Abstract
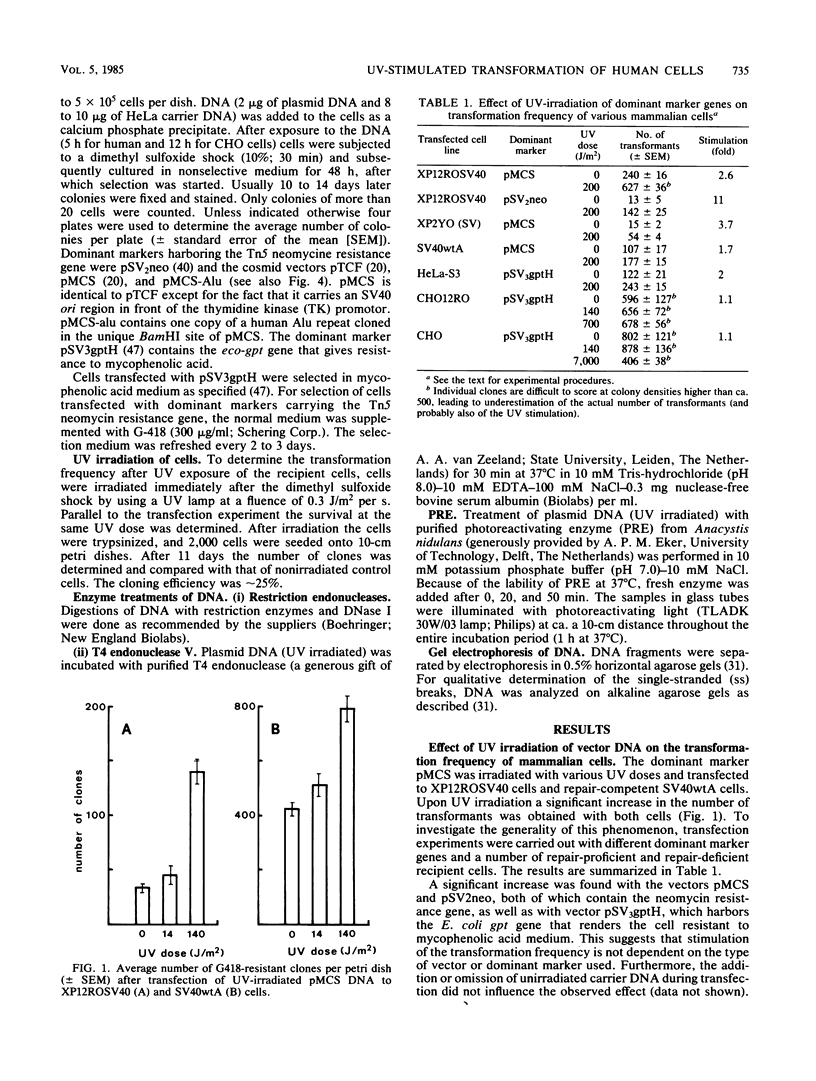
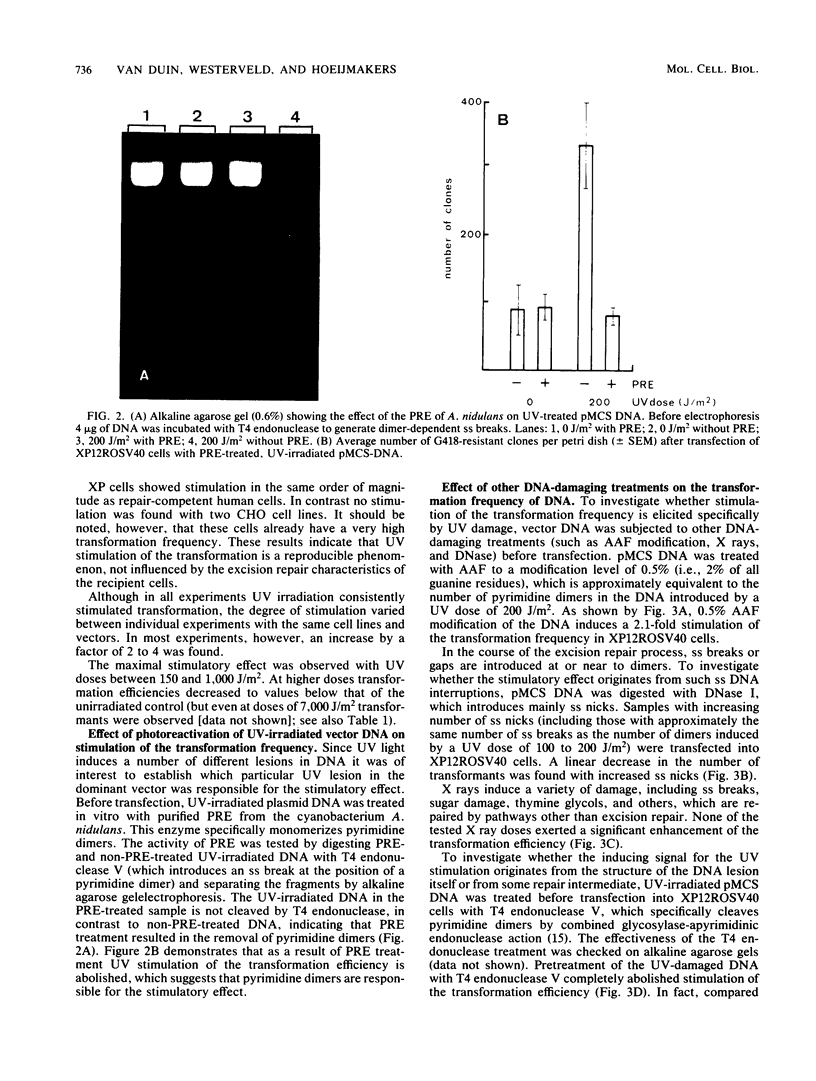
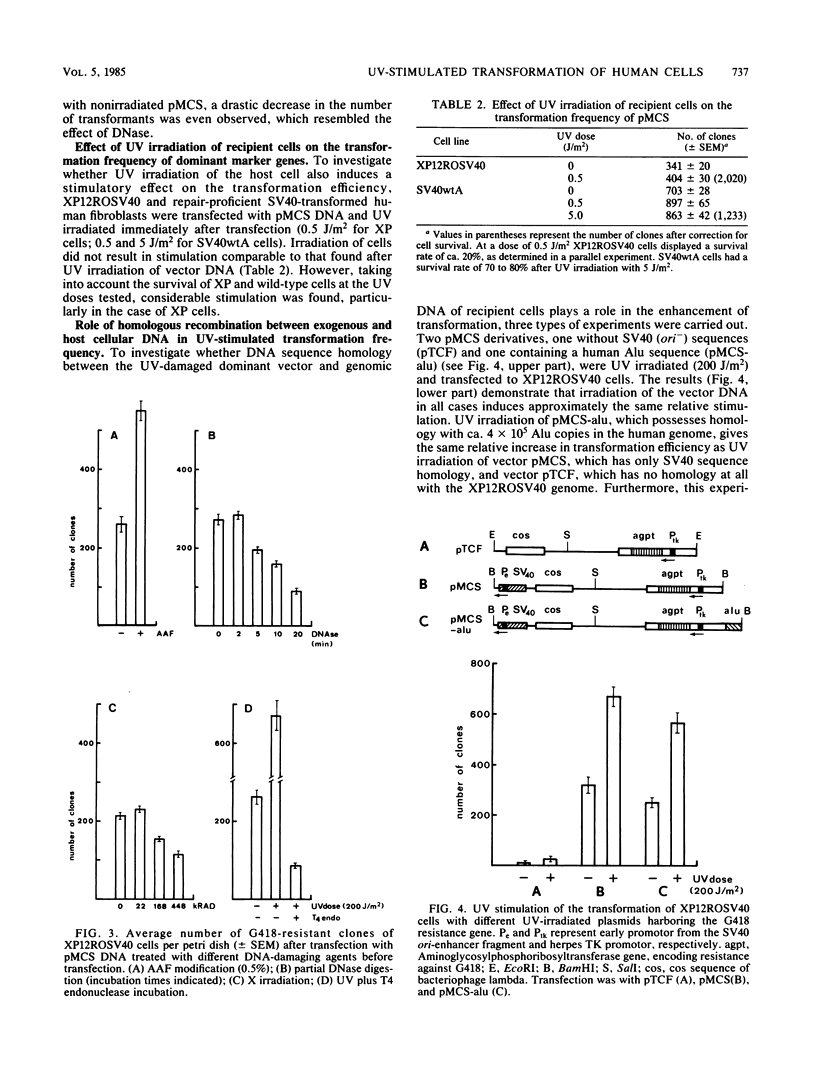
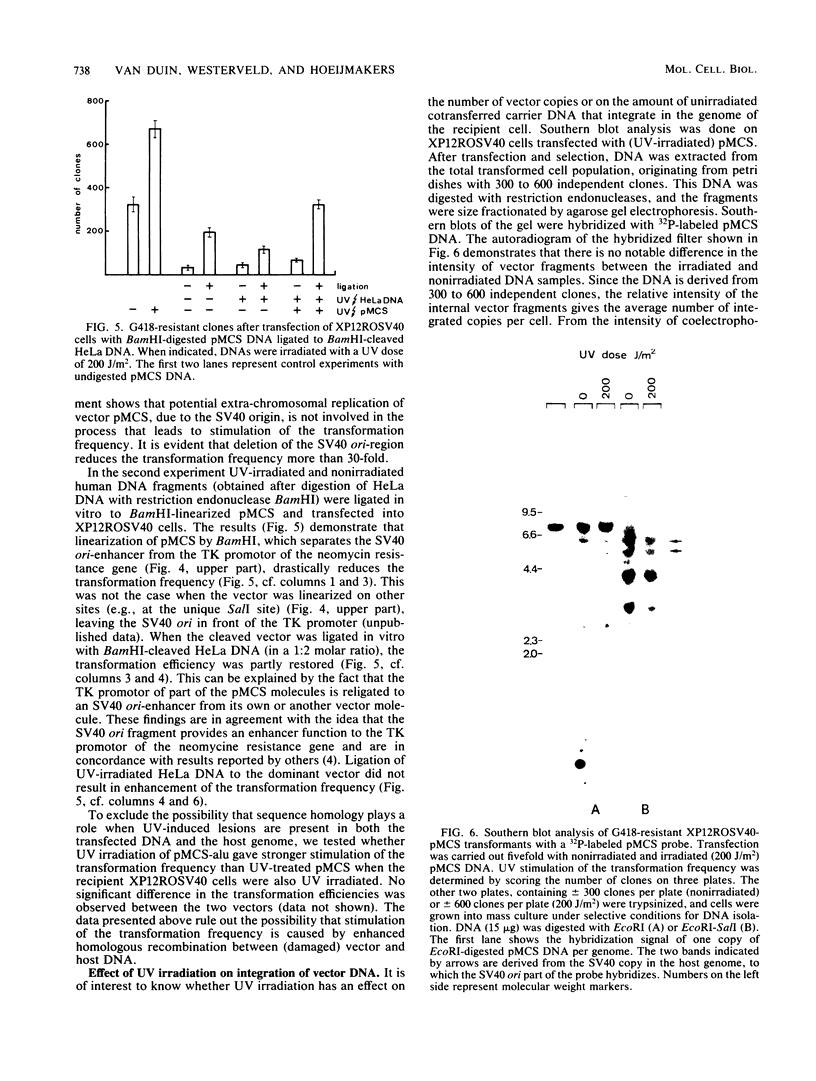
Irradiation of dominant marker DNA with UV light (150 to 1,000 J/m2) was found to stimulate the transformation of human cells by this marker from two- to more than fourfold. This phenomenon is also displayed by xeroderma pigmentosum cells (complementation groups A and F), which are deficient in the excision repair of UV-induced pyrimidine dimers in the DNA. Also, exposure to UV of the transfected (xeroderma pigmentosum) cells enhanced the transfection efficiency. Removal of the pyrimidine dimers from the DNA by photoreactivating enzyme before transfection completely abolished the stimulatory effect, indicating that dimer lesions are mainly responsible for the observed enhancement. A similar stimulation of the transformation efficiency is exerted by 2-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene modification of the DNA. No stimulation was found after damaging vector DNA by treatment with DNase or gamma rays. These findings suggest that lesions which are targets for the excision repair pathway induce the increase in transformation frequency. The stimulation was found to be independent of sequence homology between the irradiated DNA and the host chromosomal DNA. Therefore, the increase of the transformation frequency is not caused by a mechanism inducing homologous recombination between these two DNAs. UV treatment of DNA before transfection did not have a significant effect on the amount of DNA integrated into the xeroderma pigmentosum genome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Lytle C. D. Decreased host cell reactivation of irradiated SV40 virus in xeroderma pigmentosum. Nature. 1970 Oct 24;228(5269):359–361. doi: 10.1038/228359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams P. J., Van der Eb A. J. Host-cell reactivation of ultraviolet-irradiated SV40 DNA in five complementation groups of xeroderma pigmentosum. Mutat Res. 1976 Apr;35(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(76)90164-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Kato S., Camerini-Otero R. D. A pattern of partially homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):206–210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg P. E., Anderson W. F. Correlation of gene expression and transformation frequency with the presence of an enhancing sequence in the transforming DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):368–370. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockstahler L. E. Induction and enhanced reactivation of mammalian viruses by light. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;26:303–313. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60413-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourre F., Sarasin A. Targeted mutagenesis of SV40 DNA induced by UV light. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):68–70. doi: 10.1038/305068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis J. J., Su Z. Z., Rommelaere J. Direct and indirect effects of ultraviolet light on the mutagenesis of parvovirus H-1 in human cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):693–699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01232.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta U. B., Summers W. C. Ultraviolet reactivation of herpes simplex virus is mutagenic and inducible in mammlian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2378–2381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsart C., Cornelis J. J., Klein B., van der Eb A. J., Rommelaere J. Transfection with extracellularly UV-damaged DNA induces human and rat cells to express a mutator phenotype towards parvovirus H-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):324–328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubbs D. R., Rachmeler M., Kit S. Recombination between temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):161–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Wong E. A., Wahl G., Capecchi M. R. Patterns of integration of DNA microinjected into cultured mammalian cells: evidence for homologous recombination between injected plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1372–1387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. P., Seeberg E. pBR322 plasmid DNA modified with 2-acetylaminofluorene derivatives: transforming activity and in vitro strand cleavage by the Escherichia coli uvrABC endonuclease. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):757–760. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01880.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. I., Low K. B. Indirect stimulation of genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1401–1405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L. Enzymes involved in the repair of damaged DNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Oct 15;211(2):511–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Lund T., Murray E. J., Mellor A. L., Dahl H. H., Flavell R. A. The construction of cosmid libraries which can be used to transform eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6715–6732. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. D., Featherston J. D., Almy R. E. Evidence for repair of ultraviolet light-damaged herpes virus in human fibroblasts by a recombination mechanism. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):490–500. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanawalt P. C., Cooper P. K., Ganesan A. K., Smith C. A. DNA repair in bacteria and mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Etude génétique d'un bactériophage tempéré d'Escherichia coli. III. Effet du rayonnement ultraviolet sur la recombinaison génétique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1955 Jun;88(6):724–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano Y., Fujiwara Y. Defective thymine dimer excision from xeroderma pigmentosum chromatin and its characteristic catalysis by cell-free extracts. Carcinogenesis. 1983 Nov;4(11):1419–1424. doi: 10.1093/carcin/4.11.1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer P. J., Bowman A. H., Huberman M. H., Sanders-Haigh L., Killos L., Anderson W. F. Recovery of recombinant bacterial plasmids from E. coli transformed with DNA from microinjected mouse cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6199–6217. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriek E., Miller J. A., Juhl U., Miller E. C. 8-(N-2-fluorenylacetamido)guanosine, an arylamidation reaction product of guanosine and the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-2-fluorenylacetamide in neutral solution. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):177–182. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegent J. E., Jasen in de Wal N., Baan R. A., Hoeijmakers J. H., Van der Ploeg M. 2-Acetylaminofluorene-modified probes for the indirect hybridocytochemical detection of specific nucleic acid sequences. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Mount D. W. The SOS regulatory system of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. K., Temin H. M. High-efficiency ligation and recombination of DNA fragments by vertebrate cells. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):606–609. doi: 10.1126/science.6301012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. C., Juhl U., Miller J. A. Nucleic acid guanine: reaction with the carcinogen N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene. Science. 1966 Sep 2;153(3740):1125–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3740.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortelmans K., Friedberg E. C., Slor H., Thomas G., Cleaver J. E. Defective thymine dimer excision by cell-free extracts of xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2757–2761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz B. J., Naujokas M., Hassell J. A. Homologous recombination between transfected DNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1680–1685. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Ripley S., Henderson A. S., Axel R. Transforming DNA integrates into the host chromosome. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarasin A., Bourre F., Benoit A. Error-prone replication of ultraviolet-irradiated simian virus 40 in carcinogen-treated monkey kidney cells. Biochimie. 1982 Aug-Sep;64(8-9):815–821. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira G., Stachelek J. L., Letsou A., Soodak L. K., Liskay R. M. Novel use of synthetic oligonucleotide insertion mutants for the study of homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4827–4831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J., Scangos G. Recombination during gene transfer into mouse cells can restore the function of deleted genes. Science. 1983 Jan 14;219(4581):174–176. doi: 10.1126/science.6294829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak G., Ganesan A. K., Hanawalt P. C. Enhanced transformation of human cells by UV-irradiated pSV2 plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1169–1171. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. E., Bakken A. H., Reeder R. H. Plasmids containing mouse rDNA do not recombine with cellular ribosomal genes when introduced into cultured mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):576–582. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., Reuser A., Bootsma D. Isolation of Chinese hamster ovary cells with reduced unscheduled DNA synthesis after UV irradiation. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Sep;8(5):635–642. doi: 10.1007/BF01542856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Berg P. Homologous and nonhomologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1040–1052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell R. M. Exposure of nondividing populations of primary human fibroblasts to UV (254 nm) radiation induces a transient enhancement in capacity to repair potentially lethal cellular damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):781–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle J. J. Induction of Mutations in a Bacterial Virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Jul;39(7):628–636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.7.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerveld A., Hoeijmakers J. H., van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Pastink A., Wood R. D., Bootsma D. Molecular cloning of a human DNA repair gene. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):425–429. doi: 10.1038/310425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Takebe H. Establishment by SV40 transformation and characteristics of a cell line of xeroderma pigmentosum belonging to complementation group F. Mutat Res. 1983 Feb;112(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(83)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge A. J., Vermeulen W., Klein B., Hoeijmakers J. H. Microinjection of human cell extracts corrects xeroderma pigmentosum defect. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):637–641. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Vincent B. R., Wahl G. M. Homologous recombination in mammalian cells mediates formation of a functional gene from two overlapping gene fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]