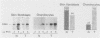Abstract
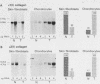
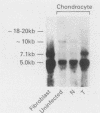
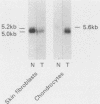
We have analyzed the effects of transformation by Rous sarcoma virus on expression of types I and II collagen and fibronectin genes in vertebral chondrocytes and compared them with expression of these genes in skin fibroblasts. Transformed chondrocytes display a dramatically decreased amount of type II collagen RNA, which can account fully for the decreased synthetic rate of this protein. Paradoxically, these cells also display greatly increased amounts of type I collagen RNAs, which are translated efficiently in vitro, but not in the intact cells. We show here that the type I collagen RNAs in transformed chondrocytes are nearly indistinguishable from those found in skin fibroblasts, and that they clearly differ from the type I collagen RNAs found in normal chondrocytes. Transformed chondrocytes also display an increased amount of fibronectin RNAs, which can account fully for the increased synthetic rate of this protein. Thus, the effects of transformation by Rous sarcoma virus on type I collagen and fibronectin RNAs in chondrocytes are the opposite of those observed in fibroblasts, which display decreased amounts of these three RNAs. These data indicate that the effects of transformation on the genes encoding type I collagen and fibronectin must be modulated by host cell-specific factors. They also imply that the types I and II collagen genes may be regulated by different mechanisms, the type I genes being controlled at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels, and the type II gene being controlled primarily at the transcriptional level.
Full text
PDF
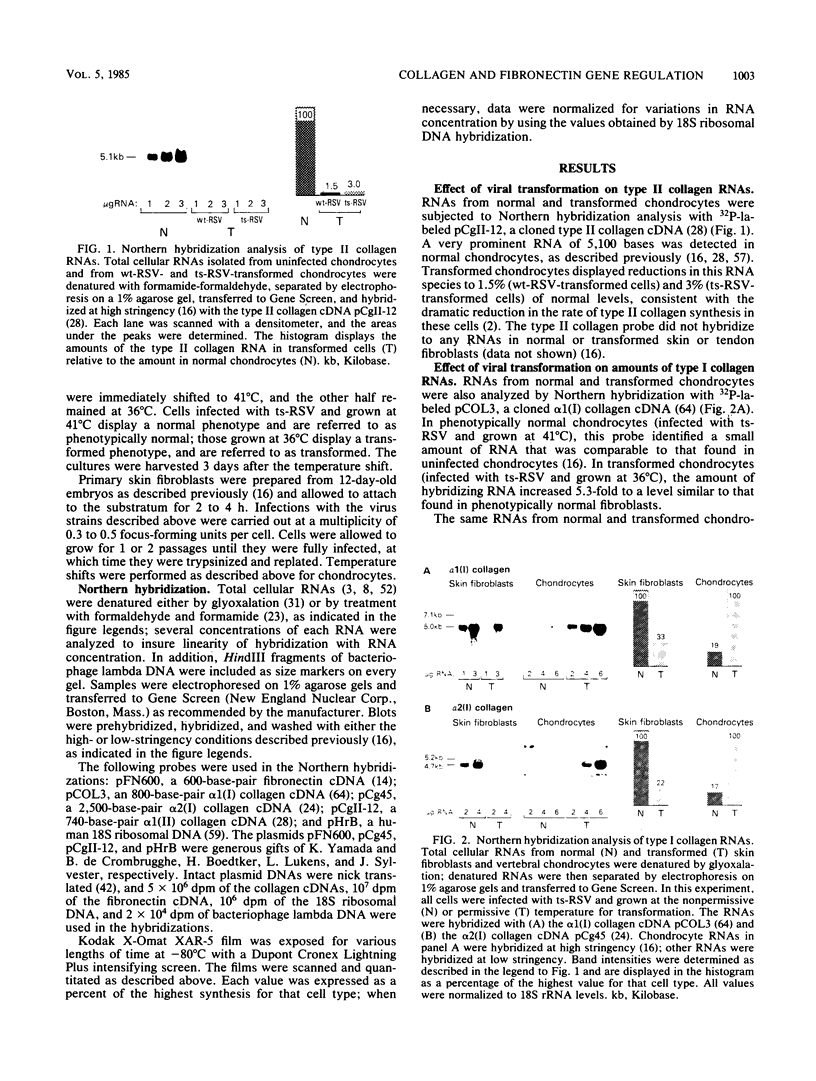
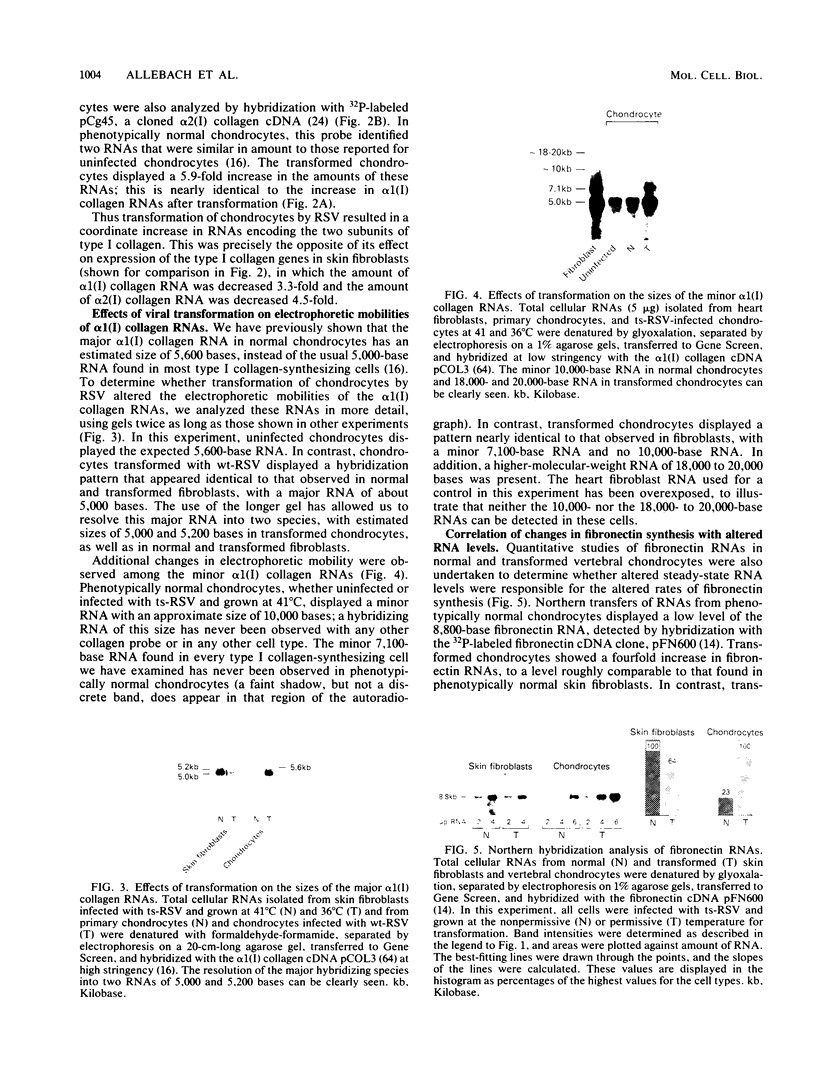




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Alwine J. C., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Use of recombinant plasmids to characterize collagen RNAs in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4935–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. L., Boettiger D., Focht R. J., Holtzer H., Pacifici M. Regulation of the synthesis of extracellular matrix components in chondroblasts transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S. L., Sobel M. E., Howard B. H., Olden K., Yamada K. M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Levels of translatable mRNAs for cell surface protein, collagen precursors, and two membrane proteins are altered in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3399–3403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho S., Tate V., Boedtker H. Multiple 3' ends of the chicken pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5443–5450. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D., Padilla S. R., Nimni M. E. The progeny of rabbit articular chondrocytes synthesize collagen types I and III and type I trimer, but not type II. Verifications by cyanogen bromide peptide analysis. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):865–872. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boettiger D., Roby K., Brumbaugh J., Biehl J., Holtzer H. Transformation of chicken embryo retinal melanoblasts by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko S., Abbott J., Holtzer S., Holtzer H. The loss of phenotypic traits by differentiated cells. VI. Behavior of the progeny of a single chondrocyte. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):417–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., de Wet W., Bernard M., Ding J. F., Morabito M., Myers J., Williams C., Ramirez F. Human pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene structure reveals evolutionary conservation of a pattern of introns and exons. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):337–340. doi: 10.1038/310337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delclos K. B., Blumberg P. M. Decrease in collagen production in normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts induced by phorbol myristate acetate. Cancer Res. 1979 May;39(5):1667–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessau W., von der Mark H., von der Mark K., Fischer S. Changes in the patterns of collagens and fibronectin during limb-bud chondrogenesis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1980 Jun;57:51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson L. A., Ninomiya Y., Bernard M. P., Pesciotta D. M., Parsons J., Green G., Eikenberry E. F., de Crombrugghe B., Vogeli G., Pastan I. The exon/intron structure of the 3'-region of the pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8407–8415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durban E. M., Boettiger D. Differential effects of transforming avian RNA tumor viruses on avian macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3600–3604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. B., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Sequence rearrangement and duplication of double stranded fibronectin cDNA probably occurring during cDNA synthesis by AMV reverse transcriptase and Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):3055–3064. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. B., Sobel M. E., Yamada K. M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Effects of transformation on fibronectin gene expression using cloned fibronectin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):520–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht R. J., Adams S. L. Tissue specificity of type I collagen gene expression is determined at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1843–1852. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstenfeld L. C., Crawford D. R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Expression of type I and III collagen genes during differentiation of embryonic chicken myoblasts in culture. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1483–1492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gionti E., Capasso O., Cancedda R. The culture of chick embryo chondrocytes and the control of their differentiated functions in vitro. Transformation by rous sarcoma virus induces a switch in the collagen type synthesis and enhances fibronectin expression. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7190–7194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. H., Adams S. L., Sobel M. E., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Decreased levels of collagen mRNA in rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5869–5874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamine J., Rubin H. Coordinate control of collagen synthesis and cell growth in chick embryo fibroblasts and the effect of viral transformation on collagen synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jul;92(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno K., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the amino-terminal portion of the pro-alpha 1(II) chain of cartilage collagen. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13668–13673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: cell specific alternative mRNA splicing generates polypeptide chains differing in the number of internal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5853–5868. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Construction and characterization of a 2.5-kilobase procollagen clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5417–5421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Bhatnagar R. S., Liu T. Z. Loss of ability to synthesize collagen in fibroblasts transformed by rous sarcoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Oct;55(4):807–810. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.4.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Toole B. P., Trelstad R. L. Temporal and spatial transitions in collagen types during embryonic chick limb development. Dev Biol. 1973 Dec;35(2):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe M. E., Pacifici M., Holtzer H. Effects of phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate on the phenotypic program of cultured chondroblasts and fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2350–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukens L. N., Frischauf A. M., Pawlowski P. J., Brierley G. T., Lehrach H. Construction and characterization of type II collagen complementary deoxyribonucleic acid clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):6021–6039. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.6021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R., Vail M. S., Mayne P. M., Miller E. J. Changes in type of collagen synthesized as clones of chick chondrocytes grow and eventually lose division capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1674–1678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon C., Ohkubo H., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Unusual methylation pattern of the alpha 2 (l) collagen gene. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., McKeon C., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Regulation of the expression of genes encoding types I, II, and III collagen during chick embryonic development. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10041–10048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dickson L. A., de Wet W. J., Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Di Liberto M., Pepe G., Sangiorgi F. O., Ramirez F. Analysis of the 3' end of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Utilization of multiple polyadenylation sites in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10128–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya Y., Olsen B. R. Synthesis and characterization of cDNA encoding a cartilage-specific short collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Yamada K. M. Mechanism of the decrease in the major cell surface protein of chick embryo fibroblasts after transformation. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):957–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacifici M., Boettiger D., Roby K., Holtzer H. Transformation of chondroblasts by Rous sarcoma virus and synthesis of the sulfated proteoglycan matrix. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):891–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry G., Soo W. J., Bissell M. J. The uncoupled regulation of fibronectin and collagen synthesis in Rous sarcoma virus transformed avian tendon cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11763–11766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski P. J., Brierley G. T., Lukens L. N. Changes in the type II and type I collagen messenger RNA population during growth of chondrocytes in 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7695–7698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Moen R. C., Davidson J. M., Byers P. H., Bornstein P., Palmiter R. D. Correlation of procollagen mRNA levels in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts with different rates of procollagen synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1581–1590. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. J., Prentice H. L., Kravis D., Upholt W. B. Structure and sequence of the chicken type II procollagen gene. Characterization of the region encoding the carboxyl-terminal telopeptide and propeptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7826–7834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeyer S., Bornstein P. Declining procollagen mRNA sequences in chick embryo fibroblasts infected with rous sarcoma virus. Correlation with procollagen synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4950–4953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeyer S., Gallis B., Bornstein P. Coordinate transcriptional regulation of type I procollagen genes by Rous sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5022–5028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. I., Farson D. A., Soo W. J., Bissell M. J. Primary avian tendon cells in culture. An improved system for understanding malignant transformation. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):672–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter A. M., Pesciotta D. M., Eikenberry E. F., Yamamoto T., Pastan I., DeCrombrugghe B., Fietzek P. P., Olsen B. R. Nucleotide sequence of a collagen cDNA-fragment coding for the carboxyl end of pro alpha 1(I)-chains. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80761-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel M. R., Yamamoto T., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Regulation or procollagen messenger ribonucleic acid levels in Rous sarcoma virus transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2678–2684. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohman R. C., Moss P. S., Micou-Eastwood J., Spector D., Przybyla A., Paterson B. Messenger RNA for myosin polypeptides: isolation from single myogenic cell cultures. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi J. S., Hirano H., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Transcriptional control of the fibronectin gene in chick embryo fibroblasts transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5787–5793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio E., Sandell L., Kravis D., Sheffield V. C., Vuorio T., Dorfman A., Upholt W. B. Construction and partial characterization of two recombinant cDNA clones for procollagen from chicken cartilage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1175–1192. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C. M., Lanza R., Rosenbloom J., Lowe M., Holtzer H., Avdalovic N. Fibronectin alters the phenotypic properties of cultured chick embryo chondroblasts. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):491–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Szura L. L., Rushford C., Jackson D., Erickson J. Structure and variation of human ribosomal DNA: the external transcribed spacer and adjacent regions. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Jan;34(1):32–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyke J. A. The selective isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90357-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Kühn K., de Crombrugghe B. A conserved nucleotide sequence, coding for a segment of the C-propeptide, is found at the same location in different collagen genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2733–2744. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Mudryj M., Sullivan M., de Crombrugghe B. Isolation and characterization of a genomic clone encoding chick alpha 1 type III collagen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2758–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. A uniquely conserved regulatory signal is found around the translation initiation site in three different collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14914–14919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Sobel M. E., Adams S. L., Avvedimento V. E., DiLauro R., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B., Showalter A., Pesciotta D., Fietzek P. Construction of a recombinant bacterial plasmid containing pro-alpha 1(I) collagen DNA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2612–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Jimenez S. A., Kaji A. Effects of viral transformation on synthesis and secretion of collagen and fibronectin-like molecules by embryonic chick chondrocytes in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9111–9117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. F., Vogeli G., Nunez A. M., Fernandez M. P., Sullivan M., Sobel M. E. Isolation of cDNA and genomic DNA clones encoding type II collagen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4207–4228. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark H., von der Mark K., Gay S. Study of differential collagen synthesis during development of the chick embryo by immunofluorescence. I. Preparation of collagen type I and type II specific antibodies and their application to early stages of the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1976 Feb;48(2):237–249. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., Gauss V., von der Mark H., Müller P. Relationship between cell shape and type of collagen synthesised as chondrocytes lose their cartilage phenotype in culture. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):531–532. doi: 10.1038/267531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H., Gay S. Study of differential collagen synthesis during development of the chick embryo by immunofluroescence. II. Localization of type I and type II collagen during long bone development. Dev Biol. 1976 Oct 15;53(2):153–170. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]