Abstract
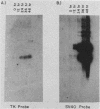
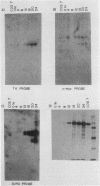
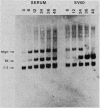
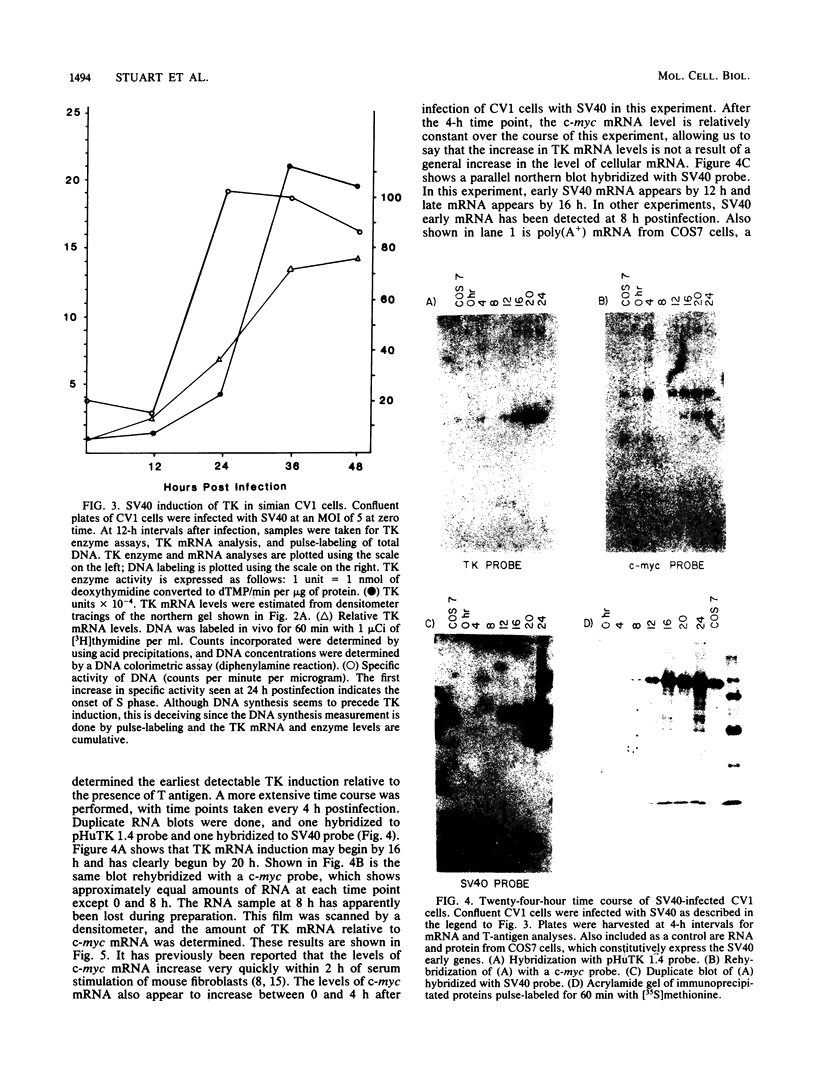
The thymidine kinase (TK) gene has been isolated from human genomic DNA. The gene was passaged twice by transfection of LTK- cells with human chromosomal DNA, and genomic libraries were made in lambda Charon 30 from a second-round TK+ transformant. When the library was screened with a human Alu probe, seven overlapping lambda clones from the human TK locus were obtained. None of the seven contained a functional TK gene as judged by transfection analysis, but several combinations of clones gave rise to TK+ colonies when cotransfected into TK- cells. A functional cDNA clone encoding the human TK gene has also been isolated. Using this cDNA clone as a probe in restriction enzyme/blot hybridization analyses, we have mapped the coding sequences and direction of transcription of the gene. We have also used a single-copy subclone from within the coding region to monitor steady-state levels of TK mRNA in serum-stimulated and simian virus 40-infected simian CV1 tissue culture cells. Our results indicate that the previously reported increase in TK enzyme levels seen after either treatment is paralleled by an equivalent increase in the steady-state levels of TK mRNA. In the case of simian virus 40-infected cells, the induction was delayed by 8 to 12 h, which is the length of time after infection required for early viral protein synthesis. In both cases, induction of TK mRNA coincides with the onset of DNA synthesis, but virally infected cells ultimately accumulate more TK mRNA than do serum-stimulated cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Clayton D. A. A genetically distinct thymidine kinase in mammalian mitochondria. Exclusive labeling of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2722–2729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Deininger P. L. Human thymidine kinase gene: molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA expressible in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2316–2320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw H. D., Jr Molecular cloning and cell cycle-specific regulation of a functional human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5588–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M., Dulbecco R. Induction of DNA synthesis by SV40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):736–740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ives D. H., Durham J. P., Tucker V. S. Rapid determination of nucleoside kinase and nucleotidase activities with tritium-labeled substrates. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):192–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90170-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Rao L. G., Muench A. J. Regulation of thymidine kinase enzyme level in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Growth-dependent expression of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA from modular cDNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1598–1608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Frearson P. M., Melnick J. L. Enzyme induction in SV40-infected green monkey kidney cultures. Virology. 1966 May;29(1):69–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S. Viral-induced enzymes and the problem of viral oncogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1968;11:73–221. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Kan Y. W. Direct isolation of the functional human thymidine kinase gene with a cosmid shuttle vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):414–418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leys E. J., Kellems R. E. Control of dihydrofolate reductase messenger ribonucleic acid production. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):961–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. F., Yamaizumi M., Murphy P. D., Egg A., Ruddle F. H. Partial purification and characterization of the mRNA for human thymidine kinase and hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4290–4294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. F., Zhao S. Y., Ruddle F. H. Genomic cloning and preliminary characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6528–6532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill G. F., Harland R. M., Groudine M., McKnight S. L. Genetic and physical analysis of the chicken tk gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1769–1776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill G. F., Hauschka S. D., McKnight S. L. tk Enzyme expression in differentiating muscle cells is regulated through an internal segment of the cellular tk gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1777–1784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Lipsich L., Wigler M. Isolation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene by plasmid rescue. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):207–210. doi: 10.1038/285207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Levine A. J. The requirement of simian virus 40 gene A product for the stimulation of cellular thymidine kinase activity after viral infection. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):206–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosser C. A., Steglich C., deWet J. R., Scheffler I. E. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of thymidine kinase activity introduced into mouse LMTK- cells by DNA and chromatin-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1119–1123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E., Mueller G. C. Thymidine kinase activity in synchronized HeLa cell cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):535–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]