Abstract
Rhizobitoxine has previously been shown to inactivate irreversibly β-cystathionase isolated from spinach. In the present studies, rhizobitoxine was shown to inhibit partially β-cystathionase of spinach and corn seedlings in vivo. An activity of 30 to 40% of normal remained in toxin-treated seedlings of both spinach and corn. Possible reasons for the partial inhibition are discussed.
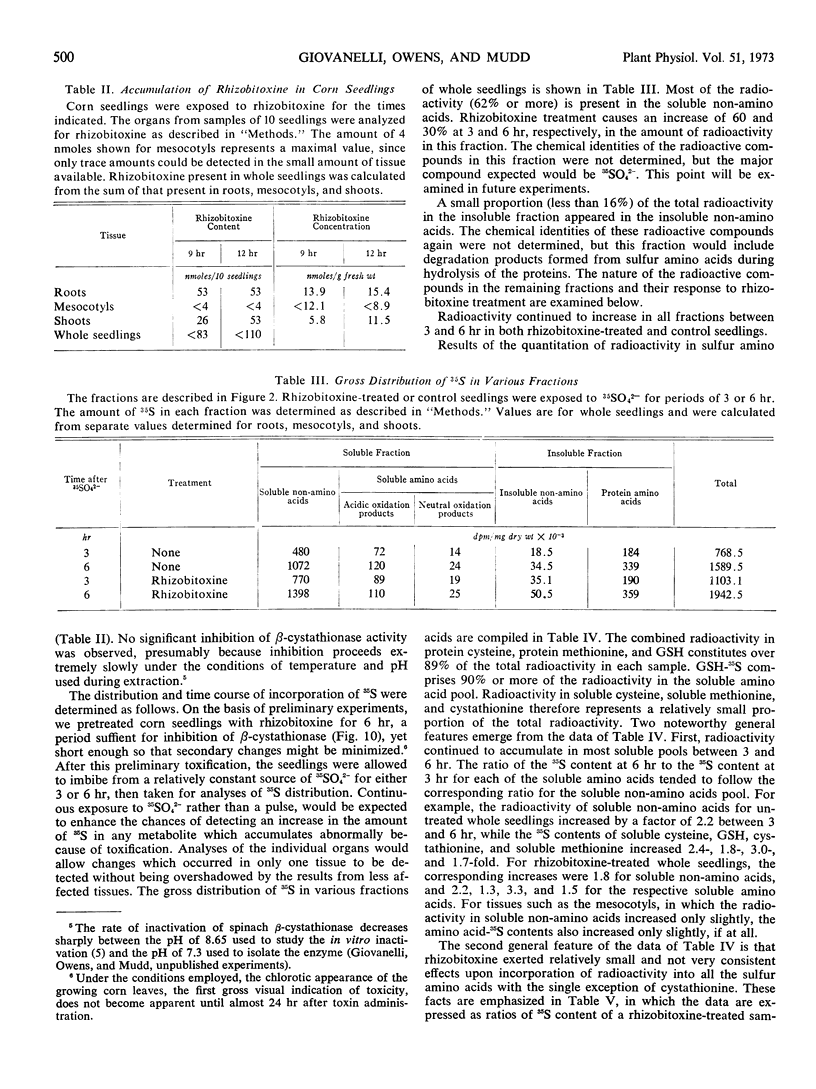
Rhizobitoxine-treated and control corn seedlings were allowed to assimilate 35SO42− for 3 or 6 hours, and the radioactivity incorporated into sulfur amino acids at these times was studied. The most striking effect of rhizobitoxine was an increase (up to 22-fold) in radioactive cystathionine. Accumulation of radioactivity in methionine was only slightly inhibited by rhizobitoxine treatment. The results strongly suggest that the transsulfuration pathway contributes to methionine biosynthesis, and that metabolism via this pathway is impaired, but not entirely eliminated, by rhizobitoxine treatment.
The present data do not permit decisions about the relative contributions of the transsulfuration and the direct sulfhydration pathways to methionine biosynthesis, or whether the pathological effects of rhizobitoxine are due chiefly to inhibition of β-cystathionase.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DELAVIER-KLUTCHKO C., FLAVIN M. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS AND CLEAVAGE OF CYSTATHIONINE IN FUNGI AND BACTERIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2537–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H. Enzymatic synthesis of cystathionine by extracts of spinach, requiring O-acetylhomoserine or O-succinylhomoserine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Nov 11;25(3):366–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90787-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H. Synthesis of homocysteine and cysteine by enzyme extracts of spinach. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):150–156. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H. Transsulfuration in higher plants. Partial purification and properties of beta-cystathionase of spinach. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 10;227(3):654–670. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Owens L. D., Mudd S. H. Mechanism of inhibition of spinach beta-cystathionase by rhizobitoxine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 10;227(3):671–684. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S. H., Finkelstein J. D., Irreverre F., Laster L. Transsulfuration in mammals. Microassays and tissue distributions of three enzymes of the pathway. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4382–4392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngo T. T., Shargool P. D. The formation of sulphur-containing amino acids in germinating seeds of rape (Brassica napus L.). Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):985–991. doi: 10.1042/bj1260985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Guggenheim S., Hilton J. L. Rhizobium-synthesized phytototoxin: an inhibitor of beta-cystathionase in Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May;158(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D. Toxins in plant disease: structure and mode of action. Science. 1969 Jul 4;165(3888):18–25. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3888.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Wright D. A. Production of the Soybean-Chlorosis Toxin by Rhizobium japonicum in Pure Culture. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):931–933. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Wright D. A. Rhizobial-Induced Chlorosis in Soybeans: Isolation, Production in Nodules, and Varietal Specificity of the Toxin. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):927–930. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



