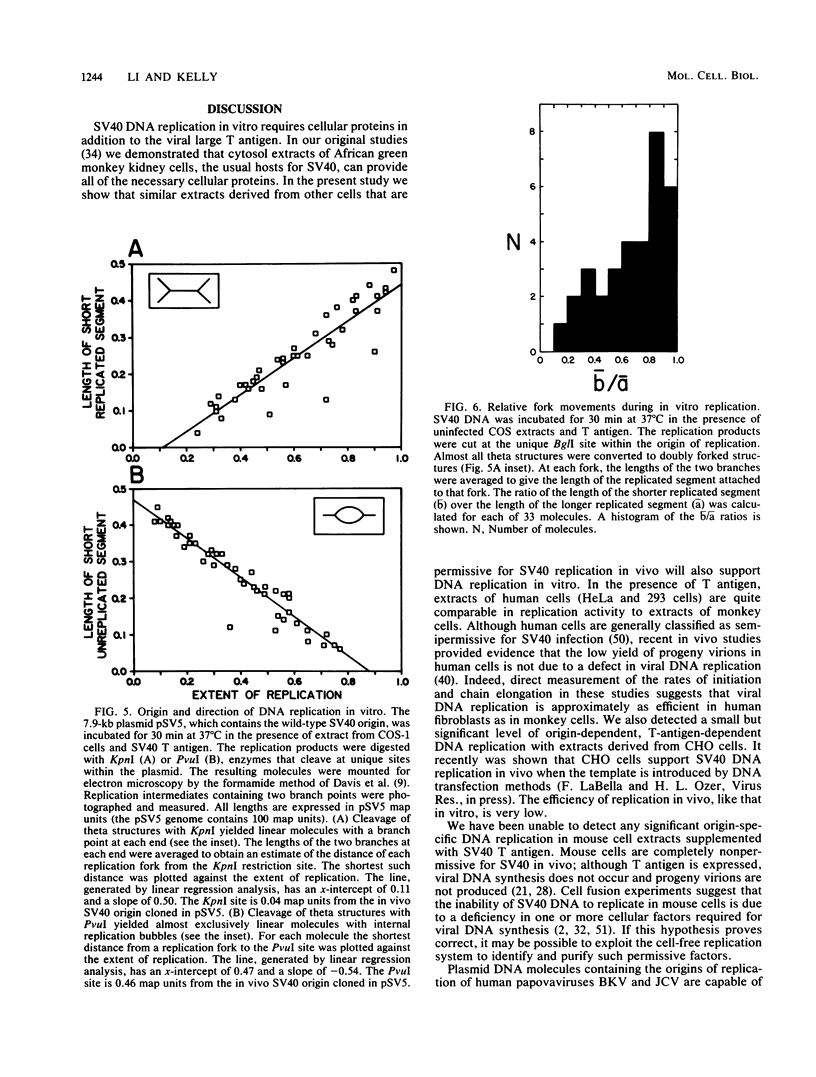
Abstract
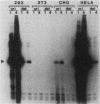
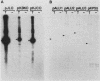
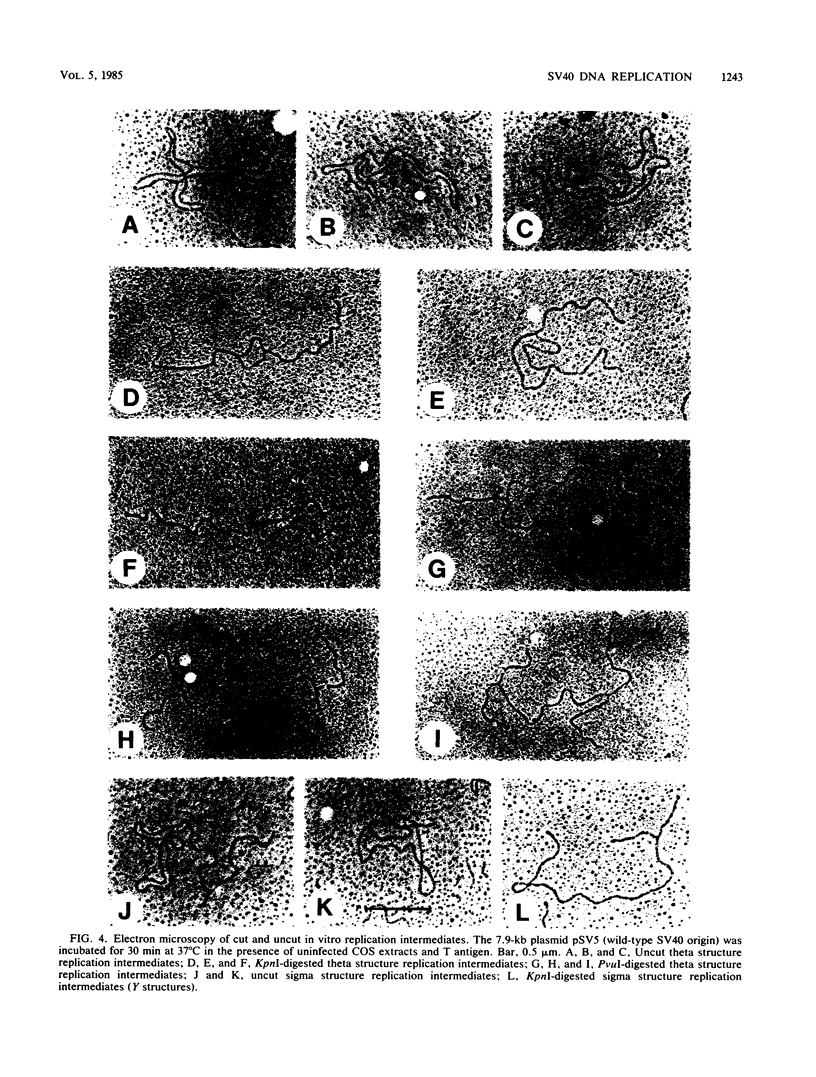
We recently described a soluble cell-free system derived from monkey cells that is capable of replicating exogenous plasmid DNA molecules containing the simian virus 40 (SV40) origin of replication (J.J. Li, and T.J. Kelly, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81:6973-6977, 1984). Replication in the system is completely dependent upon the addition of the SV40 large T antigen. In this report we describe additional properties of the in vitro replication reaction. Extracts prepared from cells of several nonsimian species were tested for the ability to support origin-dependent replication in the presence of T antigen. The activities of extracts derived from human cell lines HeLa and 293 were approximately the same as those of monkey cell extracts. Chinese hamster ovary cell extracts also supported SV40 DNA replication in vitro, but the extent of replication was approximately 1% of that observed with human or monkey cell extracts. No replication activity was detectable in extracts derived from BALB/3T3 mouse cells. The ability of these extracts to support replication in vitro closely parallels the ability of the same cells to support replication in vivo. We also examined the ability of various DNA molecules containing sequences homologous to the SV40 origin to serve as templates in the cell-free system. Plasmids containing the origins of human papovaviruses BKV and JCV replicated with an efficiency 10 to 20% of that of plasmids containing the SV40 origin. Plasmids containing Alu repeat sequences (BLUR8) did not support detectable DNA replication in vitro. Circular DNA molecules were found to be the best templates for DNA replication in the cell-free system; however, linear DNA molecules containing the SV40 origin also replicated to a significant extent (10 to 20% of circular molecules). Finally, electron microscopy of replication intermediates demonstrated that the initiation of DNA synthesis in vivo takes place at a unique site corresponding to the in vivo origin and that replication is bidirectional. These findings provide further evidence that replication in the cell-free system faithfully mimics SV40 DNA replication in vivo.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariga H. Replication of cloned DNA containing the Alu family sequence during cell extract-promoting simian virus 40 DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1476–1482. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. Studies on simian virus 40 excision from cellular chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):709–719. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman W. W., Nathans D. The isolation of simian virus 40 variants with specifically altered genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):942–946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Eukaryotic DNA replication: viral and plasmid model systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:901–934. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Avila J., Martin R. G. Viral DNA synthesis in cells infected by temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.116-124.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C., Pignatti P. F., Croissant O., Yaniv M. Chromatin-like structures in polyoma virus and simian virus 10 lytic cycle. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.204-211.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Replication of eukaryotic chromosomes: a close-up of the replication fork. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:627–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. Effect of mutations at a T antigen binding site on DNA replication and expression of viral genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):531–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Nathans D. Purification of simian virus 40 large T antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1001–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1001-1004.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareed G. C., Garon G. F., Salzman N. P. Origin and direction of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):484–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.484-491.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Bream G. L., Cannella M. T. Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):458–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.458-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. D., Field A. M., Coleman D. V., Hulme B. New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1253–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91776-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon D., Sachs L., Winocour E. The induction of cellular DNA synthesis by simian virus 40 in contact-inhibited and in x-irradiated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):918–925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Frisque R. J., Sambrook J. Origin-defective mutants of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):293–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P., Black P. H., Oxman M. N., Weissman S. M. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in mouse cell line 3T3 by Simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1170–1176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Mayer A., Levine A. Replicating SV40 molecules containing closed circular template DNA strands. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 15;233(37):72–75. doi: 10.1038/newbio233072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Jensen F. C., Steplewski Z. Activation of production of infectious tumor virus SV40 in heterokaryon cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):127–133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Goldman N. D., Khoury G. Functional similarity between the early antigens of simian virus 40 and human papovavirus BK. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):141–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.141-147.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major E. O., Matsumura P. Human embryonic kidney cells: stable transformation with an origin-defective simian virus 40 DNA and use as hosts for human papovavirus replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):379–382. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Setlow V. P. The initiation of SV40 DNA synthesis is not unique to the replication origin. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90624-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. H., Takemoto K. K. Complementation between BK human papovavirus and a simian virus 40 tsA mutant. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):1060–1062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.1060-1062.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer H. L., Slater M. L., Dermody J. J., Mandel M. Replication of simian virus 40 DNA in normal human fibroblasts and in fibroblasts from xeroderma pigmentosum. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.481-489.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., DeLucia A. L., Tegtmeyer P. Binding of SV40 a protein to the BK virus origin of DNA replication. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90412-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebring E. D., Kelly T. J., Jr, Thoren M. M., Salzman N. P. Structure of replicating simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid molecules. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):478–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.478-490.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. The genome of human papovavirus BKV. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):963–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. R., Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of the simian virus 40 replicon: pseudorevertants of mutants with a defective replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Anderson S., DePamphilis M. L. Distribution of replicating simian virus 40 DNA in intact cells and its maturation in isolated nuclei. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):877–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.877-892.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., DePamphilis M. L. Preferred DNA sites are involved in the arrest and initiation of DNA synthesis during replication of SV40 DNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. F., Dulbecco R. Production of SV40 virus in heterokaryons of transformed and susceptible cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1396–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. J., DeLucia A. L., Tegtmeyer P. Sequence-specific binding of simian virus 40 A protein to nonorigin and cellular DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2631–2638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]