Abstract
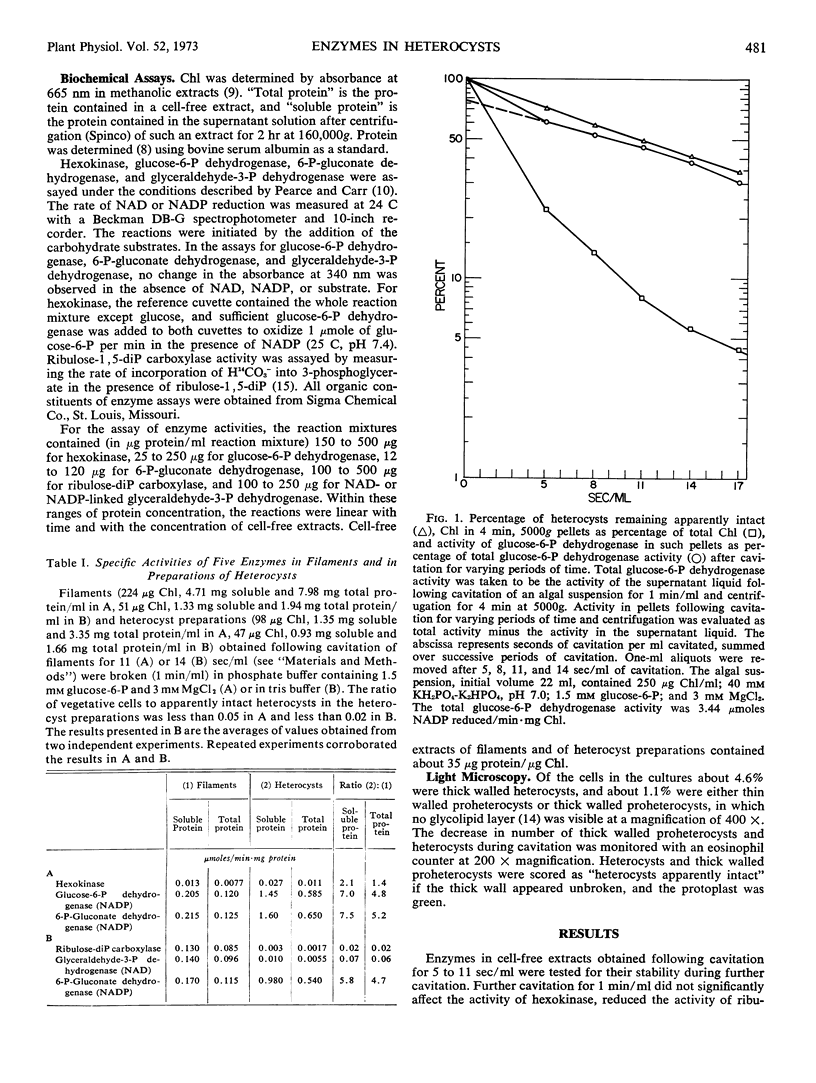
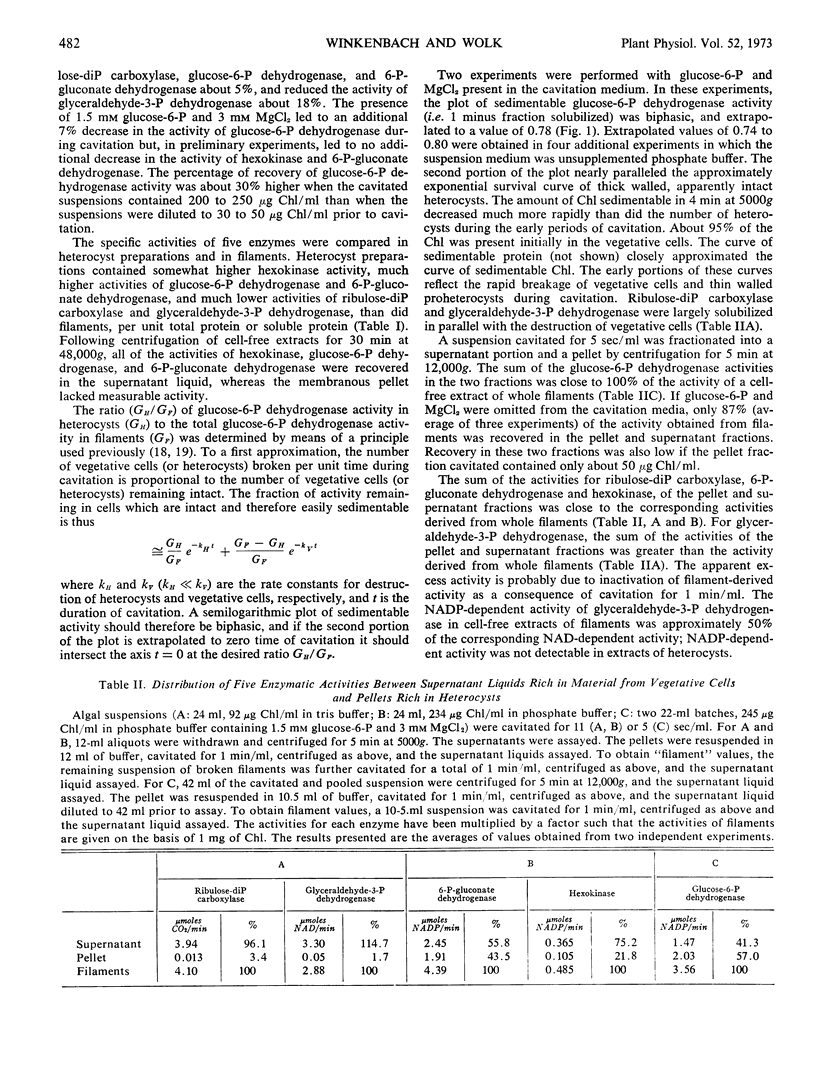
Preparations of heterocysts of Anabaena cylindrica Lemm. had 7- to 8-fold higher activities of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, 2-fold more hexokinase activity, and 0.02 to 0.06 times as much ribulose diphosphate carboxylase and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase activities as did whole filaments per milligram soluble protein in cell-free extracts. Time courses of solubilization of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity indicated that heterocysts contain 74 to 80% of the total activity of this enzyme in filaments.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. B., Arnon D. I. Studies on Nitrogen-Fixing Blue-Green Algae. I. Growth and Nitrogen Fixation by Anabaena Cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):366–372. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y., Gibbs M. Dark and photometabolism of sugars by a blue green alga: Tolypothrix tenuis. Plant Physiol. 1966 Apr;41(4):731–737. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donze M., Haveman J., Schiereck P. Absence of photosystem 2 in heterocysts of the blue-green alga Anabaena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 21;256(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. H., Simon R. D., Wolk C. P. Incorporation of amino sugars into walls during heterocyst differentiation. Dev Biol. 1971 Sep;26(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P., Kulasooriya S. A. Tetrazolium reduction and nitrogenase activity in heterocystous blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;87(4):341–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00409133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P., Stewart W. D., Walsby A. E., Fogg G. E. Is the heterocyst the site of nitrogen fixation in blue-green algae? Nature. 1968 Nov 23;220(5169):810–812. doi: 10.1038/220810b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J., Carr N. G. The incorporation and metabolism of glucose by Anabaena variabilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):451–462. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Bassham J. A. Photosynthetic and dark carbon metabolism in unicellular blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;86(1):25–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00412397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Rippka R., Stanier R. Y. Metabolism of glucose by unicellular blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;87(4):303–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00409131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



