Abstract
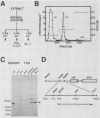
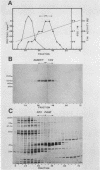
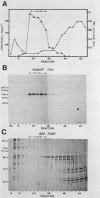
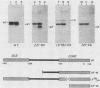
A whole-cell HeLa extract was fractionated into two components required for accurate in vitro transcription of human rRNA. One fraction contained endogenous RNA polymerase I, and the second component contained a factor (SL1) that confers promoter selectivity to RNA polymerase I. Analysis of mutant templates suggests that the core control element of the rRNA promoter is required for activation of transcription by SL1. We purified SL1 approximately 100,000-fold by column chromatography and have shown that the addition of SL1 can reprogram the otherwise nonpermissive mouse transcription system to recognize and initiate accurate RNA synthesis from human rDNA. Antibodies raised against SL1 bind preferentially to a protein localized in the nucleolus of primate cells and specifically inhibit in vitro transcription initiating from the human rRNA promoter. By contrast, anti-SL1 does not react with the nucleolus of rodent cells and has no effect on the in vitro synthesis of mouse rRNA by a transcription system derived from mouse cells. These findings suggest that SL1 is a selectivity factor present in the nucleolus that imparts promoter recognition to RNA polymerase I and that can discriminate between rRNA promoters from different species.
Full text
PDF

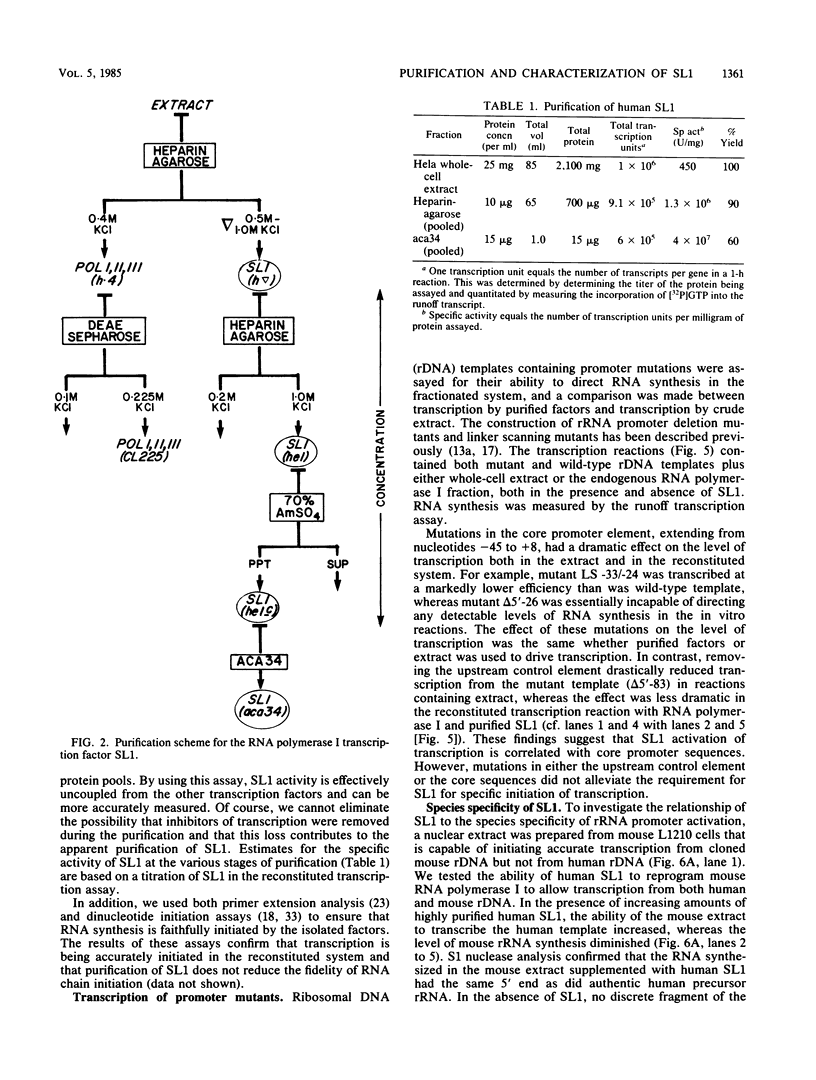
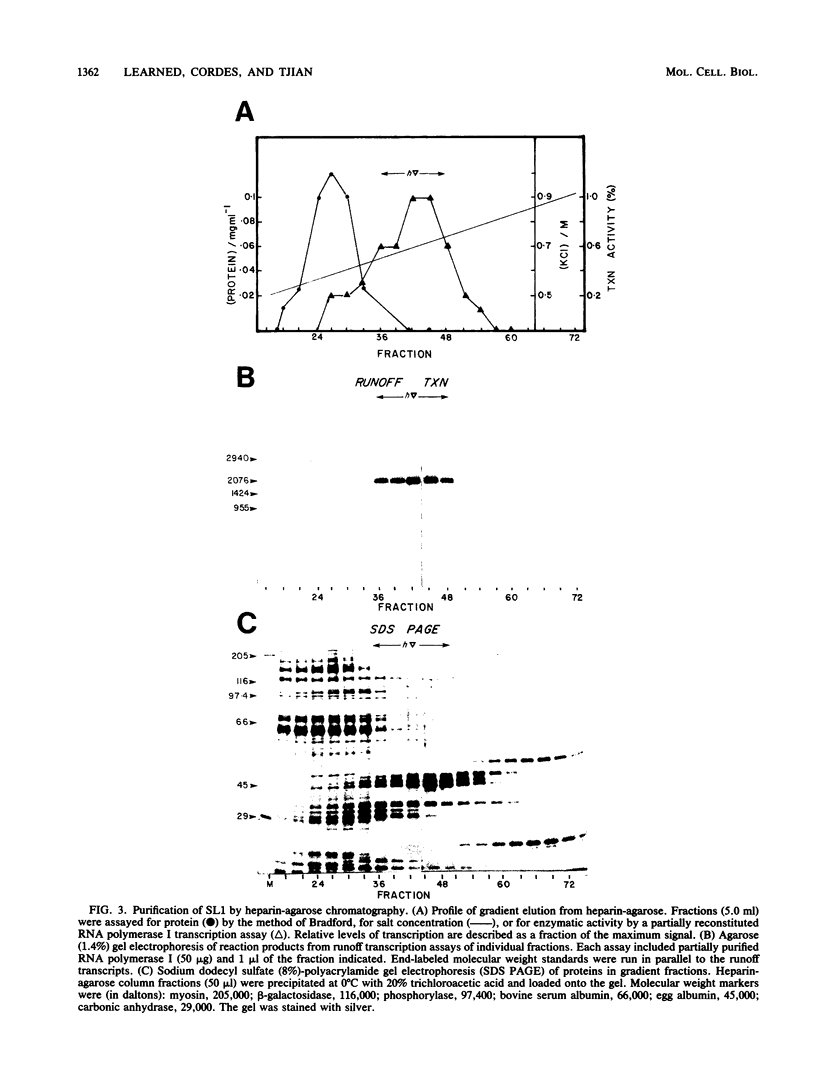
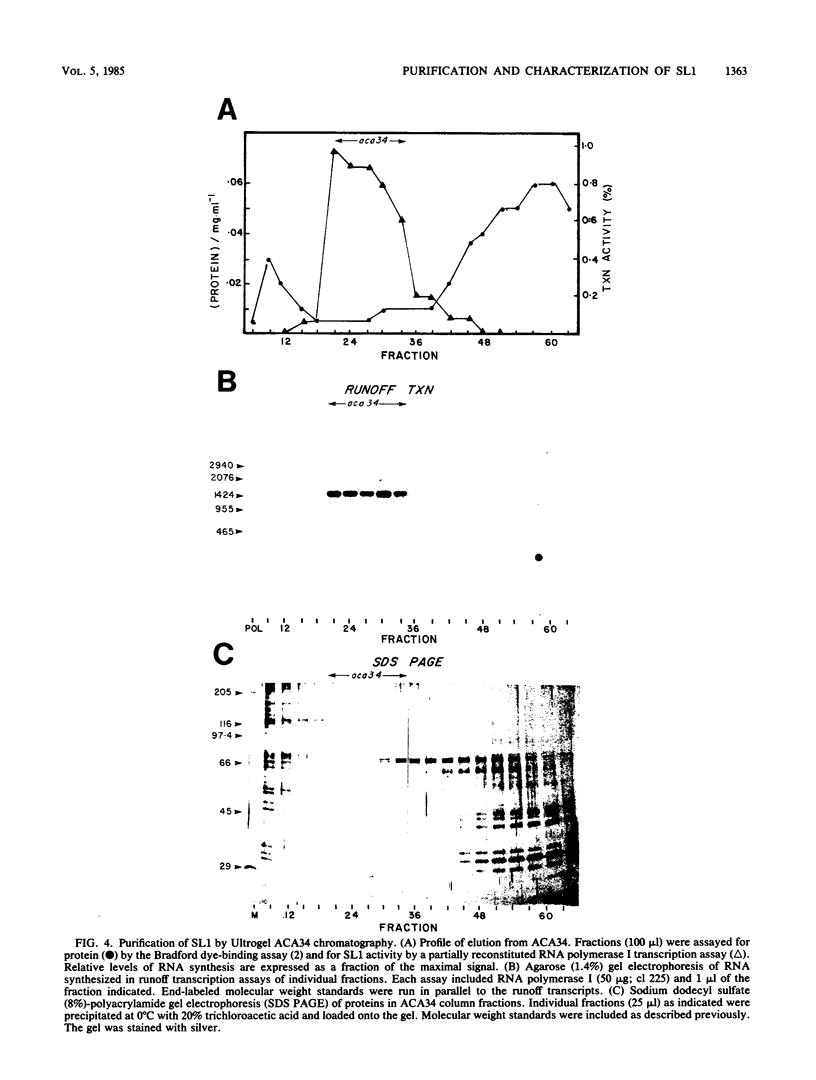
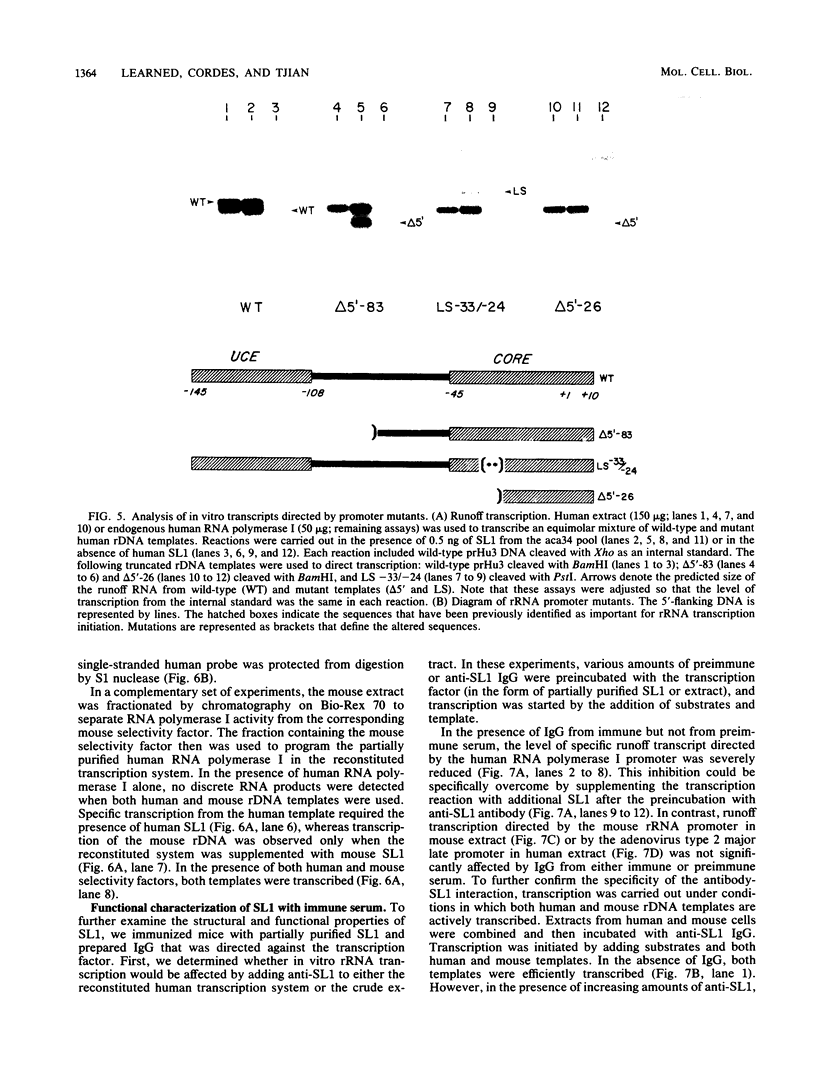




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry J., Gorski J. Uterine ribonucleic acid polymerase. Effect of estrogen on nucleotide incorporation into 3' chain termini. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 8;10(12):2384–2390. doi: 10.1021/bi00788a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Leighton T., Rabinowitz J. C. Purification of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with heparin-agarose. In vitro transcription of phi 29 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9220–9226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Financsek I., Mizumoto K., Mishima Y., Muramatsu M. Human ribosomal RNA gene: nucleotide sequence of the transcription initiation region and comparison of three mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Nucleotide sequence requirements for specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6908–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Smith V. A., Grummt F. Amino acid starvation affects the initiation frequency of nucleolar RNA polymerase. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiner M., Kempe T., Tjian R. A novel strategy for constructing clustered point mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):1015–1025. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Mamont P., Shields R., Tomkins G. M. "Pleiotypic response". Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug;232(33):206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. B., SOBER H. A. A simple chromatographic method for preparation of gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:250–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Smale S. T., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. Regulation of human ribosomal RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3558–3562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Tjian R. In vitro transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P., May E., Bordé J. Stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis in mouse-kidney cell cultures infected with SV40 virus. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jul;100(2):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWELL P. C. Phytohemagglutinin: an initiator of mitosis in cultures of normal human leukocytes. Cancer Res. 1960 May;20:462–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskas H. J., Thomas D. C., Green M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication. XVII. Ribosome synthesis in uninfected and infected KB cells. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):893–902. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon C., Türler H., Weil R. Polyoma-induced stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis is paralleled by changed expression of the viral genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1483–1503. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions: nucleotide sequence requirements for initiation by RNA polymerase II and III. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:25–46. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. Transcription of herpes simplex virus tk sequences under the control of wild-type and mutant human RNA polymerase I promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):352–362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano K. J., Dev V. G., Croce C. M., Baserga R. Reactivation of silent rRNA genes by simian virus 40 in human-mouse hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3885–3889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. A., Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Dinucleotide primers facilitate convenient identification of the mouse ribosomal DNA transcription initiation site. A general method for analysis of transcription by RNA polymerases I and III. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13919–13928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]