Abstract
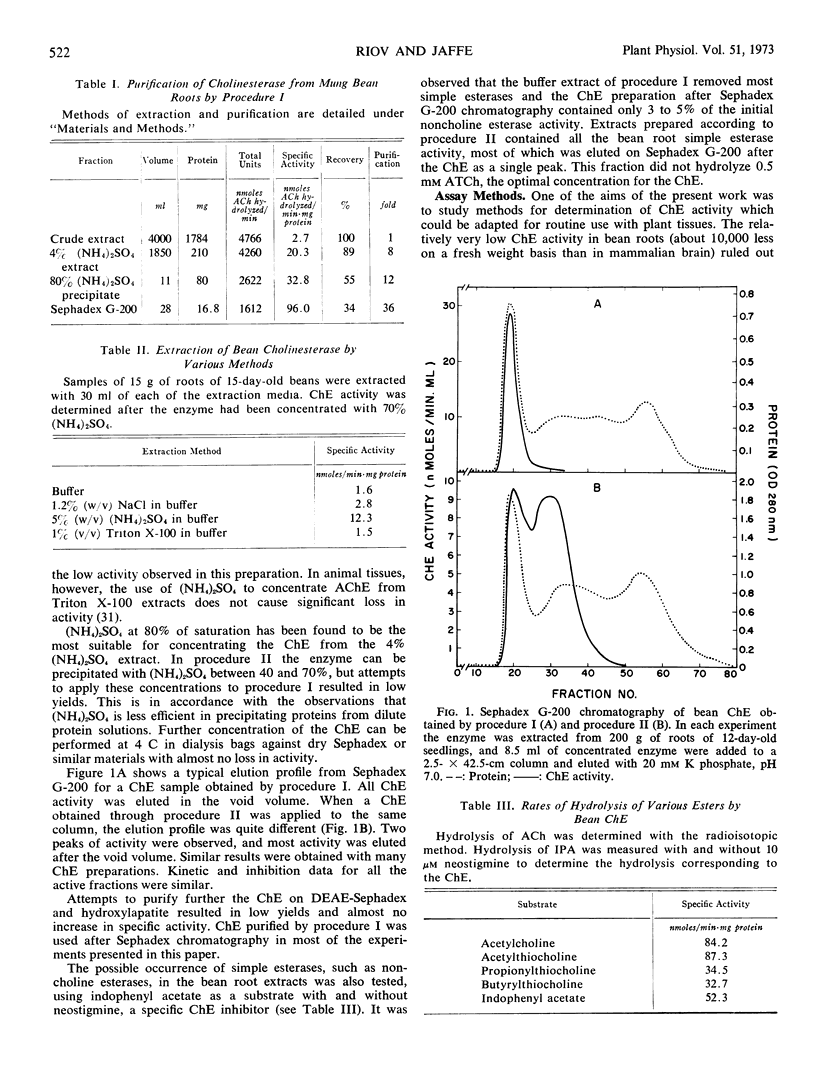
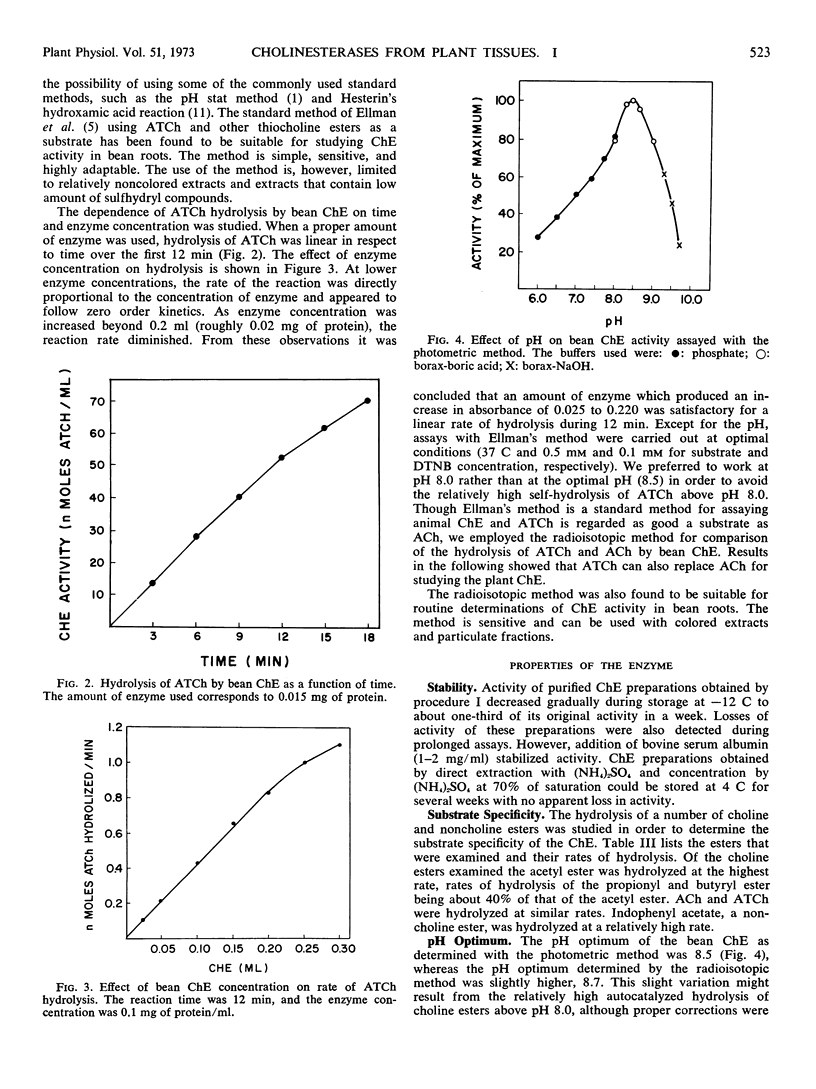
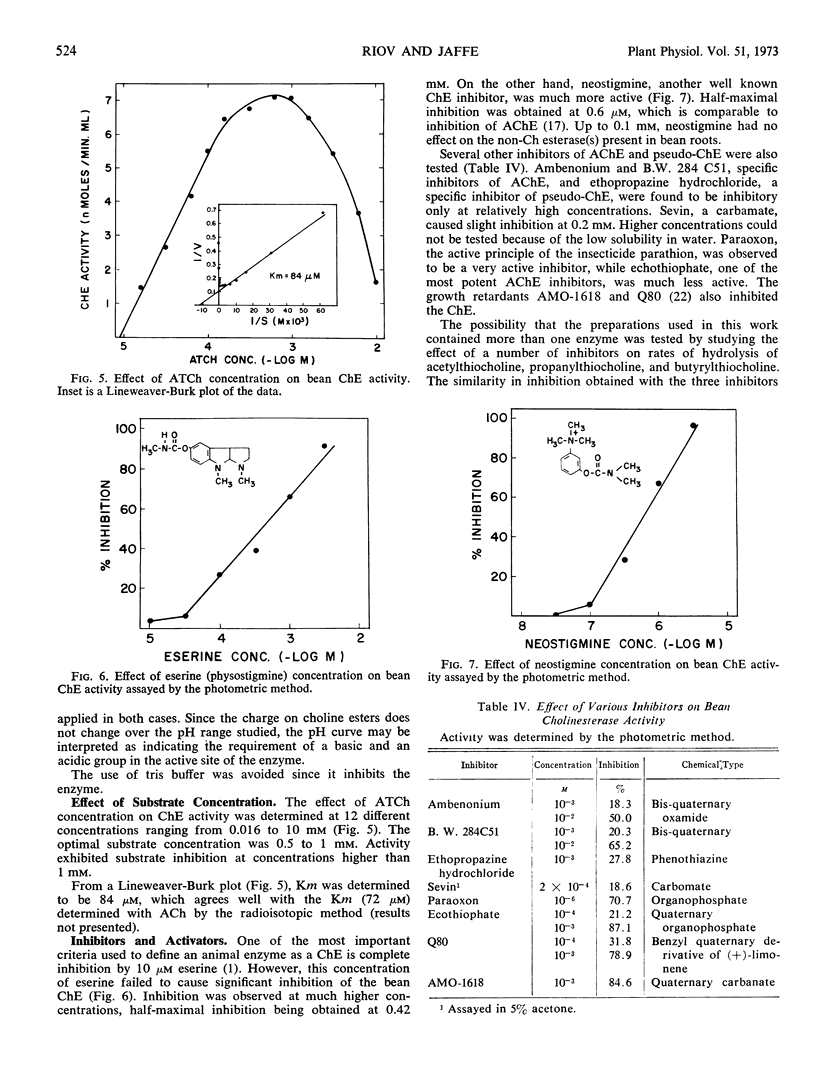
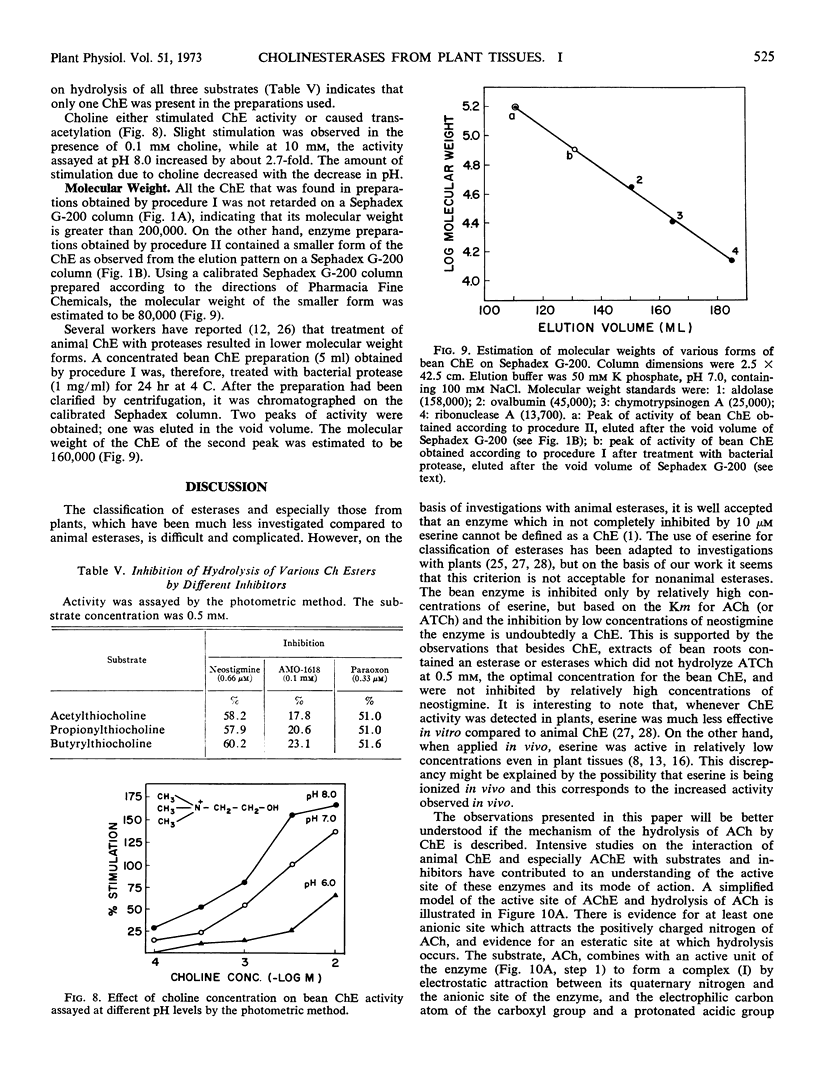
A cholinesterase was purified 36-fold from mung bean (Phaseolus aureus) roots by a combination of differential extraction media and gel filtration. The enzyme could be effectively extracted only by high salt concentration, indicating that it is probably membrane-bound. Methods used for assaying animal cholinesterases were tested, two of which were adapted for use with the bean cholinesterase. The bean enzyme hydrolyzed choline and noncholine esters but showed its highest affinity for acetylcholine and acetylthiocholine. The pH optimum was 8.5 for acetylthiocholine and 8.7 for acetylcholine. The Michaelis constants were 72 and 84 μm for acetylcholine and acetylthiocholine, respectively. The cholinesterase was relatively insensitive to eserine (half-maximum inhibition at 0.42 mm) but showed high sensitivity to neostigmine (half-maximum inhibition at 0.6 μm). Other animal cholinesterase inhibitors were also found to inhibit the bean enzyme but most of them at higher concentrations than are generally encountered. Choline stimulated enzymatic activity. The molecular weight of the cholinesterase was estimated to be greater than 200,000, but at least one smaller form was observed. It is suggested that the large form of cholinesterase is converted to the smaller form by proteolysis.
Full text
PDF

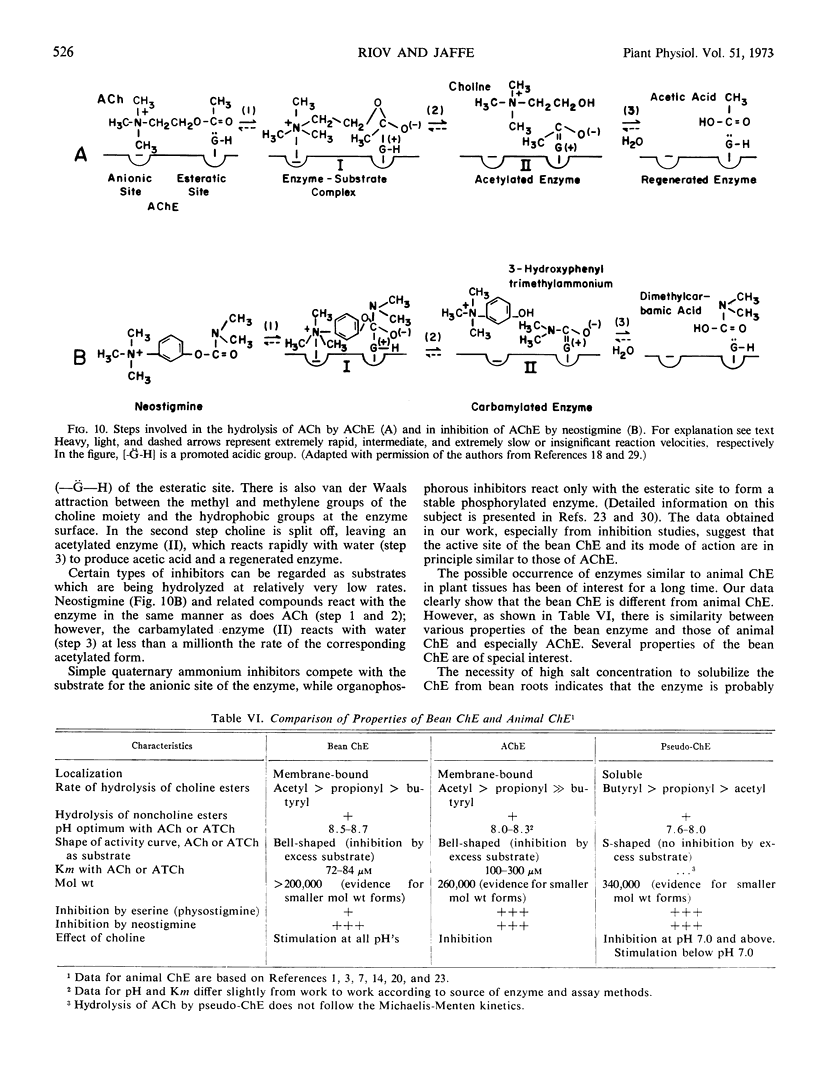


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark S. W., Glaubiger G. A., La Du B. N. Properties of plasma cholinesterase variants. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Jul 31;151(2):710–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb48253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DETTBARN W. D. Acetylcholinesterase activity in Nitella. Nature. 1962 Jun 23;194:1175–1176. doi: 10.1038/1941175b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. K., Liddell J. Purification and properties of human serum cholinesterase. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):875–881. doi: 10.1042/bj1160875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner G., Pike C. S., Rice H. V., Briggs W. R. "Disaggregation" of phytochrome in vitro-a consequence of proteolysis. Plant Physiol. 1971 Dec;48(6):686–693. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.6.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gressel J., Strausbauch L., Galun E. Photomimetic effect of acetylcholine on morphogenesis in Trichoderma. Nature. 1971 Aug 27;232(5313):648–649. doi: 10.1038/232648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks S. B., Borthwick H. A. The function of phytochrome in regulation of plant growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2125–2130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. K., Ellman G. L. Triton solubilized acetylcholinesterase of brain. J Neurochem. 1969 Nov;16(11):1505–1513. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb09905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Aprison M. H. Mammalian brain acetylcholinesterase. Purification and properties. J Neurochem. 1966 Dec;13(12):1351–1365. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe M. J. Evidence for the regulation of phytochrome-mediated processes in bean roots by the neurohumor, acetylcholine. Plant Physiol. 1970 Dec;46(6):768–777. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.6.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe M. J. Phytochrome-mediated bioelectric potentials in mung bean seedlings. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1016–1017. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantai K. E., Hind G. On the mechanism and stoichiometry of the oxidation of hydrazine by illuminated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jul;48(1):5–8. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed D. J., Goto K., Wang C. H. A direct radioisotopic assay for acetylcholinesterase. Anal Biochem. 1966 Jul;16(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeed S. A., Chadwick G. R., Mill P. J. Action of proteases on human plasma cholinesterase isoenzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):186–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A. Metabolism of Sinapine in Mustard Plants. II. Purification & Some Properties of Sinapine Esterase. Plant Physiol. 1963 Mar;38(2):207–213. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


