Abstract
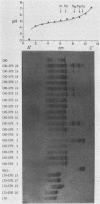
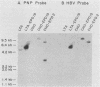
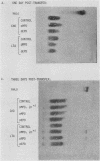
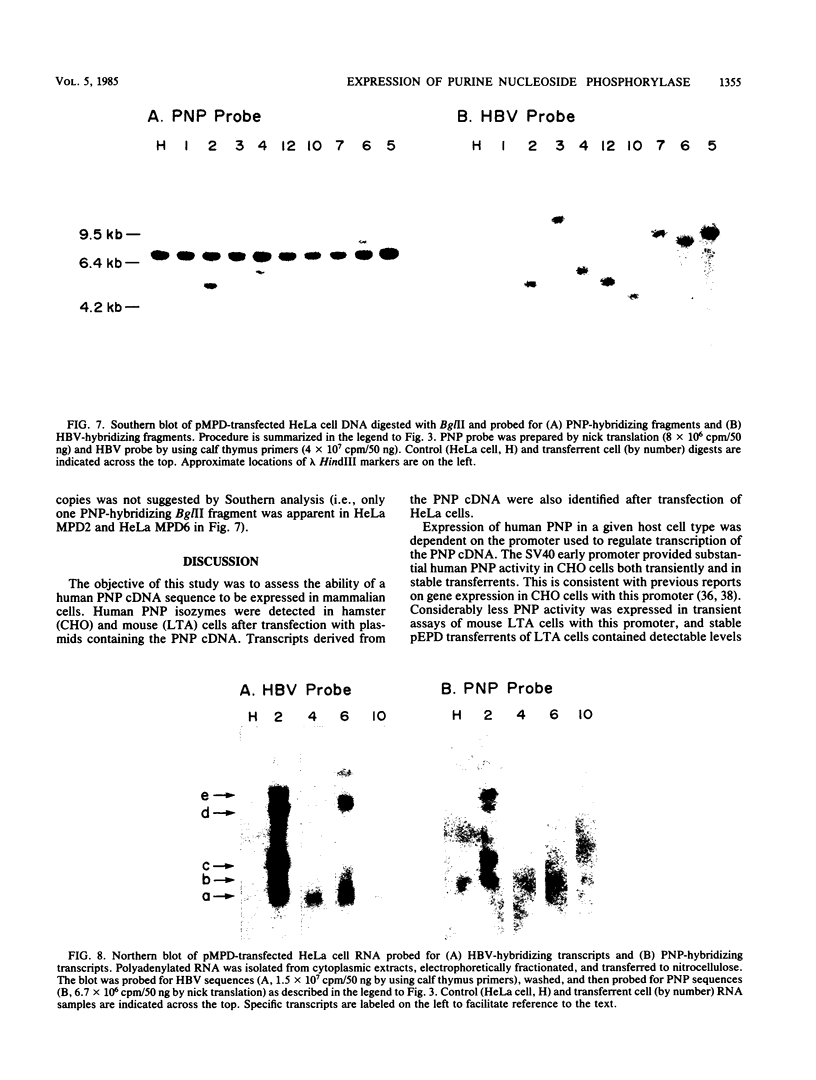
A cDNA sequence which contains the entire coding region for human purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) was recombined for selection and expression in mammalian cells. Plasmids containing either the simian virus 40 early promoter or the mouse metallothionein promoter positioned just upstream of the PNP coding sequence were constructed. These plasmids also contained the gene for a methotrexate-resistant dihydrofolate reductase, allowing for selection and amplification of positive transferrents after transfection of cells by the DNA-calcium phosphate coprecipitation technique. Expression of human PNP activity was readily detected in both mouse (L) and CHO cells by isoelectric focusing of cell extracts followed by histochemical staining for PNP activity. The simian virus 40 early promoter directed considerable expression of human PNP activity in CHO cells but only scant activity in mouse cells. The mouse metallothionein promoter was not successful in effecting human PNP expression in CHO cells but provided substantial human PNP activity in mouse cells and was inducible by incubation with zinc. HeLa cell transferrents were isolated and screened for the presence of transferred PNP cDNA sequences by Southern hybridization analysis. RNA transcripts derived from the transferred PNP cDNA were identified in one of these cell lines.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal R. P., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from human erythrocytes. IV. Crystallization and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):644–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Stang H., Mercola K., Morse L., Ruprecht R., Brown J., Salser W. Gene transfer in intact animals. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):422–425. doi: 10.1038/284422a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Perrin F., Gannon F., Palmiter R. D. Isolation and characterization of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards Y. H., Hopkinson D. A., Harris H. Inherited variants of human nucleoside phosphorylase. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 May;34(4):395–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1971.tb00252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Ammann A. J., Wara D. W., Sandman R., Diamond L. K. Nucleoside-phosphorylase deficiency in a child with severely defective T-cell immunity and normal B-cell immunity. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):1010–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91950-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Structure of mouse metallothionein-I gene and its mRNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):267–269. doi: 10.1038/292267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard J. M., Caput D., Williams S. R., Martin D. W., Jr Cloning of human purine-nucleoside phosphorylase cDNA sequences by complementation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith B. B., Walters R. A., Enger M. D., Hildebrand C. E., Griffith J. K. cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequence comparison of Chinese hamster metallothionein I and II mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):901–910. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Construction of a modular dihydrofolate reductase cDNA gene: analysis of signals utilized for efficient expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1304–1319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Oppermann H., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Integration and expression of several molecular forms of Rous sarcoma virus DNA used for transfection of mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1260–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Jr, Gelfand E. W. Biochemistry of diseases of immunodevelopment. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:845–877. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Warren R., Palmiter R. D. The mouse metallothionein-I gene is transcriptionally regulated by cadmium following transfection into human or mouse cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Eckner R. J., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. Expression of a retrovirus encoding human HPRT in mice. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.6377498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Anton D. L., Weber J. L. Chinese hamster purine-nucleoside phosphorylase: purification, structural, and catalytic properties. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):4967–4973. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne W. R. Human red cell purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Purification by biospecific affinity chromatography and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7089–7092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T., Kao F. T. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells. V. Treatment with 5-bromodeoxyuridine and visible light for isolation of nutritionally deficient mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1227–1234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., SCHILDKRAUT C. L., APOSHIAN H. V., KORNBERG A. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. XIV. FURTHER PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:222–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G., Dieckmann B., Lee F. Co-expression and amplification of dihydrofolate reductase cDNA and the Escherichia coli XGPRT gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(3):165–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Analysis of processing and polyadenylation signals of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene by using simian virus 40-hepatitis B virus chimeric plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2250–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman B., Gudas L. J., Clift S. M., Martin D. W., Jr Isolation and characterization of purine-nucleoside phosphorylase-deficient T-lymphoma cells and secondary mutants with altered ribonucleotide reductase: genetic model for immunodeficiency disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Lemischka I. R., Nathan D. G., Mulligan R. C. Introduction of new genetic material into pluripotent haematopoietic stem cells of the mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):476–480. doi: 10.1038/310476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. R., Goddard J. M., Martin D. W., Jr Human purine nucleoside phosphorylase cDNA sequence and genomic clone characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5779–5787. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V., Doyle D., Martin D. W., Jr Purification and characterization of human erythrocyte purine nucleoside phosphorylase and its subunits. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):504–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Tyndall C., Schaffner W. Transcriptional 'enhancers' from SV40 and polyoma virus show a cell type preference. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7965–7976. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]