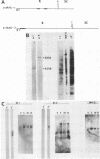
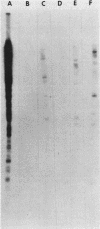
Abstract
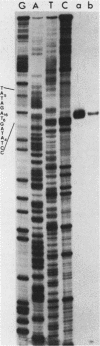
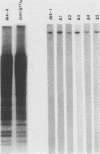
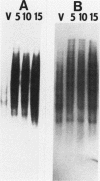
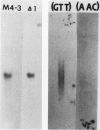
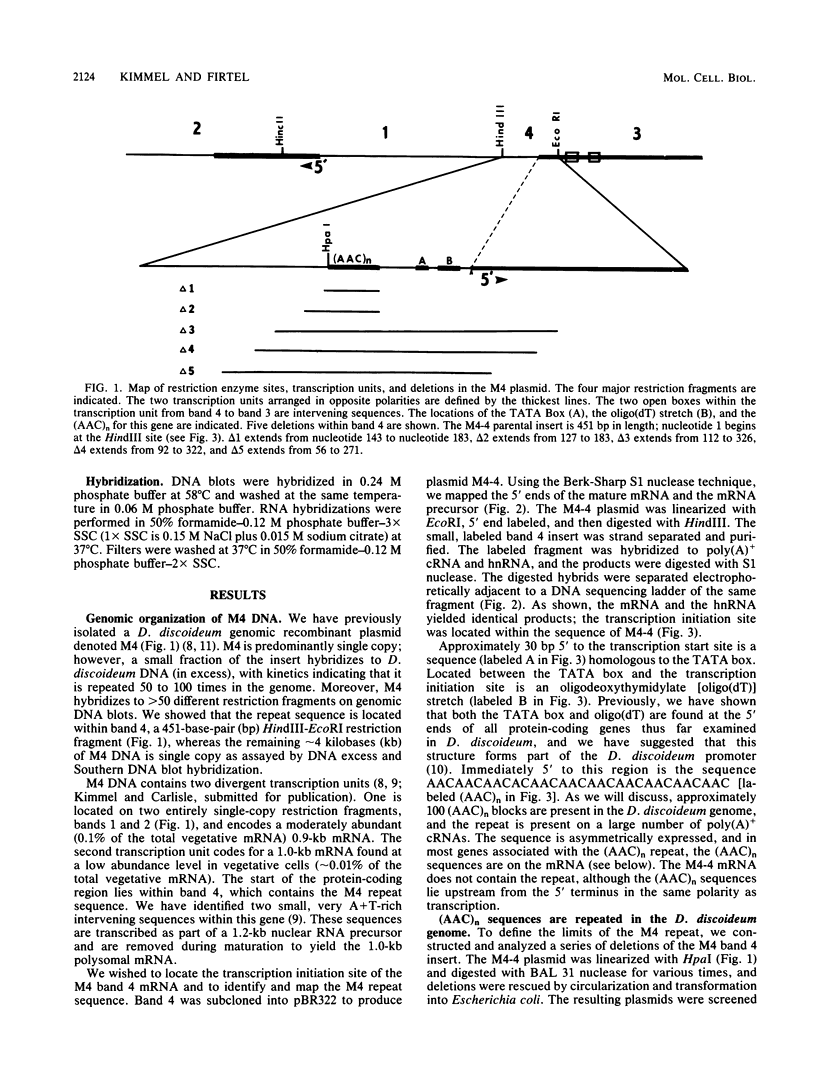
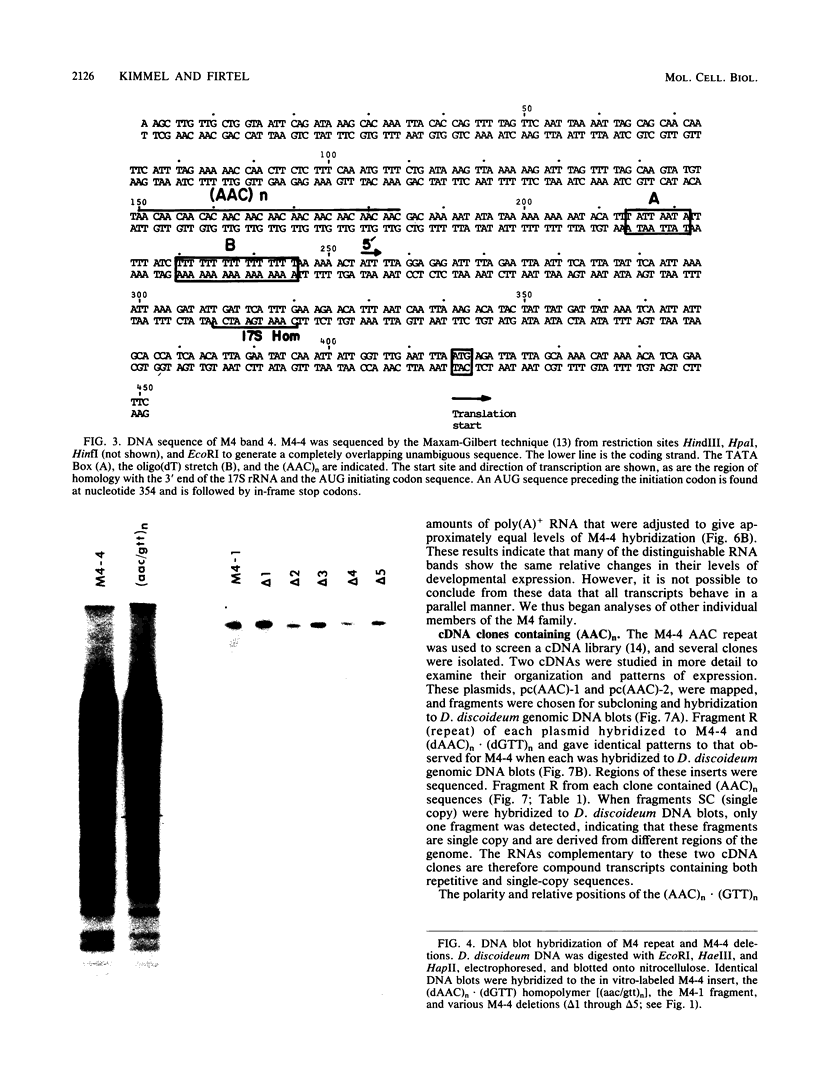
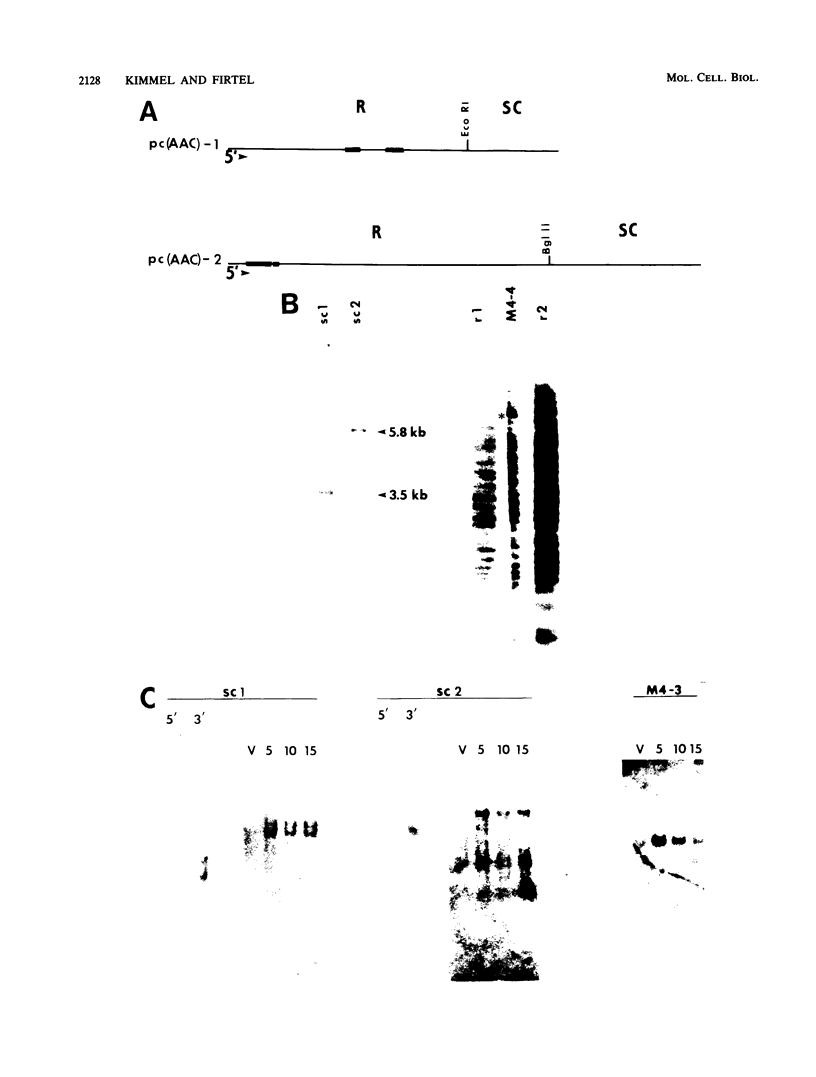
We have examined the genomic organization and developmental expression pattern of a short, transcribed, interspersed repeat element and its associated single-copy sequences. We have previously shown that 1% of the polyadenylated [poly(A)+] RNA from vegetative cells contains sequences that hybridize to this repeat. The complementary RNA is heterogeneous in size, and 90% of its mass hybridizes to single-copy DNA. In this study, we examined a series of genomic DNAs and cDNAs derived from poly(A)+ RNAs which are complementary to the repeat. Comparisons of sequence data from various genomic and cDNA clones indicated that (AAC)n X (GTT)n is the common sequence element. The tandem repeat occurred in approximately 100 short segments (approximately 35 to 150 base pairs) per haploid genome interspersed with single-copy DNA. Probes from regions adjacent to this element hybridized to unique restriction fragments on DNA blots and unique poly(A)+ RNA species on RNA blots. The (AAC)n X (GTT)n sequence was asymmetrically transcribed with only (AAC)n sequences represented in RNA. The repeat was localized within the transcribed regions of several genes and 70 base pairs 5' to the transcription initiation site of another gene. Individual (AAC)n-containing RNAs exhibited a developmental pattern of expression suggestive of the coordinate expression of many AAC gene family members.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carpenter C. D., Bruskin A. M., Spain L. M., Eldon E. D., Klein W. H. The 3' untranslated regions of two related mRNAs contain an element highly repeated in the sea urchin genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7829–7842. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F. D., Scheller R. H., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequence transcripts in the mature sea urchin oocyte. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):173–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Galau G. A., Angerer R. C., Britten R. J. Comparative aspects of DNA organization in Metazoa. Chromosoma. 1975 Jul 21;51(3):253–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00284818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Jacobs H. T., Britten R. J. Very short repeats and coordinate induction of genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):468–470. doi: 10.1038/301468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Posakony J. W. Repetitive sequence transcripts in development. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):633–635. doi: 10.1038/297633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Setzer D. R., Schimke R. T. A family of repeated DNA sequences, one of which resides in the second intervening sequence of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2480–2487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. A family of short, interspersed repeat sequences at the 5' end of a set of Dictyostelium single-copy mRNAs. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Intervening sequences in a Dictyostelium gene that encodes a low abundance class mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5599–5610. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Sequence organization in Dictyostelium: unique structure at the 5'-ends of protein coding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):541–552. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Firtel R. A. Evidence that populations of Dictyostelium single-copy mRNA transcripts carry common repeat sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2403–2422. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. L. Immunoglobulin genes have enhancers. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):735–737. doi: 10.1126/science.6410507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdy M. C., Ratner D., Firtel R. A. Induction and modulation of cell-type-specific gene expression in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):763–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Wahl G. M., Stark G. R. Properties of dispersed, highly repeated DNA within and near the hamster CAD gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):302–307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Mukai T., Morrow J. F. Repeated DNA sequences near the 5'-end of the silk fibroin gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4033–4041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posakony J. W., Flytzanis C. N., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Interspersed sequence organization and developmental representation of cloned poly(A) RNAs from sea urchin eggs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):361–389. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Jagodzinski L. L., Yang M., Bonner J. Fine structure and evolution of the rat serum albumin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):871–883. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., Costantini F. D., Kozlowski M. R., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Specific representation of cloned repetitive DNA sequences in sea urchin RNAs. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):189–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Bloom F. E., Lerner R. A. Common 82-nucleotide sequence unique to brain RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchurikov N. A., Naumova A. K., Zelentsova E. S., Georgiev G. P. A cloned unique gene of Drosophila melanogaster contains a repetitive 3' exon whose sequence is present at the 3' ends of many different mRNAs. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Watanabe Y., Nakai Y., Imura H., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Repetitive DNA sequences in the human corticotropin-beta-lipotrophin precursor gene region: Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1471–1479. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):298–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7209528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]