Abstract
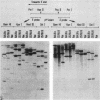
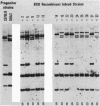
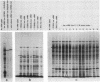
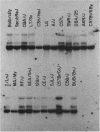
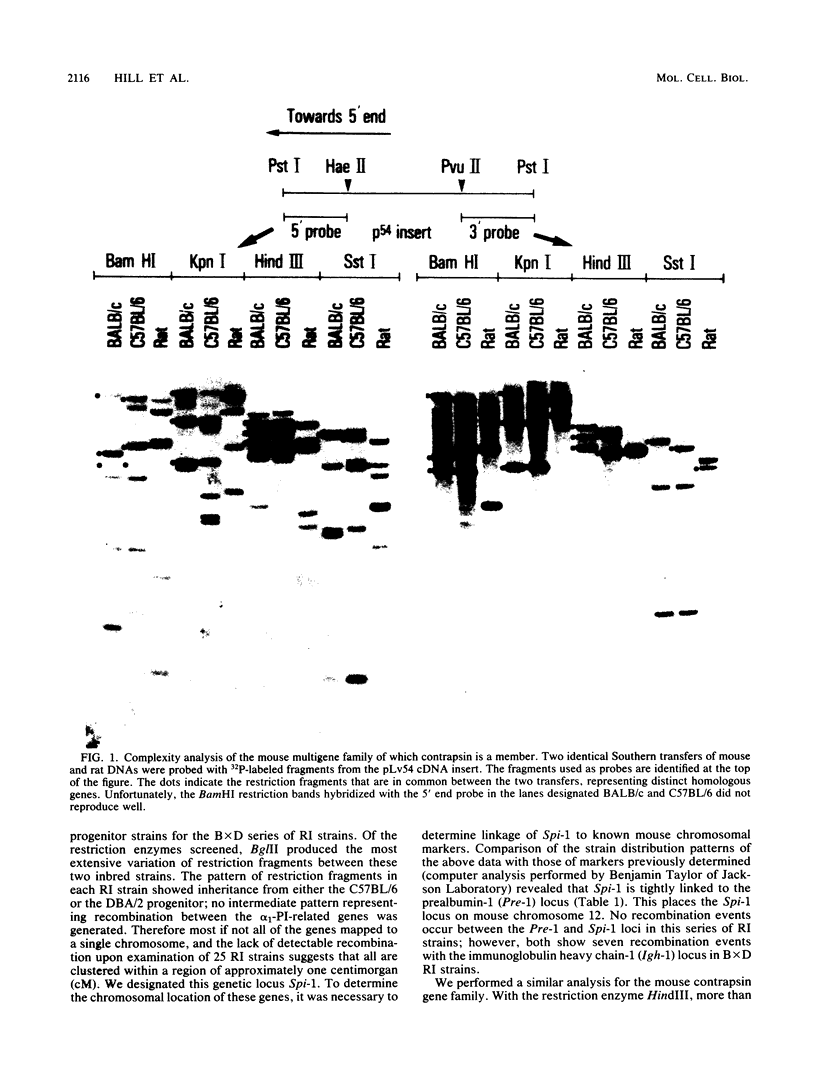
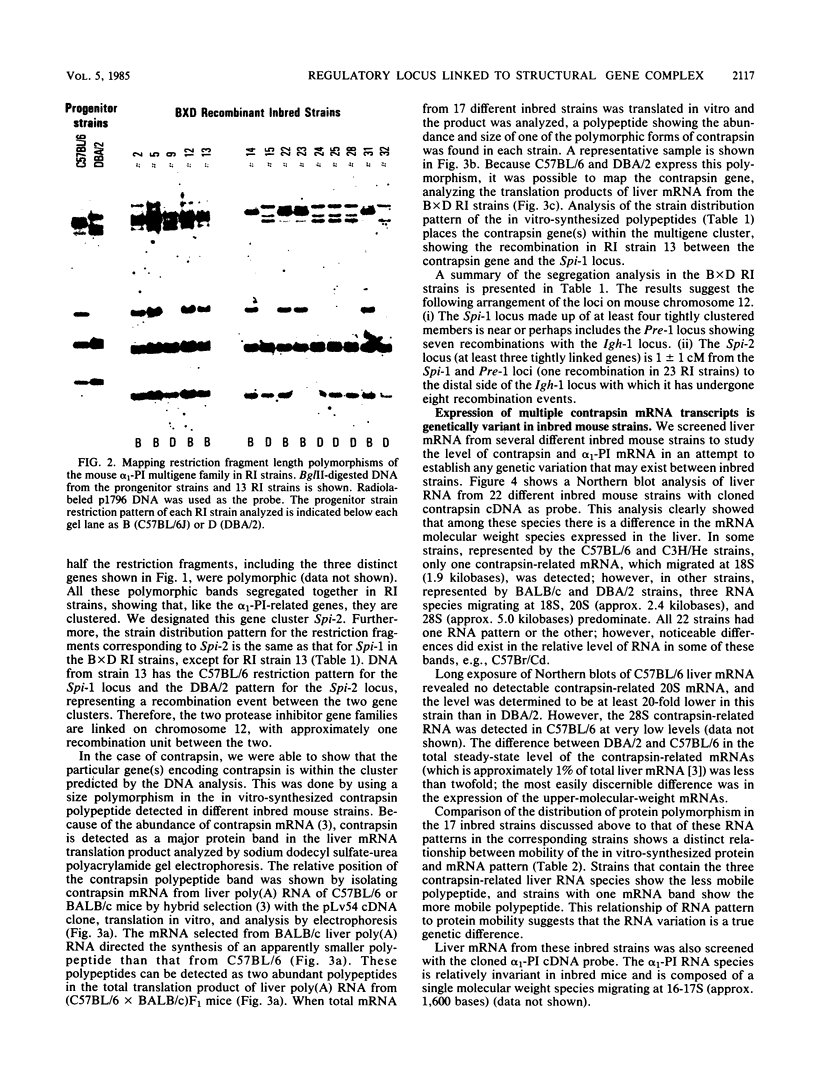
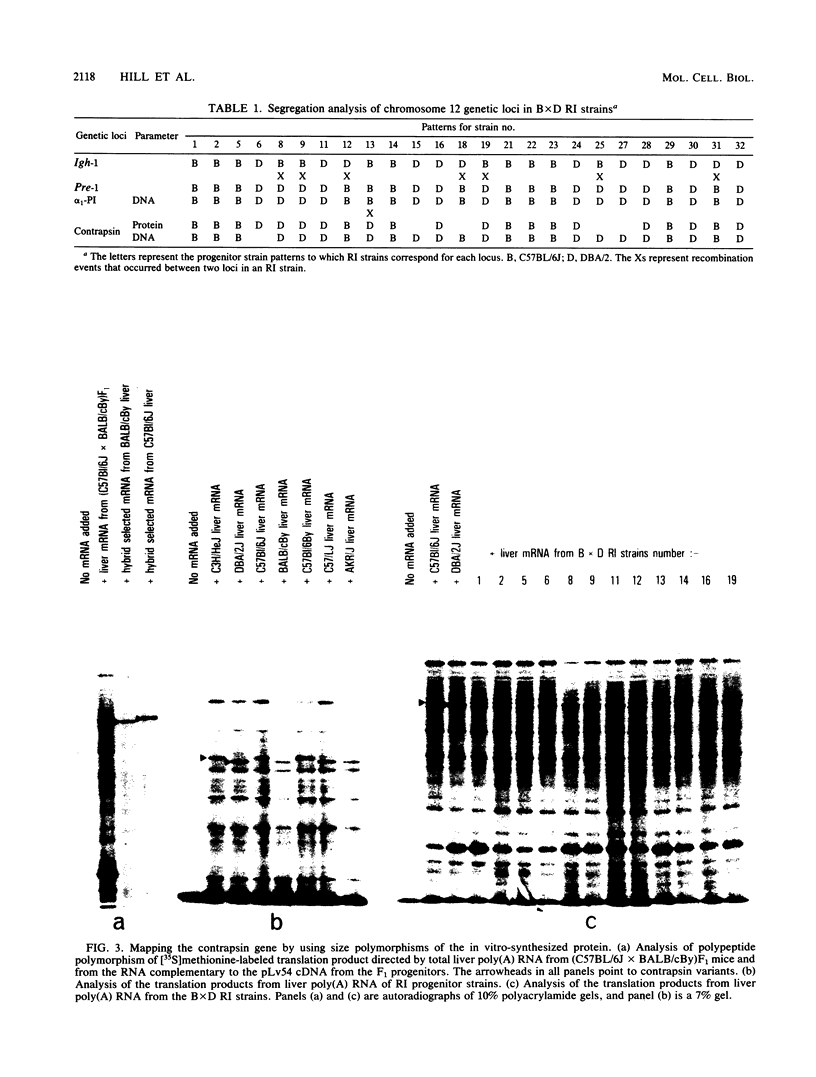
The two major protease inhibitors in mouse plasma are alpha 1-protease inhibitor (alpha 1-PI), putative inhibitor of neutrophil elastase, and contrapsin, an inhibitor in vitro of trypsinlike proteases. We have shown by nucleotide sequence analysis that these two inhibitors are related (R. E. Hill, P. H. Shaw, P. A. Boyd, H. Baumann, and N. D. Hastie, Nature (London) 311:175-177, 1984). Here, we show that the contrapsin and alpha 1-PI genes are members of two different multigene families, each containing at least three genes in mice and rats. We established the chromosomal locations of these genes by analyzing the segregation of restriction fragment length polymorphisms in recombinant inbred mouse strains. These experiments show that the multiple genes in each family are clustered and that the two gene families are closely linked on chromosome 12. Thus the genes for contrapsin and alpha 1-PI are likely to have evolved by duplication of a common ancestral gene. The contrapsin multigene family codes for multiple mRNA transcripts in the liver. There is a genetic difference among inbred mouse strains in the regulation of two of these transcripts. In some inbred strains the transcripts are synthesized constitutively; in others they are induced by inflammation. We mapped in recombinant inbred strains the regulatory locus responsible for this genetic variation and found it is linked to the contrapsin multigene family, which suggests a cis-acting regulatory element. We also found that the contrapsin and the alpha 1-PI multigene families have acquired very different regulatory responses since the time of the gene duplication event.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronsen K. F., Ekelund G., Kindmark C. O., Laurell C. B. Sequential changes of plasma proteins after surgical trauma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:127–136. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey D. W. Recombinant-inbred strains. An aid to finding identity, linkage, and function of histocompatibility and other genes. Transplantation. 1971 Mar;11(3):325–327. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197103000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth R. K., Gross K. W., Gremke L. C., Hastie N. D. Developmentally regulated mRNAs in mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):500–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Jahreis G. P., Gaines K. C. Synthesis and regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in primary cultures of mouse hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):866–876. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. L., Lalley P. A., Barth R. K., Hastie N. D. Mapping the structural genes coding for the major urinary proteins in the mouse: combined use of recombinant inbred strains and somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1220–1224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Mileham K., Haas M., Nesbitt M. N., Harper M. E., Simon M. I. Chromosomal mapping of the mink cell focus-inducing and xenotropic env gene family in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6298–6302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R., Owen M., Brennan S., Vaughan L. Carboxy terminal fragment of human alpha-1-antitrypsin from hydroxylamine cleavage: homology with antithrombin III. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):1032–1037. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91983-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney M., Jallat S., Tessier L. H., Benavente A., Crystal R. G., Lecocq J. P. Synthesis in E. coli of alpha 1-antitrypsin variants of therapeutic potential for emphysema and thrombosis. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):149–151. doi: 10.1038/313149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Markovic V. D., Teshima I. E. Genes for immunoglobulin heavy chains and for alpha 1-antitrypsin are localized to specific regions of chromosome 14q. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):428–430. doi: 10.1038/297428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Angiotensinogen is related to the antitrypsin-antithrombin-ovalbumin family. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):417–419. doi: 10.1126/science.6604942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. W., Berger F. G. DNA sequence polymorphism in an androgen-regulated gene is associated with alteration in the encoded RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):501–504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., West K., Gallagher J. F. Importance of initiation factor preparations in the translation of reovirus and globin mRNAs lacking a 5'-terminal 7-methylguanosine. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8489–8497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Shaw P. H., Boyd P. A., Baumann H., Hastie N. D. Plasma protease inhibitors in mouse and man: divergence within the reactive centre regions. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):175–177. doi: 10.1038/311175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O. A surprising new protein superfamily containing ovalbumin, antithrombin-III, and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 31;95(2):864–871. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90867-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Kao F. T., Law M. L., Woo S. L. Assignment of the alpha 1-antitrypsin gene and a sequence-related gene to human chromosome 14 by molecular hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 May;35(3):385–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leicht M., Long G. L., Chandra T., Kurachi K., Kidd V. J., Mace M., Jr, Davie E. W., Woo S. L. Sequence homology and structural comparison between the chromosomal human alpha 1-antitrypsin and chicken ovalbumin genes. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):655–659. doi: 10.1038/297655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall A. J., Burgoyne L. A. Interpretation of the properties of chromatin extracts from mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Apr;3(4):1101–1110. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.4.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan R. R., Barlow D. P., Hill R. E., Hogan B. L., Hastie N. D. Pattern of serum protein gene expression in mouse visceral yolk sac and foetal liver. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1881–1885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02062.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. C., Brennan S. O., Lewis J. H., Carrell R. W. Mutation of antitrypsin to antithrombin. alpha 1-antitrypsin Pittsburgh (358 Met leads to Arg), a fatal bleeding disorder. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 22;309(12):694–698. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309223091203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S., Barr P. J., Najarian R. C., Hallewell R. A. Synthesis in yeast of a functional oxidation-resistant mutant of human alpha-antitrypsin. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):77–80. doi: 10.1038/312077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore G. C., Tata J. R. Two fractions of rough endoplasmic reticulum from rat liver. II. Cytoplasmic messenger RNA's which code for albumin and mitochondrial proteins are distributed differently between the two fractions. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):726–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahara H., Sinohara H. Inhibitory spectrum of mouse contrapsin and alpha-1-antitrypsin against mouse serine proteases. J Biochem. 1983 May;93(5):1411–1419. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahara H., Sinohara H. Mouse plasma trypsin inhibitors. Isolation and characterization of alpha-1-antitrypsin and contrapsin, a novel trypsin inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2438–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]