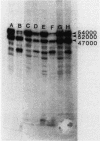
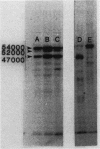
Abstract
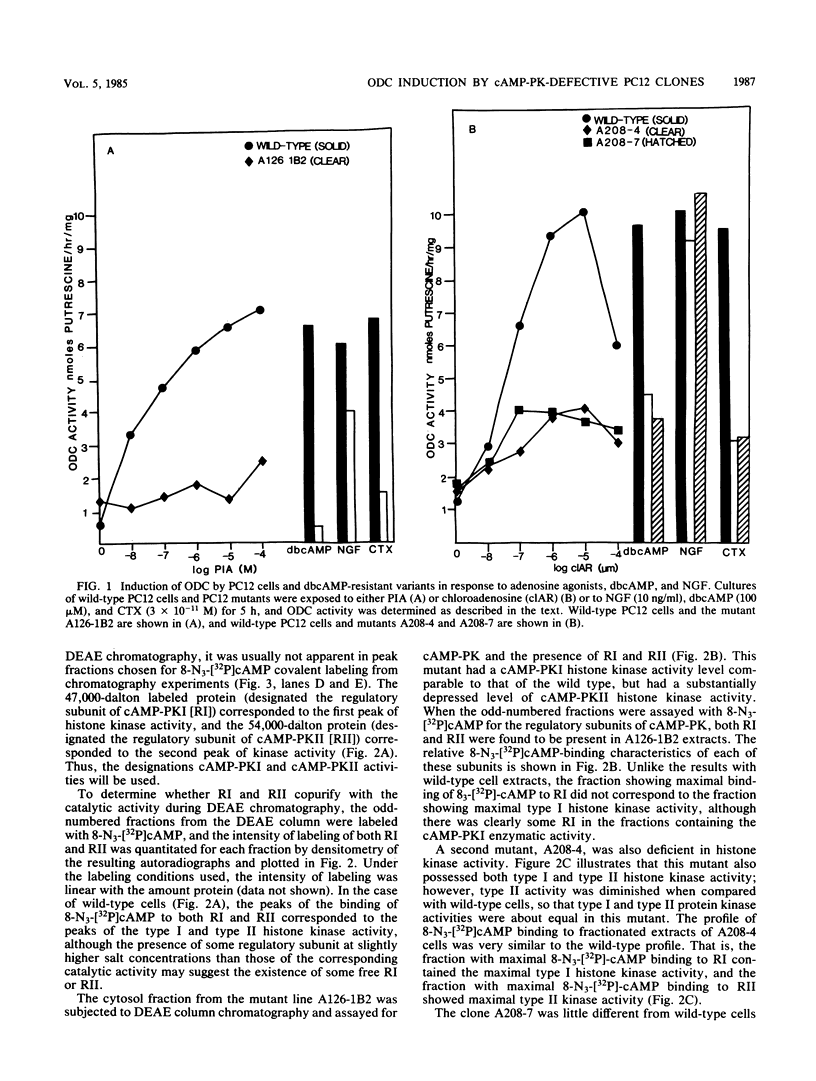
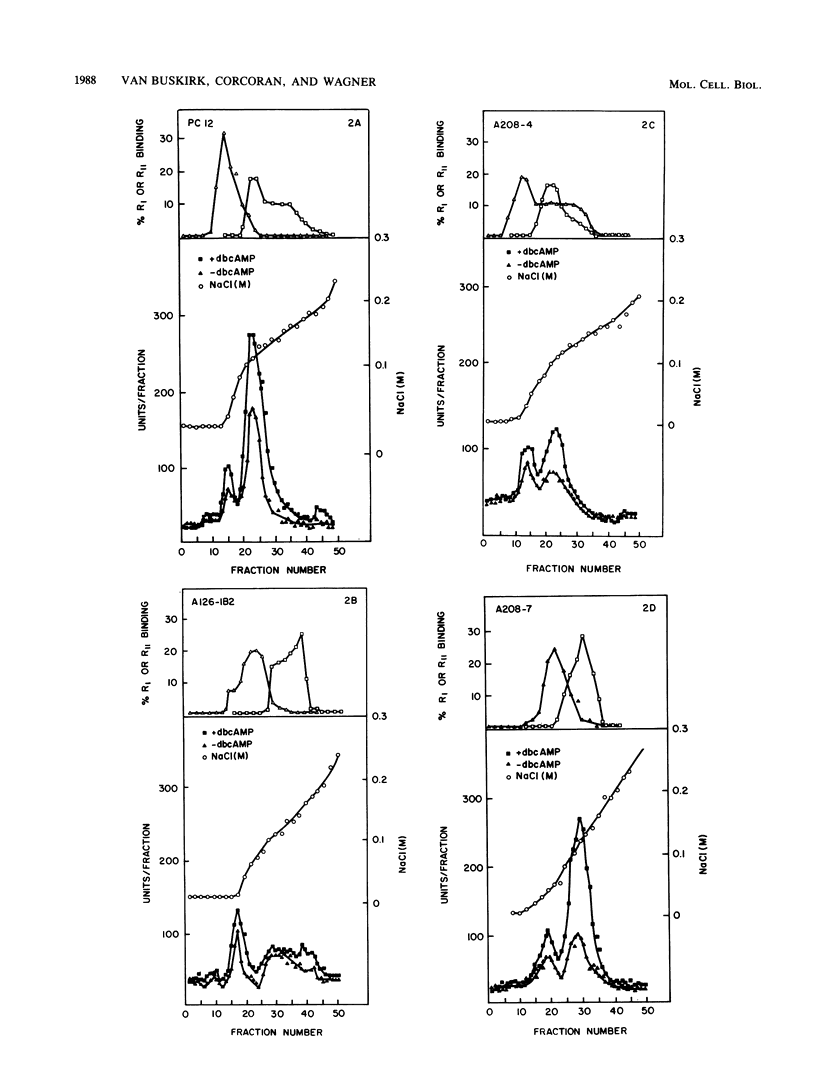
We have isolated and partially characterized three mutants of the pheochromocytoma line PC12 by using dibutyryl cyclic AMP (cAMP) as a selective agent. Each of these variants, A126-1B2, A208-4, and A208-7, was resistant to both dibutyryl cAMP and cholera toxin when cell growth was measured. In comparison to wild-type PC12 cells, each of these mutants was deficient in the ability to induce ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) in response to agents that act via a cAMP-dependent pathway. In contrast, each of these mutants induced ODC in response to nerve growth factor. To understand the nature of the mutations, the cAMP-dependent protein kinases of the wild type and of each of these mutants were studied by measuring both histone kinase activity and 8-N3-[32P]cAMP labeling. Wild-type PC12 cells contained both cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I (cAMP-PKI) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II (cAMP-PKII). Regulatory subunits were detected in both soluble and particulate fractions. The mutant A126-1B2 contained near wild-type PC12 levels of cAMP-PKI but greatly reduced levels of cAMP-PKII. Furthermore, when compared with wild-type PC12 cells, this cell line had an altered distribution in ion-exchange chromatography of regulatory subunits of cAMP-PKI and cAMP-PKII. The mutant A208-4 demonstrated wild-type-level binding of 8-N3-[32P]cAMP to both type I and type II regulatory subunits, but only half the wild-type level of type II catalytic activity. The mutant A208-7 had type I and type II catalytic activities equivalent to those in wild-type cells. However, the regulatory subunit of cAMP-PKI occurring in A208-7 demonstrated decreased levels of binding 8-N3-[32P]cAMP in comparison with the wild type. Furthermore, all mutants were defective in their abilities to bind 8-N3-[32P]cAMP to the type II regulatory protein in the particulate fraction. Thus, cAMP-PK was altered in each of these mutants. We conclude that both cAMP-PKI and cAMP-PKII are apparently required to induce ODC in response to increases in cAMP. Finally, since all three mutants induced ODC in response to nerve growth factor, the nerve growth factor-dependent induction of OCD was not mediated by an increase in cAMP that led to an activation of cAMP-PK. These mutants will be useful in the elucidation of the many functions controlled by cAMP and nerve growth factor.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Mechanisms of control for cAMP-dependent protein kinase from skeletal muscle. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:241–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Moolenaar W. H., Harrison P. H., Moed P., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Ionic responses and growth stimulation induced by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):92–98. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. A., Schechter A. L., Vaughn K. M. Clonal variants of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells with altered response to nerve growth factor. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom M. A., Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. A cyclic 3',5'-amp-stimulated protein kinase from cardiac muscle. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1970;8:191–203. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(70)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butley M. S., Beer D. G., Malkinson A. M. Functional changes in the regulatory subunit of the type II cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase isozyme during normal and neoplastic lung development. Cancer Res. 1984 Jun;44(6):2689–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Perlman R. L. Studies of a transplantable rat pheochromocytoma: biochemical characterization and catecholamine secretion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):615–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. L., Greene L. A., Viscarello R. R., Riley W. D. Rapid, sequential changes in surface morphology of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells in response to nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):820–827. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L. Characterization and regulation of heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):910–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Tischler A. S., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced increase in electrical excitability and acetylcholine sensitivity of a rat pheochromocytoma cell line. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):501–504. doi: 10.1038/268501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djurhuus R. Ornithine decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.17) assay based upon the retention of putrescine by a strong cation-exchange paper. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 15;113(2):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D. H., Thoenen H. Selective enzyme induction in a nerve growth factor-responsive pheochromocytoma cell line (PC 12). Brain Res. 1978 Oct 6;154(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- End D., Tolson N., Hashimoto S., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor-induced decrease in the cell-free phosphorylation of a soluble protein in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6549–6555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlichman J., Hirsch A. H., Rosen O. M. Interconversion of cyclic nucleotide-activated and cyclic nucleotide-independent forms of a protein kinase from beef heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erny R. E., Berezo M. W., Perlman R. L. Activation of tyrosine 3-monooxygenase in pheochromocytoma cells by adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1335–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erny R., Wagner J. A. Adenosine-dependent activation of tyrosine hydroxylase is defective in adenosine kinase-deficient PC12 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4974–4978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Garren L. D. A cyclic-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate dependent protein kinase from the adrenal cortex: comparison with a cyclic AMP binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 11;39(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90581-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. Using mutants to study cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:197–206. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Liem R. K., Shelanski M. L. Regulation of a high molecular weight microtubule-associated protein in PC12 cells by nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):76–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., McGuire J. C. Induction of ornithine decarboxylase by nerve growth factor dissociated from effects on survival and neurite outgrowth. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):191–194. doi: 10.1038/276191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guroff G., Dickens G., End D., Londos C. The action of adenosine analogs on PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1981 Dec;37(6):1431–1439. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb06312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Patrick J. Nerve growth factor mediates phosphorylation of specific proteins. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):571–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka H., Otten U., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor-mediated selective induction of ornithine decarboxylase in rat pheochromocytoma; a cyclic AMP-independent process. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80777-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. R., Adelstein R. S., Klee C. B. Interaction of calmodulin with myosin light chain kinase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase in bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff K. R., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor-induced reduction in epidermal growth factor responsiveness and epidermal growth factor receptors in PC12 cells: an aspect of cell differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90960-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffaker T., Corcoran T., Wagner J. A. Adenosine inhibits cell division and promotes neurite extension in PC12 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Aug;120(2):188–196. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041200212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumon A., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. Mode of action of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate on protein kinase from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 9;41(5):1290–1297. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. IV. Widespread occurrence of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1349–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Chan T., Chen K. Y. Induction of the regulatory subunit of type I adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in differentiated N-18 mouse neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4579–4587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y. Differentiation-specific increase of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in the 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):298–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Fiske W. W., Chen K. Y. Regulation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-binding protein in N-18 mouse neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Nov;40(11):4100–4108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto E., Petzold G. L., Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Dissociation and activation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases by cyclic nucleotides and by substrate proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):179–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R. L., Stafford P. H., Taylor S. Regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase I from porcine skeletal muscle: purification and proteolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter R. L., Taylor S. S. Relationships between structural domains and function in the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinases I and II from porcine skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2413–2418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race H. M., Wagner J. A. Nerve growth factor affects cyclic AMP metabolism, but not by directly stimulating adenylate cyclase activity. J Neurochem. 1985 May;44(5):1588–1592. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangel-Aldao R., Kupiec J. W., Rosen O. M. Resolution of the phosphorylated and dephosphorylated cAMP-binding proteins of bovine cardiac muscle by affinity labeling and two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2499–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Erlichman J. Reversible autophosphorylation of a cyclic 3':5'-AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7788–7794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Erlichman J., Rubin C. S. Molecular structure and characterization of bovine heart protein kinase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., LaCorbiere M., Whitlock C., Stallcup W. Alterations in the surface properties of cells responsive to nerve growth factor. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):718–723. doi: 10.1038/273718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Whitlock C. Alteration of cellular adhesion by nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4055–4058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwoch G., Hamann A., Hilz H. Antiserum against the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Reactivity towards various protein kinases. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj1920223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh T. J., Roth C., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. H. Characterization of cyclic AMP-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants lacking type I protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):926–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M., Salas M. L., Lipmann F. Mechanism of activation by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate of a protein phosphokinase from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):408–414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Lee C. Y., Swain L., Stafford P. H. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase: purification of the holoenzyme by affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1976 Nov;76(50):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theurkauf W. E., Vallee R. B. Molecular characterization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase bound to microtubule-associated protein 2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3284–3290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Costa M. R., Breakefield X. O., Greengard P. Presence of free cyclic AMP receptor protein and regulation of its level by cyclic AMP in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3251–3255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Uno I., Liu A. Y., Greengard P. Identification, characterization, and quantitative measurement of cyclic AMP receptor proteins in cytosol of various tissues using a photoaffinity ligand. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6494–6500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S., Chute R. N. Pheochromocytoma. Cancer. 1972 Feb;29(2):327–331. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197202)29:2<327::aid-cncr2820290210>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt J. J., Roskoski R., Jr Rapid protein kinase assay using phosphocellulose-paper absorption. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90743-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M. W., Tolson N. W., Guroff G. Increased phosphorylation of specific nuclear proteins in superior cervical ganglia and PC12 cells in response to nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10481–10492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Kerlavage A. R., Taylor S. S. Structural comparisons of cAMP-dependent protein kinases I and II from porcine skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2408–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]