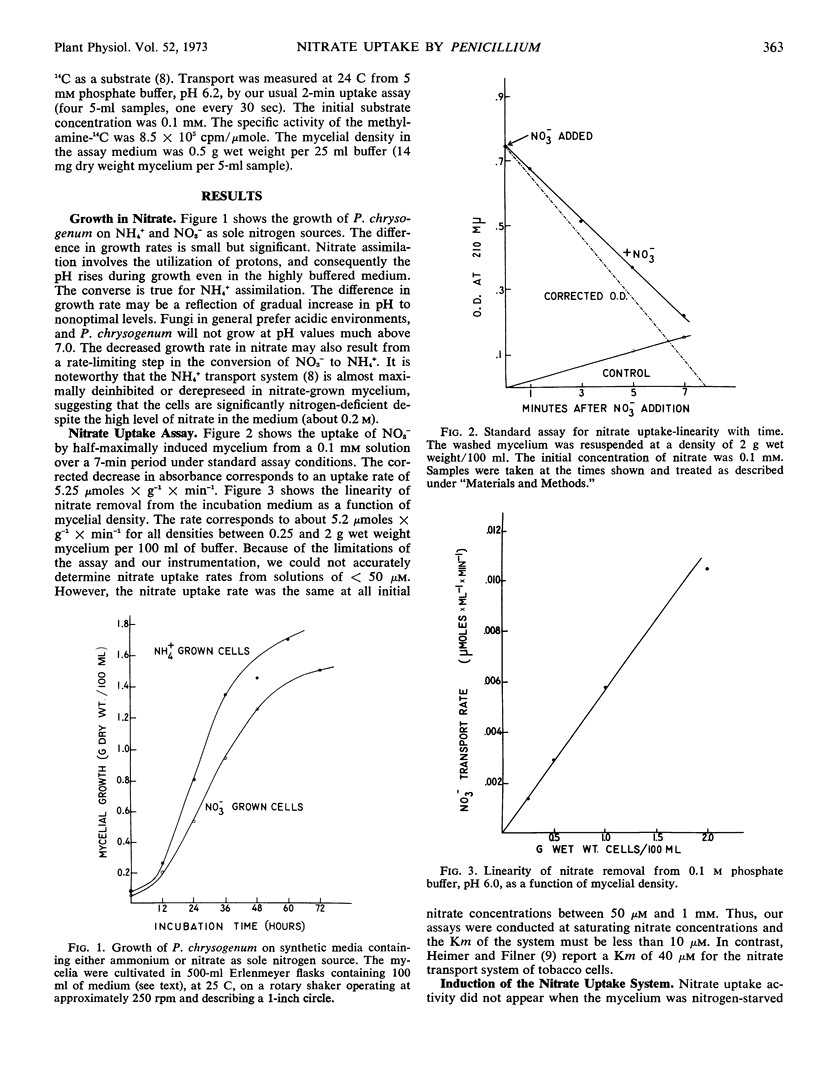
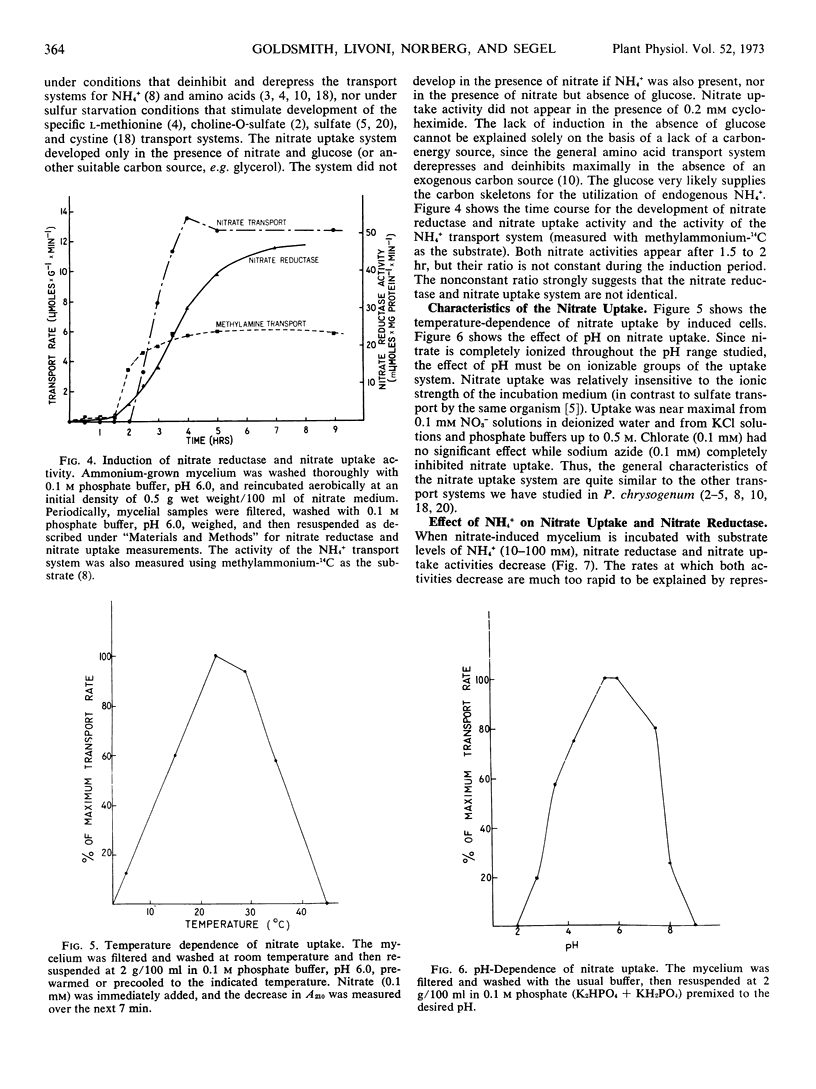
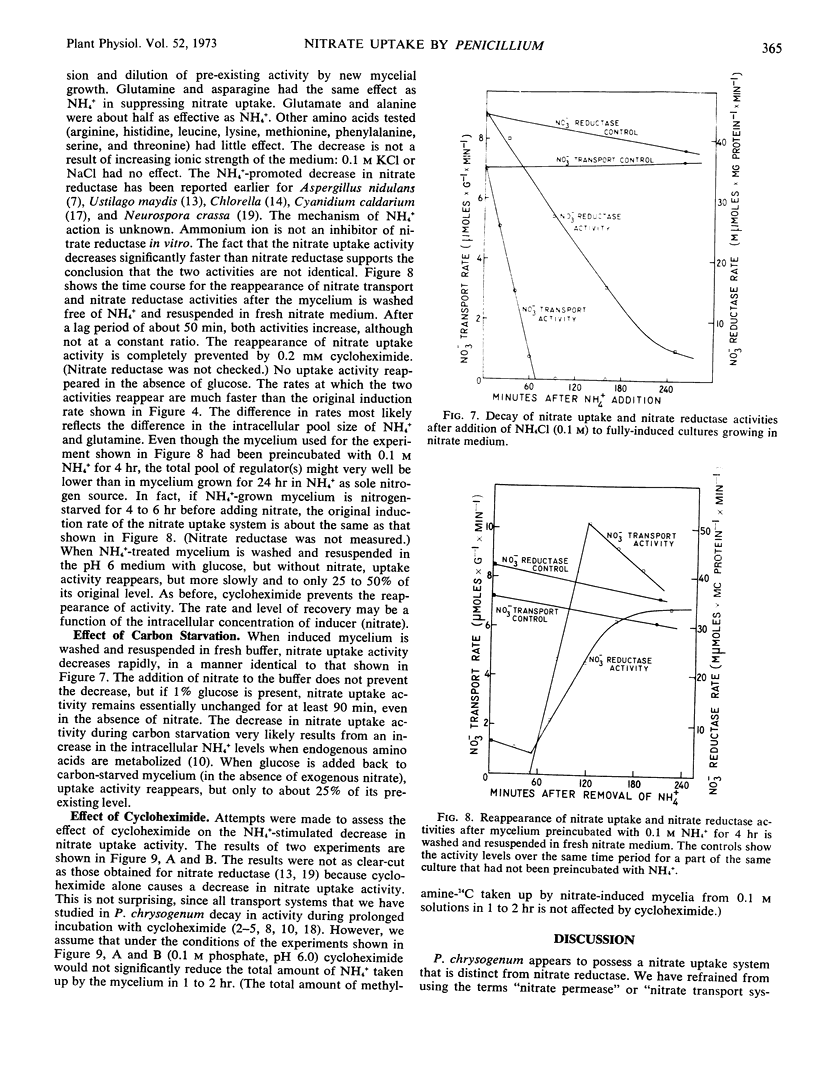
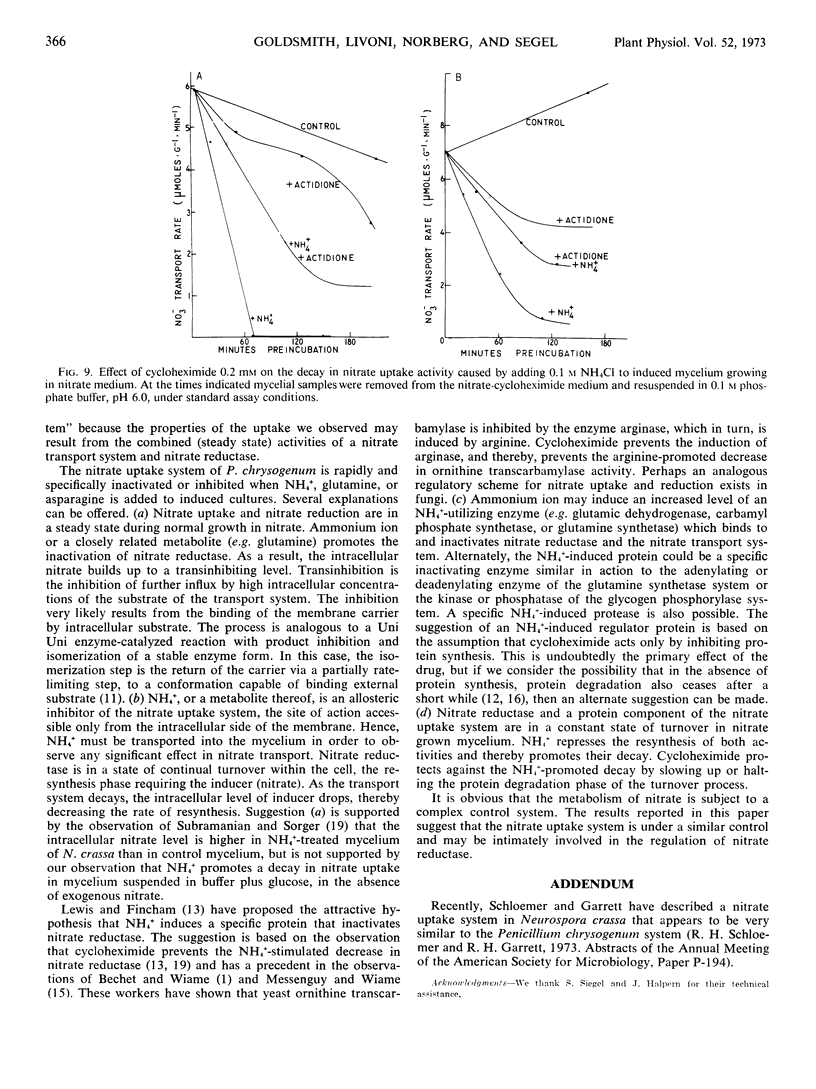
Abstract
A nitrate uptake system is induced (along with nitrate reductase) when NH4+-grown Penicillium chrysogenum is incubated with inorganic nitrate in synthetic medium in the absence of NH4+. Nitrate uptake and nitrate reduction are probably in steady state in fully induced mycelium, but the ratios of the two activities are not constant during the induction period. Substrate concentrations of ammonium cause a rapid decay of nitrate uptake and nitrate reductase activity. The two activities are differentially inactivated (the uptake activity being more sensitive). Glutamine and asparagine are as effective as NH4+ in suppressing nitrate uptake activity. Glutamate and alanine were about half as effective as NH4+. Cycloheximide interferes with the NH4+-induced decay of nitrate uptake activity. The ammonium transport system is almost maximally deinhibited (or derepressed) in nitrate-grown mycelium.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bechet J., Wiame J. M. Indication of a specific regulatory binding protein for ornithinetranscarbamylase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 8;21(3):226–234. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellenger N., Nissen P., Wood T. C., Segel I. H. Specificity and control of choline-O-sulfate transport in filamentous fungi. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1574–1585. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1574-1585.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benko P. V., Wood T. C., Segel I. H. Multiplicity and regulation of amino acid transport in Penicillium chrysogenum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):498–508. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield G., Somerfield P., Meyn T., Holby M., Babcock D., Bradley D., Segel I. H. Regulation of sulfate transport in filamentous fungi. Plant Physiol. 1970 Nov;46(5):720–727. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.5.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. The induction and repression of nitrate reductase in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 11;113(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackette S. L., Skye G. E., Burton C., Segel I. H. Characterization of an ammonium transport system in filamentous fungi with methylammonium-14C as the substrate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4241–4250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer Y. M., Filner P. Regulation of the nitrate assimilation pathway in cultured tobacco cells. 3. The nitrate uptake system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 23;230(2):362–372. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. R., Segel I. H. Acidic and basic amino acid transport systems of Penicillium chrysogenum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):168–183. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90466-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. R., Segel I. H. Control of the general amino acid permease of Penicillium chrysogenum by transinhibition and turnover. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):387–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney F. T. Turnover of rat liver tyrosine transaminase: stabilization after inhibition of protein synthesis. Science. 1967 Apr 28;156(3774):525–528. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3774.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. M., Fincham J. R. Regulation of nitrate reductase in the basidiomycete Ustilago maydis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.55-61.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losada M., Paneque A., Aparicio P. J., Vega J. M., Cárdenas J., Herrera J. Inactivation and repression by ammonium of the nitrate reducing system in chlorella. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1009–1015. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messenguy F., Wiame J. -M. The control of ornithinetranscarbamylase activity by arginase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1969 Apr;3(1):47–49. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Tomkins G. M. Effect of inhibitors of nucleic acid synthesis on steroid-mediated induction of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigano C. Studies on nitrate reductase from Cyanidium caldarium. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;76(3):265–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00409121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skye G. E., Segel I. H. Independent regulation of cysteine and cystine transport in Penicillium chrysogenum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 May;138(1):306–318. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90311-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Sorger G. J. Regulation of nitrate reductase in Neurospora crassa: stability in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):538–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.538-546.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto L. A., Segel I. H. The inorganic sulfate transport system of Penicillium chrysogenum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jun;114(3):523–538. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90376-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



