Abstract
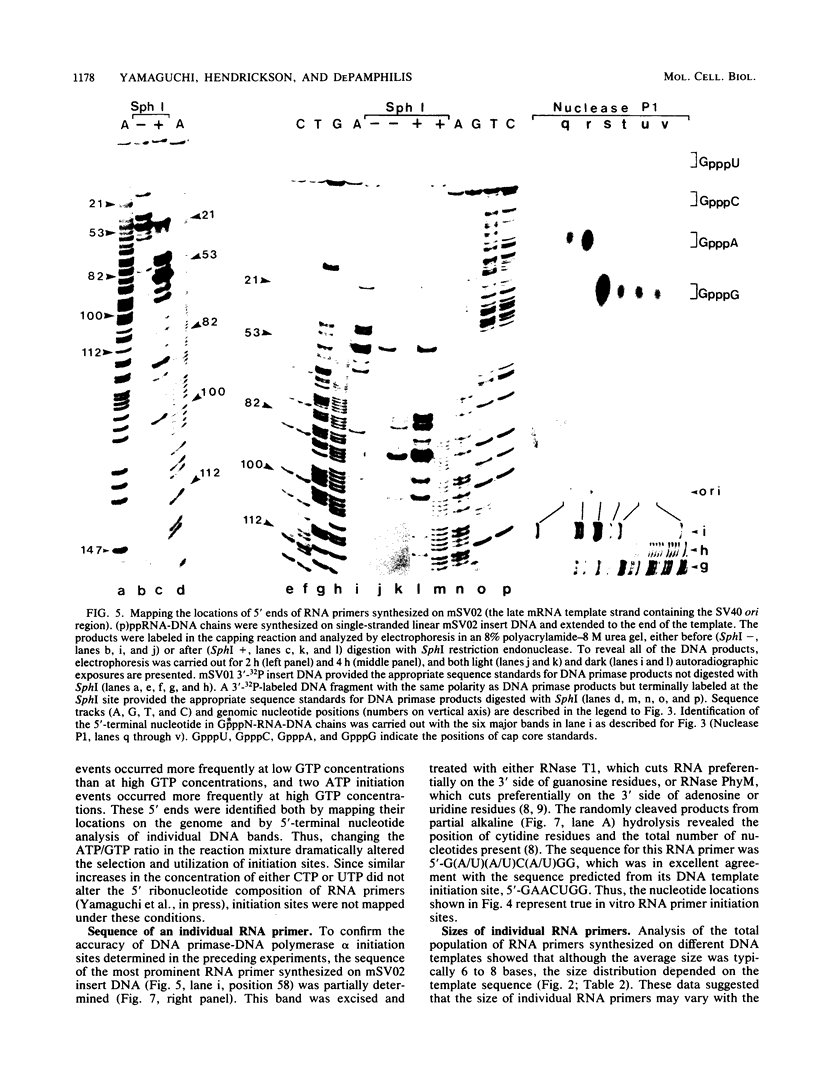
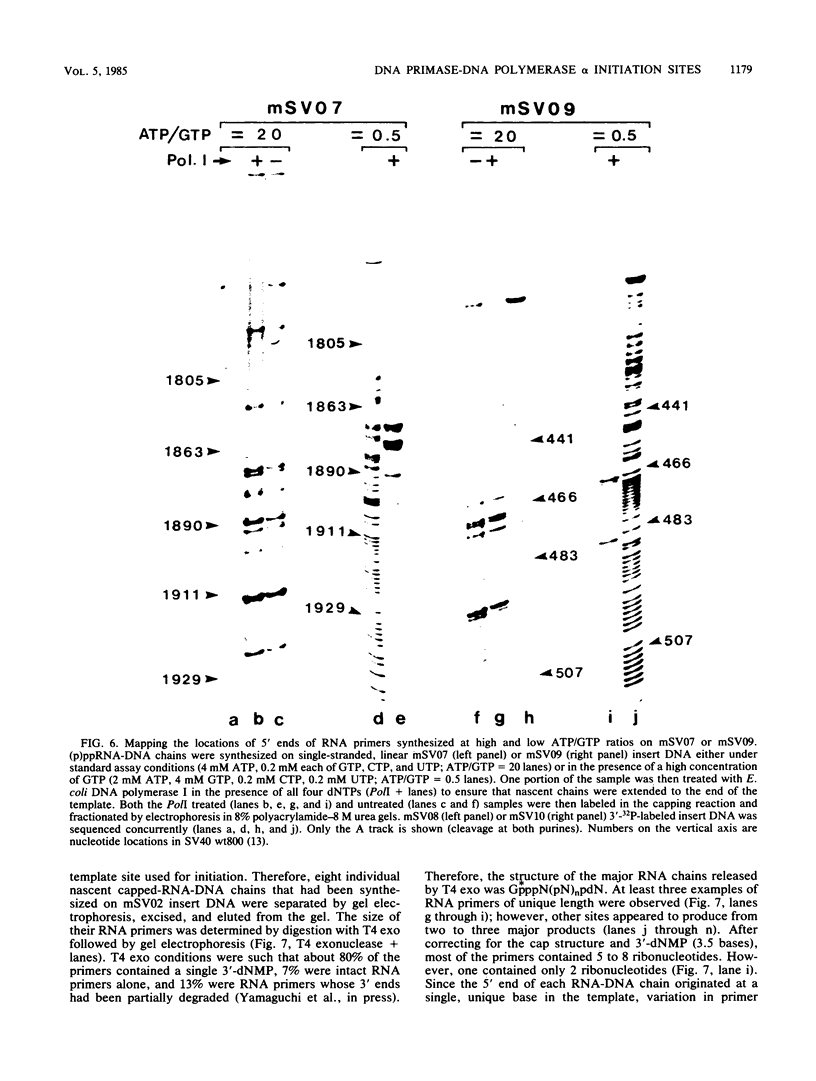
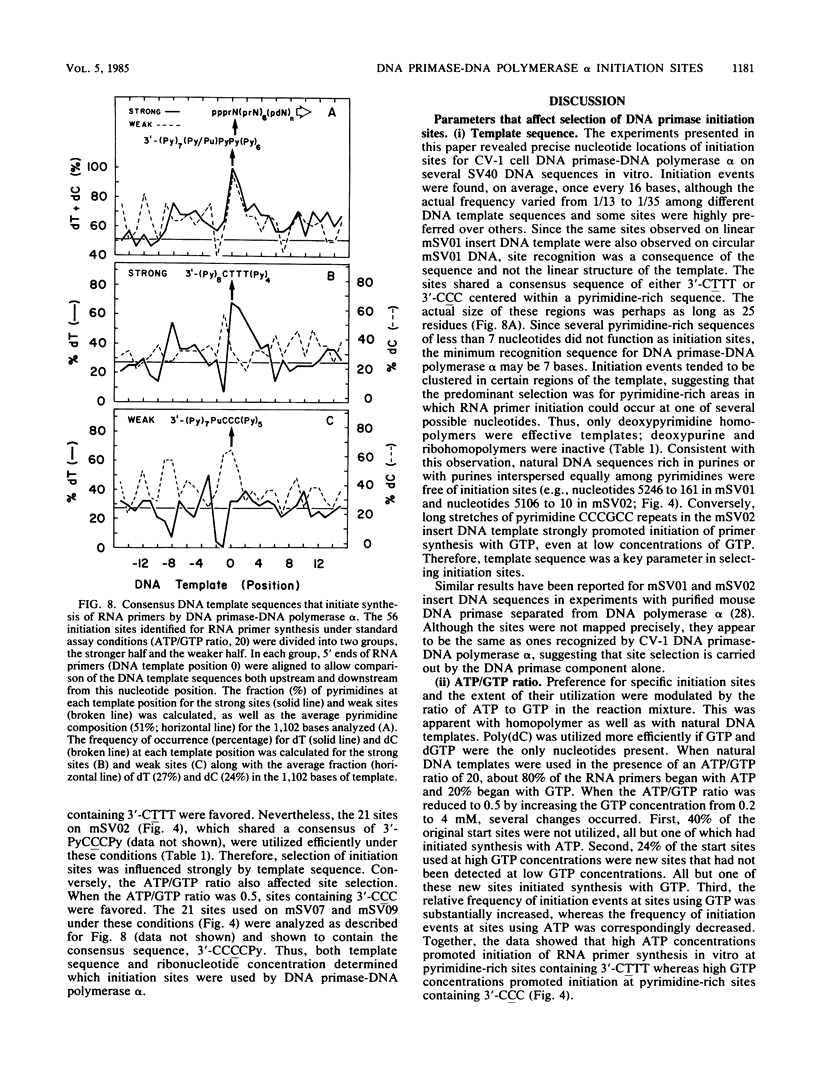
Unique single-stranded regions of simian virus 40 DNA, phage M13 virion DNA, and several homopolymers were used as templates for the synthesis of (p)ppRNA-DNA chains by CV-1 cell DNA primase-DNA polymerase alpha. Intact RNA primers, specifically labeled with an RNA capping enzyme, were typically 6 to 8 ribonucleotides long, although their lengths ranged from 1 to 9 bases. The fraction of intact RNA primers 1 to 4 ribonucleotides long was 14 to 73%, depending on the template used. RNA primer length varied among primers initiated at the same nucleotide, as well as with primers initiated at different sites. Thus, the size of an RNA primer depended on template sequence. Initiation sites were identified by mapping 5' ends of nascent RNA-DNA chains on the template sequence, identifying the 5'-terminal ribonucleotide, and partially sequencing one RNA primer. A total of 56 initiation events were identified on simian virus 40 DNA, an average of 1 every 16 bases. Some sites were preferred over others. A consensus sequence for initiation sites consisted of either 3'-dCTTT or 3'-dCCC centered within 7 to 25 pyrimidine-rich residues; the 5' ends of RNA primers were complementary to the dT or dC. High ATP/GTP ratios promoted initiation of RNA primer synthesis at 3'-dCTTT sites, whereas low ATP/GTP ratios promoted initiation at 3'-dCCC sites. Similarly, polydeoxythymidylic acid and polydeoxycytidylic acid were the only effective homopolymer templates. Thus, both template sequence and ribonucleoside triphosphate concentrations determine which initiation sites are used by DNA primase-DNA polymerase alpha. Remarkably, initiation sites selected in vitro were strikingly different from initiation sites selected during simian virus 40 DNA replication in vivo.
Full text
PDF



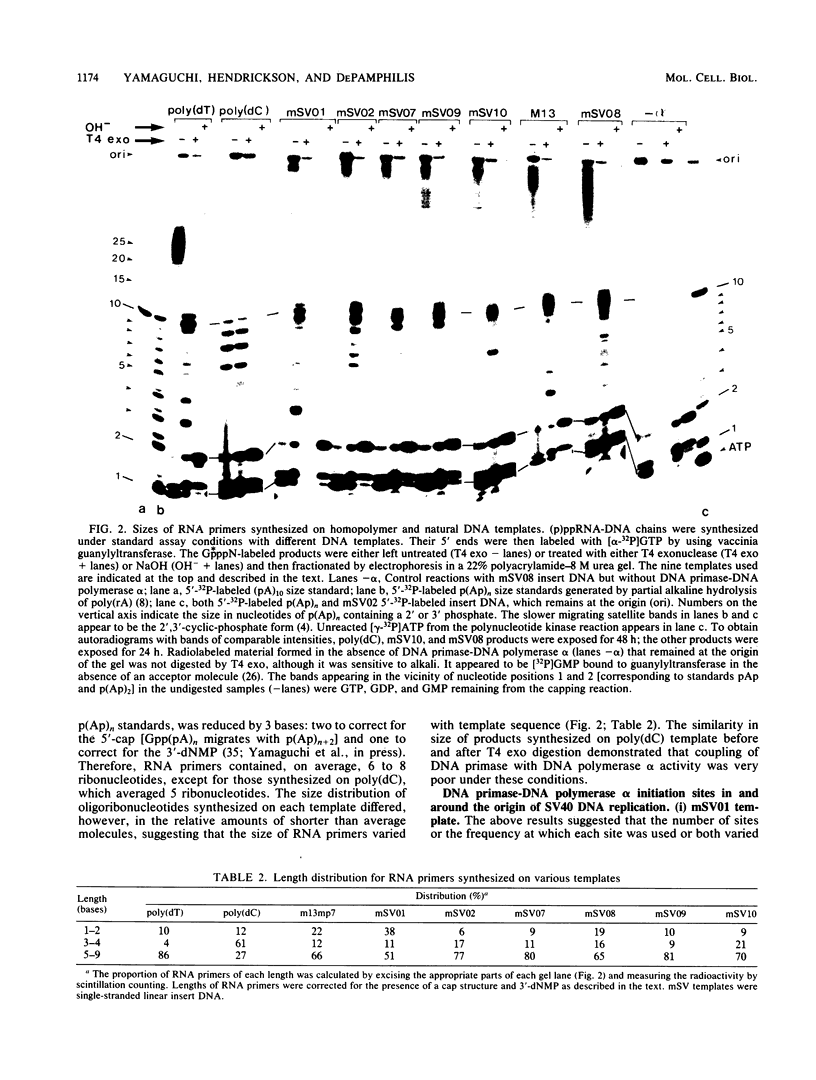

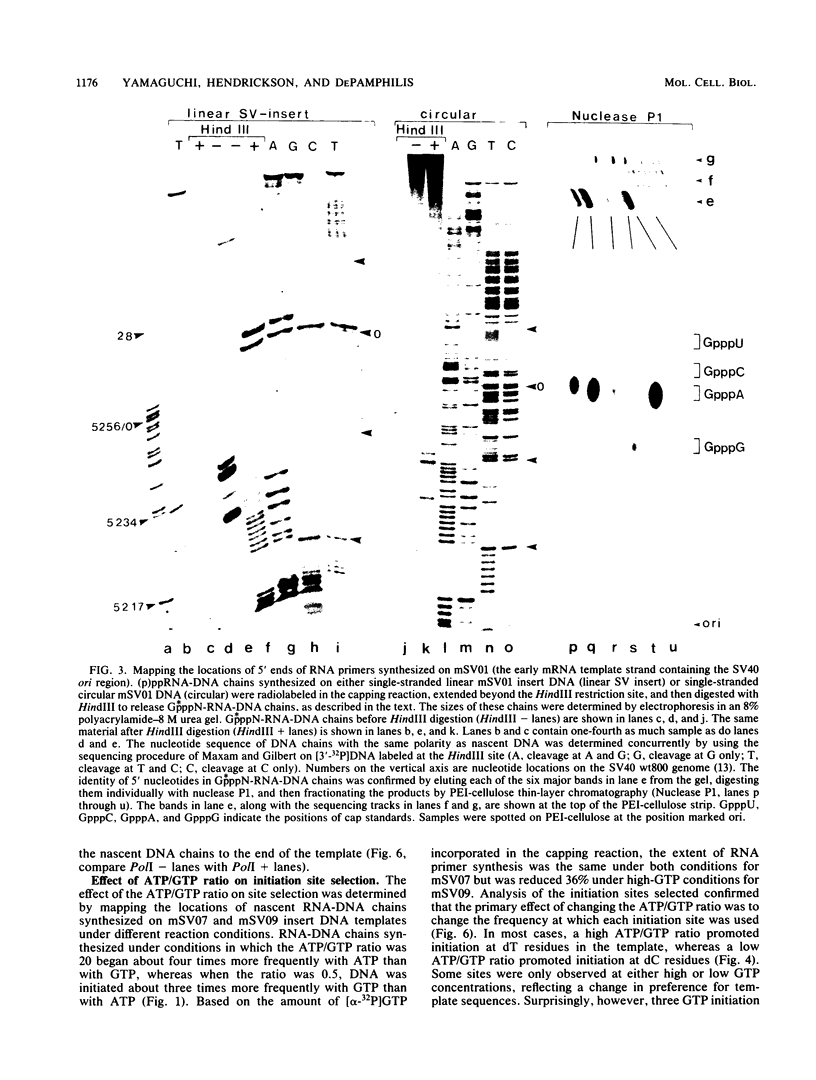
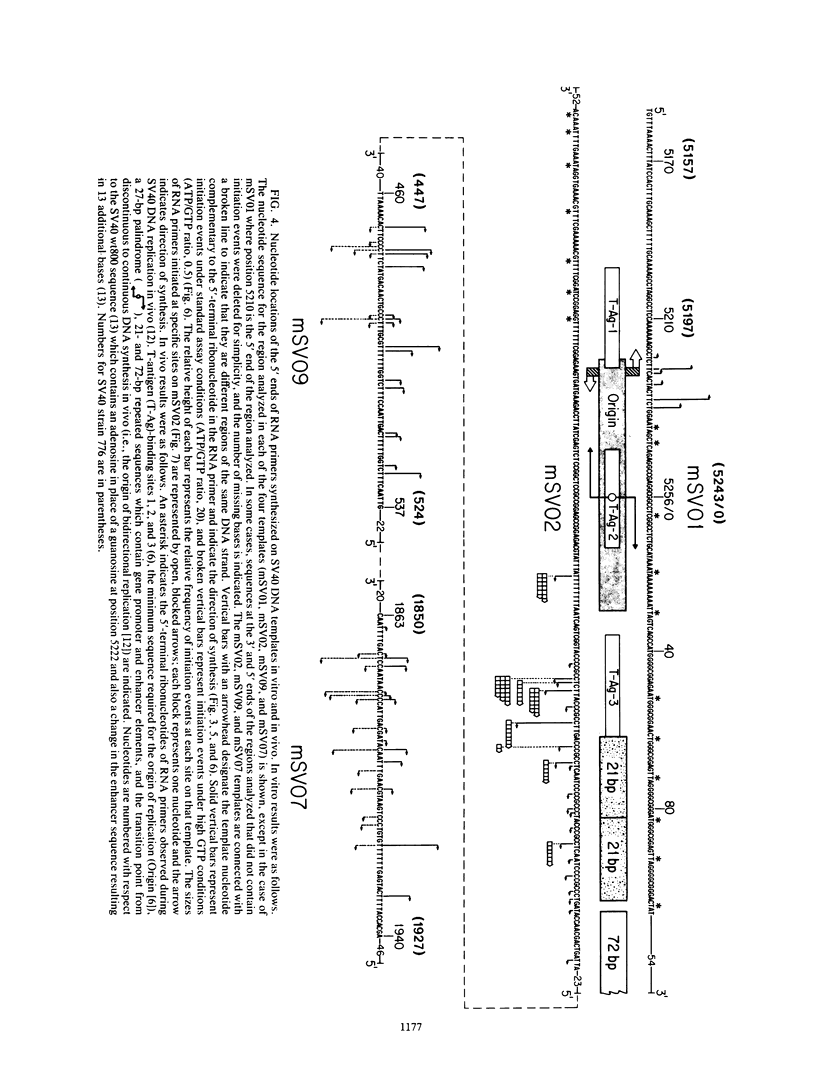



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., DePamphilis M. L. Metabolism of Okazaki fragments during simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11495–11504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Kornberg A. Mechanism of dnaB protein action. II. ATP hydrolysis by dnaB protein dependent on single- or double-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5253–5259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai K., Kornberg A. Mechanism of dnaB protein action. IV. General priming of DNA replication by dnaB protein and primase compared with RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5267–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Replication of eukaryotic chromosomes: a close-up of the replication fork. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:627–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Phy M: an RNase activity specific for U and A residues useful in RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3133–3142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Korn D. Enzymological characterization of KB cell DNA polymerase-alpha. III. The polymerization reaction with single-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11040–11046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M., Field J., Hurwitz J. Purification of a primase activity associated with DNA polymerase alpha from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9479–9486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., Hendrickson E. A., DePamphilis M. L. Sequence specificity for the initiation of RNA-primed simian virus 40 DNA synthesis in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 15;175(2):131–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M., LeGrange J., Austin B. Dependence of DNA helix flexibility on base composition. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):752–754. doi: 10.1038/304752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitani T., Yoda K., Okazaki T. Discontinuous DNA replication of Drosophila melanogaster is primed by octaribonucleotide primer. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1591–1596. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., Okazaki T. Structure of the RNA portion of the RNA-linked DNA pieces in bacteriophage T4-infected Escherichia coli cells. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 25;135(4):841–861. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Arai K., Okazaki T. Site selection and structure of DNA-linked RNA primers synthesized by the primosome in phage phi X174 DNA replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13353–13358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. R., Chae C. B. A method for isolation of a large amount of a single-stranded DNA fragment. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. G., DePamphilis M. L. Preparation of DNA polymerase alpha X C1C2 by reconstituting DNA polymerase alpha with its specific stimulatory cofactors, C1C2. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9801–9809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. G., Weaver D. T., Baril E. F., DePamphilis M. L. DNA polymerase alpha cofactors C1C2 function as primer recognition proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9810–9819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reha-Krantz L. J., Hurwitz J. The dnaB gene product of Escherichia coli. II. Single stranded DNA-dependent ribonucleoside triphosphatase activity. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4051–4057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Hurwitz J. Mechanism of mRNA capping by vaccinia virus guanylyltransferase: characterization of an enzyme--guanylate intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):187–191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims J., Benz E. W., Jr Initiation of DNA replication by the Escherichia coli dnaG protein: evidence that tertiary structure is involved. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):900–904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng B. Y., Ahlem C. N. Mouse primase initiation sites in the origin region of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2342–2346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu C. P., Cohen S. N. 3'-end labeling of DNA with [alpha-32P]cordycepin-5'-triphosphate. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Gershowitz A., Moss B. Modification of the 5' end of mRNA. Association of RNA triphosphatase with the RNA guanylyltransferase-RNA (guanine-7-)methyltransferase complex from vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):903–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. T., DePamphilis M. L. The role of palindromic and non-palindromic sequences in arresting DNA synthesis in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):961–986. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Blakesley R. W., Hardies S. C., Horn G. T., Larson J. E., Selsing E., Burd J. F., Chan H. W., Dodgson J. B., Jensen K. F. The role of DNA structure in genetic regulation. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1977;4(3):305–340. doi: 10.3109/10409237709102561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. H., Matsukage A., Bohn E. W., Chen Y. C., Sivarajan M. Polynucleotide recognition by DNA alpha-polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):3981–3996. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.3981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagura T., Kozu T., Seno T. Mechanism of stimulation by a specific protein factor of de novo DNA synthesis by mouse DNA replicase with fd phage single stranded circular DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6369–6380. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoda K., Okazaki T. Primer RNA for DNA synthesis on single-stranded DNA template in a cell free system from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3433–3450. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B. The three-dimensional structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:395–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]