Abstract
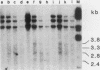
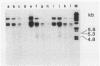
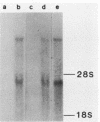
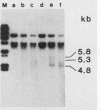
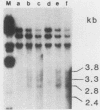
Alterations in the chromatin structure of endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus genes accompany glucocorticoid induction of viral RNA synthesis in the C57BL/6 T lymphoma cell line T1M1. These alterations are defined by the appearance of sites of DNase I hypersensitivity within proviral DNA in isolated nuclei, as well as by changes in the moderate nuclease sensitivity of entire proviral transcription units. Induced hypersensitive sites, termed type I, appear with a time course comparable to that required for induction of the rate of viral RNA synthesis and are maintained only in the continuous presence of hormone. Two such sites map to analogous positions in the 5' and 3' long terminal repeats of proviral DNA within, or very near, sequences that have been shown to comprise positions of specific binding of the glucocorticoid receptor in vitro and that are required for hormone-inducible transcription in vivo. A third type I site maps to another position of in vitro receptor binding near the 3' long terminal repeat. Some sites of DNase I hypersensitivity, termed type II, appear not to be markedly hormone dependent; two such sites are present in corresponding positions in each long terminal repeat. Comparison of the moderate DNase I sensitivity of mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA suggests that the three different endogenous units in T1M1 cells can be maintained in distinct chromatin conformations that are determined by factors related to the site of provirus insertion. It seems possible that altered chromatin conformations may reflect, or actually encode, important mechanistic features of these hormone-responsive genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. Y., Folsom V., Wooley J. DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of immunoglobulin kappa light chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C. The appearance of DNase I hypersensitive sites at the 5' end of the late SV40 genes is correlated with the transcriptional switch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein S. C., Ross S. R., Yamamoto K. R. Chromosomal position effects determine transcriptional potential of integrated mammary tumor virus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):549–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisse S., Scheidereit C., Westphal H. M., Hynes N. E., Groner B., Beato M. Glucocorticoid receptors recognize DNA sequences in and around murine mammary tumour virus DNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1613–1619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V., Spiess E., Majors J. Purified glucocorticoid receptor-hormone complex from rat liver cytosol binds specifically to cloned mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeats in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5157–5161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Dieckmann B. S., Schroer T. A., Ringold G. M. Isolation of glucocorticoid-unresponsive rat hepatoma cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Saragosti S., Blangy D., Yaniv M. Fine structure of the origin-proximal DNAase I-hypersensitive region in wild-type and EC mutant polyoma. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):651–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M., Geiser M. Preferential binding of estrogen-receptor complex to a region containing the estrogen-dependent hypomethylation site preceding the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. M., Knoll B. J., March C. J., Woo S. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of 5' and 3' structural boundaries of the chromatin domain containing the ovalbumin multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequences at host-proviral junctions for mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):253–258. doi: 10.1038/289253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S. L., Smith S. W., Sarkar N. H. Quantitative of murine mammary tumor virus-related RNA in mammary tissues of low- and high-mammary-tumor-incidence mouse strains. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):87–95. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.87-95.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod J. J., Bourgeois S., Defer N., Crépin M. Demethylation and expression of murine mammary tumor proviruses in mouse thymoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):110–114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod J. J., Intrière L., MacLeod C. L., Bourgeois S. Characterization of a new type of thymoma variants supersensitive to dexamethasone. J Steroid Biochem. 1981 Dec;15:25–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(81)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Fisher L. M., Kuroda R., Ford A. M., Gould H. J. DNase I hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of human mu immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):809–812. doi: 10.1038/306809a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Granner D. K. Chromatin changes accompany immunoglobulin kappa gene activation: a potential control region within the gene. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):449–451. doi: 10.1038/299449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., DeFranco D., Firestone G. L., Edgar B., Wrange O., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Purified glucocorticoid receptors bind selectively in vitro to a cloned DNA fragment whose transcription is regulated by glucocorticoids in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6628–6632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. O., Kriz K. G., Marich J. E., Toohey M. G. Sequence organization and molecular cloning of mouse mammary tumor virus DNA endogenous to C57BL/6 mice. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):525–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.525-531.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl M. Specific binding of the glucocorticoid-receptor complex to the mouse mammary tumor proviral promoter region. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Glucocorticoid-stimulated accumulation of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: increased rate of synthesis of viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2879–2883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Fine structure of the regulatory region of simian virus 40 minichromosomes revealed by DNAase I digestion. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Firestone G. L., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoids and chromosomal position modulate murine mammary tumor virus transcription by affecting efficiency of promoter utilization. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):551–561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Ross S. R., Yamamoto K. R. Mammary tumor virus DNA contains sequences required for its hormone-regulated transcription. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Yamamoto K. R. Early events in the stimulation of mammary tumor virus RNA synthesis by glucocorticoids. Novel assays of transcription rates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7416–7420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Medeiros E., Bishop J. M., Nowinski R. C., Sarkar N. H. Transcription of mouse mammary tumor virus genes in tissues from high and low tumor incidence mouse strains. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 5;79(4):663–679. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. Active chromatin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):289–295. doi: 10.1038/297289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Stallcup M. R., Ring J., Ringold G. M. Mammary tumor virus DNA: a glucocorticoid-responsive transposable element. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):625–638. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]