Background: GABA promotes terminal differentiation during late development of Dictyostelium discoideum.
Results: GABA metabolism is tightly controlled and regulates early development.
Conclusion: Distinct genes regulate GABA signaling during different developmental stages.
Significance: This is the first systematic study of GABA metabolism in Dictyostelium discoideum and broadens our knowledge of the evolution and function of GABA metabolism.
Keywords: Cell Signaling, Development, Dictyostelium, GABA Receptors, Sporulation
Abstract
While GABA has been suggested to regulate spore encapsulation in the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum, the metabolic profile and other potential functions of GABA during development remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the homeostasis of GABA metabolism by disrupting genes related to GABA metabolism and signaling. Extracellular levels of GABA are tightly regulated during early development, and GABA is generated by the glutamate decarboxylase, GadB, during growth and in early development. However, overexpression of the prespore-specific homologue, GadA, in the presence of GadB reduces production of extracellular GABA. Perturbation of extracellular GABA levels delays the process of aggregation. Cytosolic GABA is degraded by the GABA transaminase, GabT, in the mitochondria. Disruption of a putative vesicular GABA transporter (vGAT) homologue DdvGAT reduces secreted GABA. We identified the GABAB receptor-like family member GrlB as the major GABA receptor during early development, and either disruption or overexpression of GrlB delays aggregation. This delay is likely the result of an abolished pre-starvation response and late expression of several “early” developmental genes. Distinct genes are employed for GABA generation during sporulation. During sporulation, GadA alone is required for generating GABA and DdvGAT is likely responsible for GABA secretion. GrlE but not GrlB is the GABA receptor during late development.
Introduction
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)2 is a non-protein four carbon amino acid that exists in most, if not all, prokaryotes and eukaryotes (1–4). It is synthesized primarily from glutamate catalyzed by cytosolic glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). Cytosolic GABA is transported by membrane-bound transporters into the extracellular environment and to different organelles and plays various roles. GABA is first metabolically catabolized by mitochondrial GABA transaminase (GABA-T) into succinic-semialdehyde (SSA), and then into succinate by succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH), which ultimately allows the GABA carbon skeleton to enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. This pathway composed of these three enzymes (GAD, GABA-T, SSADH) bypasses two steps of the TCA cycle and is called the GABA shunt (5).
The presence of GABA is ubiquitous and multiple functions have evolved for this amino acid. In plants, GABA is rapidly accumulated in response to a variety of biotic and abiotic stresses, including bacterial invasion, insect herbivorous behavior, and oxidative stress and osmotic shock. The GABA shunt also contributes to nitrogen metabolism and the carbon:nitrogen balance, demonstrating its importance as a metabolite in many physiological processes (6). GABA can also function as a signaling molecule in pollen tube growth and guidance (7). In invertebrates and vertebrates, GABA acts as a potent inhibitory neurotransmitter. GABA achieves postsynaptic inhibition by hyperpolarizing the cell through ionotropic and G protein-coupled metabotropic receptors in the adult brain (8). However, opposite effects of GABA have been reported during nervous system development (9). Misregulation of GABA has been linked to several neuronal diseases, including epilepsy (10) and Huntington disease (11).
The social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum preys on bacteria during the solitary vegetative stage, and thousands of cells aggregate to form multicellular structures when the food source is depleted (12). This organism also produces GABA in both vegetative and developmental stages (13). Two genes encoding GAD, gadA and gadB, have been identified in the D. discoideum genome (14). These two proteins share high protein sequence identity (73%) but display a distinct temporal expression pattern, suggesting they function non-redundantly in growth and development. Microarray analysis showed that the gadA mRNA expression dramatically increases at 10 h after development and peaks at 18 h during the culmination stage (15), whereas gadB mRNA is expressed in vegetative cells and diminishes after the onset of starvation (14). Only one GABA transaminase gene, gabT, was identified in the D. discoideum genome (16). No D. discoideum ionotropic GABA receptor homologue was found. Strikingly, 17 genes (grlA-H, grlJ-R) encoding homologues of GABAB metabotropic receptors have been reported (17–19). Among them, only GrlE shares a well conserved N-terminal ligand binding domain (20), and this has been proven to be a bona fide GABA receptor (21).
The role of GABA has been clearly defined as a signaling cue in sporulation in D. discoideum. Disruption of GadA, which theoretically abolishes GABA synthesis in prespore cells, prevents the GABA triggered release of the acyl-CoA-binding protein (a precursor of SDF-2) and thus results in decreased viable spores (21). Consistent with this finding, disruption of GrlE, the GABA receptor at this stage, phenocopies the gadA− mutant (21). In addition, either disruption of gabT or direct addition of the irreversible GABA transaminase inhibitor vigabatrin promotes SDF-2 production and induces spore maturation (16). grlE− cells also exhibit rapid growth in suspension and delay in early development (20), however, the mechanism remains unknown. Functions of several other members of the GABAB receptor-like family which are induced in sporulation have also been explored. Disruption of GrlA shows delay in late development and GrlA possibly acts as the SDF-3 receptor (16, 22), while loss of GrlJ shows precocious development and malformed spores (23).
Although the role of GABA in late development has been studied, the role of GABA in other developmental stages remains obscure. In addition, there is very little fundamental data on the homeostasis of GABA. In this study, we identified a GABAB receptor-like family member GrlB as a GABA receptor during early development and further characterized the synthesis, degradation, and signaling of GABA in D. discoideum.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Materials
GABA, GTPγS, and vigabatrin were purchased from Sigma, GABAB receptor antagonist CGP55845 from Tocris (Ellisville, MO), Mitotracker Red CMXRos from Invitrogen (Eugene, OR) and 2,3-3H(N)-GABA from American Radiolabeled Chemical (St. Louis, MO). The pLPBLP vector, the plasmid pDEX-NLS-Cre and a series of the actin15 promoter-driven pDM expressing vectors were provided by dictyBase. Mouse anti-CsA antibody (33-294-17) and mouse anti-Discoidin I (80-52-13) monoclonal antibodies were obtained from the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank at the University of Iowa. Mouse anti-actin monoclonal antibody (MAB1501R) was purchased from Millipore.
Cell Culture and Development
For axenic growth in HL5 medium at 22 °C, all cell strains were either cultured in Petri dishes or shaken in suspension at 175 rpm. For development, vegetative cells were washed twice with developmental buffer (DB: 5 mm Na2HPO4, 5 mm KH2PO4, 0.2 mm CaCl2, 2 mm MgSO4, pH 6.5) and spread on 30 mm non-nutrient DB agarose (15 mg/ml) plates at a density of 5 × 105 cells/cm2.
Generation of Mutants and Overexpression Strains
All mutants were generated in the wild-type AX2 background. gadA− cells were generated by homologous recombination using the vector pLPBLP (24). The 514 bp 5′ homologous region and the 1071 bp 3′ homologous region were amplified from genomic DNA and directionally cloned into the vector pLPBLP. The resulting construct was linearized by NotI and 2 μg of linear DNA was electroporated into 5 × 106 cells. Cells were then selected with 10 μg/ml Blasticidin S for 10 days, and successful gene disruption in transformants was confirmed by PCR of genomic DNA using one primer inside the Bsr cassette and one primer outside the homologous region on the genome (25). At least 2 different clones were isolated, and phenotypes were confirmed.
The same strategy was used to disrupt gadB, DdvGAT (dictyBase ID: DDB_G0293074), grlB, and grlE, respectively. The strategy used for disrupting gabT was similar as described (16). The primers used are listed in supplemental Table S1. To generate gadA−/gadB− cells, the nuclear-localized Cre protein from the plasmid pDEX-NLS-cre (24) was transiently expressed in gadA- cells to remove the Bsr cassette, and then gadB was subsequently disrupted. For grlB−/grlE− cells, grlB− cells were treated with Cre and grlE was subsequently disrupted.
gadA cDNA was amplified from cDNA prepared from AX2 cells starved for 14 h. gadB genomic DNA was amplified from genomic DNA. gabT, DdvGAT, and grlB cDNA was amplified from cDNA prepared from vegetative cells. These genes were cloned into the expressing vector pDM304 and C-terminal GFP-tagged vector pDM323 or N-terminal GFP-tagged vector pDM317. The primers used are also listed in supplemental Table S1. These expression plasmids were transformed into 5 × 106 cells, and cells were selected with 20 μg/ml G418.
qPCR Analysis
Total RNA was prepared from axenic cells or cells starved on non-nutrient DB agarose for 4 h using the TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). Total RNA extracts were treated with amplification grade DNase I (Invitrogen) to remove contaminating DNA. 1 μg of total DNase I-treated RNA was reverse-transcribed into first strand cDNA using the SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis System (Invitrogen). Quantitative PCR was performed on MyiQ Single-Color Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad) using iQ SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad) according to the manufacturer's directions. All samples were prepared and run in triplicate. rnlA (IG7) was used as the reference gene, and the expression ratio was determined using the 2−(ΔΔCt) method as described previously (26). The primers used are also listed in the supplemental Table S1.
GABA Content Measurements
For extracellular GABA content, 5 × 106 cells were washed twice with DB, and then suspended in 100 μl of DB. The suspension was shaken gently at 120 rpm, 22 °C. At indicated time points, the suspension was centrifuged at 1,500 × g for 1 min. 40 μl supernatant was analyzed for amino acids including GABA via HPLC by the Neurochemistry Core at Vanderbilt University's Center for Molecular Neuroscience Cores. Each measurement was performed at least in triplicate.
GABA Binding Assays
Whole cell GABA binding assay was performed as described (21). Briefly, vegetative cells were washed three times with 10 ml MES buffer (20 mm MES, 20 mm NaCl, 20 mm KCl, 1 mm CaCl2, 1 mm MgSO4, pH 6.2), and prepared at 107 cells/ml in ice-cold MES buffer, 500 μl cell suspension was incubated with 0.2 nm [3H]GABA in the presence or absence of 200 μm CGP55845 on ice for 1 h. Cells were then collected on GF/C glass filters (Whatman) and rinsed three times with 5 ml of cold buffer before the radioactivity of bound [3H]GABA was counted in a liquid scintillation counter.
For the cell lysate GABA binding assay, 5 × 107 vegetative cells were washed twice with cold MES buffer and suspended in 1 ml of cold MES buffer. The cells were lysed by passing through an Acrodisc 5 μm pore size syringe filter (Pall). The identical procedure was performed for the same amount of cells in 1 ml of cold MES buffer supplemented with 100 μm GTPγS. 100 μl of cell lysate with or without GTPγS was incubated with 0.2 nm 3H-GABA in the presence or absence of 200 μm CGP55845 on ice for 10 min. The crude membrane fraction was collected by centrifugation at 17,000 × g for 5 min at 4 °C. The membrane pellet was washed three times with 1 ml of MES buffer and finally dissolved in 80 μl of 1% SDS solution (27). The radioactivity of membrane-bound [3H]GABA was then counted.
Microscopy
Images of developing cells on non-nutrient DB agarose were acquired with a Leica MZ16 stereomicroscope with a Q-Imaging Retiga 1300 camera and QCapture software. Vegetative cells were washed twice with DB and images were acquired in DB in Lab-Tek chambers (Nalge Nunc International) on a Nikon Eclipse Ti microscope with an Apo 60× objective (NA 1.49) using a Quorum WaveFX spinning disk confocal system.
Spore Viability Assay
1 × 107 cells were washed with KK2 buffer (16.2 mm KH2PO4, 4.0 mm K2HPO4, pH 6.1) and starved on KK2-saturated filters. After 48 h, the filter was put in a 50 ml tube and washed repeatedly with 4 ml of KK2 buffer containing 0.4% Nonidet P-40. The tube was rocked gently at 150 rpm for 10 min and then the filter was discarded. The density of ovoid spores was counted by a hemacytometer. 100 spores were collected and plated with Klebsiella aerogenes bacteria on SM plates. The number of plaques was then counted 5 days later.
Western Blotting
5 × 106 cells were washed twice with DB and lysed with 1× NuPAGE LDS Sample Buffer (Invitrogen) and 5% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma) in a total volume of 50 μl. Cell lysate was incubated at 90 °C for 5 min and 5 μl cell lysate was analyzed on 10% mini-protean TGX precast gel (Bio-Rad). After electrophoresis, proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blocked with the Odyssey blocking buffer and incubated with the indicated antibodies. The rabbit anti-cAR1 antibody was pre-absorbed with 50% methanol/DB fixed cells before use. A 1:1000 dilution was used for primary antibodies and a 1:10000 dilution was used for secondary antibodies. Secondary antibodies IRDye 680LT Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (LI-COR, 926-68022) and IRDye 800CW Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (LI-COR, 926-32211) were used for 2-color detection. The nitrocellulose membrane was developed using the Odyssey Infrared Imaging System (LI-COR).
Statistical Analysis
The statistical significance of differences was determined by the one-way ANOVA with Tukey's honestly significant difference using software OriginPro 8.6.0 (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA). p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
A GABAB Receptor-like Protein GrlB Is Involved in Early Development
GrlB belongs to the GABAB receptor-like family which contains 17 members in D. discoideum (19). A previous microarray analysis reported that the transcriptional levels of gadB and grlB were substantially up-regulated when cells were incubated with bacteria (28). We confirmed the transcriptional change of grlB under this condition and speculated that GrlB might be involved in phagocytosis or sensing of the bacterial metabolite folic acid. However, the disruption of grlB did not impair the growth of cells on bacteria or the ability of cells to chemotax toward folic acid (data not shown).
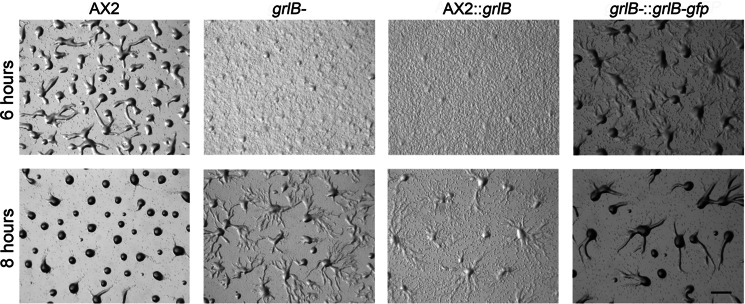
We further examined the developmental process of grlB- cells. Wild-type AX2 cells usually stream at ∼4.5 h when plated on a non-nutrient agarose plate. At 6 h, most wild-type cells had finished aggregation and had started to form loose mounds, whereas only tiny aggregates were formed by grlB− cells (Fig. 1). At 8 h, tight mounds were formed in wild-type cells but grlB− cells were still streaming and only a few loose mounds were formed (Fig. 1). Accordingly, grlB− cells exhibited a delay of about 2 h in aggregation. Expression of full-length GrlB or C-terminal GFP-tagged GrlB under the control of the act15 promoter in grlB− cells ameliorated the developmental postponement but could not fully rescue the delay (Fig. 1). The high expression level of GrlB in grlB− cells may have been responsible for the partial rescue since overexpression of GrlB in WT cells caused a more severe delay (Fig. 1). This indicates GrlB is involved in early development. Both grlB− cells and GrlB overexpression cells successfully completed the life cycle without any morphological defects (data not shown).
FIGURE 1.
Early developmental phenotypes of grlB mutants. 5 × 106 vegetative cells were washed with DB twice and plated on non-nutrient DB-agarose plates. Images were taken at indicated hours after development. AX2::grlB, grlB was overexpressed in wild-type AX2 cells; grlB−::grlB-gfp, grlB-gfp fusion was overexpressed in grlB− cells. Bar, 1 mm.
GABA Is Generated by GadB during Growth and Early Development
GABA acts as the natural agonist for GABAB receptors, and glutamate has also been shown to bind to the GABAB receptor GrlE in the social amoeba (21). Therefore the effect of GABA and glutamate on early development was examined. Unexpectedly, direct addition of up to 1 mm GABA or glutamate to the agarose substrate barely affected aggregation (Fig. 2A), with the same results acquired when cells were developed on buffer-saturated filters (data not shown). This is consistent with a previous study which reported that the presence of 1 mm GABA or glutamate had no effect on the cAMP chemotactic response (20). We also tested the ability of cells to migrate directionally toward a wide range of GABA gradients (1 nm to 10 mm) using a micropipette assay. Vegetative cells or cells starved for 1–6 h did not chemotax toward GABA while exposed to any of these concentration gradients, suggesting GABA is probably not a chemoattractant (data not shown).
FIGURE 2.
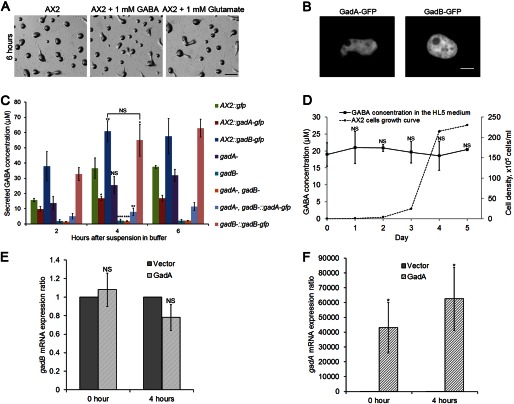
GABA synthesis and secretion in wild-type and mutant D. discoideum strains. A, development of wild-type AX2 cells with the addition of 1 mm GABA or 1 mm glutamate on DB-agarose plates at 6 h. 5 × 106 vegetative cells were developed on agarose plates. Bar, 1 mm. B, C-terminal GFP-tagged GadA and GadB were expressed in WT cells. Cells were plated in a one-well glass chamber filled with DB, and images were taken at a 60× objective on a confocal microscope. Bar, 5 μm. C, 5 × 106 vegetative cells were washed twice with DB, suspended, and shaken in 100 μl of DB. At indicated time points after starvation, suspensions were centrifuged. 40 μl of supernatant were analyzed for amino acid content via HPLC. GABA concentrations from different genotypes at 4 h were compared with the GABA concentration of wild-type AX2:gfp cells. Values are means ± S.D. NS, non-significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA was used. D, WT cultures with an initial density of 1 × 104 cells/ml were shaken in HL5 medium at 175 rpm, 22 °C. At indicated cell density, amino acids content in the medium was measured via HPLC and compared with values of HL5 medium. Values are means ± S.D. NS, non-significant. One-way ANOVA was used. E, qPCR analysis showing gadB mRNA expression change when gadA was overexpressed. cDNA of WT cells expressing an empty vector or gadA was prepared at vegetative stage (0 h) or early development (4 h after starvation on DB agarose). rnlA was used as the housekeeping gene. gadB transcript level in WT cells expressing gadA was compared with gadB expression level in WT cells expressing an empty vector, and gadB level in WT cells expressing am empty vector was normalized to 1. Ratios are means ± S.D. NS, non-significant. One-way ANOVA was used. F, qPCR analysis showing gadA mRNA expression change when gadA was overexpressed. Same cDNA was used as in E. Ratios are means ± S.D. *, p < 0.05. One-way ANOVA was used.
We next tested whether perturbation of GABA synthesis by manipulating GAD expression would affect extracellular GABA concentration and early development. Both C-terminal GFP-tagged GadA and GadB were found localized in the cytosol (Fig. 2B). To determine the extracellular GABA concentration, the secretion of GABA during development was measured. Supernatant was measured every 2 h after starvation in control cells and in various gad mutants (Fig. 2C). Wild-type cells expressing GFP were used as controls. The extracellular GABA concentration reached a plateau between 2–4 h, suggesting that the GABA synthesis, degradation, and uptake reached equilibrium by this time. The GABA concentration at 4 h was used as a representative time point and analyzed. Consistent with its expression pattern, disruption of gadB mostly eliminated extracellular GABA with merely 2 μm remaining, and overexpression of gadB-gfp in WT cells showed a substantially elevated level of 60 μm extracellular GABA, as compared with a 35 μm extracellular concentration of GABA in control cells. Overexpression of gadB-gfp in gadA−/gadB− cells also showed a similar extracellular GABA level when compared with gadB-gfp overexpression in WT cells, suggesting GadB is the main functioning glutamate decarboxylase during this period. Disruption of gadA showed statistically indistinguishable extracellular GABA levels as compared with control cells, which correlated with previous results that gadA is transcribed at basal levels during growth and early development (15). Interestingly, overexpression of untagged or tagged gadA in WT cells significantly decreased extracellular GABA level to 16 μm, and overexpression of gadA-gfp in gadA−/gadB− cells exhibited an even lower extracellular GABA level of 8 μm.
Secreted factors usually accumulate during growth in suspension culture. Several secreted chalones, which accumulate according to cell density, inhibit growth and promote development, have already been identified (29). We speculated that GABA might also be accumulating during growth based on the secretion data during cell starvation. We measured GABA secretion as wild-type cells grew from a very low density of 1 × 104 cells/ml to a stationary stage in HL5 medium. The HL5 medium contained an average concentration of 20 μm GABA (Day 0 at Fig. 2D). The GABA concentration in HL5 medium was tightly regulated and remained near 20 μm during all stages of growth (Fig. 2D), though we had expected that the higher densities of cells would result in significant increases of extracellular GABA concentration.
Overexpression of the prespore-specific gadA in WT cells may compensate the production of GABA by GadB and therefore suppress the expression of gadB, which leads to lower concentration of extracellular GABA. To validate this possibility, we performed qPCR to show the gadB mRNA expression change when gadA was overexpressed (Fig. 2E). gadB mRNA level was not significantly altered when gadA was overexpressed at either vegetative stage or early development, suggesting overexpression of gadA does not induce or suppress expression of gadB. Because of the extremely low expression of gadA at vegetative and early development stages, the overexpression of gadA up-regulated gadA mRNA level more than 2 × 104-fold (Fig. 2F). Although gadA was also strongly induced when overexpressed in gadA−/gadB− cells, it produces only a low level of extracellular GABA (Fig. 2C). These results indicate that gadA and gadB are non-redundant.
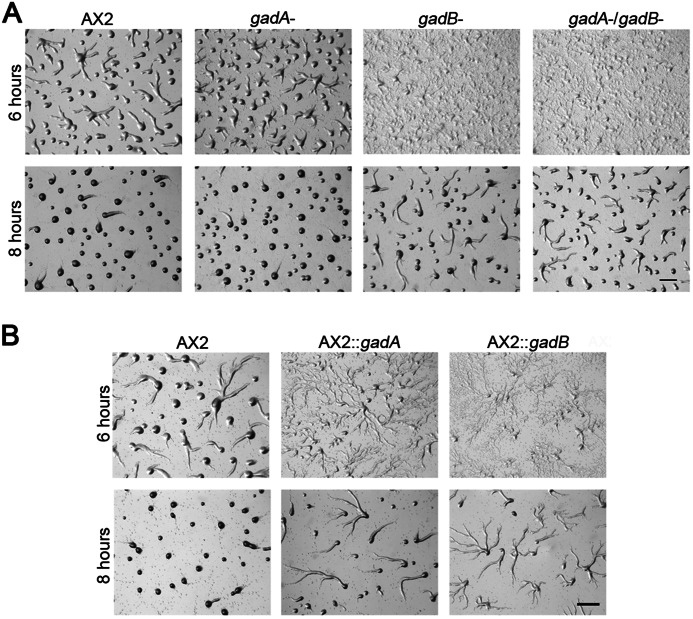
The phenotypes of mutants with different levels of extracellular GABA during early development were then examined. gadA− cells aggregated normally, while disruption of gadB delayed the aggregation about 2 h, and gadA−/gadB− cells exhibited similar delay as gadB− cells (Fig. 3A). WT cells overexpressing gadA showed a delay in aggregation (Fig. 3B), which may be due to a lack of sufficient GABA, as described above. WT cells overexpressing gadB were similarly delayed in aggregation (Fig. 3B), which was likely caused by excessive extracellular GABA. All gad null and overexpressing cells showed normal late development without any visible morphological defects (data not shown).
FIGURE 3.
Early developmental phenotypes of gad mutants. For both A and B, 5 × 106 vegetative cells were developed on a non-nutrient DB-agarose plates. Images were taken at indicated hours after development. WT::gadA, gadA was overexpressed in WT cells, WT::gadB, gadB was overexpressed in WT cells. Bar, 1 mm.
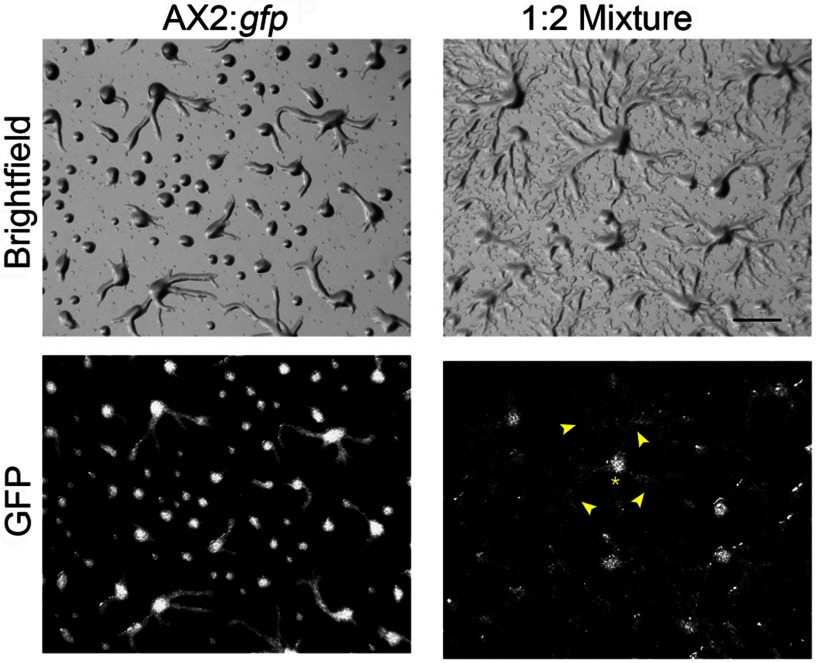
To test whether GABA is secreted as an autocrine signal, we mixed WT cells expressing GFP with WT cells overexpressing gadB in a 1:2 ratio and co-developed them on agarose substrate. Unlike homogenous WT cells, which mostly formed loose mounds at 6 h after development, a considerable amount of WT cells in the mixture were still streaming at this time (Fig. 4 arrowheads). However, most WT cells still occupied the aggregation center (Fig. 4, asterisk). The aggregation delay of WT cells in the mixture implied that GABA was secreted as an autocrine signal and functioned non-autonomously.
FIGURE 4.
Co-development of WT::gfp and WT::gadB cells. 5 × 106 vegetative cells underwent development on agarose plates. For co-development, WT::gfp and WT::gadB cells were mixed in a 1:2 ratio. Images were taken at 6 h. The asterisk denotes one aggregation center, and arrowheads show streaming WT::gfp cells toward the aggregation center. Bar, 1 mm.
GABA Is Degraded in the Mitochondrion
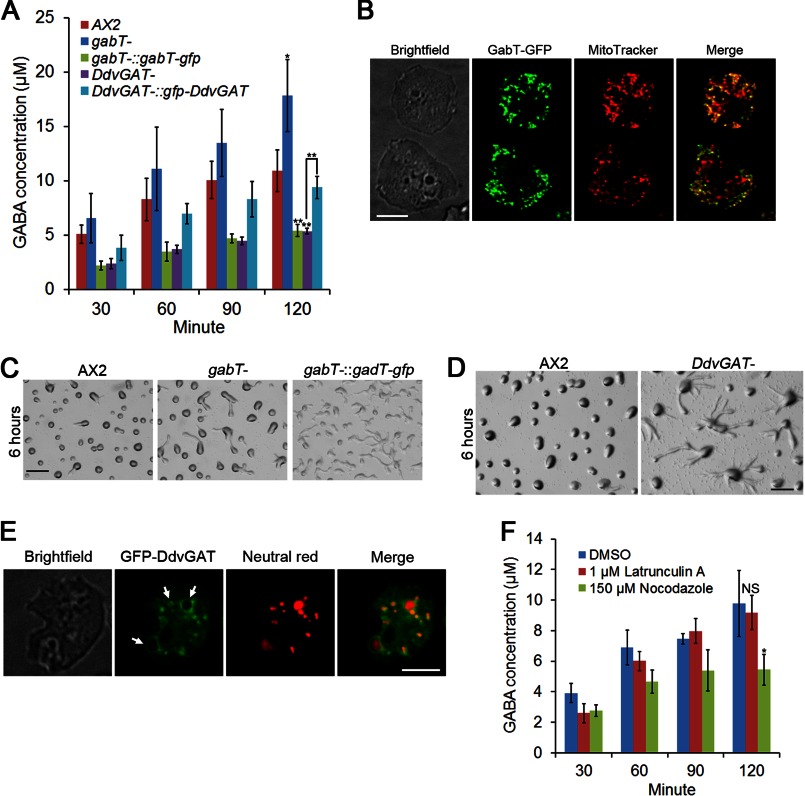
The extracellular amount of GABA is not only decided by the synthesis rate of GABA, but also by the degradation and transport of GABA out of the cell. We first studied the degradation of GABA. GABA is degraded in the mitochondria by a GABA transaminase in most eukaryotes except in yeast, which has a cytosolic GABA transaminase (30). A single GABA transaminase homologue in D. discoideum, gabT, was previously identified (16). Here we disrupted gabT, and measured extracellular GABA after starvation. Based on our previous data that extracellular GABA concentrations saturated between 2–4 h, we measured GABA at 30 min intervals for 2 h, and compared the GABA concentrations at 2 h in the different mutants. Disruption of gabT significantly increased extracellular GABA levels to 18 μm, and overexpression of a C-terminal GFP-tagged GabT in gabT- cells reduced extracellular GABA to around 5 μm (Fig. 5A). However, incubation of WT cells with 5 μm of the irreversible GABA transaminase inhibitor vigabatrin did not achieve a similar effect in increasing extracellular GABA levels (data not shown). GabT-GFP showed a punctate expression pattern, and co-localized with most of the mitotracker staining (Fig. 5B). Interestingly, GabT-GFP localized in a large fraction, but not all of the mitochondria (Fig. 5B).
FIGURE 5.
Regulation of GABA degradation and secretion. A, 5 × 106 vegetative cells were suspended and shaken in 100 μl of DB. At indicated time points after starvation, the cell suspension was centrifuged. 40 μl of supernatant were analyzed for amino acids content via HPLC. GABA concentrations from different genotypes at 120 min were compared with GABA concentration of WT cells, and GABA concentrations between DdvGAT− cells and DdvGAT− cells overexpressing GFP-DdvGAT were also compared. Values are means ± S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. One-way ANOVA was used. B, C-terminal GFP tagged GabT was expressed in gabT− cells. Cells were placed in a one-well glass chamber filled with DB, and stained with 100 nm Mitotracker red CMXRos (Invitrogen, M7512) for 30 min in DB at room temperature. Bar, 5 μm. 5 × 106 vegetative cells were developed on DB-agarose, and images were taken at 6 h for C and D. Bar, 1 mm. E, DdvGAT− cells expressing N-terminal GFP-tagged DdvGAT were placed in a glass chamber in DB, and then stained with 0.5 μm neutral red (Sigma, N4638) for 20 min. Arrows indicate representative lysosomes. Bar, 5 μm. F, 5 × 106 vegetative cells were suspended in 100 μl of DB with 1 μm Latrunculin A or 150 μm Nocodazole. Same procedure was performed as in A. Values are mean ± S.D. NS, non-significant; *, p < 0.05. One-way ANOVA was used.
We also observed the early development of gabT− and gabT-gfp overexpressing cells. gabT− cells did not exhibit a delay in early development, while gabT-gfp-overexpressing cells showed delays in aggregation (Fig. 5C). Both gabT null and overexpression cells underwent normal late development. Normal early development of gabT− cells suggested that only a high level of secreted GABA, as in GadB-overexpressing cells, interfered with early development.
DdvGAT Is Partially Required for GABA Secretion
Because extracellular GABA levels plateau between 2–4 h and appear to be regulated (Fig. 2C), we decided to examine the uptake and secretion of GABA in D. discoideum. GABA is actively transported into neurons and glia by GABA transporters (GATs). All four mammalian GATs identified so far (GAT 1–3 and Betaine transporter, BGT-1 or GAT4) belong to the superfamily of sodium and chloride-dependent transporters (31–33). A careful search of the D. discoideum genome did not reveal any homologues of the four GATs. Novel mechanisms may be employed for GABA uptake. Normally, GABA is packaged into synaptic vesicles by the vesicular GABA transporter (vGAT) in neurons (34) and released to the synaptic cleft through exocytosis. vGAT belongs to the SLC32 family (35), and shares no resemblance to the GATs. One vGAT homologue gene DDB_G0293074, was identified in D. discoideum, and we named it DdvGAT. Disruption of DdvGAT reduced extracellular GABA levels to ∼5 μm, and overexpression of an N-terminal GFP-tagged DdvGAT restored extracellular GABA concentration to about 10 μm, which is similar to wild-type cells (Fig. 5A). Previous studies revealed that the GABA transaminase inhibitor vigabatrin could also inhibit GABA transport activity of rat vGAT almost as potently as GABA (34). This may explain why the addition of vigabatrin did not increase the extracellular GABA level at 2 h after development. DdvGAT− cells also exhibited a delay in aggregation (Fig. 5D), but appeared to form normal fruiting bodies. GFP-DdvGAT was distributed on the membrane of vesicles, and these vesicles were stained with neutral red (Fig. 5E), suggesting GFP-DdvGAT is localized on the membrane of lysosomes, which is consistent with a recent mass spectrometry study of the macropinocytic proteome, which identified this protein from vesicles including macropinosomes and lysosomes (36). We also tested whether microtubules were required for GABA secretion. Addition of 150 μm Nocodazole reduced extracellular GABA levels to 5 μm (Fig. 5F), suggesting microtubules were involved in GABA secretion. Addition of 1 μm Latrunculin A had no effect on GABA secretion (Fig. 5F), indicating that actin was not required for this process.
GrlB Is the Major GABA Receptor at the Growth Stage and Early Development
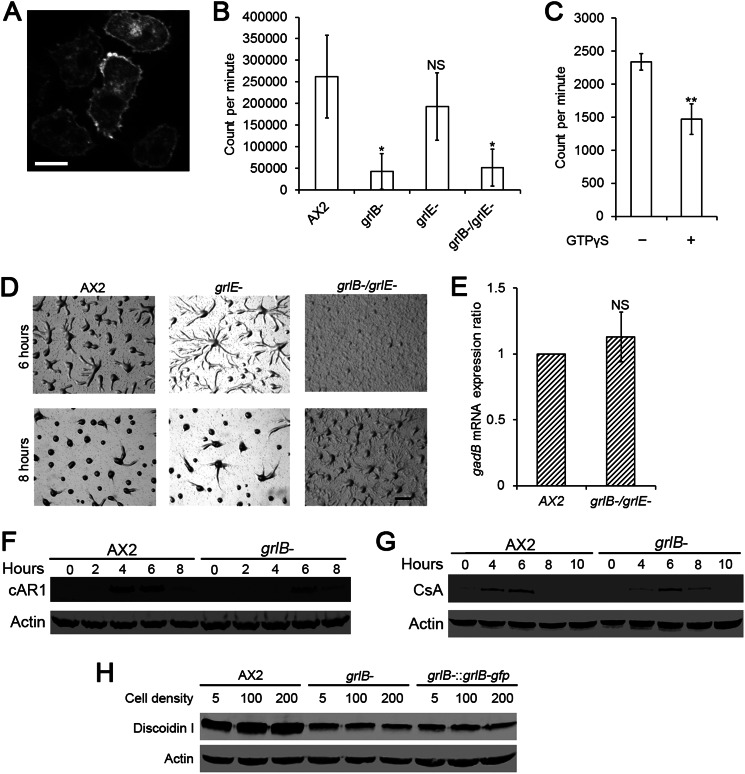
A previous study suggested that GrlE, another GABAB receptor-like family member, was the main GABA receptor during sporulation (21). Disruption of grlE reduced the amount of the bound GABA antagonist CGP54626 in whole cells by 90% (21). We decided to validate whether GrlB is also a GABA receptor. First we confirmed the localization of GrlB. In vegetative cells, the GrlB-GFP was mostly localized on the plasma membrane of cells (Fig. 6A). Next, we tested the GABA binding capacity of GrlB. We incubated 5 × 106 axenically grown cells with 0.2 nm tritium-labeled GABA for total binding. Nonspecific binding was measured by adding 1 × 106 fold excess CGP55845. We found that both grlB− cells and grlB−/grlE− cells showed only about 20% specifically bound GABA as compared with WT cells, whereas no significant difference was found between grlE− cells and WT cells (Fig. 6B). When combined with the expression profile of GrlE, whose mRNA peaks at 4 h after development (21), the binding assay results suggested that GrlB is the major GABA receptor at growth stage and early development. To further confirm that GrlB is a G protein-coupled receptor, we tested whether the non-hydrolyzable GTP analog GTPγS could desensitize GrlB and reduce GABA binding. Crude membrane fraction were prepared and treated with 0.1 mm GTPγS. The treatment of GTPγS reduced specifically bound [3H]GABA to about 63% of the untreated control (Fig. 6C). This suggested that GrlB is coupled to a heterotrimeric G protein, as would be predicted from its membrane-spanning topology.
FIGURE 6.
GABA binding in vegetative cells and early gene expression in grlB- cells. A, C-terminal GFP tagged GrlB was expressed in grlB− cells. Cells from HL5 were washed with DB and plated in a glass chamber filled with DB before photographed. Bar, 5 μm. B, specific [3H]GABA binding to whole vegetative cells was shown as radioactivity (Count per minute) per 5 × 106 cells. Values are means ± S.D. NS, non-significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. One-way ANOVA was used. C, specific [3H]GABA binding to vegetative cell membrane fraction was shown as radioactivity (count per minute) per membrane fraction from 5 × 107 cells. Values are means ± S.D. **, p < 0.01. One-way ANOVA was used. D, 5 × 106 vegetative cells were washed with DB twice and plated on a non-nutrient DB-agarose plates. Images were taken at indicated hours. Bar, 1 mm. E, qPCR analysis showing gadB mRNA expression change in axenic grlB−/grlE− cells. gadB transcript level in wild-type AX2 cells was normalized to 1. Ratios are means ± S.D., NS, non-significant. One-way ANOVA was used. For F and G, 5 × 106 vegetative cells were developed on DB-agarose. At indicated hours, cells were collected and lysed for Western blotting. Actin was used as the loading control. H, 1 × 104 cells were shaken in HL5 medium at 175 rpm, 22 °C. At indicated cell densities (×105 cells/ml), an equal amount of cells was collected and lysed for Western blotting.
A previous study reported a delay of at least 2 h in early development of grlE− cells, and showed that this delay could be rescued by overexpressing GrlE (20). We were skeptical that GrlE functioned redundantly at the transition from growth to development and also in early development, therefore we generated our own grlE− cells and our grlE− cells exhibited a slight delay in aggregation at 6 h after development. The grlB−/grlE− cells showed the same phenotype as the grlB− cells (Figs. 1 and 6D), suggesting that GrlE does not function redundantly with GrlB. Both grlE− and grlB−/grlE− cells appeared to exhibit normal morphology during late development (data not shown). We also tested whether removing GrlB and GrlE have a feedback effect on GABA production and therefore modulate the expression of GadB. qPCR showed that disruption of both grlB and grlE did not significantly change gadB mRNA expression (Fig. 6E).
To better explain why excess GABA also delays early development, we examined whether GABA could trigger the internalization of GrlB. 1 mm GABA was added to vegetative grlB− cells expressing GrlB-GFP in DB buffer, and the distribution of GrlB-GFP was recorded by time-lapse microscopy. After 20 min, no significant reduction of the plasma membrane localization of GrlB was observed (data not shown). However, when grlB− cells expressing GrlB-GFP were starved on non-nutrient DB agar, GrlB-GFP began to lose its plasma membrane localization after 4 h of starvation and was clearly enriched in the cytoplasm at 6 h (data not shown), suggesting GABA signaling through GrlB is down-regulated as cells polarize during aggregation.
Dictyostelium cells exhibit a dramatic gene expression pattern shift after starvation, and necessary “early genes” start to express during early development (14). Thus we examined the expression profiles of early genes including cAR1 and csA in grlB− cells. Developed cells were collected from an agarose substrate at different time points and analyzed. The cAMP receptor cAR1 was induced rapidly several hours after development and reached a peak at 4–6 h, and then dropped drastically in WT cells. However, cAR1 was not expressed until 6 h, and the expression tapered off at 8 h in grlB− cells (Fig. 6F). Consistent with the cAR1 expression profile, grlB− cells were poorly polarized and showed defects in their ability to display robust chemotaxis toward cAMP at 6 h (data not shown). The glycoprotein contact site A (CsA) mediates an EDTA-insensitive cell-cell cohesion via homophilic interaction during aggregation (37). In WT cells, csA peaked at 6 h and decreased thereafter. While csA also peaked at 6 h in grlB- cells, there was little expression at 4 h and continued expression until 8 h (Fig. 6G).
Although aggregation is affected and expression of chemotaxis and adhesion genes required for early development are delayed, it is difficult to conclude that GABA signaling interacts directly with the cAMP signaling pathway. Previous work has demonstrated that excess GABA had no effect on cAMP chemotaxis (20). To clearly understand the function of GABA during growth and development, we examined events occurring before aggregation. The pre-starvation response is one of many cellular processes induced by nutrient depletion, and the marker protein Discoidin I is expressed in axenically grown cells and sharply induced according to cell density (38, 39). Although Discoidin I was expressed at a relatively high level at low WT cell density (5 × 105 cells/ml) in our hands, it was induced to the highest level at saturation density (2 × 107 cells/ml) (Fig. 6H). However, the induction of Discoidin I by cell density was totally abolished in grlB− cells and grlB−:grlB-gfp cells. The expression of discoidin I remained at a low level at all densities (Fig. 6H).
Different Genes Required for Spore Formation
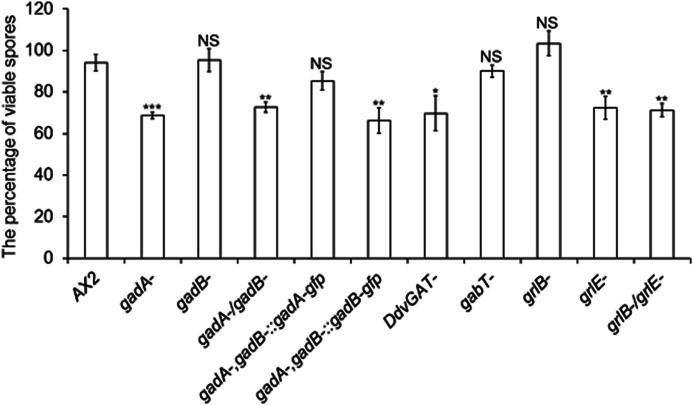
GABA has been suggested to induce spore formation, and GadA and GrlE were suggested as two components of GABA signaling (21). However, whether genes involved in GABA metabolism and signaling in growth and early development are also required for this process is still unknown. Therefore we examined the spore formation in different mutants related to GABA metabolism (Fig. 7). Most of the wild-type spores were detergent-resistant, and only about 70% of spores from gadA− cells were viable after Nonidet P-40 treatment as previously described (21). However, gadB− cells formed a similar percentage of viable spores as did wild-type cells, suggesting that GadB is not required for spore formation. According to the expression pattern of gadB, GadB may not exist during sporulation. To test whether GadB could functionally complement GadA, we overexpressed GadB-GFP under the control of the actin15 promoter in gadA−/gadB− cells and examined viable spores. gadA−/gadB− cells formed significantly reduced viable spores. Overexpression of GadA-GFP in gadA−/gadB− cells successfully recovered the reduced viable spores number to normal level as compared with wild-type cells, whereas gadA−/gadB− cells overexpressing GadB-GFP still exhibited reduced viable spores, suggesting GadB could not functionally complement GadA during sporulation.
FIGURE 7.
The percentage of detergent-resistant spores in different GABA mutants. 1 × 107 cells were developed on buffer-saturated filters. After 48 h, spores were collected and treated with 0.4% Nonidet P-40 for 10 min. 100 spores were then counted and cultured with bacteria. The plaques formed from detergent-resistant spores were counted after 5 days. Values are means ± S.D., NS, non-significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA was used.
grlE
grlE cells only formed about 70% viable spores, whereas grlB− cells formed similar percentage of viable spores as wild-type cells (Fig. 7), suggesting GrlB is not required for spore formation. grlB−/grlE− cells generated similar viable spores as grlE− cells. As we expected, gabT− cells generated similar viable spores as wild-type cells. Interestingly, DdvGAT− cells generated significantly reduced viable spores, suggesting that DdvGAT is likely responsible for GABA secretion in prespore cells.
DISCUSSION
The evolutionary history of glutamate decarboxylase appears to be quite complicated. In the lower prokaryote Escherichia coli, two isozymes of GadA and GadB show identical biochemical properties (40). However, two human isoforms of GADs, GAD65 and GAD67, differ in many aspects including subcellular localization, enzymatic activity and expression region and level (41, 42). These divergences indicate that GAD65 and GAD67 are both spatially and temporally regulated. In D. discoideum, two isozymes, GadA and GadB, are most similar to their homologues in E. coli., but are temporally regulated. GadB is expressed in vegetative and early development stages, and decreases before the rising expression of GadA. This mutually exclusive expression pattern of GadA and GadB could be explained by our data. Disruption of gadB eliminates production of GABA, and gadA is not up-regulated to compensate the loss of gadB. A previous study reported that the disruption of gadA alone leads to the sporulation defect (21), and our data suggest that GadB is not required for sporulation. Besides, GadB could not functionally complement GadA when overexpressed in the sporulation stage, possibly because GadB is inactive during this stage. These results suggest that GadA and GadB are differentially regulated. In addition, as we show here, co-expression of GadA and GadB would reduce the production of extracellular GABA. Because overexpression of GadA does not alter the transcript level of GadB, one plausible explanation for reduced GABA production in wild-type cells expressing gadA is that GadA has a much stronger affinity for the enzyme cofactor pyridoxal phosphate than GadB and sequesters the cofactor when overexpressed, therefore GadB is devoid of pyridoxal phosphate and remains as an apoenzyme. Recombinant GAD65 has been reported to be more preferable to the enzyme cofactor than GAD67 (42).
It seems that the enzymatic activity of GadA and GadB are not identical, although they are highly similar to each other. Overexpressing GadA alone drastically induces gadA mRNA level in gadA−/gadB− cells but still results in low extracellular GABA levels during early development, suggesting the activity of GadA is extremely low and/or the environment is optimal for GadB but not GadA. On the basis of weak activity of GadA, it can be inferred that only a small amount of GABA is required for spore formation. It has been shown that GadA expression is enriched in pre-spore cells and GABA generated from pre-spore cells can induce sporulation (15, 21). 1 nm GABA is sufficient to maximally induce spore formation (21). The weak enzymatic activity of GadA could also explain why a huge amount of gadA mRNA is enriched in pre-spore cells for generating enough GABA to induce cell differentiation (21, 43). Our data support the idea that the GadB is responsible for GABA shunt in vegetative stage and regulation of early development, and GadA is specific for sporulation.
In mammalian systems, GABA is actively transported into the cell in favor of the ionic gradient by GABA transporters (GATs), while amoebae lack most of the counterpart homologues. However, there are still several putative amino acid transporters in the D. discoideum genome, including tmem104, ctrA-C, DDB_G0287423, DDB_G0267504, and DDB_G0287303. The functions of these proteins remain largely unknown. Another possible way for GABA absorption is through pinocytosis. Axenic cells acquire nutrients from liquid medium through pinosomes, and it is likely that GABA in the medium can also be absorbed.
vGAT is responsible for synaptic GABA release only in neurons. However, DdvGAT is responsible for GABA secretion in the social amoeba, implying that it is an ancient mechanism for GABA secretion. The disruption of DdvGAT reduced secreted GABA to 50% of normal levels at 2 h after starvation, which suggests the existence of other mechanisms for GABA secretion. Loss of DdvGAT causes the similar defect in sporulation as loss of GadA, indicating this mechanism likely exists in pre-spore cells to release GABA.
Extracellular GABA levels need to be tightly regulated, with low and high levels both leading to a delay in early development. When WT cells were mixed with GadB-overexpressing cells, the increased extracellular levels of GABA presumably also delayed the development of the WT cells. Moreover, it seems that only very high levels of GABA have these effects. WT cells secrete about 11 μm GABA at 2 h after starvation, and WT cells expressing gadB secrete about 38 μm at the same time and exhibit a significant delay in aggregation, whereas gabT- cells, which increase GABA level to about 18 μm, aggregate normally. Compared with wild-type cells, gabT− cells don't show very high extracellular GABA, suggesting that newly synthesized GABA is partially degraded in the mitochondria.
Two confusing questions still remain unanswered in this study. First, why does exogenous addition of GABA not delay aggregation? The GABA secretion data we collected were from cells in suspension, and they may not reflect the real GABA secretion when cells develop on surface, which is very difficult to measure. Crawling cells on a surface may only sense GABA from their surrounding cells and respond to it, and they might also secrete an unknown enzyme to clear GABA in their environment. This enzyme is probably not the GabT, which we found is localized in the mitochondria. If a gradient in the microenvironment surrounding a cell is required for the function of GABA, the uniform application of GABA would not exhibit any effects. One well known secreted factor in early development of Dictyostelium is cAMP. During streaming toward an aggregation center, rearguard localized Adenylate Cyclase of Aggregation stage (ACA) secrets cAMP guiding chemotaxis of subsequent cells, and cells secrete cAMP phosphodiesterase (PDE) to remove surrounding cAMP (44, 45). Another possibility is that intracellular GABA causes the phenotypes and also controls the levels of external GABA. GABA is generated in the GABA shunt, which is required for energy metabolism. Thus intracellular GABA levels might represent the nutritional or energy state of a cell. These metabolic states clearly specify whether a cell would start to develop. If this is the case, direct addition of GABA would also have no effect.
Secondly, why do deficient and excess extracellular GABA levels both generate the delay in aggregation? It is easy to understand that insufficient extracellular GABA could lead to the abolishment of the pre-starvation response and result in the delay in early genes expression, and the aggregation process. However, the mechanism by which excess extracellular GABA works is unclear. Maybe high GABA levels down-regulate the GABA receptor. We tested the internalization of GFP-labeled GrlB when excess GABA was provided, but the plasma membrane localization of GrlB-GFP was barely changed after 20 min of treatment, strongly suggesting that receptor internalization is not responsible for the gadB overexpression phenotype.
GABA signaling during early development is also regulated through the regulation of the localization of GABA receptor GrlB. The GrlB-GFP fusion showed internalization when cells start to become polarized. Although most highly polarized cells lose the plasma membrane localization of GrlB-GFP, overexpression of GrlB might still leave trace amount of receptors at the membrane. This continuous GABA signaling might jeopardize the onset of aggregation. This could explain why overexpression of GrlB in WT cell shows more severe delay in aggregation than in grlB− cells. In vegetative cells, both co-culture with bacteria and periodic folic acid pulsing greatly increase transcript levels of grlB. These two treatments sharply up-regulate the capacity of axenic cells to chemotax toward folic acid, indicating that folic acid signaling somehow interacts with GABA signaling and regulates expression of GrlB. It is possible that there is crossover at the level of the heterotrimeric G proteins. Given that many G protein mutants are available, it may be worth examining GABA signaling in the various Gα subunit nulls, including Gα4, which is coupled to the folic acid receptor(s) (46).
In summary, we have investigated the homeostasis of GABA and explored its function during early development of D. discoideum for the first time. GABA is converted from glutamate mainly by the cytosolic glutamic acid decarboxylase GadB. Because of its trace expression level, the glutamic acid decarboxylase GadA generates little or no GABA at this time. However, elevated expression of GadA suppresses production of GABA possibly by sequestering the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate. Newly synthesized GABA is secreted through two potential pathways. DdvGAT, the only homologue of vGAT, is expressed on the membrane of lysosomes and likely transports GABA into the lysosomes. GABA is then released through exocytosis. It is also possible that GABA is transported directly by an unknown plasma membrane bound transporter(s). GABA is degraded in the mitochondria by the GABA transaminase GabT. Secreted GABA binds to the G protein-coupled receptor GrlB of surrounding cells, which in turn triggers the pre-starvation response and regulates early development.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank dictyBase, Drs. Peter Devreotes and William Loomis for generously providing cell strains and reagents, and we also thank Raymond Johnson for technical assistance with HPLC.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant GM080370 (to C. J.).

This article contains supplemental Table S1.
- GABA
- γ-aminobutyric acid
- GAD
- glutamic acid decarboxylase
- vGAT
- vesicular GABA transporter
- SSA
- succinic-semialdehyde
- TCA
- tricarboxylic acid cycle
- ACA
- adenylate cyclase of aggregation stage
- GTPγS
- guanosine 5′-3-O-(thio)triphosphate.
REFERENCES
- 1. Jakoby W. B., Fredericks J. (1959) Pyrrolidine and putrescine metabolism: gamma-aminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 234, 2145–2150 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Roberts E., Ayengar P., Posner I. (1953) Transamination of gamma-aminobutyric acid and beta-alanine in microorganisms. J. Biol. Chem. 203, 195–204 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Roberts E., Frankel S. (1950) gamma-Aminobutyric acid in brain: its formation from glutamic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 187, 55–63 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Steward F. C., Thompson J. F., Dent C. E. (1949) γ-Aminobutyric acid: a constituent of the potato tuber? Science 110, 439–440 [Google Scholar]
- 5. Shelp B. J., Mullen R. T., Waller J. C. (2012) Compartmentation of GABA metabolism raises intriguing questions. Trends Plant Sci. 17, 57–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Bouché N., Fromm H. (2004) GABA in plants: just a metabolite? Trends Plant Sci. 9, 110–115 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Palanivelu R., Brass L., Edlund A. F., Preuss D. (2003) Pollen tube growth and guidance is regulated by POP2, an Arabidopsis gene that controls GABA levels. Cell 114, 47–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Kleppner S. R., Tobin A. J. (2002) in Encyclopedia of the Human Brain (Ramachandran V. S., ed) pp. 353–367 [Google Scholar]
- 9. Owens D. F., Kriegstein A. R. (2002) Is there more to GABA than synaptic inhibition? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 715–727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Meldrum B. S. (1989) GABAergic mechanisms in the pathogenesis and treatment of epilepsy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 27, 3S–11S [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Reddy P. H., Williams M., Tagle D. A. (1999) Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of Huntington's disease. Trends Neurosci 22, 248–255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kessin R. H. (2001) Dictyostelium: The Evolution, Cell Biology, and Development of a Social Organism, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ehrenman K., Yang G., Hong W. P., Gao T., Jang W., Brock D. A., Hatton R. D., Shoemaker J. D., Gomer R. H. (2004) Disruption of aldehyde reductase increases group size in dictyostelium. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 837–847 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Iranfar N., Fuller D., Loomis W. F. (2003) Genome-wide expression analyses of gene regulation during early development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Eukaryot Cell 2, 664–670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Iranfar N., Fuller D., Sasik R., Hwa T., Laub M., Loomis W. F. (2001) Expression patterns of cell-type-specific genes in Dictyostelium. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 2590–2600 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Anjard C., Su Y., Loomis W. F. (2009) Steroids initiate a signaling cascade that triggers rapid sporulation in Dictyostelium. Development 136, 803–812 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Eichinger L., Pachebat J. A., Glöckner G., Rajandream M. A., Sucgang R., Berriman M., Song J., Olsen R., Szafranski K., Xu Q., Tunggal B., Kummerfeld S., Madera M., Konfortov B. A., Rivero F., Bankier A. T., Lehmann R., Hamlin N., Davies R., Gaudet P., Fey P., Pilcher K., Chen G., Saunders D., Sodergren E., Davis P., Kerhornou A., Nie X., Hall N., Anjard C., Hemphill L., Bason N., Farbrother P., Desany B., Just E., Morio T., Rost R., Churcher C., Cooper J., Haydock S., van Driessche N., Cronin A., Goodhead I., Muzny D., Mourier T., Pain A., Lu M., Harper D., Lindsay R., Hauser H., James K., Quiles M., Madan Babu M., Saito T., Buchrieser C., Wardroper A., Felder M., Thangavelu M., Johnson D., Knights A., Loulseged H., Mungall K., Oliver K., Price C., Quail M. A., Urushihara H., Hernandez J., Rabbinowitsch E., Steffen D., Sanders M., Ma J., Kohara Y., Sharp S., Simmonds M., Spiegler S., Tivey A., Sugano S., White B., Walker D., Woodward J., Winckler T., Tanaka Y., Shaulsky G., Schleicher M., Weinstock G., Rosenthal A., Cox E. C., Chisholm R. L., Gibbs R., Loomis W. F., Platzer M., Kay R. R., Williams J., Dear P. H., Noegel A. A., Barrell B., Kuspa A. (2005) The genome of the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature 435, 43–57 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Prabhu Y., Eichinger L. (2006) The Dictyostelium repertoire of seven transmembrane domain receptors. Eur J. Cell Biol. 85, 937–946 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Heidel A. J., Lawal H. M., Felder M., Schilde C., Helps N. R., Tunggal B., Rivero F., John U., Schleicher M., Eichinger L., Platzer M., Noegel A. A., Schaap P., Glöckner G. (2011) Phylogeny-wide analysis of social amoeba genomes highlights ancient origins for complex intercellular communication. Genome Res 21, 1882–1891 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Taniura H., Sanada N., Kuramoto N., Yoneda Y. (2006) A metabotropic glutamate receptor family gene in Dictyostelium discoideum. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 12336–12343 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Anjard C., Loomis W. F. (2006) GABA induces terminal differentiation of Dictyostelium through a GABAB receptor. Development 133, 2253–2261 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Prabhu Y., Mondal S., Eichinger L., Noegel A. A. (2007) A GPCR involved in post aggregation events in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev. Biol. 312, 29–43 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Prabhu Y., Müller R., Anjard C., Noegel A. A. (2007) GrlJ, a Dictyostelium GABAB-like receptor with roles in post-aggregation development. BMC Dev. Biol. 7, 44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Faix J., Kreppel L., Shaulsky G., Schleicher M., Kimmel A. R. (2004) A rapid and efficient method to generate multiple gene disruptions in Dictyostelium discoideum using a single selectable marker and the Cre-loxP system. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, e143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Charette S. J., Cosson P. (2004) Preparation of genomic DNA from Dictyostelium discoideum for PCR analysis. BioTechniques 36, 574–575 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Aarskog N. K., Vedeler C. A. (2000) Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. A new method that detects both the peripheral myelin protein 22 duplication in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A disease and the peripheral myelin protein 22 deletion in hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies. Hum. Genet. 107, 494–498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Snaar-Jagalska B. E., Van Es S., Kesbeke F., Van Haastert P. J. (1991) Activation of a pertussis-toxin-sensitive guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory protein during desensitization of Dictyostelium discoideum cells to chemotactic signals. Eur. J. Biochem. 195, 715–721 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Sillo A., Bloomfield G., Balest A., Balbo A., Pergolizzi B., Peracino B., Skelton J., Ivens A., Bozzaro S. (2008) Genome-wide transcriptional changes induced by phagocytosis or growth on bacteria in Dictyostelium. BMC Genomics 9, 291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Gomer R. H., Jang W., Brazill D. (2011) Cell density sensing and size determination. Dev. Growth Differ. 53, 482–494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Huh W. K., Falvo J. V., Gerke L. C., Carroll A. S., Howson R. W., Weissman J. S., O'Shea E. K. (2003) Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 425, 686–691 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Liu Q. R., López-Corcuera B., Nelson H., Mandiyan S., Nelson N. (1992) Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the transporter of taurine and β-alanine in mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 12145–12149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Lopez-Corcuera B., Liu Q. R., Mandiyan S., Nelson H., Nelson N. (1992) Expression of a mouse brain cDNA encoding novel γ-aminobutyric acid transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 17491–17493 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Liu Q. R., López-Corcuera B., Mandiyan S., Nelson H., Nelson N. (1993) Molecular characterization of four pharmacologically distinct γ-aminobutyric acid transporters in mouse brain. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 2106–2112 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. McIntire S. L., Reimer R. J., Schuske K., Edwards R. H., Jorgensen E. M. (1997) Identification and characterization of the vesicular GABA transporter. Nature 389, 870–876 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Gasnier B. (2004) The SLC32 transporter, a key protein for the synaptic release of inhibitory amino acids. Pflugers Arch. 447, 756–759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Journet A., Klein G., Brugière S., Vandenbrouck Y., Chapel A., Kieffer S., Bruley C., Masselon C., Aubry L. (2012) Investigating the macropinocytic proteome of Dictyostelium amoebae by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Proteomics 12, 241–245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Siu C. H., Sriskanthadevan S., Wang J., Hou L., Chen G., Xu X., Thomson A., Yang C. (2011) Regulation of spatiotemporal expression of cell-cell adhesion molecules during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev. Growth Differ. 53, 518–527 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Maeda Y. (2011) Cell-cycle checkpoint for transition from cell division to differentiation. Dev. Growth Differ. 53, 463–481 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Clarke M., Kayman S. C., Riley K. (1987) Density-dependent induction of discoidin-I synthesis in exponentially growing cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation 34, 79–87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. De Biase D., Tramonti A., John R. A., Bossa F. (1996) Isolation, overexpression, and biochemical characterization of the two isoforms of glutamic acid decarboxylase from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 8, 430–438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Soghomonian J. J., Martin D. L. (1998) Two isoforms of glutamate decarboxylase: why? Trends Pharmacol Sci 19, 500–505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Erlander M. G., Tillakaratne N. J., Feldblum S., Patel N., Tobin A. J. (1991) Two genes encode distinct glutamate decarboxylases. Neuron 7, 91–100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Maruo T., Sakamoto H., Iranfar N., Fuller D., Morio T., Urushihara H., Tanaka Y., Maeda M., Loomis W. F. (2004) Control of cell type proportioning in Dictyostelium discoideum by differentiation-inducing factor as determined by in situ hybridization. Eukaryot. Cell 3, 1241–1248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Sucgang R., Weijer C. J., Siegert F., Franke J., Kessin R. H. (1997) Null mutations of the Dictyostelium cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase gene block chemotactic cell movement in developing aggregates. Dev. Biol. 192, 181–192 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Kriebel P. W., Barr V. A., Parent C. A. (2003) Adenylyl cyclase localization regulates streaming during chemotaxis. Cell 112, 549–560 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Hadwiger J. A., Wilkie T. M., Strathmann M., Firtel R. A. (1991) Identification of Dictyostelium Gα genes expressed during multicellular development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 8213–8217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.