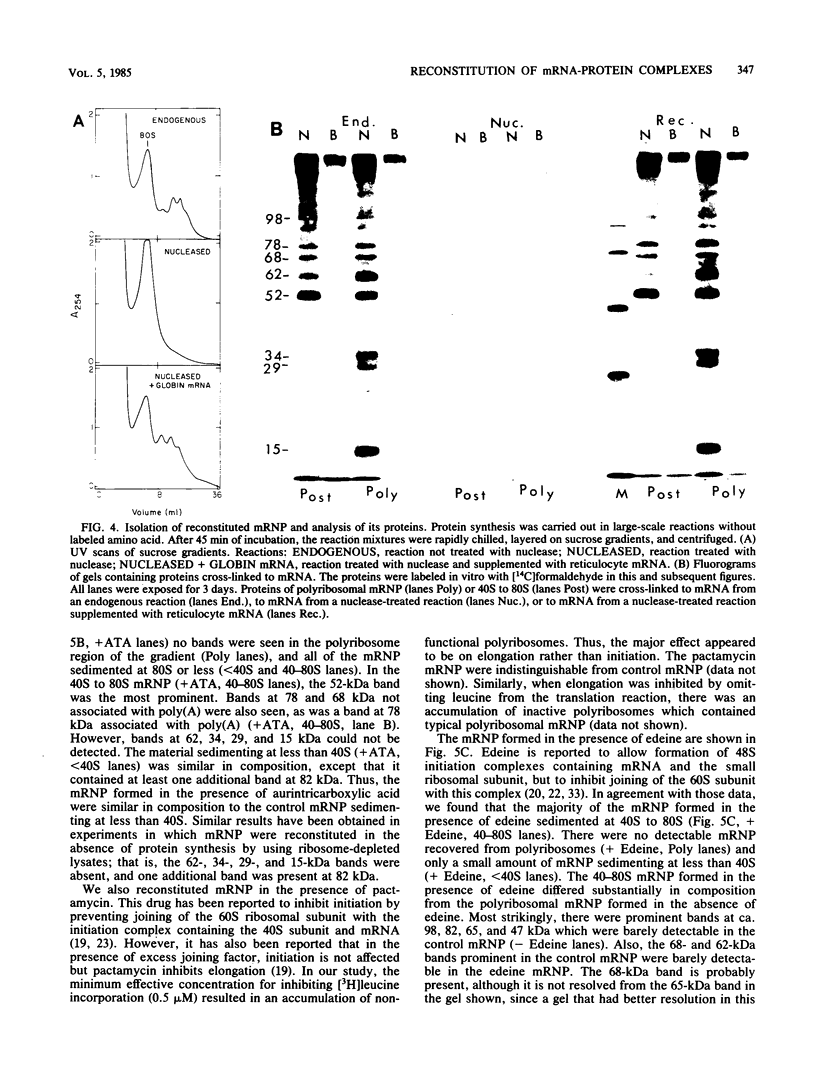
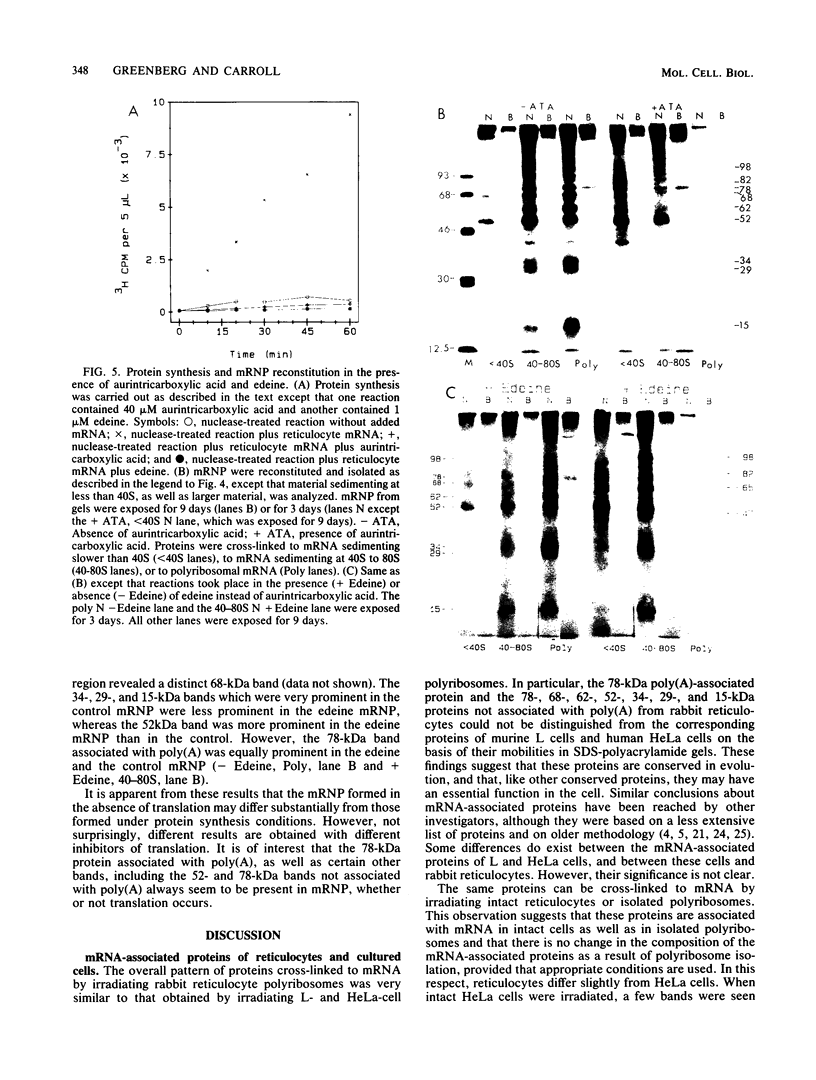
Abstract
A variety of evidence suggests that the cytoplasmic mRNA-associated proteins of eucaryotic cells are derived from the cytoplasm and function there, most likely in protein synthesis or some related process. Furthermore, the evidence suggests that protein-free mRNA added to a cell-free translation system should become associated with a set of proteins similar to those associated with mRNA in native polyribosomes. To test this hypothesis, we added deproteinized rabbit reticulocyte mRNA to a homologous cell-free translation system made dependent on exogenous mRNA by treatment with micrococcal nuclease. The resulting reconstituted complexes were irradiated with UV light to cross-link the proteins to mRNA, and the proteins were analyzed by gel electrophoresis. The proteins associated with polyribosomal mRNA in the reconstituted complexes were indistinguishable from those associated with polyribosomal mRNA in intact reticulocytes. Furthermore, reticulocyte mRNA-associated proteins were very similar to those of cultured mammalian cells. The composition of the complexes varied with the translational state of the mRNA; that is, certain proteins present in polyribosomal mRNA-protein complexes were absent or reduced in amount in 40S to 80S complexes and in complexes formed in the absence of translation. However, other proteins, including a 78-kilodalton protein associated with polyadenylate, were present irrespective of translational state, or else they were preferentially associated with untranslated mRNA. These findings are in agreement with previous data suggesting that proteins associated with cytoplasmic mRNA are derived from the cytoplasm and that they function in translation or some other cytoplasmic process, rather than transcription, RNA processing, or transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF


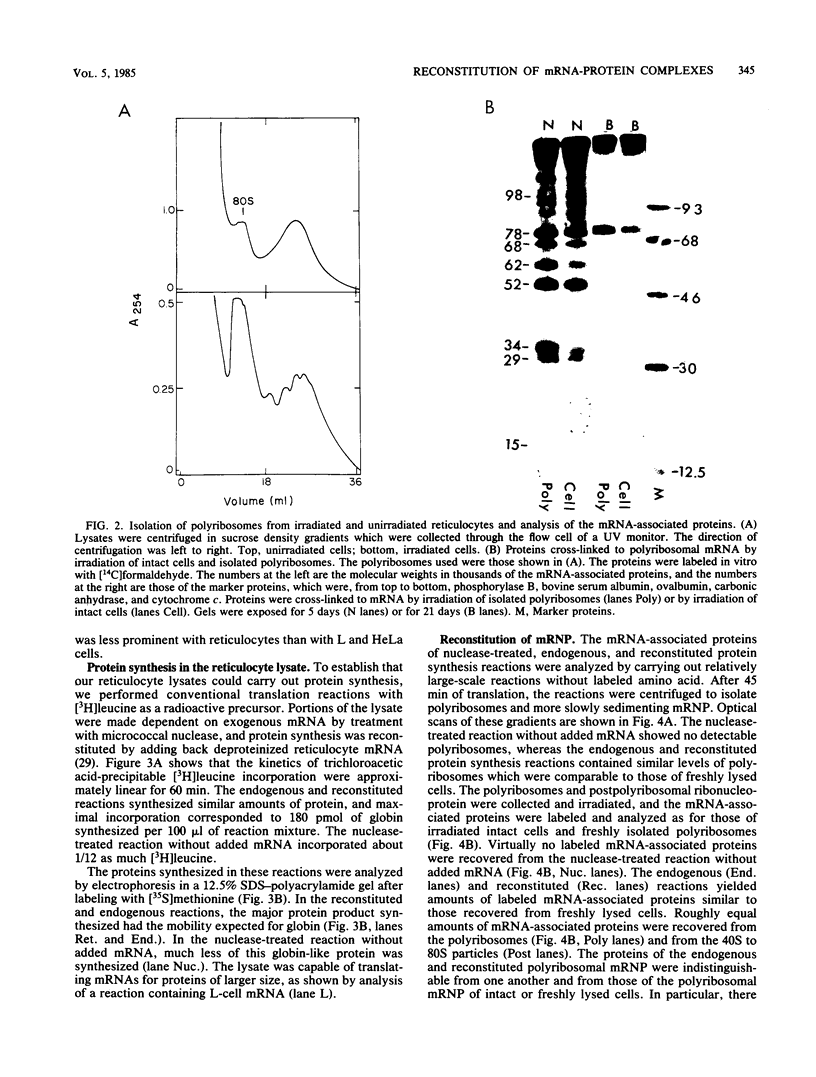
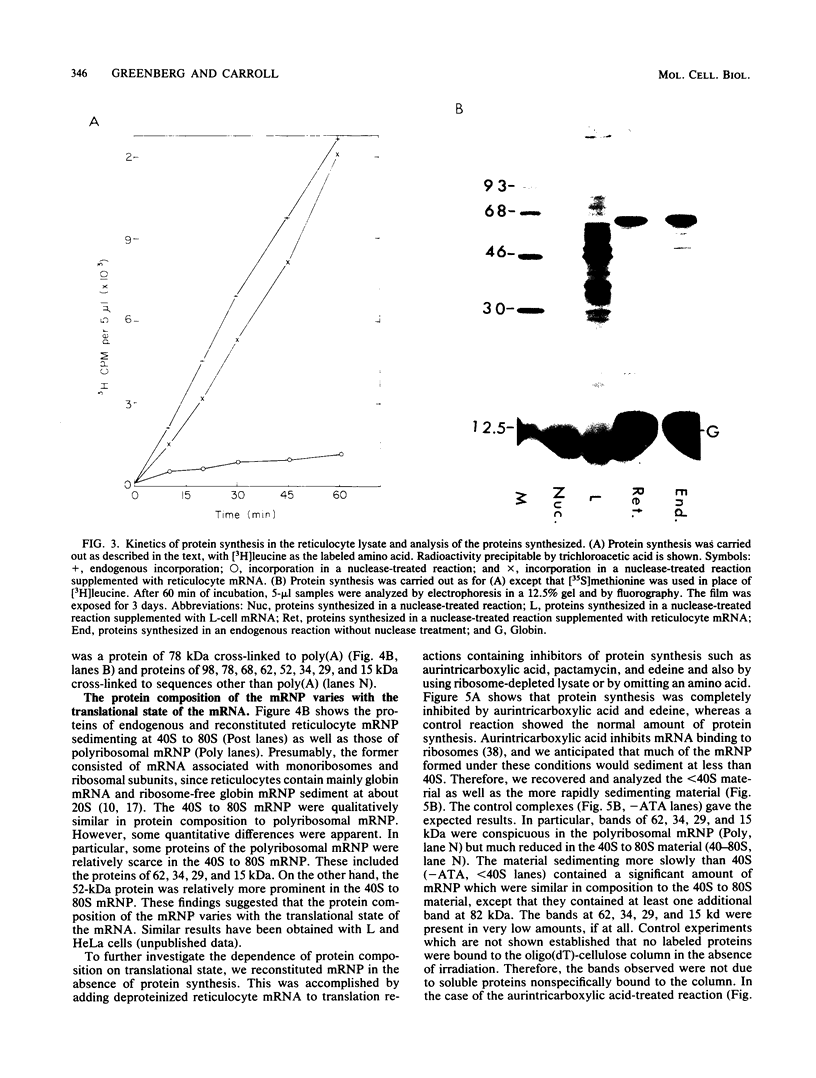



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer B. W., Kornberg R. D. Repeating structure of cytoplasmic poly(A)-ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1890–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Wong C., Luedi M., Hershey J. W. Purification and characterization of initiation factor IF-E2 from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7675–7681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Morton J. G., Rosbash M., Richardson M. Three abundance classes in HeLa cell messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):199–204. doi: 10.1038/250199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A protein of molecular weight 78,000 bound to the polyadenylate region of eukaryotic messenger RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):924–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan R. N., Hayashi M. Two proteins are bound to most species of polysomal mRNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 29;244(139):271–274. doi: 10.1038/newbio244271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher P. D., Arnstein H. R. Efficient translation and polyribosome binding of 125I-labelled rabbit globin messenger ribonucleoprotein. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervera M., Dreyfuss G., Penman S. Messenger RNA is translated when associated with the cytoskeletal framework in normal and VSV-infected HeLa cells. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. C. On the regulation of the synthesis of ribosomal proteins in L-cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 14;55(1):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gander E. S., Stewart A. G., Morel C. M., Scherrer K. Isolation and characterization of ribosome-free cytoplasmic messenger-ribonucleoprotein complexes from avian erythroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 18;38(3):443–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. Proteins crosslinked to messenger RNA by irradiating polyribosomes with ultraviolet light. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5685–5701. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. The polyribosomal mRNA--protein complex is a dynamic structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2923–2926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. Ultraviolet light-induced crosslinking of mRNA to proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):715–732. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Bishop J. O. The expression of three abundance classes of messenger RNA in mouse tissues. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):761–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick D., Schwarz W., Pitzel S., Tiedemann H. Messenger ribonucleoprotein-directed globin synthesis in an embryonic brain cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 27;340(3):278–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90273-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S., Windass J., Williamson R. Mouse globin gene expression in erythroid and non-erythroid tissues. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Lorena, Baglioni C. Synthesis of rabbit globin by reticulocyte postribosomal supernatant and heterologous ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun 15;35(3):559–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Lorena M., Baglioni C. Messenger RNA for globin in the postribosomal supernatant of rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1425–1428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen L. S., Goldberg I. H. Analysis of the two steps in polypeptide chain initiation inhibited by pactamycin. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):811–818. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Migration of 40 S ribosomal subunits on messenger RNA in the presence of edeine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6568–6577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Pederson T. Comparison of proteins bound to heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 15;96(3):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Robertson H. D. The binding of 125I-labelled rabbit globin messenger RNA to reticulocyte ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 5;106(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Kyner D., Acs G. Protein synthesis initiation in eukaryotes. Characterization of ribosomal factors from mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6416–6425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liautard J. P., Setyono B., Spindler E., Köhler K. Comparison of proteins bound to the different functional classes of messenger RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Sundquist B. Isolation of messenger ribonucleoproteins from mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):451–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur G., Schweiger A. Identical properties of an mRNA-bound protein and a cytosol protein with high affinity for polyadenylate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 13;80(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Lebleu B., Zehavi-Willner T., Revel M. Mesenger ribonucleoprotein and initiation factors in rabbit-reticulocyte polyribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 1;33(2):314–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov L. P., Spirin A. S., Erni B., Staehelin T. RNA-binding proteins of rabbit reticulocytes contain the two elongation factors and some of the initiation factors of translation. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 1;88(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80598-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Means G. E. Radioactive labeling of proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):831–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., McCarthy B. J. Polyadenylated RNA complementary to repetitive DNA in mouse L-cells. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 8;14(7):1385–1389. doi: 10.1021/bi00678a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Kemper W., Jagus R. Identification of a 48 S preinitiation complex in reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3384–3386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid H. P., Köhler K., Setyono B. Possible involvement of messenger RNA-associated proteins in protein synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):893–898. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setyono B., Greenberg J. R. Proteins associated with poly(A) and other regions of mRNA and hnRNA molecules as investigated by crosslinking. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setyono B., Grossmann M., Liautard J. P. Evidence that proteins bound to the polysomal messenger RNA exist also free in the cytoplasm of HeLa cells. Biochimie. 1977;59(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(77)80084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setyono B., Schmid H. P., Köhler K. The role of acidic proteins from cytoplasmic fractions of Krebs II ascites cells for efficient translation. Z Naturforsch C. 1979 Jan-Feb;34(1-2):64–75. doi: 10.1515/znc-1979-1-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. L., Grollman A. P., Huang M. T. Aurintricarboxylic acid: inhibitor of initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):97–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomcsányi T., Molnár J., Tigyi A. Structural characterization of nuclear poly(A)-protein particles in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):283–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasik T. N., Ovchinnikov L. F., Radjabov K. M., Spirin A. S. Translation factors of the wheat embryo extract are RNA-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 1;88(1):18–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80597-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. The assembly of ribosomes in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):383–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]