Abstract
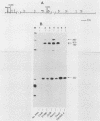
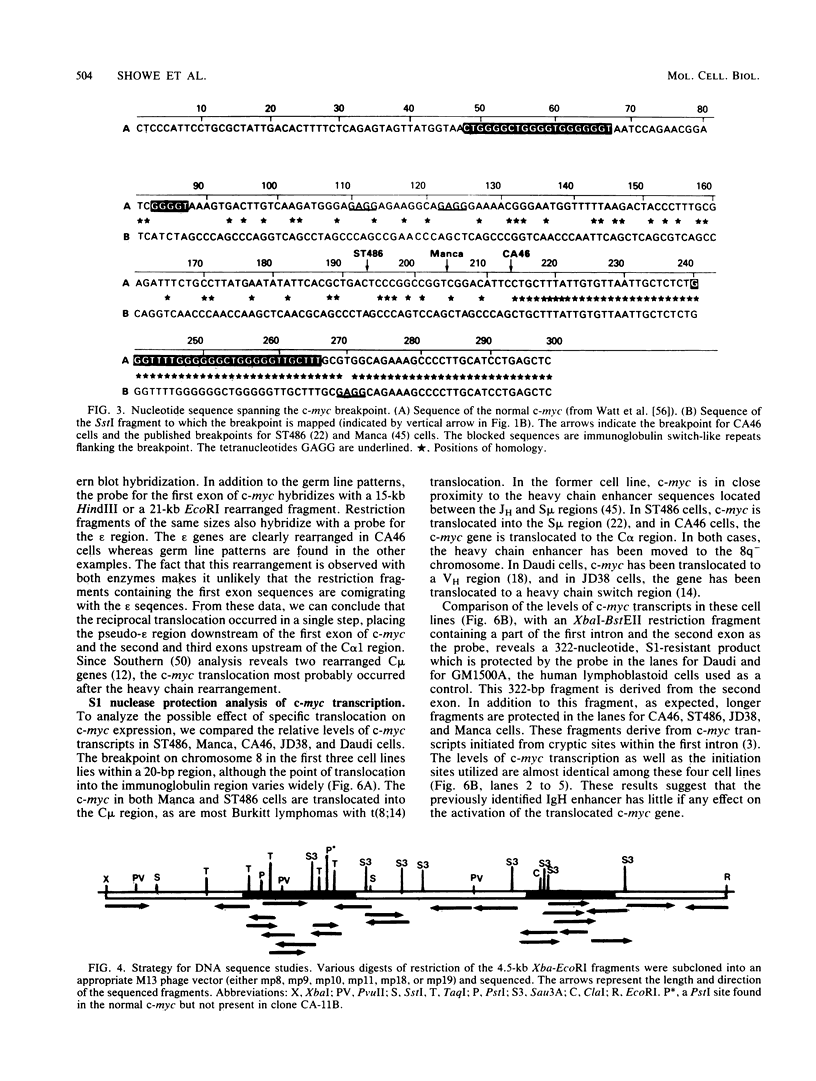
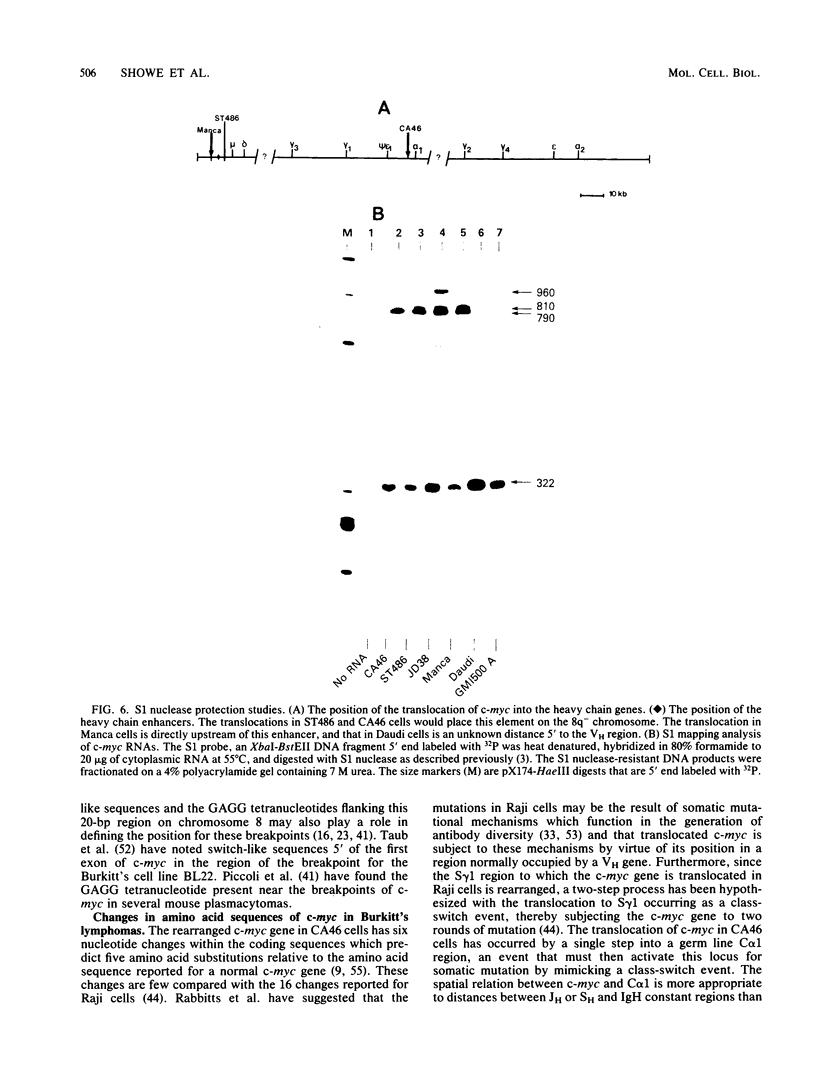
We have cloned and sequenced the translocated c-myc gene from the Burkitt's lymphoma CA46 cell line that carries a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 8 and 14. The breakpoint lies within the first intron of c-myc, so that the first noncoding exon of the gene remains on the 8q- chromosome. The second and third coding exons are translocated to the 14q+ chromosome into the switch region of C-alpha 1. The orientation of the c-myc gene with relationship to alpha 1 is 5' to 5', with directions of transcription in opposite orientation. DNA sequencing studies predict five changes in the amino acid sequence of the myc protein, two of which occur in a region within the second exon which is highly conserved in evolution. Southern blotting data indicate that the first exon of c-myc is rearranged 3' to 3' with the pseudo-epsilon gene. Because CA46 cells contain two rearranged mu genes, the translocation must have occurred after immunoglobulin rearrangement. The position of the breakpoint in CA46 occurs within a 20-base-pair region of the first intron of c-myc to which breakpoints have been mapped for two additional B-cell lymphomas with the t(8;14) translocation, ST486 and the Manca cell line. The region of the heavy chain locus to which c-myc has translocated is different in each case. Comparisons have been made of the levels of transcripts of the translocated c-myc gene in ST486 and CA46, where the gene is not associated with the heavy chain enhancer, with its expression in the Manca cell, in which it is. The c-myc gene is transcribed at similar levels in all three cases.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Corcoran L. M., Cory S. Cellular myc oncogene is altered by chromosome translocation to an immunoglobulin locus in murine plasmacytomas and is rearranged similarly in human Burkitt lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1982–1986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Bishop J. M., Smith D. H., Chen E. Y., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Nucleotide sequence to the v-myc oncogene of avian retrovirus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin D., Magrath I. T., Maguire R., Janus C., Todd H. D., Parsons R. G. Immunoglobulin secretion by cell lines derived from African and American undifferentiated lymphomas of Burkitt's and non-Burkitt's type. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1336–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calame K., Kim S., Lalley P., Hill R., Davis M., Hood L. Molecular cloning of translocations involving chromosome 15 and the immunoglobulin C alpha gene from chromosome 12 in two murine plasmacytomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6994–6998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Chen E. Y., Smith D. H., Levinson A. D. Identification and nucleotide sequence of a human locus homologous to the v-myc oncogene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):722–725. doi: 10.1038/301722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Erikson J., ar-Rushdi A., Aden D., Nishikura K. Translocated c-myc oncogene of Burkitt lymphoma is transcribed in plasma cells and repressed in lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Thierfelder W., Erikson J., Nishikura K., Finan J., Lenoir G. M., Nowell P. C. Transcriptional activation of an unrearranged and untranslocated c-myc oncogene by translocation of a C lambda locus in Burkitt. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Gelmann E. P., Martinotti S., Franchini G., Papas T. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Cloning and characterization of different human sequences related to the onc gene (v-myc) of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Martinotti S., Gallo R. C., Erikson J., Croce C. M. Translocation and rearrangements of the c-myc oncogene locus in human undifferentiated B-cell lymphomas. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.6401867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Kent R. B., Sonenshein G. E. Transcriptional activation of immunoglobulin alpha heavy-chain genes by translocation of the c-myc oncogene. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):443–446. doi: 10.1038/305443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick W., Shell B. E., Dery C. DNA sequences near the site of reciprocal recombination between a c-myc oncogene and an immunoglobulin switch region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7269–7273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Finan J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Translocation of immunoglobulin VH genes in Burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5611–5615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Nishikura K., ar-Rushdi A., Finan J., Emanuel B., Lenoir G., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Translocation of an immunoglobulin kappa locus to a region 3' of an unrearranged c-myc oncogene enhances c-myc transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7581–7585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., ar-Rushdi A., Drwinga H. L., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Transcriptional activation of the translocated c-myc oncogene in burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelmann E. P., Psallidopoulos M. C., Papas T. S., Dalla-Favera R. Identification of reciprocal translocation sites within the c-myc oncogene and immunoglobulin mu locus in a Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):799–803. doi: 10.1038/306799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S., Cory S., Adams J. M. Translocation of the myc cellular oncogene to the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in murine plasmacytomas is an imprecise reciprocal exchange. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn P. H., Rabbitts T. H. Translocation joins c-myc and immunoglobulin gamma 1 genes in a Burkitt lymphoma revealing a third exon in the c-myc oncogene. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):135–139. doi: 10.1038/304135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Murray K. Packaging recombinant DNA molecules into bacteriophage particles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Battey J., Lenoir G., Moulding C., Murphy W., Potter H., Stewart T., Taub R. Translocations among antibody genes in human cancer. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):765–771. doi: 10.1126/science.6356357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Harris L. J., Stanton L. W., Erikson J., Watt R., Croce C. M. Transcriptionally active c-myc oncogene is contained within NIARD, a DNA sequence associated with chromosome translocations in B-cell neoplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):519–523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Battey J., Ney R., Kirsch I. R., Leder P. Duplication and deletion in the human immunoglobulin epsilon genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Huppi K., Bell M., Staudt L., Gerhard W., Weigert M. Generation of antibody diversity in the immune response of BALB/c mice to influenza virus hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikori M., Hansen H., Jhanwar S., Fried J., Sordillo P., Koziner B., Lloyd K., Clarkson B. Establishment of a near-tetraploid B-cell lymphoma line with duplication of the 8;14 translocation. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 May;12(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., ar-Rushdi A., Erikson J., DeJesus E., Dugan D., Croce C. M. Repression of rearranged mu gene and translocated c-myc in mouse 3T3 cells X Burkitt lymphoma cell hybrids. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):399–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6424234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., ar-Rushdi A., Erikson J., Watt R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Differential expression of the normal and of the translocated human c-myc oncogenes in B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4822–4826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli S. P., Caimi P. G., Cole M. D. A conserved sequence at c-myc oncogene chromosomal translocation breakpoints in plasmacytomas. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):327–330. doi: 10.1038/310327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Baer R., Hamlyn P. H. Transcription enhancer identified near the human C mu immunoglobulin heavy chain gene is unavailable to the translocated c-myc gene in a Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):806–809. doi: 10.1038/306806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Hamlyn P., Baer R. Effect of somatic mutation within translocated c-myc genes in Burkitt's lymphoma. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):592–597. doi: 10.1038/309592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Hamlyn P. H., Baer R. Altered nucleotide sequences of a translocated c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):760–765. doi: 10.1038/306760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hayday A. C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of the c-myc gene by translocation: a model for translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Berk A. J., Berget S. M. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):750–768. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Keath E. J., Piccoli S. P., Cole M. D. Novel myc oncogene RNA from abortive immunoglobulin-gene recombination in mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J. Physical map of polyoma viral DNA fragments produced by cleavage with a restriction enzyme from Haemophilus aegyptius, endonuclease R-HaeIII. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):946–953. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.946-953.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., Reddy E. P., Duesberg P. H., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chicken c-myc gene reveals homologous and unique coding regions by comparison with the transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29, delta gag-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2146–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R., Nishikura K., Sorrentino J., ar-Rushdi A., Croce C. M., Rovera G. The structure and nucleotide sequence of the 5' end of the human c-myc oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6307–6311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R., Stanton L. W., Marcu K. B., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M., Rovera G. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA of human c-myc oncogene. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):725–728. doi: 10.1038/303725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Payne G., Varmus H. E. Proviral deletions and oncogene base-substitutions in insertionally mutagenized c-myc alleles may contribute to the progression of avian bursal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):843–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ar-Rushdi A., Nishikura K., Erikson J., Watt R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Differential expression of the translocated and the untranslocated c-myc oncogene in Burkitt lymphoma. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):390–393. doi: 10.1126/science.6414084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]