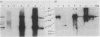Abstract
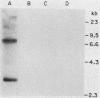
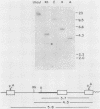
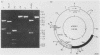
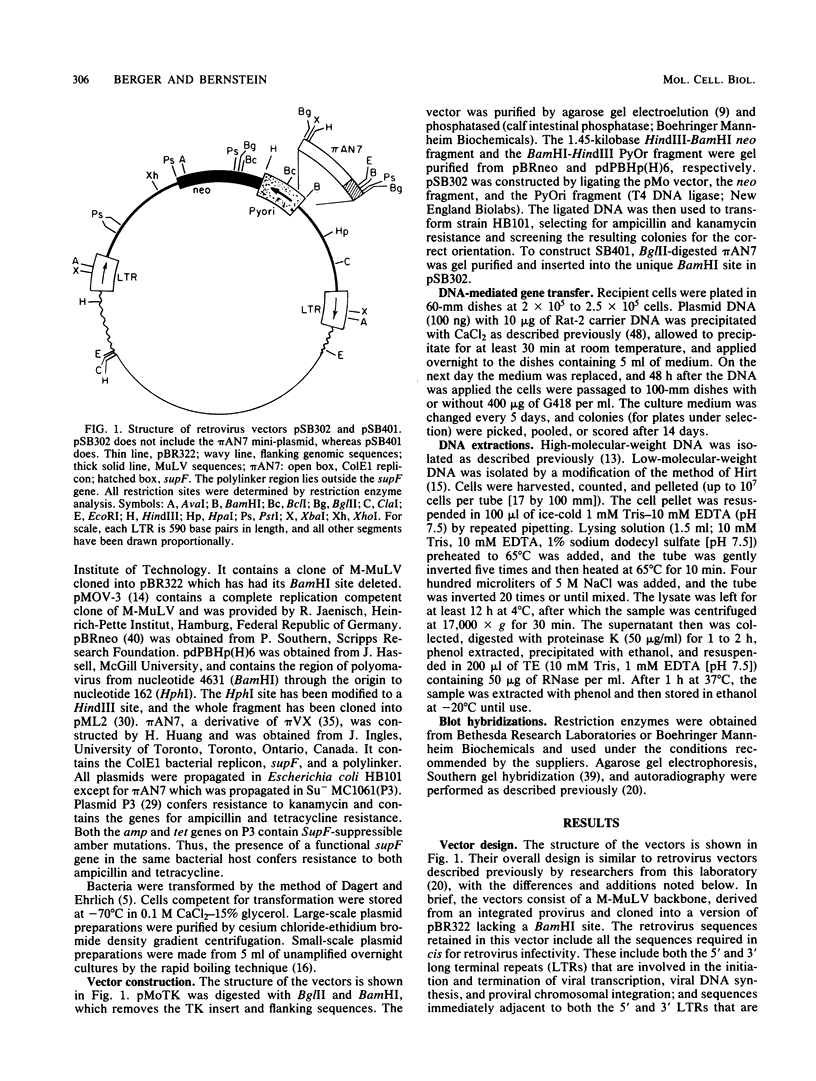
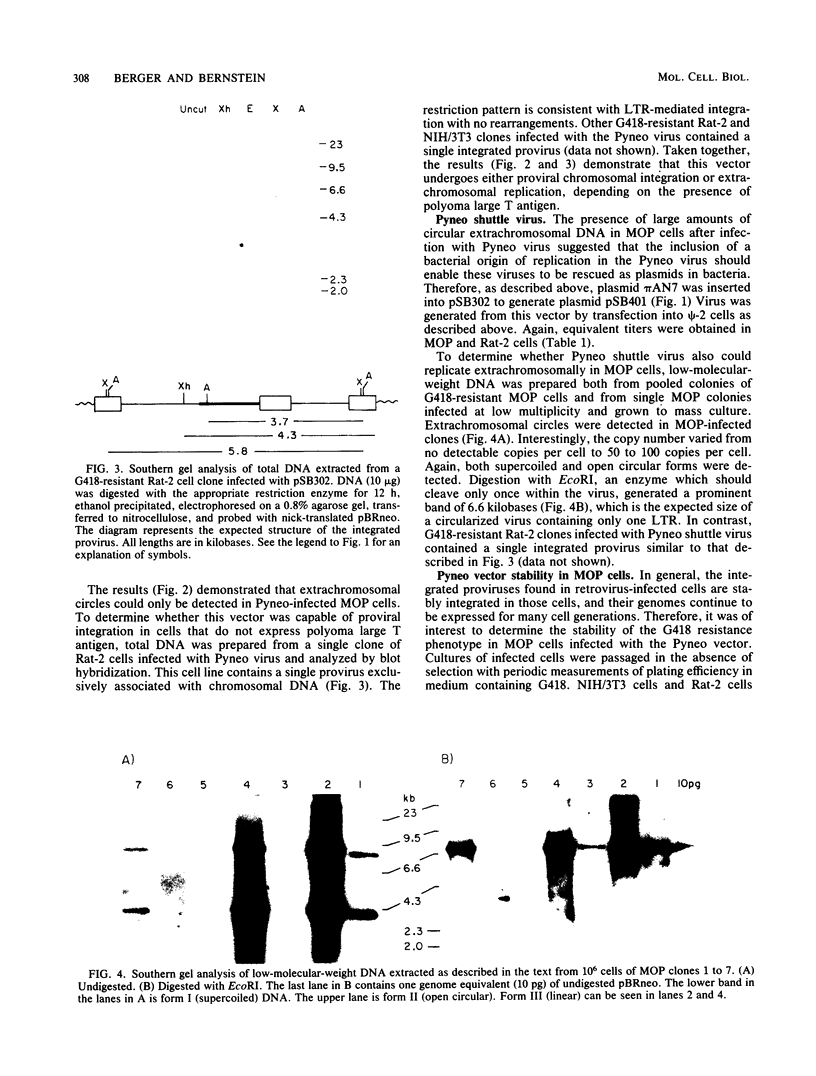
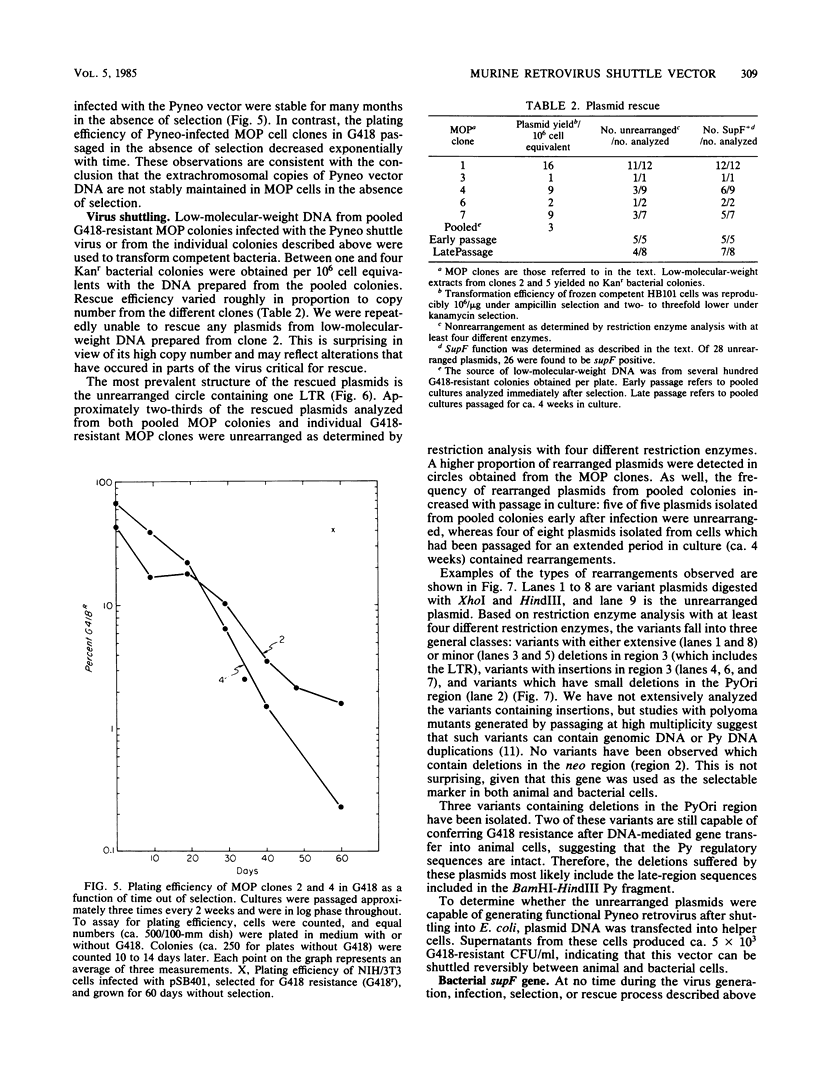
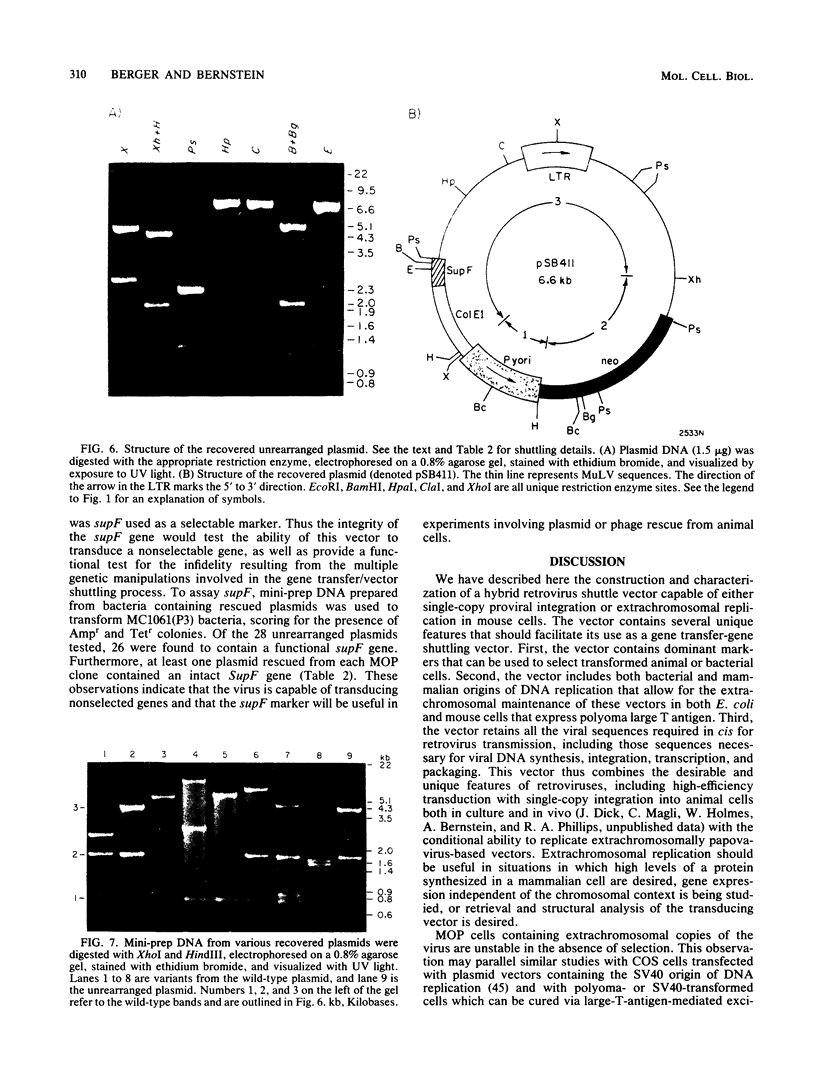
A retrovirus shuttle vector is described that contains the dominant selectable neo gene which confers resistance to kanamycin in bacteria and to the drug G418 in animal cells. The bacterial supF gene and the origins of DNA replication from polyomavirus and the ColE1 replicon also have been included in this vector. Infection of normal rodent cells results in single-copy proviral integration, whereas infection of mouse (MOP) cells expressing polyoma large T antigen results in extrachromosomal replication of the DNA form of the virus. The copy number of the extrachromosomal circles in MOP cells varies from 0 to 100 copies per cell. G418-resistant MOP cells lose their drug-resistant phenotype after passage under nonselective conditions, suggesting that maintenance of the extrachromosomal circles is unstable. The extrachromosomal form of the virus can be recovered as plasmids in Escherichia coli. Two-thirds of the circles analyzed were found to be structurally intact. The others have undergone rearrangements including deletions and insertions. The bacterial supF gene was found to be intact in the majority of recovered plasmids. The data presented here suggest that these retroviruses should be useful as gene transfer vectors for animal cells in culture or in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basilico C., Gattoni S., Zouzias D., Valle G. D. Loss of integrated viral DNA sequences in polyomatransformed cells is associated with an active viral A function. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):645–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Sambrook J. Integration and excision of SV40 DNA from the chromosome of a transformed cell. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Pellegrini S., Basilico C. Deletion of the origin of replication impairs the ability of polyomavirus DNA to transform cells and to form tandem insertions. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):984–987. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.984-987.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Jimenez A. A new selective agent for eukaryotic cloning vectors. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Sep;29(5 Suppl):1089–1092. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Bovine papillomavirus vector that propagates as a plasmid in both mouse and bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4030–4034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgell M. H., Polsky F. I. Use of preparative gel electrophoresis for DNA fragment isolation. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):319–327. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. T., Spritz R. A., Weissman S. M. Simian virus 40 as a eukaryotic cloning vehicle. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:295–340. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareed G. C., Davoli D. Molecular biology of papovaviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:471–522. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. DNA methylation and gene expression: endogenous retroviral genome becomes infectious after molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Harbers K., Schnieke A., Löhler J., Chumakov I., Jähner D., Grotkopp D., Hoffmann E. Germline integration of moloney murine leukemia virus at the Mov13 locus leads to recessive lethal mutation and early embryonic death. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L., Bernstein A. Retrovirus transduction: generation of infectious retroviruses expressing dominant and selectable genes is associated with in vivo recombination and deletion events. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2180–2190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L., Bernstein A. Retrovirus transduction: segregation of the viral transforming function and the herpes simplex virus tk gene in infectious Friend spleen focus-forming virus thymidine kinase vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2191–2202. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A., Keller G., Phillips R. A., Bernstein A. Retrovirus transfer of a bacterial gene into mouse haematopoietic progenitor cells. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):556–558. doi: 10.1038/305556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Characterization of the bovine papilloma virus plasmid maintenance sequences. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthias P. D., Bernard H. U., Scott A., Brady G., Hashimoto-Gotoh T., Schütz G. A bovine papilloma virus vector with a dominant resistance marker replicates extrachromosomally in mouse and E. coli cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1487–1492. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneguzzi G., Binétruy B., Grisoni M., Cuzin F. Plasmidial maintenance in rodent fibroblasts of a BPV1-pBR322 shuttle vector without immediately apparent oncogenic transformation of the recipient cells. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):365–371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. A transmissible retrovirus expressing human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT): gene transfer into cells obtained from humans deficient in HPRT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Cohen J., Weisburd M. Isolation of nonsense suppressor mutants in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):177–182. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.177-182.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Mueller C. R., Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus origin for DNA replication comprises multiple genetic elements. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):586–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.586-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Naujokas M. A., Hassell J. A. Isolation of large T antigen-producing mouse cell lines capable of supporting replication of polyomavirus-plasmid recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2406–2412. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Hayward W. S., Robinson H. L., Fang J., Astrin S. M. Avian leukosis virus-induced tumors have common proviral integration sites and synthesize discrete new RNAs: oncogenesis by promoter insertion. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins A. S., Kirschmeier P. T., Gattoni-Celli S., Weinstein I. B. Design of a retrovirus-derived vector for expression and transduction of exogenous genes in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1123–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Transformation and replication in mouse cells of a bovine papillomavirus--pML2 plasmid vector that can be rescued in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Purification of genomic sequences from bacteriophage libraries by recombination and selection in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2427–2445. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Hughes S. H., Kung H. J., Majors J. E., Quintrell N., Guntaka R. V., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mapping unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: termini of linear DNA bear 300 nucleotides present once or twice in two species of circular DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1383–1395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Temin H. M. Formation of infectious progeny virus after insertion of herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene into DNA of an avian retrovirus. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Hughes S. H. Splicing of intervening sequences introduced into an infectious retroviral vector. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):547–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanners C. P., Eliceiri G. L., Green H. Two types of ribosome in mouse-hamster hybrid cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 10;230(10):52–54. doi: 10.1038/newbio230052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Hoffmann J. W., Goff S. P., Weinberg R. A. Adaptation of a retrovirus as a eucaryotic vector transmitting the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):426–436. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui L. C., Breitman M. L., Siminovitch L., Buchwald M. Persistence of freely replicating SV40 recombinant molecules carrying a selectable marker in permissive simian cells. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Ortiz S. Retroviruses as mutagens: insertion and excision of a nontransforming provirus alter expression of a resident transforming provirus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., Gibson M., Spear P. G., Scolnick E. M. Construction and isolation of a transmissible retrovirus containing the src gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):935–944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.935-944.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Weinberg R. A. Restriction endonuclease cleavage of linear and closed circular murine leukemia viral DNAs: discovery of a smaller circular form. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]