled ozone was delivered to the chamber as the oxidizing agent, maintaining the chamber pressure at 1.0 × 10−7 Torr at the growth temperature of 300°C. 99.9% pure Fe was deposited from a differentially pumped dual-filament Knudsen cell. Prior to film growth, the deposition rate was measured using a quartz-crystal thickness monitor (QCM), which is 0.035 ~ 0.045 Å/sec with a drift of ~ 0.5% per hour. When deposition was complete, the sample was cooled to room temperature in ozone at the same pressure. This growth conditions were refined by depositing epitaxial Fe3O4 films on MgO (001), MgAl2O4 (001) and PMN-PT (001) substrates and carrying out detailed structural, magnetic and electrical characterization (Supplementary).
Author Contributions
M.L. and A.B. planned the experiments. M.L. made the samples and performed all magnetic and electronic measurements, with assistance from J.H. and B.N.C. P.F.M. scans were performed by J.W. and J.Z. The paper was written by M.L and A.B. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary info.
Acknowledgments
Work at Argonne National Laboratory, including use of facilities at the Center for Nanoscale Materials, was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. Ming Liu was supported by a Directors' Postdoctoral Fellowship at Argonne. The work in Beijing Normal University was supported by National Science Foundation of China under contract No.11274045.
References
- Inoue I. H. & Rozenberg M. J. Taming the Mott transition for a novel Mott transistor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18, 2289–2292 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Ko C. Y. & Ramanathan S. Oxide Electronics Utilizing Ultrafast Metal-Insulator Transitions. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 41, 337–367 (2011). [Google Scholar]
- Theis T. N. & Solomon P. M. It's Time to Reinvent the Transistor!. Science 327, 1600–1601 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn C. H., Triscone J. M. & Mannhart J. Electric field effect in correlated oxide systems. Nature 424, 1015–1018 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp T. & Mannhart J. Calculation of the capacitances of conductors: Perspectives for the optimization of electronic devices. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 064504 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Scherwitzl R. et al. Electric-Field Control of the Metal-Insulator Transition in Ultrathin NdNiO3 Films. Adv. Mater. 22, 5517–5520 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn C. H. et al. Local, Nonvolatile Electronic Writing of Epitaxial Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3/SrRuO3 Heterostructures. Science 276, 1100–1103 (1997). [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. et al. Collective bulk carrier delocalization driven by electrostatic surface charge accumulation. Nature 487, 459–462 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotan H., Asanuma H. Takeya J. & Iwasa Y. Electrolyte-gated charge accumulation in organic single crystals. Applied Physics Letters 89, 203501–203503 (2006). [Google Scholar]
- Jeong J. et al. Suppression of MetalInsulator Transition in VO2 by Electric Field�Induced Oxygen Vacancy Formation. Science 339, 1402–1405 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H. et al. A strong ferroelectric ferromagnet created by means of spin-lattice coupling. Nature 466, 954–958 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennie C. J. & Rabe K. M. Magnetic and Electric Phase Control in Epitaxial EuTiO_{3} from First Principles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 267602 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H. & Rabe K. M. Coupled Magnetic-Ferroelectric Metal-Insulator Transition in Epitaxially Strained SrCoO3 from First Principles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 067601 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He C. et al. Metal-insulator transitions in epitaxial LaVO3 and LaTiO3 films. Phys. Rev.B 86, 081401 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Ahn K. H., Lookman T. & Bishop A. R. Strain-induced metal-insulator phase coexistence in perovskite manganites. Nature 428, 401–404 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko K.-T. et al. Concurrent transition of ferroelectric and magnetic ordering near room temperature. Nat. Commun. 2, 567 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante I. C. et al. Bridging Multiferroic Phase Transitions by Epitaxial Strain in BiFeO3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 057601 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeni J. H. et al. Room-temperature ferroelectricity in strained SrTiO3. Nature 430, 758–761 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ederer C. & Spaldin N. A. Effect of Epitaxial Strain on the Spontaneous Polarization of Thin Film Ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 257601 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach R. S. et al. Enhanced Curie temperatures and magnetoelastic domains in Dy/Lu superlattices and films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 3502–3505 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele C., Dörr K., Bilani O., Rödel J. & Schultz L. Influence of strain on the magnetization and magnetoelectric effect in La0.7A0.3MnO3/PMN-PT(001) (A = Sr,Ca). Phys. Rev. B 75, 054408 (2007). [Google Scholar]
- Catalan G. et al. Flexoelectric rotation of polarization in ferroelectric thin films. Nat. Mater. 10, 963–967 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilani-Zeneli O. et al. SrTiO[sub 3] on piezoelectric PMN-PT(001) for application of variable strain. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 054108–054105 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng R. et al. Ferroelectric poling and converse-piezoelectric-effect-induced strain effects in La0.7Ba0.3MnO3 thin films grown on ferroelectric single-crystal substrates. Phys. Rev. B 79, 1–7 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Dale D., Fleet A., Brock J. D. & Suzuki Y. Dynamically tuning properties of epitaxial colossal magnetoresistance thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3725–3727 (2003). [Google Scholar]
- Eerenstein W., Wiora M., Prieto J. L., Scott J. F. & Mathur N. D. Giant sharp and persistent converse magnetoelectric effects in multiferroic epitaxial heterostructures. Nature Mater. 6, 348–351 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. et al. Strong magnetoelectric coupling in ferrite/ferroelectric multiferroic heterostructures derived by low temperature spin-spray deposition. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42, 045007 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Rata A. D., Herklotz A., Nenkov K., Schultz L. & Dörr K. Strain-Induced Insulator State and Giant Gauge Factor of La0.7Sr0.3CoO3 Films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 076401 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng R. K. et al. Investigation of substrate-induced strain effects in La0.7Ca0.15Sr0.15MnO3 thin films using ferroelectric polarization and the converse piezoelectric effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 102904 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- Baek S. H. et al. Ferroelastic switching for nanoscale non-volatile magnetoelectric devices. Nature Mater. 9, 309–314 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. et al. Domain engineered switchable strain states in ferroelectric (011) [Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3](1 − x)-[PbTiO3]x (PMN-PT, x≈0.32) single crystals. J Appl. Phys. 109, 124101 (2011). [Google Scholar]
- Walz F. The Verwey transition-a topical review. J.Phys.: Condens. Matter. 14, R285 (2002). [Google Scholar]
- Senn M. S., Wright J. P. & Attfield J. P. Charge order and three-site distortions in the Verwey structure of magnetite. Nature 481, 173–176 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenberg G. K., Hearne G. R., Pasternak M. P., Metcalf P. A. & Honig J. M. Nature of the Verwey transition in magnetite (Fe3O4) to pressures of 16 GPa. Phys. Rev.B 53, 6482–6487 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todo S., Takeshita N., Kanehara T., Mori T. & Mori N. Metallization of magnetite (Fe3O4) under high pressure. J Appl. Phys. 89, 7347–7349 (2001). [Google Scholar]
- Ding Y. et al. Novel Pressure-Induced Magnetic Transition in Magnetite (Fe3O4). Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 18–21 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M., Lou J., Li S. D. & Sun N. X. E-Field Control of Exchange Bias and Deterministic Magnetization Switching in AFM/FM/FE Multiferroic Heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 2593–2598 (2011). [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh R. & Spaldin N. A. Multiferroics: progress and prospects in thin films. Nature mater. 6, 21–29 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz C. A. F., Hoffman J., Ahn C. H. & Ramesh R. Magnetoelectric Coupling Effects in Multiferroic Complex Oxide Composite Structures. Adv. Mater. 22, 2900–2918. (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan G. Magnetoelectric Composites. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 153–178 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- Hu J.-M., Li Z., Chen L.-Q. & Nan C.-W. Design of a Voltage-Controlled Magnetic Random Access Memory Based on Anisotropic Magnetoresistance in a Single Magnetic Layer. Adv. Mater. 24, 2869–2873 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. et al. Giant Electric Field Tuning of Magnetic Properties in Multiferroic Ferrite/Ferroelectric Heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 1826–1831 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Wong J. J. I., Swartz A. G., Zheng R., Han W. & Kawakami R. K. Electric field control of the Verwey transition and induced magnetoelectric effect in magnetite. Phys. Rev. B 86, 060409 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- Herklotz A. et al. Electrical characterization of PMN--28%PT(001) crystals used as thin-film substrates. J Appl. Phys. 108, 094101–094107 (2010). [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez B. J., Gruverman A., Kingon A. I., Nemanich R. J. & Cross J. S. Three-dimensional high-resolution reconstruction of polarization in ferroelectric capacitors by piezoresponse force microscopy. J Appl. Phys. 95, 1958–1962 (2004). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. et al. Electric-Field Control of Nonvolatile Magnetization in Co40Fe40B20/Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.7Ti0.3O3 Structure at Room Temperature. Physical Review Letters, 108, 137203 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eerenstein W., Palstra T., Saxena S. & Hibma T. Spin-Polarized Transport across Sharp Antiferromagnetic Boundaries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 1–4 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofin R., Arora S. & Shvets I. Positive antiphase boundary domain wall magnetoresistance in Fe3O4 (110) heteroepitaxial films. Phys. Rev. B 83, 1–9 (2011). [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary info.